list转换dict的方式以及zip的用法
注意:由于Python不支持列表作为键, dict的键只能是散列对象。 如果希望将列表的内容作为键,需要将列表转换为元组。
但是,如果确实要使用列表,则可以使用其字符串表示形式。如:{'[1, 2, 3]': 'value'}
用一个list建立一个只有键没有值的 dict
b = ['a','b','c']
#方法一:
dict.fromkeys(b)
Out: {'a': None, 'b': None, 'c': None}
#方法二:
dict(zip(b, [None]*len(b)))
Out: {'a': None, 'b': None, 'c': None}
#方法三
{key: None for key in b}
Out: {'a': None, 'b': None, 'c': None}
用一个list和一个值,建立一个键不同但值相同的 dict
dict(zip(b, [8]*len(b)))
Out: {'a': 8, 'b': 8, 'c': 8}
{key: 6 for key in b}
Out: {'a': 6, 'b': 6, 'c': 6}
两个list合成dict
1.两个等长的list直接通过zip合并
a = [1,2,3]
b = ['a','b','c']
dict(zip(a,b))
{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c'}
2.两个不等长的list通过zip合并时,会自动截取等长
a = [1,2,3]
d = ['a','b','c','d','e']
dict(zip(a,d))
{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c'}
3.构建函数list2dict()通过循环得出dict
list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
list2 = ["a", "b", "c", "d","e"]
def list2dict(list1,list2):
dict={}
i=0
length=len(list2)
while i<length:
'dict[list1[i]]=list2[i];这种方法也可以'
dit={list1[i]:list2[i]}
dict.update(dit)
i+=1
return dict;
4.通过map和lambda合成两个list
list1 = ['k1','k2','k3']
list2 = ['v1','v2','v3']
dic = dict(map(lambda x,y:[x,y],list1,list2))
>>> print(dic)
{'k3': 'v3', 'k2': 'v2', 'k1': 'v1'}
5.写个小循环体:
l1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
l2=[4,5,6,7,8,9]
{k:v for k,v in zip(l1,l2)}
>>>{1: 4, 2: 5, 3: 6, 4: 7, 5: 8, 6: 9}
TIPs:将字典中的v和k调换
x = {1: 4, 2: 5, 3: 6, 4: 7, 5: 8, 6: 9}
{v:k for k,v in x.items()}
{4: 1, 5: 2, 6: 3, 7: 4, 8: 5, 9: 6}
pandas的df转换成dict
1. 对于没有标题行的df,直接转换:
data=df(xxx)
data_dict = dict(data)
2. 有标题行的df,可以先提取各列值, 再进行转换
import pandas as pd
item = pd.DataFrame({'item_id': [100120, 10024504, 1055460], 'item_category': [87974, 975646, 87974]}, index=[0, 1, 2])
# 将item_id,item_category两列数值转为dict字典
# 注意:同种商品类别肯定会对应不同商品,即一对多,进行字典映射,一定要是item_id作为键,item_category作为值
# 由于原始数据为int类型,结果将是字符串之间的映射,因此需要对列值进行数据类型转换
item.item_id = (item['item_id']).astype(str)
item.item_category = (item['item_category']).astype(str)
item_dict = item.set_index('item_id')['item_category'].to_dict()
print(item_dict)
{'100120': '87974', '10024504': '975646', '1055460': '87974'}
或者也可以直接用zip的方法提取两列,简化为:
item_dict = dict(zip(item['item_id'].astype(str),item['item_category']))
3.
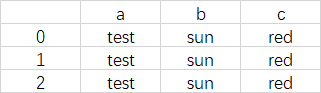
要获得:
{'a' : [test,test,test], 'b' : [sun,sun,sun], 'c' : [red,red,red]}
这样的字典,只要下面一句话:
{col:df[col].tolist() for col in df.columns}
4. 使用 pandas 中的 to_dict 对 DataFrame 类型的数据进行转换
可以选择六种的转换类型,分别对应于参数 ‘dict’, ‘list’, ‘series’, ‘split’, ‘records’, ‘index’,可以试一下不同参数的转换结果 ,有惊喜
官方文档:
Help on method to_dict in module pandas.core.frame:
Function: Convert DataFrame to dictionary.
to_dict(orient='dict') method of pandas.core.frame.DataFrame instance
Parameters:
orient : str {'dict', 'list', 'series', 'split', 'records', 'index'}
Determines the type of the values of the dictionary.
