netstat源码阅读笔记
参考
netstat 介绍
netstat是net-tools里面的一个子命令(net-tools里还有ifconfig、route、arp等子命令),netstat可以查看TCP/UDP的网络状态、路由信息、网卡信息等。
使用场景
查看网络连接
查看本机启动的TCP服务
使用netstat -nltp命令可以查看本机启动的TCP服务(状态为LISTEN),从下面的结果可以看出还展示了TCP服务监听的IP和端口。各个参数的含义如下。
n:以点分十进制显示IP,以数字形式显示端口;l:显示监听的socket;t:显示TCP协议;p:显示使用socket的进程的PID和进程名;
$ sudo netstat -nltp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 32716/cupsd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.53:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 596/systemd-resolve
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 35172/sshd: ydev@pt
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:8081 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 34938/./server
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 836/sshd: /usr/sbin
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 32716/cupsd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:6010 :::* LISTEN 35172/sshd: ydev@pt
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 836/sshd: /usr/sbin
查看已建立连接的TCP连接
使用netstat -ntp可以查看本机建立的TCP连接(状态是ESTABLISHED)。另外还可以加上-c选项,这个选项很有意思,-c能让netstat循环执行(频率似乎是1s/次),如果要查看网络服务的连接状态(ESTABLISHED)是可以使用netstat -ntp | grep PARTTERN。
$ sudo netstat -ntp
Active Internet connections (w/o servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 192.168.56.108:22 192.168.56.1:58098 ESTABLISHED 35114/sshd: ydev [p
查看路由表
使用netstat -r可以查看路由表。
$ netstat -r
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface
default _gateway 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 enp0s3
10.0.2.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 enp0s3
link-local 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 enp0s8
192.168.56.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 enp0s8
命令原理
netstat -nltp
netstat -nltp命令的原理是:当程序判断到命令行指定了t选项时就去读取/proc/net/tcp和/proc/net/tcp6文件,并解析文件内容,输出便于阅读的形式。nltp各个参数的实现原理如下:
n:如果指定了-n,则以数字形式显示IP/Port,否则IP显示为hostname,Port如果为熟知端口,则显示此协议的名称(如端口为443,则会显示为https);l:显示状态为LISTEN的socket。netstat并不是根据/proc/net/tcp文件中的st对应的列来判断状态的,而是根据remote_port是否为0判断是否为LISTEN的socket;t:显示TCP协议的socket。p:如果指定了-p,根据/proc/net/tcp文件中的inode找到使用此socket的进程,然后根据进程的/proc/PID/cmdline就可以获取进程名;
root@ydev-VirtualBox:/home/ydev/github/net-tools# cat /proc/net/tcp
