5773. 【NOIP2008模拟】简单数学题
(File IO): input:math.in output:math.out
Time Limits: 1000 ms Memory Limits: 262144 KB Detailed Limits
Goto ProblemSet做法:经过一系列推导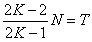 ,
,
 View Code
View Code
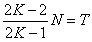 ,
,
也就是说,我们要使 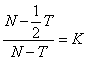 是一个正整数,那么我们只需要让是的(奇数)因数(当然1是不能算的)。
是一个正整数,那么我们只需要让是的(奇数)因数(当然1是不能算的)。
那么,答案为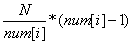 ,(其中(num[i])为N的因子)
,(其中(num[i])为N的因子)
代码如下:

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <cmath> 6 #define LL long long 7 #define N 1000007 8 using namespace std; 9 LL n; 10 LL num[N], ans; 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 freopen("math.in", "r", stdin); 15 freopen("math.out", "w", stdout); 16 scanf("%lld", &n); 17 if (n > 5) 18 { 19 LL p = sqrt(n); 20 for (int i = 1; i <= p + 1; i++) 21 if (n % i == 0) 22 { 23 if (i % 2 != 0 && i != 1) num[++ans] = i; 24 if ((n / i) % 2 != 0) 25 num[++ans] = n / i; 26 } 27 if (n % p == 0) num[ans--] = 0; 28 sort(num + 1, num + ans + 1); 29 printf("%lld ", ans); 30 for (int i = 1; i <= ans; i++) 31 { 32 LL g = n / num[i]; 33 printf("%lld ", g * (num[i] - 1)); 34 } 35 } 36 else 37 { 38 if (n == 3) 39 printf("1 2"); 40 else if (n == 5) 41 printf("1 4"); 42 else printf("0"); 43 } 44 }




