使用QCustomplot创建多轴多曲线
QCustomplot功能很强大,可example给的不够用,
需求是:创建多个轴,每个轴可以显示多个曲线
网上搜集后整理如下:
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h" Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent) : QWidget(parent) , ui(new Ui::Widget) { ui->setupUi(this); m_pCPlot = new QCustomPlot(this); m_pCPlot->plotLayout()->clear(); m_pCPlot->setInteractions(QCP::iRangeDrag | QCP::iRangeZoom | QCP::iSelectPlottables); QCPAxisRect *axisRect1 = new QCPAxisRect(m_pCPlot); //axisRect1->setupFullAxesBox(true); axisRect1->addAxis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->setTickLabelColor(QColor("#6050F8")); m_pCPlot->plotLayout()->addElement(0,0,axisRect1); QCPAxisRect *axisRect2 = new QCPAxisRect(m_pCPlot); //axisRect2->setupFullAxesBox(true); axisRect2->addAxis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->setTickLabelColor(QColor("#1050F8")); m_pCPlot->plotLayout()->addElement(1,0,axisRect2); QVector<double> x(101),y0(101),y1(101),y2(101),y3(101); for(int i=0;i<101;i++) { x[i] = i/50.0-1; y0[i]= qExp(-x[i]*x[i]*2)+2; y1[i]=qSin(x[i]*3); y2[i]=qCos(x[i]*3); y3[i]=qTan(x[i]*3); } QCPGraph *graph0 = m_pCPlot->addGraph(axisRect1->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom),axisRect1->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); graph0->setData(x,y0); graph0->setPen(QPen(Qt::blue)); graph0->rescaleAxes(); QCPGraph *graph1 = m_pCPlot->addGraph(axisRect1->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom),axisRect1->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); graph1->setData(x,y1); graph1->setPen(QPen(Qt::red)); graph1->rescaleAxes(); QCPGraph *graph2 = m_pCPlot->addGraph(axisRect2->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom),axisRect2->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); graph2->setData(x,y1); graph2->setPen(QPen(Qt::green)); graph2->rescaleAxes(); QCPGraph *graph3 = m_pCPlot->addGraph(axisRect2->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom),axisRect2->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); graph3->setData(x,y2); graph3->setPen(QPen(Qt::black)); graph2->rescaleAxes(); // make axis rects' left side line up: QCPMarginGroup *group = new QCPMarginGroup(m_pCPlot); //m_pCPlot->axisRect()->setMarginGroup(QCP::msLeft|QCP::msRight, group); //wideAxisRect->setMarginGroup(QCP::msLeft|QCP::msRight, group); for(int j=0;j<m_pCPlot->axisRectCount();j++) { m_pCPlot->axisRect(j)->setMarginGroup(QCP::msLeft|QCP::msRight, group); } QSplitter *mainSplitter = new QSplitter(Qt::Vertical,this); mainSplitter->addWidget(m_pCPlot); QVBoxLayout *vLayout = new QVBoxLayout(this); vLayout->addWidget(mainSplitter); m_pCPlot->replot(); }
其它参考:
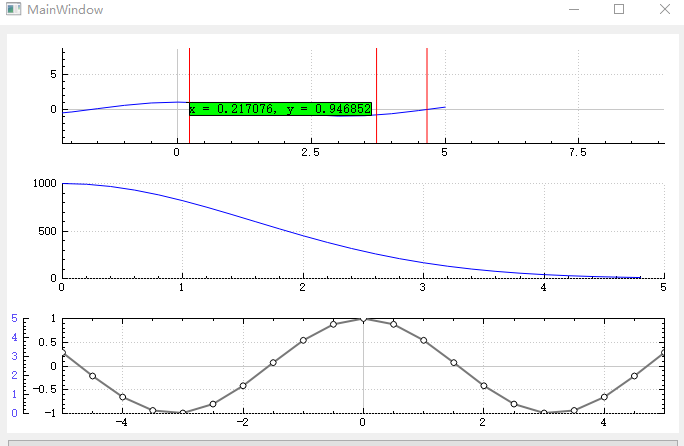
关于QCustomplot多坐标轴的QCPItemTracer的游标问题!