sl local_address rem_address st tx_queue rx_queue tr tm->when retrnsmt uid timeout inode
0: 0100007F:8D8B 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 1000 0 48506 1 ffff920c886ac600 100 0 0 10 0
1: 00000000:0016 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 0 0 22745 1 ffff920c845088c0 100 0 0 10 0
2: 3500007F:0035 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 101 0 20016 1 ffff920c8a44a300 100 0 0 10 5
3: 0100007F:0277 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 0 0 47267 1 ffff920c8260a300 100 0 0 10 0
4: 0100007F:9E12 0100007F:8D8B 01 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 1000 0 41857 1 ffff920c84509a40 20 4 2 10 -1
5: 0100007F:8D8B 0100007F:9E10 01 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 1000 0 42520 1 ffff920c8450d780 20 4 30 10 -1
6: 6C38A8C0:0016 0138A8C0:DF13 01 00000000:00000000 02:0004E84C 00000000 0 0 41824 2 ffff920c86aba300 21 4 28 10 56
7: 0100007F:9E10 0100007F:8D8B 01 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 1000 0 41856 1 ffff920c8450f1c0 21 4 28 10 -1
8: 0100007F:8D8B 0100007F:9E12 01 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 1000 0 42522 1 ffff920c8450c600 20 4 28 10 -1
9: 6C38A8C0:0016 0138A8C0:DEA7 01 00000000:00000000 02:0004DAC2 00000000 0 0 41743 2 ffff920c86ab9a40 24 4 2 10 100
root@ydev-VirtualBox:/home/ydev/github/net-tools# netstat -nltp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:36235 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7949/node
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 838/sshd: /usr/sbin
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.53:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 526/systemd-resolve
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7867/cupsd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 7867/cupsd
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 838/sshd: /usr/sbin
这里给出/proc/net/tcp中的内容和netstat -nltp输出结果之间的关系图。
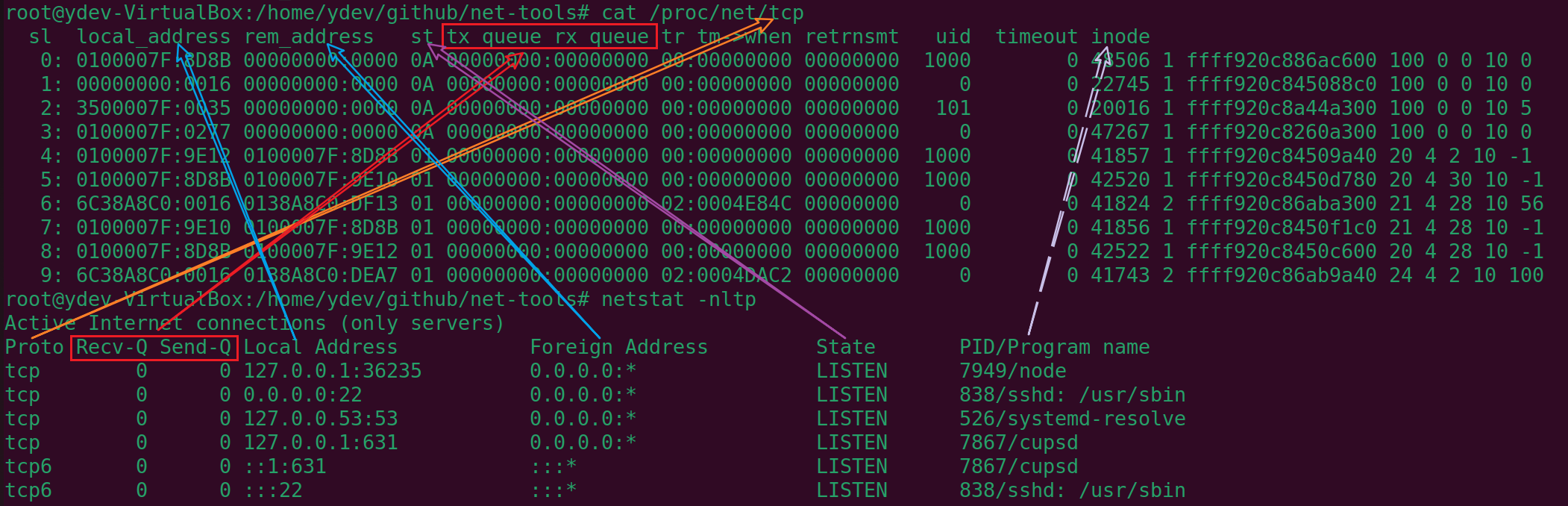
下面是具体的代码分析,首先在netstat.c:main()中解析命令行参数,然后会根据参数执行相应的操作,如指定了-t,则会flag_tcp会调用tcp_info函数,tcp_info就会输出结果。
#if HAVE_AFINET
if (!flag_arg || flag_tcp) {
i = tcp_info();
if (i)
return (i);
}
// ...