- dict (default) : dict like {column -> {index -> value}}
- list : dict like {column -> [values]}
- series : dict like {column -> Series(values)}
- split : dict like {index -> [index], columns -> [columns], data -> [values]}
- records : list like [{column -> value}, ... , {column -> value}]
- index : dict like {index -> {column -> value}}
Abbreviations are allowed. `s` indicates `series` and `sp` indicates `split`.
Returns
-------
result : dict like {column -> {index -> value}}
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame({'colA' : list('AABCA'), 'colB' : ['X',np.nan,'Ya','Xb','Xa'],'colC' : [100,50,30,50,20], 'colD': [90,60,60,80,50]})
Out[df]:
colA colB colC colD
0 A X 100 90
1 A NaN 50 60
2 B Ya 30 60
3 C Xb 50 80
4 A Xa 20 50
In [1]: df.to_dict(orient='dict')
Out[1]:
{'colA': {0: 'A', 1: 'A', 2: 'B', 3: 'C', 4: 'A'},
'colB': {0: 'X', 1: nan, 2: 'Ya', 3: 'Xb', 4: 'Xa'},
'colC': {0: 100, 1: 50, 2: 30, 3: 50, 4: 20},
'colD': {0: 90, 1: 60, 2: 60, 3: 80, 4: 50}}
In [2]: df.to_dict(orient='list')
Out[2]:
{'colA': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'A'],
'colB': ['X', nan, 'Ya', 'Xb', 'Xa'],
'colC': [100, 50, 30, 50, 20],
'colD': [90, 60, 60, 80, 50]
In [3]: df.to_dict(orient='series')
Out[3]:
{'colA': 0 A
1 A
2 B
3 C
4 A
Name: colA, dtype: object, 'colB': 0 X
1 NaN
2 Ya
3 Xb
4 Xa
Name: colB, dtype: object, 'colC': 0 100
1 50
2 30
3 50
4 20
Name: colC, dtype: int64, 'colD': 0 90
1 60
2 60
3 80
4 50
Name: colD, dtype: int64}
In [4]: df.to_dict(orient='split')
Out[4]:
{'columns': ['colA', 'colB', 'colC', 'colD'],
'data': [['A', 'X', 100, 90],
['A', nan, 50, 60],
['B', 'Ya', 30, 60],
['C', 'Xb', 50, 80],
['A', 'Xa', 20, 50]],
'index': [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]}
In [5]: df.to_dict(orient='records')
Out[5]:
[{'colA': 'A', 'colB': 'X', 'colC': 100, 'colD': 90},
{'colA': 'A', 'colB': nan, 'colC': 50, 'colD': 60},
{'colA': 'B', 'colB': 'Ya', 'colC': 30, 'colD': 60},
{'colA': 'C', 'colB': 'Xb', 'colC': 50, 'colD': 80},
{'colA': 'A', 'colB': 'Xa', 'colC': 20, 'colD': 50}]
In [6]: df.to_dict(orient='index')
Out[6]:
{0: {'colA': 'A', 'colB': 'X', 'colC': 100, 'colD': 90},
1: {'colA': 'A', 'colB': nan, 'colC': 50, 'colD': 60},
2: {'colA': 'B', 'colB': 'Ya', 'colC': 30, 'colD': 60},
3: {'colA': 'C', 'colB': 'Xb', 'colC': 50, 'colD': 80},
4: {'colA': 'A', 'colB': 'Xa', 'colC': 20, 'colD': 50}}
另一个例子
有一个字典:c = {'A': [0, 120, 115, 100, 91, 103], 'B': [0, 107, 25, 26, 121, 118]}
想要转换成这样:
方法一:从字典中构建一个键值元组列表,然后使用pandas将其转换为df。
c = {'A': [0, 120, 115, 100, 91, 103], 'B': [0, 107, 25, 26, 121, 118]}
data = [(i, j) for i in c.keys() for j in c[i]]
print(data):
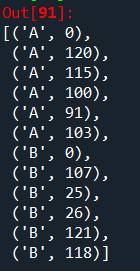
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["keys", "values"])
print(df)
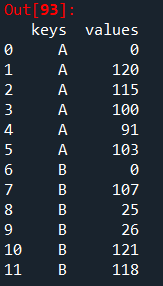
