理解爬虫原理
1. 简单说明爬虫原理
使用python的requests模块模拟浏览器向服务器发送http请求,服务器接收到请求后向爬虫返回html数据,爬虫将返回的html数据保存下来,并利用bs4进行分析,将需要的数据截取下来并保存。
2. 理解爬虫开发过程
1).简要说明浏览器工作原理
在浏览器的地址栏输入网址并按回车后,浏览器就会向服务器发送http请求,服务器接收到请求后进行业务处理并向浏览器返回请求的资源,浏览器将获取到的返回数据进行解析、渲染,形成网页。
2).使用 requests 库抓取网站数据
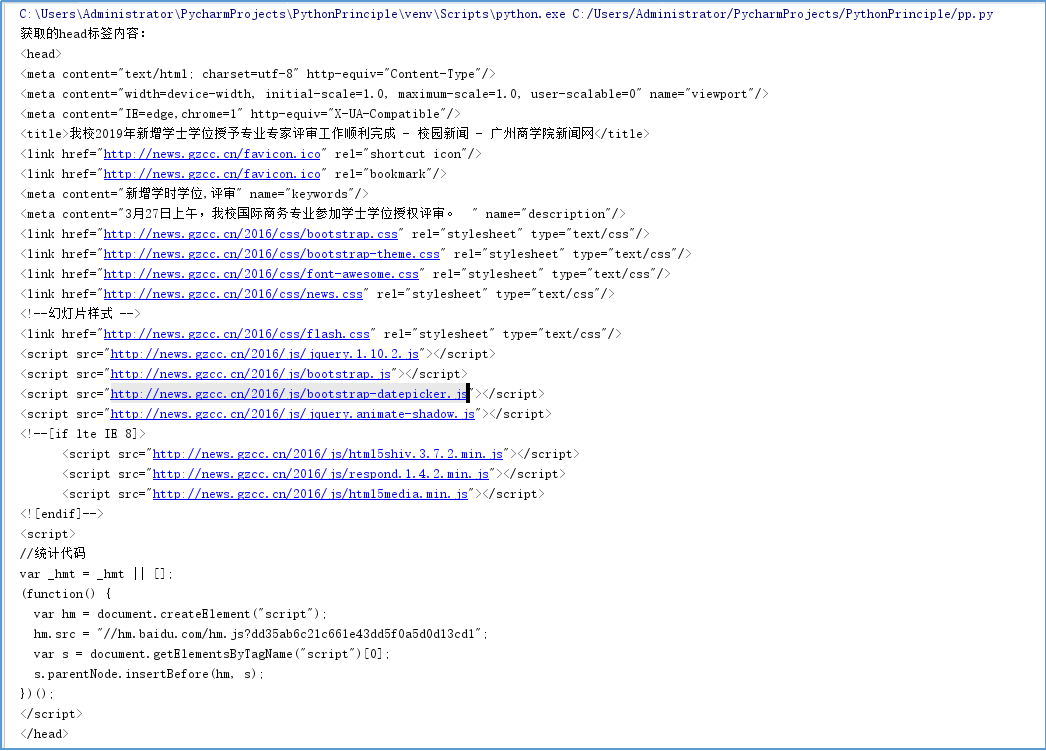
requests.get(url) 获取校园新闻首页html代码
1 html_url = 'http://news.gzcc.cn/html/2019/xiaoyuanxinwen_0328/11086.html' 2 resourses = requests.get(html_url) 3 resourses.encoding = 'UTF-8' 4 soup = BeautifulSoup(resourses.text, 'html.parser') 5 print("获取的head标签内容:") 6 print(soup.head)
运行结果:
3).了解网页
写一个简单的html文件,包含多个标签,类,id
1 html = ' \ 2 <html> \ 3 <body> \ 4 <h1 id="title">Hello</h1> \ 5 <a href="# link1" class="link" id="link1"> This is link1</a>\ 6 <a href="# link2" class="link" id="link2"> This is link2</a>\ 7 </body> \ 8 </html> '
4).使用 Beautiful Soup 解析网页;
通过BeautifulSoup(html_sample,'html.parser')把上述html文件解析成DOM Tree
select(选择器)定位数据
找出含有特定标签的html元素
找出含有特定类名的html元素
找出含有特定id名的html元素
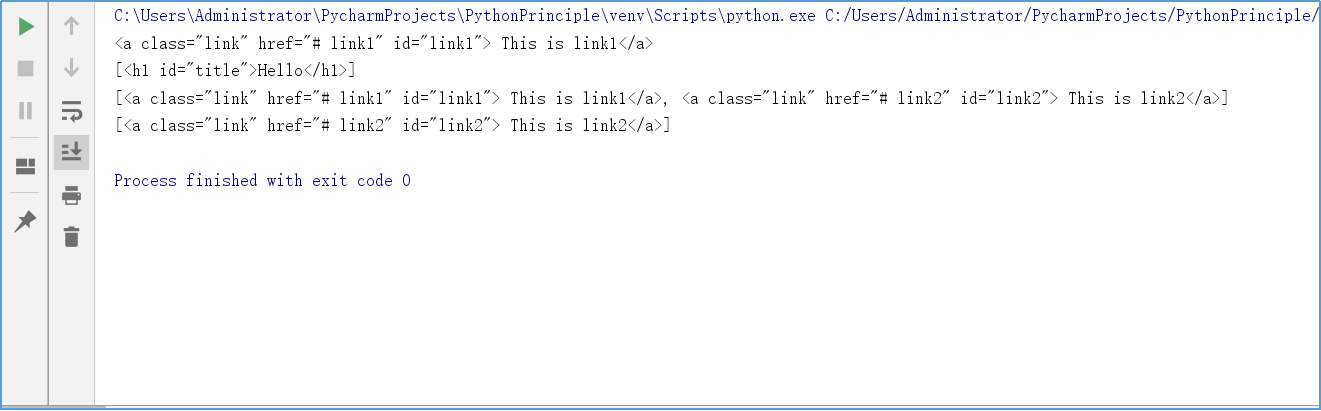
1 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 2 3 html = ' \ 4 <html> \ 5 <body> \ 6 <h1 id="title">Hello</h1> \ 7 <a href="# link1" class="link" id="link1"> This is link1</a>\ 8 <a href="# link2" class="link" id="link2"> This is link2</a>\ 9 </body> \ 10 </html> ' 11 soups = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser') 12 a = soups.a # 获取文档中的第一个与‘a’同名的标签,返回类型为Tag 13 h1 = soups.select('h1') # 获取标签名为‘h1’的标签的内容,返回类型为list 14 link_class = soups.select('.link') # 获取类名为‘link’的标签的内容,返回类型为list 15 link_id = soups.select('#link2') # 获取id为‘link2’的标签的内容,返回类型为list 16 print(a) 17 print(h1) 18 print(link_class) 19 print(link_id)
运行效果截图:
3.提取一篇校园新闻的标题、发布时间、发布单位、作者、点击次数、内容等信息
提取的校园新闻url = 'http://news.gzcc.cn/html/2019/xiaoyuanxinwen_0328/11086.html'
发布时间为datetime类型,点击次数为数值型,其它是字符串类型。

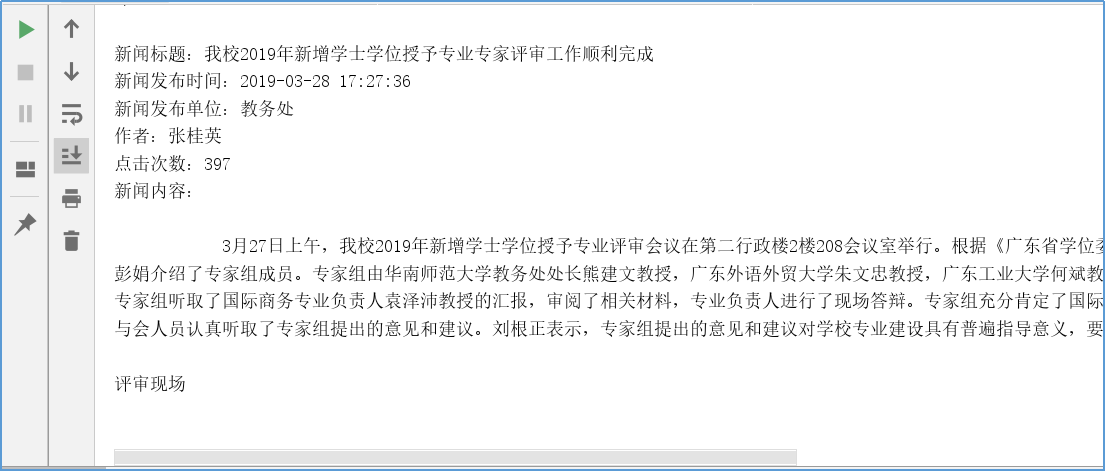
