SpringMVC学习笔记
1. 什么是SpringMVC?
Spring MVC是一个基于Java的实现了MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,通过把Model,View,Controller分离,将web层进行职责解耦,把复杂的web应用分成逻辑清晰的几部分,简化开发,减少出错。
作用:就是从请求中接收传入的参数,将处理后的结果数据返回给页面展示。
2. SpringMVC工作流程(工作原理)?
springMVC的几个重要组件:
- 前端控制器 (DispatcherServlet) 作用:接收请求、响应结果,相当于转发器
- 处理映射器(HandlerMapping) 作用:根据请求的URL来查找Handler
- 处理器(Hander,平时也叫Controller) (需要程序员开发)
- 处理器适配器(HandlAdapter) 作用:通过HandAdapter对处理器进行执行
- 视图解析器(ViewResolver) 作用:将处理结果生成View视图
- 视图(View) (需要程序员开发具体的jsp页面)
说明:在springmvc的各个组件中,处理器映射器HandlerMapping、处理器适配器HandlAdapter、视图解析器ViewResolver称为springmvc的三大组件。需要用户开放的组件有Hander、View。
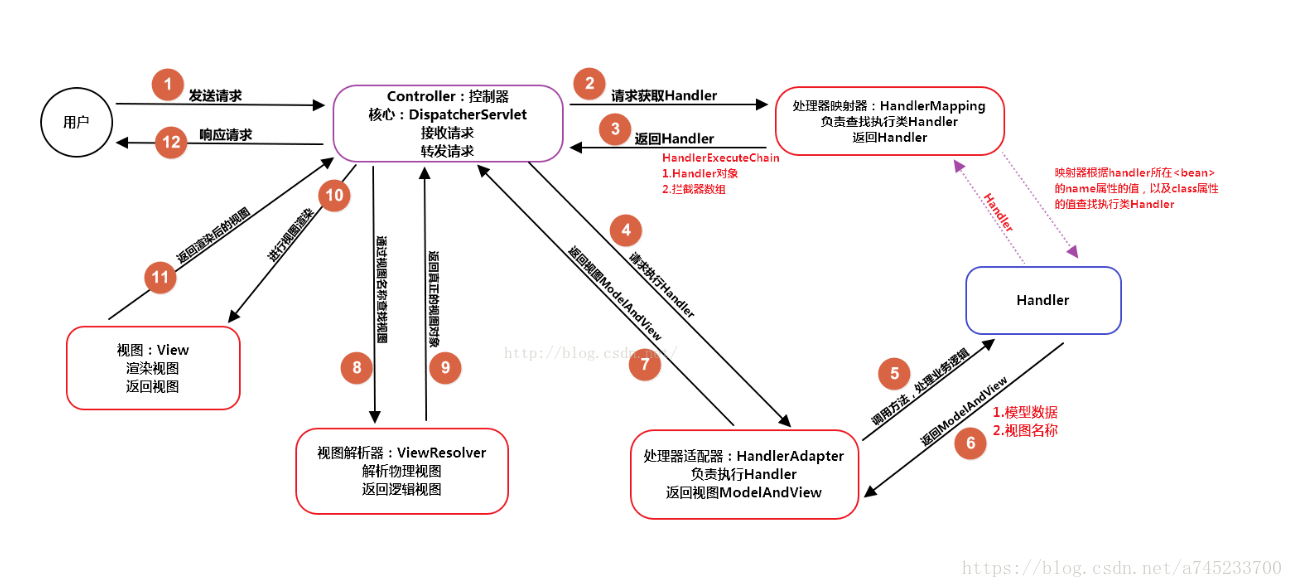
(1)用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet;
(2) DispatcherServlet收到请求后,调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器,请求获取Handle;
(3)处理器映射器根据请求url找到具体的处理器,生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet;
(4)DispatcherServlet 调用 HandlerAdapter处理器适配器;
(5)HandlerAdapter 经过适配调用 具体处理器(Handler,也叫后端控制器);
(6)Handler执行完成返回ModelAndView;
(7)HandlerAdapter将Handler执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet;
(8)DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewResolver视图解析器进行解析;
(9)ViewResolver解析后返回具体View;
(10)DispatcherServlet对View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)
(11)DispatcherServlet响应用户。
3. 入门程序demo
使用springmvc实现商品列表的展示,展示页面itemList.jsp
(1)ItemsController :在类上添加@Controller注解
@Controller publicclass ItemController { @RequestMapping("/itemList") //@RequestMapping注解指定请求的url,其中“.action”可以加也可以不加(在web.xml配置了后面加.action) public ModelAndView itemList() throws Exception { List<Items>itemList = new ArrayList<>(); //商品列表 Items items_1 = new Items(); items_1.setName("联想笔记本_3"); items_1.setPrice(6000f); itemList.add(items_1);
//创建modelandView对象 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); //添加model modelAndView.addObject("itemList", itemList); //在ModelAndView对象中,将视图设置为“/WEB-INF/jsp/itemList.jsp” modelAndView.setViewName("/WEB-INF/jsp/itemList.jsp"); returnmodelAndView; } }
(2)springmvc.xml :
<!-- 扫描controller注解 --> <context:component-scanbase-package="cn.ztt.springmvc.controller"/>
(3)在web.xml中配置前端控制器DispatcherServlet
<!-- 前端控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
注解映射器和适配器、视图解析器:
1、组件扫描器: 使用组件扫描器省去在spring容器配置每个controller类的繁琐。使用<context:component-scan>自动扫描标记@controller的控制器类,配置如下:
<!-- 扫描controller注解,多个包中间使用半角逗号分隔 --> <context:component-scanbase-package="cn.ztt.springmvc.controller.first"/>
[2]、注解式处理器映射器 RequestMappingHandlerMapping :对类中标记@ResquestMapping的方法进行映射。
根据ResquestMapping定义的url匹配ResquestMapping标记的方法,匹配成功返回HandlerMethod对象给前端控制器,HandlerMethod对象中封装url对应的方法Method。
(@RequestMapping:定义请求url到处理器功能方法的映射)
<!--注解映射器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"/>
[3]、注解式处理器适配器 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter :对标记@ResquestMapping的方法进行适配。
<!--注解适配器 --> <beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"/>
4、 <mvc:annotation-driven>
springmvc使用<mvc:annotation-driven>自动加载RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,可用在springmvc.xml配置文件中使用<mvc:annotation-driven>替代注解处理器和适配器的配置。
<!-- 加载注解驱动 代替上述[2]、[3]--> <mvc:annotation-driven/>