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : QMainWindow(parent) , ui(new Ui::MainWindow) { ui->setupUi(this); test(); for ( int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { tracer[i] = new QCPItemTracer(ui->customPlot); tracer[i]->setPen(QPen(Qt::DashLine)); tracer[i]->setStyle(QCPItemTracer::tsPlus);//游标样式:十字星、圆圈、方框等 tracerLabel[i] = new QCPItemText(ui->customPlot); //生成游标说明 //下面的代码就是设置游标说明的外观和对齐方式等状态 tracerLabel[i]->setLayer("overlay"); tracerLabel[i]->position->setCoords(0.5, 0); tracerLabel[i]->setFont(QFont(font().family(), 10)); tracerLabel[i]->setPen(QPen(Qt::black)); tracerLabel[i]->setPositionAlignment(Qt::AlignLeft | Qt::AlignTop); tracerLabel[i]->setBrush(Qt::green); //下面这个语句很重要,它将游标说明锚固在tracer位置处,实现自动跟随 tracerLabel[i]->position->setParentAnchor(tracer[i]->position); m_lineV[i] = new QCPItemStraightLine(ui->customPlot); QPen linesPen(Qt::red, 1, Qt::SolidLine); m_lineV[i]->setLayer("overlay"); m_lineV[i]->setPen(linesPen); m_lineV[i]->setClipToAxisRect(true); m_lineV[i]->point1->setCoords(0, 0); m_lineV[i]->point2->setCoords(0, 0); } connect(ui->customPlot, &QCustomPlot::mouseMove, this, &MainWindow::myMoveEvent); } MainWindow::~MainWindow() { delete ui; } void MainWindow::myMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event) { double xValue; double yValue; qDebug() << "aaaa"; double yy = wideAxisRect->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->pixelToCoord(event->pos().x()); m_lineV[0]->point1->setCoords(yy, 1); m_lineV[0]->point2->setCoords(yy, 0); tracer[0]->setGraph(mainGraphCos);//将游标和该曲线图层想连接 tracer[0]->position->setAxes(wideAxisRect->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom), wideAxisRect->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); tracer[0]->setGraphKey(yy); //将游标横坐标(key)设置成刚获得的横坐标数据 tracer[0]->setInterpolating(true); //游标的纵坐标可以通过曲线数据线性插值自动获得(这就不用手动去计算了) tracer[0]->updatePosition(); //使得刚设置游标的横纵坐标位置生效 //以下代码用于更新游标说明的内容 xValue = tracer[0]->position->key(); yValue = tracer[0]->position->value(); //设置游标说明(tracerLabel)的内容 tracerLabel[0]->setText(QString("x = %1, y = %2").arg(xValue).arg(yValue)); double xx = subRectLeft->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->pixelToCoord(event->pos().x()); m_lineV[1]->point1->setCoords(xx, 1); m_lineV[1]->point2->setCoords(xx, 0); tracer[1]->setGraph(subGraphRandom);//将游标和该曲线图层想连接 tracer[1]->position->setAxes(subRectLeft->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom), subRectLeft->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); tracer[1]->setGraphKey(xx); //将游标横坐标(key)设置成刚获得的横坐标数据x tracer[1]->setInterpolating(true); //游标的纵坐标可以通过曲线数据线性插值自动获得(这就不用手动去计算了) tracer[1]->updatePosition(); //使得刚设置游标的横纵坐标位置生效 //以下代码用于更新游标说明的内容 xValue = tracer[1]->position->key(); yValue = tracer[1]->position->value(); //设置游标说明(tracerLabel)的内容 tracerLabel[1]->setText(QString("x = %1, y = %2").arg(xValue).arg(yValue)); double x = subRectRight->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->pixelToCoord(event->pos().x()); m_lineV[2]->point1->setCoords(x, 