tcp_info是对INFO_GUTS6宏的封装。
#define INFO_GUTS6(file,file6,name,proc,prot4,prot6) \
char buffer[8192]; \
int rc = 0; \
int lnr = 0; \
if (!flag_arg || flag_inet) { \
INFO_GUTS1(file,name,proc,prot4) \
} \
if (!flag_arg || flag_inet6) { \
INFO_GUTS2(file6,proc,prot6) \
} \
INFO_GUTS3
static int tcp_info(void)
{
INFO_GUTS6(_PATH_PROCNET_TCP, _PATH_PROCNET_TCP6, "AF INET (tcp)",
tcp_do_one, "tcp", "tcp6");
}
将INFO_GUTS6展开,结果如下。可以看到tcp_info函数最终分别调用tcp_do_one处理/proc/net/tcp和/proc/net/tcp6两个文件的内容。
#define INFO_GUTS1(file,name,proc,prot) \
procinfo = proc_fopen((file)); \
if (procinfo == NULL) { \
if (errno != ENOENT && errno != EACCES) { \
perror((file)); \
return -1; \
} \
if (!flag_noprot && (flag_arg || flag_ver)) \
ESYSNOT("netstat", (name)); \
if (!flag_noprot && flag_arg) \
rc = 1; \
} else { \
do { \
if (fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), procinfo)) \
(proc)(lnr++, buffer,prot); \
} while (!feof(procinfo)); \
fclose(procinfo); \
}
#if HAVE_AFINET6
#define INFO_GUTS2(file,proc,prot) \
lnr = 0; \
procinfo = proc_fopen((file)); \
if (procinfo != NULL) { \
do { \
if (fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), procinfo)) \
(proc)(lnr++, buffer,prot); \
} while (!feof(procinfo)); \
fclose(procinfo); \
}
// 展开 INFO_GUTS6 的结果
static int tcp_info(void)
{
char buffer[8192];
int rc = 0;
int lnr = 0;
if (!flag_arg || flag_inet) {
INFO_GUTS1("/proc/net/tcp","AF INET (tcp)",tcp_do_one,"tcp")
}
if (!flag_arg || flag_inet6) {
INFO_GUTS2("/proc/net/tcp6",tcp_do_one,"tcp6")
}
return rc;
}
下面是一个示例,第一列表示编号,local_address和rem_address分别表示本地和远程的IP:Port,st表示状态,以及inode等信息。
$ cat /proc/net/tcp
sl local_address rem_address st tx_queue rx_queue tr tm->when retrnsmt uid timeout inode
0: 0100007F:0277 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 0 0 6666460 1 0000000000000000 100 0 0 10 0
1: 3500007F:0035 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 101 0 19727 1 0000000000000000 100 0 0 10 5
2: 0100007F:177B 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 1000 0 6922798 1 0000000000000000 100 0 0 10 0
3: 0100007F:177A 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 1000 0 6680561 1 0000000000000000 100 0 0 10 0
4: 0100007F:1F91 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 0 0 6603728 1 0000000000000000 100 0 0 10 0
5: 00000000:0016 00000000:0000 0A 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 0 0 19849 1 0000000000000000 100 0 0 10 0
6: 6C38A8C0:0016 0138A8C0:E2F2 01 00000000:00000000 02:0008CEDB 00000000 0 0 6689368 2 0000000000000000 24 4 30 10 -1
7: 6C38A8C0:0016 0138A8C0:EF34 01 00000000:00000000 02:0002E568 00000000 0 0 6924362 2 0000000000000000 23 4 30 10 52