5、视图解析器 :
<beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <propertyname="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"/> <!-- prefix 和suffix:查找视图页面的前缀和后缀,最终视图的址为:前缀+逻辑视图名+后缀 --> <propertyname="prefix"value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <propertyname="suffix"value=".jsp"/> </bean>
- InternalResourceViewResolver:支持JSP视图解析
- viewClass:JstlView表示JSP模板页面需要使用JSTL标签库,所以classpath中必须包含jstl的相关jar 包。此属性可以不设置,默认为JstlView。
- prefix 和suffix:查找视图页面的前缀和后缀,最终视图的址为:前缀+逻辑视图名+后缀,逻辑视图名需要在controller中返回ModelAndView指定,比如逻辑视图名为hello,则最终返回的jsp视图地址 “WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp”
4. SSM整合案例
整合目标:控制层采用springmvc、持久层使用mybatis实现
整合思路:
Dao层:
1、SqlMapConfig.xml,空文件即可。需要文件头。
2、applicationContext-dao.xml。
a) 数据库连接池
b) SqlSessionFactory对象,需要spring和mybatis整合包下的。
c) 配置mapper文件扫描器。
Service层:(由spring管理)
1、applicationContext-service.xml 包扫描器,扫描@service注解的类。
2、applicationContext-trans.xml 配置事务。
表现层:
Springmvc.xml
1、包扫描器,扫描@Controller注解的类。
2、配置注解驱动。
3、视图解析器
Web.xml
配置前端控制器
(1)xml文件:
1)在classpath下创建 mybatis/sqlMapConfig.xml:里面没什么内容
2)applicationContext-dao.xml:配置数据源、配置SqlSessionFactory、mapper扫描器
<!-- 加载配置文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <!-- 数据库连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <propertyname="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <propertyname="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <propertyname="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <propertyname="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean>
<!-- mapper配置 --> <!-- 让spring管理sqlsessionfactory 使用mybatis和spring整合包中的 --> <beanid="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <!-- 数据库连接池 --> <propertyname="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!-- 加载mybatis的全局配置文件 --> <propertyname="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis/SqlMapConfig.xml"/> </bean> <!-- 配置Mapper扫描器 --> <beanclass="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <propertyname="basePackage"value="cn.ztt.springmvc.mapper"/> </bean>
3) applicationContext-service.xml :
<context:component-scanbase-package="cn.ztt.springmvc.service"/>
4) applicationContext-transaction.xml :
<!-- 事务管理器 --> <beanid="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!-- 数据源 --> <propertyname="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- 通知 --> <tx:adviceid="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!-- 传播行为 --> <tx:methodname="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:methodname="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:methodname="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:methodname="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:methodname="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/> <tx:methodname="get*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 切面 --> <aop:config> <aop:advisoradvice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* cn.ztt.springmvc.service.*.*(..))"/> </aop:config>
5) springmvc.xml:
<!-- 扫描带Controller注解的类 --> <context:component-scanbase-package="cn.itcast.springmvc.controller"/> <!-- 加载注解驱动 --> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <!-- 视图解析器 --> <beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <propertyname="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"/> <!-- jsp前缀 --> <propertyname="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <!-- jsp后缀 --> <propertyname="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean>
6)web.xml:
<!-- 加载spring容器 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext-*.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 配置前端控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
(2)Service层ItemServiceImpl实现类:
@Service publicclass ItemServiceImpl implements ItemService { @Autowired private ItemMapper itemMapper; @Override public List<Items> getItemsList() { List<Items> itemList = itemMapper.getItemList(); return itemList; } }
(3)controller:
@Controller publicclass ItemController { @Autowired private ItemService itemService; @RequestMapping("/itemList") public ModelAndView getItemList() { List<Items>list = itemService.getItemsList(); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.addObject("itemList", list); modelAndView.setViewName("itemList"); return modelAndView; } }
5. 参数绑定
5.1 绑定简单数据类型
需求:编辑商品信息,需要根据商品id查询商品信息,然后展示到页面。
请求的url:/itemEdit.action
参数:id(商品id)
响应结果:商品编辑页面,展示商品详细信息。
(1)Service:
@Override public Items getItemById(int id) { Items items = itemMapper.getItemById(id); return items; }
(2)Controller参数绑定:
要根据 id 查询商品数据,需要从请求的参数中把请求的 id 取出来。id 应该包含在Request对象中。可以从Request对象中取 id :
@RequestMapping("/itemEdit")
public ModelAndView itemEdit(HttpServletRequest request) {
//从Request中取id
String strId = request.getParameter("id");
Integer id = null;
//如果id有值则转换成int类型
if (strId != null&& !"".equals(strId)) {
id = new Integer(strId);
} else {
//出错
return null;
}
Items items = itemService.getItemById(id);
//创建ModelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
//向jsp传递数据
modelAndView.addObject("item", items);
//设置跳转的jsp页面
modelAndView.setViewName("editItem");
return modelAndView;
}
【注】如果想获得Request对象只需要在Controller方法的形参中添加一个参数即可。Springmvc框架会自动把Request对象传递给方法。默认支持的参数类型有:
(处理器形参中添加如下类型的参数处理适配器会默认识别并进行赋值:)
HttpServletRequest :通过request对象获取请求信息。
HttpServletResponse :通过response处理响应信息。
HttpSession :通过session对象得到session中存放的对象。
Model / ModelMap :是Model接口的实现类,通过 Model 或 ModelMap 向页面传递数据,如下:
//调用service查询商品信息 Items item = itemService.findItemById(id); model.addAttribute("item", item);
页面通过 ${item.XXXX} 获取item对象的属性值。
【注】如果使用Model则可以不使用ModelAndView对象,Model对象可以向页面传递数据,View对象则可以使用String返回值替代。不管是Model还是ModelAndView,其本质都是使用Request对象向jsp传递数据。
如果使用Model则方法可以改造成:
@RequestMapping("/itemEdit")
public String itemEdit(HttpServletRequest request, Model model) {
//从Request中取id
String strId = request.getParameter("id");
Integer id = null;
//如果id有值则转换成int类型
if (strId != null&& !"".equals(strId)) {
id = new Integer(strId);
} else {
//出错
returnnull;
}
Items items = itemService.getItemById(id);
/*创建ModelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
向jsp传递数据
modelAndView.addObject("item", items);*/
model.addAttribute("item", items);
/*设置跳转的jsp页面
modelAndView.setViewName("editItem");
return modelAndView; */
return "editItem";
}
注意绑定简单数据类型:当请求的参数名称和处理器形参名称一致时会将请求参数与形参进行绑定。从Request取参数的方法可以进一步简化:
@RequestMapping("/itemEdit")
public String itemEdit(Integer id, Model model) {
Items items = itemService.getItemById(id);
//向jsp传递数据
model.addAttribute("item", items);
//设置跳转的jsp页面
return"editItem";
}
【注】
1)参数类型推荐使用包装数据类型,因为基础数据类型不可以为null。
2)@RequestParam :常用于处理简单类型的绑定
- value :参数名字,即入参的请求参数名字,如value=“item_id”表示请求的参数区中的名字为item_id的参数的值将传入;
- required :是否必须有参数,默认是true,表示请求中一定要有相应的参数,否则将报:TTP Status 400 - Required Integer parameter 'XXXX' is not present
- defaultValue:默认值,表示如果请求中没有同名参数时的默认值
public String editItem(@RequestParam(value="item_id", required=true) String id) { } //形参名称为id,但是这里使用value="item_id"限定请求的参数名为item_id,所以页面传递参数的名必须为item_id。 //注意:如果请求参数中没有item_id将跑出异常:HTTP Status 500 - Required Integer parameter 'item_id' is not present //这里通过required=true限定item_id参数为必需传递,如果不传递则报400错误,可以使用defaultvalue设置默认值,即使required=true也可以不传item_id参数值
5.2 绑定pojo类型
如果提交的参数很多,或者提交的表单中的内容很多的时候可以使用pojo接收数据。要求pojo对象中的属性名和表单中input的name属性一致。
(1)页面定义如下:
<input type="text" name="name"/> <input type="text" name="price"/>
(2)Pojo定义:
public class Items { private Integer id; private String name; private Float price;
。。。。。。 }
(3)请求的参数名称和pojo的属性名称一致,会自动将请求参数赋值给pojo的属性:
@RequestMapping("/updateitem")
public String updateItem(Items items) {
itemService.updateItem(items);
return"success";
}
注!!解决post乱码问题:
可以使用SpringMVC提供的过滤器(CharacterEncodingFilter)来解决,只需在web.xml中配置该过滤器就可以,需要注意的是,过滤器的编码设置应该与jsp页面保持一致。
<filter> <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>utf-8</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>注!解决get乱码问题: (有2种方法)
- 修改tomcat配置文件添加编码与工程编码一致,如下:
<Connector URIEncoding="utf-8" connectionTimeout="20000" port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" redirectPort="8443"/>
- 另外一种方法对参数进行重新编码:
String userName = new String(request.getParamter("userName").getBytes("ISO8859-1"),"utf-8")
5.3 绑定包装pojo
(1)包装对象定义如下:
public classQueryVo { private Items items; }
(2)页面定义:
<input type="text" name="items.name" /> <input type="text" name="items.price" />
(3)Controller方法定义:
public String useraddsubmit(Model model,QueryVo queryVo)throws Exception{ System.out.println(queryVo.getItems()); }
(4)接收查询条件:
@RequestMapping("/queryitem")
public String queryItem(QueryVo queryVo) {
System.out.println(queryVo.getItems().getName());
System.out.println(queryVo.getItems().getPrice());
return null;
}
5.4 自定义参数绑定
例:修改商品生产日期。
由于日期数据有很多种格式,所以springmvc没办法把字符串转换成日期类型。所以需要自定义参数绑定。前端控制器接收到请求后,找到注解形式的处理器适配器,对RequestMapping标记的方法进行适配,并对方法中的形参进行参数绑定。在springmvc这可以在处理器适配器上自定义Converter进行参数绑定。如果使用<mvc:annotation-driven/> 可以在此标签上进行扩展。
(1)自定义Converter:
public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> { @Override public Date convert(String source) { SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); try { returnsimpleDateFormat.parse(source); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
(2)配置Converter:
<!-- 加载注解驱动 --> <mvc:annotation-drivenconversion-service="conversionService"/> <!-- 转换器配置 --> <bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean"> <property name="converters"> <set> <bean class="cn.ztt.springmvc.convert.DateConverter"/> </set> </property> </bean>
6.springmvc与struts2的不同?
