算法设计和数据结构学习_6(单链表的递归逆序)
单链表的逆序方法有很多种,求职过程中会碰到类似的题。比如进栈出栈;变量链表放入数组后利用数组的逆序重构链表;遍历链表时每次访问的节点都指向它的前节点;递归调用等。本次实验是用递归的方法实现单链表的逆序,网上有很多类似的code.
这次实验主要要注意的是指针引用的使用,要充分理解引用是个别名,指针的引用可以参考其它网友的一篇博文:指针的引用
实验内容是先构造一个随机指定长度的单链表,将其输出,然后逆序后输出。
代码如下:
// reverse_list.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <random> using namespace std; struct Node { int vale; Node *next; }; /*创建长度为n的一个随机整数链表*/ Node* creat_list(int n) { Node *head = new Node; head->next = NULL; Node *pre = head; srand(0); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Node *current = new Node; current->vale = rand(); current->next = NULL; pre->next = current; pre = current; } return head; } /*链表的逆序*/ Node* reverse_list(Node *plist, Node *&head) //这个函数的返回值并不是最终链表逆序后的链表头,而是尾, //它的头保存在head指针里,所以head用的是指针引用. { Node *pback = NULL; if(plist == NULL || plist->next == NULL) { head->next = plist; return plist; } else { pback = reverse_list(plist->next, head); pback->next = plist; return plist; } } /*从头节点依次显示链表里的元素,注意这里头节点里的元素没有被当做第一个元素*/ void show_list(Node *p) { while(p->next != NULL) { cout<<p->next->vale<<" "; p = p->next; //因为每个结构体的节点不是以数组的形式存在,所以其地址不是连续的,不能用p++ } cout<<endl; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { int n = 10; Node *my_list = creat_list(n); cout<<"My list is : "<<endl; show_list(my_list); Node *head = new Node; cout<<"My reverse_list is : "<<endl; reverse_list(my_list->next, head)->next = NULL; show_list(head); return 0; }
实验结果如下:
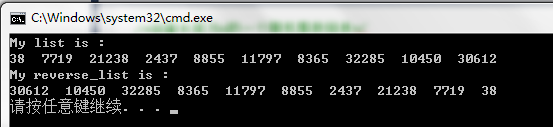
参考资料:
作者:tornadomeet
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet
欢迎转载或分享,但请务必声明文章出处。 (新浪微博:tornadomeet,欢迎交流!)