8: 0F02000A:C554 3E0012C6:01BB 01 00000000:00000000 00:00000000 00000000 1000 0 6987186 1 0000000000000000 20 0 0 10 -1
9: 0F02000A:BCFC A50012C6:01BB 08 00000000:00000019 02:0000107C 00000000 1000 0 6985115 2 0000000000000000 20 4 2 10 -1
10: 0F02000A:9C8C 490012C6:0050 06 00000000:00000000 03:00000937 00000000 0 0 0 3 0000000000000000
接下来看看tcp_do_one是如何处理/proc/net/tcp内容的,
static void tcp_do_one(int lnr, const char *line, const char *prot)
{
unsigned long rxq, txq, time_len, retr, inode;
int num, local_port, rem_port, d, state, uid, timer_run, timeout;
char rem_addr[128], local_addr[128], timers[64];
const struct aftype *ap;
struct sockaddr_storage localsas, remsas;
struct sockaddr_in *localaddr = (struct sockaddr_in *)&localsas;
struct sockaddr_in *remaddr = (struct sockaddr_in *)&remsas;
#if HAVE_AFINET6
char addr6[INET6_ADDRSTRLEN];
struct in6_addr in6;
extern struct aftype inet6_aftype;
#endif
long clk_tck = ticks_per_second();
// 忽略 /proc/net/tcp 或 /proc/net/tcp6 的第一行
if (lnr == 0)
return;
// 给local_addr等变量赋值
num = sscanf(line,
"%d: %64[0-9A-Fa-f]:%X %64[0-9A-Fa-f]:%X %X %lX:%lX %X:%lX %lX %d %d %lu %*s\n",
&d, local_addr, &local_port, rem_addr, &rem_port, &state,
&txq, &rxq, &timer_run, &time_len, &retr, &uid, &timeout, &inode);
if (num < 11) {
fprintf(stderr, _("warning, got bogus tcp line.\n"));
return;
}
// 过滤掉 `LISTEN` 状态或 `ESTABLISHED` 状态,过滤方法是根据rem_port是否为0决定(rem_port为0则表示为本地监听的socket)
// 如果指定了 `-t`(显示`LISTEN`状态的socket) 则跳过 rem_port 不为0的行
// 反之,如果没有指定 `-t`,则跳过 rem_port 为0的行
if (!flag_all && ((flag_lst && rem_port) || (!flag_lst && !rem_port)))
return;
if (strlen(local_addr) > 8) {
#if HAVE_AFINET6
/* Demangle what the kernel gives us */
sscanf(local_addr, "%08X%08X%08X%08X",
&in6.s6_addr32[0], &in6.s6_addr32[1],
&in6.s6_addr32[2], &in6.s6_addr32[3]);
inet_ntop(AF_INET6, &in6, addr6, sizeof(addr6));
inet6_aftype.input(1, addr6, &localsas);
sscanf(rem_addr, "%08X%08X%08X%08X",
&in6.s6_addr32[0], &in6.s6_addr32[1],
&in6.s6_addr32[2], &in6.s6_addr32[3]);
inet_ntop(AF_INET6, &in6, addr6, sizeof(addr6));
inet6_aftype.input(1, addr6, &remsas);
localsas.ss_family = AF_INET6;
remsas.ss_family = AF_INET6;
#endif
} else {
sscanf(local_addr, "%X", &localaddr->sin_addr.s_addr);
sscanf(rem_addr, "%X", &remaddr->sin_addr.s_addr);
localsas.ss_family = AF_INET;
remsas.ss_family = AF_INET;
}
if ((ap = get_afntype(localsas.ss_family)) == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, _("netstat: unsupported address family %d !\n"),
localsas.ss_family);
return;
}
// 格式化地址显示方式,如果命令行指定了 `-n` 则以点分十进制显示IP,否则显示hostname
addr_do_one(local_addr, sizeof(local_addr), 22, ap, &localsas, local_port, "tcp");
addr_do_one(rem_addr, sizeof(rem_addr), 22, ap, &remsas, rem_port, "tcp");