1); m_lineV[2]->point2->setCoords(x, 0); tracer[2]->setGraph(subBars);//将游标和该曲线图层想连接 tracer[2]->position->setAxes(subRectRight->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom), subRectRight->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); tracer[2]->setGraphKey(x); //将游标横坐标(key)设置成刚获得的横坐标数据x tracer[2]->setInterpolating(true); //游标的纵坐标可以通过曲线数据线性插值自动获得(这就不用手动去计算了) tracer[2]->updatePosition(); //使得刚设置游标的横纵坐标位置生效 //以下代码用于更新游标说明的内容 xValue = tracer[2]->position->key(); yValue = tracer[2]->position->value(); //设置游标说明(tracerLabel)的内容 tracerLabel[2]->setText(QString("x = %1, y = %2").arg(xValue).arg(yValue)); ui->customPlot->replot(); } void MainWindow::test() { ui->customPlot->plotLayout()->clear(); // 首先清空默认的轴矩形,让我们从头开始 ui->customPlot->setInteractions(QCP::iRangeDrag | QCP::iRangeZoom | QCP::iSelectPlottables | QCP::iSelectLegend); wideAxisRect = new QCPAxisRect(ui->customPlot); // 还记得setupDefaultAxes为true时的作用吗,忘了的话翻上去看吧 wideAxisRect->setupFullAxesBox(true); // 让四个轴关联,并全部显示出来 wideAxisRect->addAxis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->setTickLabelColor(QColor("#6050F8")); // 在左边多添加一个轴并且设置它的颜色 ui->customPlot->plotLayout()->addElement(2, 0, wideAxisRect); // 在第一行添加轴矩形 // 在第二行添加一个子布局,后面会添加两个轴矩形在里面 subRectLeft = new QCPAxisRect(ui->customPlot); // 不配置轴 subRectRight = new QCPAxisRect(ui->customPlot); ui->customPlot->plotLayout()->addElement(0, 0, subRectLeft); // 在第一列添加轴矩形 ui->customPlot->plotLayout()->addElement(1, 0, subRectRight); // 在第二列添加轴矩形 subRectLeft->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->ticker()->setTickCount(2); // 设置轴的刻度为一个固定的步进值 subRectRight->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->ticker()->setTickCount(2); // 准备数据 QVector<QCPGraphData> dataCos(21), dataGauss(50), dataRandom(100); QVector<double> x3, y3; qsrand(3); for (int i=0; i<dataCos.size(); ++i) { dataCos[i].key = i/(double)(dataCos.size()-1)*10-5.0; dataCos[i].value = qCos(dataCos[i].key); } for (int i=0; i<dataGauss.size(); ++i) { dataGauss[i].key = i/(double)dataGauss.size()*10-5.0; dataGauss[i].value = qExp(-dataGauss[i].key*dataGauss[i].key*0.2)*1000; } for (int i=0; i<dataRandom.size(); ++i) { dataRandom[i].key = i/(double)dataRandom.size()*10; dataRandom[i].value = qrand()/(double)RAND_MAX-0.5+dataRandom[qMax(0, i-1)].value; } x3 << 1 << 2 << 3 << 4; y3 << 2 << 2.5 << 4 << 1.5; // mainGraphCos和 mainGraphGauss 共享下轴,但是它们的左轴不同 mainGraphCos = ui->customPlot->addGraph(wideAxisRect->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom), wideAxisRect->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); mainGraphCos->data()->set(dataCos); mainGraphCos->valueAxis()->setRange(-1, 1); mainGraphCos->rescaleKeyAxis(); mainGraphCos->setScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle::ssCircle, QPen(Qt::black), QBrush(Qt::white), 6)); mainGraphCos->setPen(QPen(QColor(120, 120, 120), 2)); subGraphRandom = ui->customPlot->addGraph(subRectLeft->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom), subRectLeft->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); subGraphRandom->data()->set(dataCos); subGraphRandom->valueAxis()->setRange(-1,5); subBars = ui->customPlot->addGraph(subRectRight->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom), subRectRight->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)); subBars->data()->set(dataGauss); subBars->valueAxis()->setRange(0,1000); qDebug() << ui->customPlot->axisRectCount(); qDebug() << ui->customPlot->graphCount(); QCPMarginGroup *marginGroup = new QCPMarginGroup(ui->customPlot); for (int j = 0; j < ui->customPlot->axisRectCount(); j++) { ui->customPlot->axisRect(j)->setMarginGroup(QCP::msLeft|QCP::msRight, marginGroup); } }
QCustomPlot* customPlot = ui->customPlot_6; // 添加两个graph customPlot->addGraph(); customPlot->graph(0)->setPen(QPen(Qt::blue)); // 第一条曲线颜色 customPlot->graph(0)->setBrush(QBrush(QColor(0, 0, 255, 20))); // 第一条曲线和0轴围成区域填充的颜色 customPlot->addGraph(); customPlot->graph(1)->setPen(QPen(Qt::red)); // 第二条曲线颜色 // 生成数据 QVector<double> x(251), y0(251), y1(251); for (int i=0; i<251; ++i) { x[i] = i; y0[i] = qExp(-i/150.0)*qCos(i/10.0); // 指数衰减的cos y1[i] = qExp(-i/150.0); // 衰减指数 } // 配置右侧和顶部轴显示刻度,但不显示标签: customPlot->xAxis2->setVisible(true); customPlot->xAxis2->setTickLabels(false); customPlot->yAxis2->setVisible(true); customPlot->yAxis2->setTickLabels(false); // 让左边和下边轴与上边和右边同步改变范围 connect(customPlot->xAxis, SIGNAL(rangeChanged(QCPRange)), customPlot->xAxis2, SLOT(setRange(QCPRange))); connect(customPlot->yAxis, SIGNAL(rangeChanged(QCPRange)), customPlot->yAxis2, SLOT(setRange(QCPRange))); // 设置数据点 customPlot->graph(0)->setData(x, y0); customPlot->graph(1)->setData(x, y1); // 让范围自行缩放,使图0完全适合于可见区域: customPlot->graph(0)->rescaleAxes(); // 图1也是一样自动调整范围,但只是放大范围(如果图1小于图0): customPlot->graph(1)->rescaleAxes(true); // 允许用户用鼠标拖动轴范围,用鼠标滚轮缩放,点击选择图形: customPlot->setInteractions(QCP::iRangeDrag | QCP::iRangeZoom | QCP::iSelectPlottables); customPlot->replot();
(1)上下轴,左右轴范围同步
利用rangeChanged信号传递轴范围QCPRange,范围改变时将xAxis的范围传给xAxis2,yAxis也是,就能实现轴范围同步了。
connect(customPlot->xAxis, SIGNAL(rangeChanged(QCPRange)), customPlot->xAxis2, SLOT(setRange(QCPRange)));
connect(customPlot->yAxis, SIGNAL(rangeChanged(QCPRange)), customPlot->yAxis2, SLOT(setRange(QCPRange)));
(2)自动调整范围,使数据全部可见。
调用rescaleAxes (bool onlyEnlarge = false)重新调整与此绘图表关联的键和值轴,以显示所有的数据
onlyEnlarge 默认false,表示范围可以缩小放大,如果为true表示只能放大,而不会缩小范围。
例如曲线:
调用 customPlot->graph(0)->rescaleAxes();后范围被缩小了,曲线正好占满整个区域,但是调用customPlot->graph(0)->rescaleAxes(true)就不会有变化,因为区域不会缩小。
利用这点可以通过多次调用rescaleaxis来完整地显示多个graph的数据。让graph(0)自动缩放rescaleAxes(),在graph(0)范围的基础上rescaleAxes(true)只会扩大范围或不变而不缩小,这样最终能够显示graph(n)所有的数据
一些设置:
// 让范围自行缩放,使图0完全适合于可见区域: customPlot->graph(0)->rescaleAxes(); // 图1也是一样自动调整范围,但只是放大或不变范围 customPlot->graph(1)->rescaleAxes(true); // 图2也是一样自动调整范围,但只是放大或不变范围 customPlot->graph(2)->rescaleAxes(true); // 图3也是一样自动调整范围,但只是放大或不变范围 customPlot->graph(2)->rescaleAxes(true);