1 import requests # 直接导入requests模块 2 from datetime import datetime # 从datetime包导入datetime模块 3 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # 从bs4包导入BeautifulSoup模块 4 5 html_url = 'http://news.gzcc.cn/html/2019/xiaoyuanxinwen_0328/11086.html' # 校园新闻url 6 resourses = requests.get(html_url) # 发送get请求 7 resourses.encoding = 'UTF-8' # 以防获取的内容出现乱码,手动指定字符编码为UTF-8 8 soup = BeautifulSoup(resourses.text, 'html.parser') # 调用BeautifulSoup解析功能,解析请求返回的内容,解析器用html.parser 9 print("获取的head标签内容:") 10 print(soup.head) 11 print("\n新闻标题:" + soup.select('.show-title')[0].text) 12 newsDate = soup.select('.show-info')[0].text.split()[0].split(':')[1] # 使用BeautifulSoup的select方法根据元素的类名来查找元素的内容,返回的是list类型 13 newsTime = soup.select('.show-info')[0].text.split()[1] 14 dt = newsDate + " " + newsTime 15 # datetime模块的strptime能够将文本字符串格式的数据转换成时间格式的数据 16 showtime = datetime.strptime(dt, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") # strptime():将字符串类型转换成时间类型 17 print("新闻发布时间:", end="") 18 print(showtime) 19 publishing_unit = soup.select('.show-info')[0].text.split()[4].split(':')[1] 20 print("新闻发布单位:", end="") 21 print(publishing_unit) 22 print("作者:", end="") 23 writer = soup.select('.show-info')[0].text.split()[2].split(':')[1] 24 print(writer) 25 # strftime方法能够把时间格式的数据按照我们想要的时间格式输出,比如说输出这个日期的月份名字,星期几等等,扩展性十分强大 26 showtime = datetime.strftime(showtime, '%Y{Y}%m{m}%d{d} %H{H}:%M{M}:%S{s}').format(Y='年', m='月', d='日', H='时', 27 M='分', s='秒') # 将时间类型转换成字符串类型 28 click_num_url = 'http://oa.gzcc.cn/api.php?op=count&id=11086&modelid=80' 29 return_click_num = requests.get(click_num_url) 30 click_info = BeautifulSoup(return_click_num.text, 'html.parser') 31 click_num = int(click_info.text.split('.html')[3].split("'")[1]) 32 print("点击次数:", end="") 33 print(click_num) 34 print("新闻内容:" + soup.select('.show-content')[0].text.replace('\u3000', ''))
运行效果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号