timers[0] = '\0';
if (flag_opt)
switch (timer_run) {
case 0:
snprintf(timers, sizeof(timers), _("off (0.00/%ld/%d)"), retr, timeout);
break;
case 1:
snprintf(timers, sizeof(timers), _("on (%2.2f/%ld/%d)"),
(double) time_len / clk_tck, retr, timeout);
break;
case 2:
snprintf(timers, sizeof(timers), _("keepalive (%2.2f/%ld/%d)"),
(double) time_len / clk_tck, retr, timeout);
break;
case 3:
snprintf(timers, sizeof(timers), _("timewait (%2.2f/%ld/%d)"),
(double) time_len / clk_tck, retr, timeout);
break;
case 4:
snprintf(timers, sizeof(timers), _("probe (%2.2f/%ld/%d)"),
(double) time_len / clk_tck, retr, timeout);
break;
default:
snprintf(timers, sizeof(timers), _("unkn-%d (%2.2f/%ld/%d)"),
timer_run, (double) time_len / clk_tck, retr, timeout);
break;
}
// 显示格式化后的信息,状态的格式化是将state作为index,查找tcp_state数组,得到字符串
printf("%-4s %6ld %6ld %-*s %-*s %-11s",
prot, rxq, txq, (int)netmax(23,strlen(local_addr)), local_addr, (int)netmax(23,strlen(rem_addr)), rem_addr, _(tcp_state[state]));
// 如果在命令行指定了 `-p` 则根据inode查找此socket对应的进程,打印出PID和进程名
finish_this_one(uid,inode,timers);
}
tcp的状态数组定义如下。
/* These enums are used by IPX too. :-( */
enum {
TCP_ESTABLISHED = 1,
TCP_SYN_SENT,
TCP_SYN_RECV,
TCP_FIN_WAIT1,
TCP_FIN_WAIT2,
TCP_TIME_WAIT,
TCP_CLOSE,
TCP_CLOSE_WAIT,
TCP_LAST_ACK,
TCP_LISTEN,
TCP_CLOSING /* now a valid state */
};
#if HAVE_AFINET || HAVE_AFINET6
static const char *tcp_state[] =
{
"",
N_("ESTABLISHED"),
N_("SYN_SENT"),
N_("SYN_RECV"),
N_("FIN_WAIT1"),
N_("FIN_WAIT2"),
N_("TIME_WAIT"),
N_("CLOSE"),
N_("CLOSE_WAIT"),
N_("LAST_ACK"),
N_("LISTEN"),
N_("CLOSING")
};
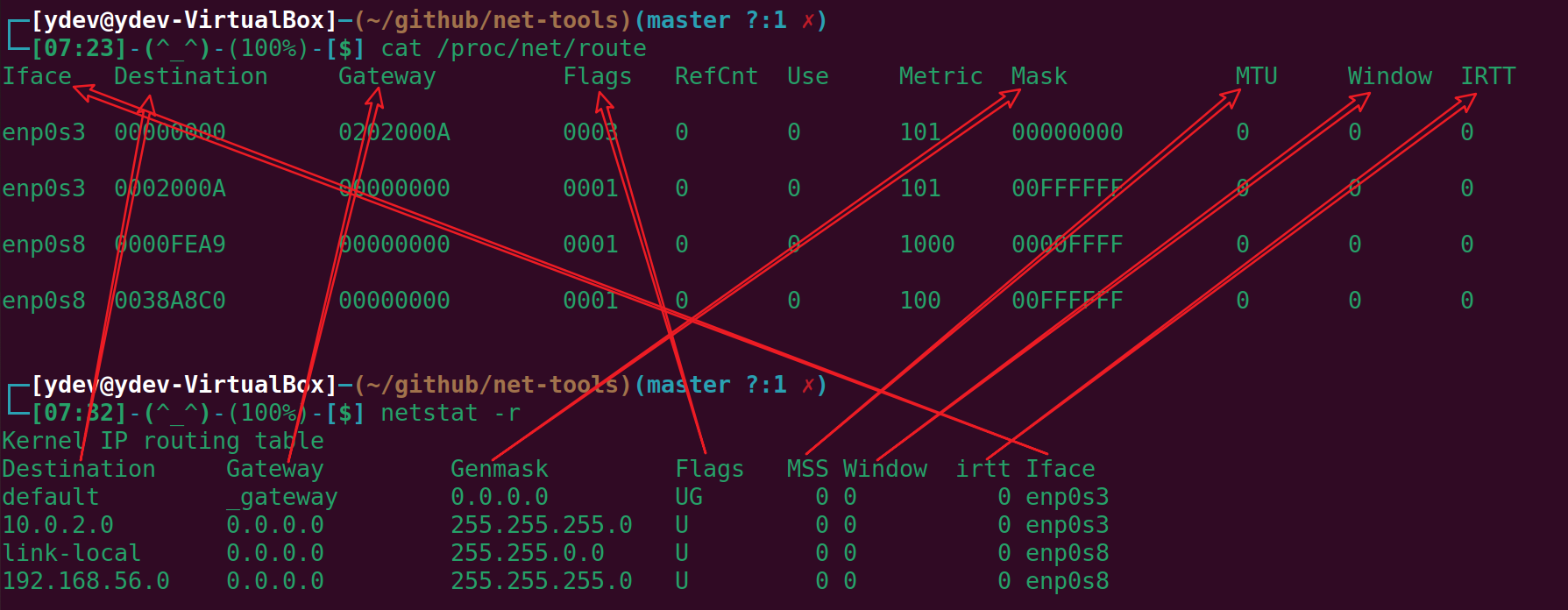
netstat -r
netstat -r命令所作的事情就是读取/proc/net/route文件,然后显示结果。几乎不需要处理,看下面一张图就很清晰了。
netstat -i
netstat -i 命令的核心和下面的示例程序类似。核心是调用socket,获取一个SOCK_DGRAM类型的fd。然后调用iotct,传入SIOCGIFCONF就可以获取网卡信息了。但是SIOCGIFCONF支持支AF_INET。不过netstat -i 还可会尝试查看其他类型的网卡。(具体可以参考ioctl和netdevice)。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BUFSIZE 1024
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int sfd, if_count, i;
struct ifconf ifc;
struct ifreq ifr[10];
char ipaddr[INET_ADDRSTRLEN] = {'\0'};
memset(&ifc, 0, sizeof(struct ifconf));
sfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
ifc.ifc_len = 10 * sizeof(struct ifreq);
ifc.ifc_buf = (char *)ifr;
/* SIOCGIFCONF is IP specific. see netdevice(7) */
ioctl(sfd, SIOCGIFCONF, (char *)&ifc);
if_count = ifc.ifc_len / (sizeof(struct ifreq));
for (i = 0; i < if_count; i++) {
printf("Interface %s : ", ifr[i].ifr_name);
inet_ntop(AF_INET,
&(((struct sockaddr_in *)&(ifr[i].ifr_addr))->sin_addr),
ipaddr, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
printf("%s\n", ipaddr);
}
close(sfd);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号