方法二:(该方法得到了列表,需要再转换成dict)
c = {'A': [0, 120, 115, 100, 91, 103], 'B': [0, 107, 25, 26, 121, 118]}
list = []
for key, value in c.items():
for i in value:
list.append([key, i])
print(list)
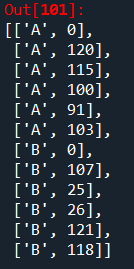
方法三:可以使用pandas创建包含两列(键和值)的数据框架,并将其保存
import pandas as pd
c = {'A': [0, 120, 115, 100, 91, 103], 'B': [0, 107, 25, 26, 121, 118]}
# define the second column name as "values"
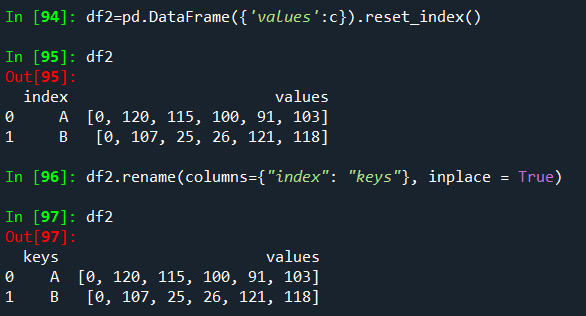
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'values': c}).reset_index()
# rename the first colum, here "keys"
df2.rename(columns={"index": "keys"}, inplace = True)
print(df2)
两个小tips
1.用列表中的值生成dict
new_list= [['key1','value1'],['key2','value2'],['key3','value3']]
new_dict = {}
for i in new_list:
new_dict[i[0]] = i[1] #字典赋值,左边为key,右边为value
得到new_dict :

2.设置key并且添加value(列表)
dict={}
dict.setdefault('a',[]).append(1)
dict.setdefault('a',[]).append(2)
dict.setdefault('a',[]).append(3)
dict.setdefault('b',[]).append(4)
得到dict:
zip函数
zip函数属于python的内建函数(内置函数),主要用来进行并行迭代,可以把两个序列合并在一起,返回一个元组的列表。
python zip 方法在 Python 2 和 Python 3 中的不同:在 Python 2.x zip() 返回的是一个列表。
示例一
#-*- coding:UTF-8 -*-
data = ['小明','小李','小方']
number = [100,200,300]
for name,num in zip(data,number):
print(f'{name}的账户余额为{num}')
运行结果:
小明的账户余额为100
小李的账户余额为200
小方的账户余额为300
zip函数可以作用于任意数量的序列,并且可以应用于不等长的序列,当短序列“耗尽”时就会停止。
示例二
#-*- coding:UTF-8 -*-
# 以python3版本演示
for num_1,num_2 in zip(range(3),range(5)):
print(f'zip函数演示:{num_1},{num_2}')
运行结果:
zip函数演示:0,0
zip函数演示:1,1
zip函数演示:2,2
由输出结果可以看到,zip函数以短序列为准,当短序列遍历结束时,for循环就会遍历结束。
将Python列表转换为字典的十种不同方法 (Ten different ways to convert a Python list to a dictionary)
1,Converting a list of tuples to a dictionary
将元组列表转换为字典
2,Converting two lists of the same length to a dictionary
将两个相同长度的列表转换为字典
3,Converting two lists of different length to a dictionary
将两个不同长度的列表转换为字典
4,Converting a list of alternative key, value items to a dictionary
将备用键,值项列表转换为字典
5,Converting a list of dictionaries to a single dictionary
将词典列表转换为单个词典
6,Converting a list into a dictionary using enumerate()
使用enumerate()将列表转换成字典
7,Converting a list into a dictionary using dictionary comprehension
使用字典理解将列表转换为字典
8,Converting a list to a dictionary using dict.fromkeys()
使用dict.fromkeys()将列表转换成字典
以下实例展示了 fromkeys()函数的使用方法:
seq = ('Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao')
dict = dict.fromkeys(seq) print "新字典1为 : %s" % str(dict)
dict = dict.fromkeys(seq, 10) print "新字典2为 : %s" % str(dict)
以上实例输出结果为:
新字典1为 : {'Google': None, 'Taobao': None, 'Runoob': None}
新字典2为 : {'Google': 10, 'Taobao': 10, 'Runoob': 10}
9,Converting a nested list to a dictionary using dictionary comprehension
使用字典理解将嵌套列表转换为字典
10,Converting a list to a dictionary using Counter()
使用Counter()将列表转换为字典





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)