1、 springMvc的入口是一个servlet即前端控制器,而struts2入口是一个filter过虑器。
2、 springMvc是基于方法开发(一个url对应一个方法),请求参数传递到方法的形参,可以设计为单例或多例(建议单例);
struts2是基于类开发,传递参数是通过类的属性,只能设计为多例。
3、 struts采用值栈存储请求和响应的数据,通过OGNL存取数据;
springmvc通过参数解析器是将request请求内容解析,并给方法形参赋值,将数据和视图封装成ModelAndView对象,最后又将ModelAndView中的模型数据通过reques域传输到页面。Jsp视图解析器默认使用jstl。
7. @RequestMapping
(1):@RequestMapping注解用在类上面有什么作用?
表示类中所有相应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。
如下:
@RequestMapping放在类名上边,设置请求前缀:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/item")
方法名上边设置请求映射url:
@RequestMapping("/queryItem ")
则访问地址为:/item/queryItem
(2)请求方法限定:
- 限定GET方法:
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
如果通过Post访问则报错:HTTP Status 405 - Request method 'POST' not supported
- 限定POST方法:
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
如果通过Post访问则报错:HTTP Status 405 - Request method 'GET' not supported
- GET和POST都可以:
@RequestMapping(method={RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
8.controller方法返回值
(1)返回 ModelAndView :
controller方法中定义ModelAndView对象并返回,对象中可添加model数据、指定view。
(2)返回 void :
在controller方法形参上可以定义request和response,使用 request 或 response 指定响应结果:
1)使用request转向页面: request.getRequestDispatcher("页面路径").forward(request, response);
2)也可以通过response页面重定向:response.sendRedirect("url");
3)也可以通过response指定响应结果,例如响应json数据如下:
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write("json串");
(3)返回字符串:
controller方法返回字符串可以指定逻辑视图名,通过视图解析器解析为物理视图地址: 例 return "item/editItem";
问题: Spring MVC怎样设定重定向和转发?
(1)转发:在返回值前面加 " forward: " 例 return "forward:queryItem.action";
(2)重定向:在返回值前面加 " redirect: " 例 return "redirect:queryItem.action";
redirect方式相当于“response.sendRedirect()”,转发后浏览器的地址栏变为转发后的地址,因为转发即执行了一个新的request和response。
由于新发起一个request原来的参数在转发时就不能传递到下一个url,如果要传参数可以/item/queryItem.action后边加参数,如:/item/queryItem?...&…..
forward方式相当于“request.getRequestDispatcher().forward(request,response)”,转发后浏览器地址栏还是原来的地址。转发并没有执行新的request和response,而是和转发前的请求共用一个request和response。所以转发前请求的参数在转发后仍然可以读取到。
9. @RequestBody与@ResponseBody
(1)@RequestBody注解 :用于读取http请求的内容(字符串),通过springmvc提供的HttpMessageConverter接口将读到的内容转换为json、xml等格式的数据并绑定到controller方法的参数上。
例 httpq请求内容:List.action?id=1&name=zhangsan&age=12 ,@RequestBody注解实现接收http请求的json数据,将json数据转换为java对象
(2)@ResponseBody注解:用于将Controller的方法返回的对象,通过HttpMessageConverter接口转换为指定格式的数据如:json,xml等,通过Response响应给客户端。
本例子应用:@ResponseBody注解实现将controller方法返回对象转换为json响应给客户端
10. Spring MVC的控制器是不是单例模式,如果是,有什么问题,怎么解决?
默认的是单例模式,所以在多线程访问的时候有线程安全问题,解决方案是在控制器里不能写字段。不要用同步,会影响性能。
单例不用每次都new。
最佳实践:
1、不要在controller中定义成员变量。
2、万一必须要定义一个非静态成员变量时候,则通过注解@Scope("prototype"),将其设置为多例模式。
例:
@Controller @RequestMapping("/demo") public class MultViewController { private static int st = 0; //静态的 private int index = 0; //非静态 @RequestMapping("/test") public void test() { System.out.println(st++ + " | " + index++); } }
默认单例的,随着请求次数的增加:
0 | 0
1 | 1
2 | 2
3 | 3
4 | 4
...
controller增加注解:
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
此时,无论多少次请求,结果为:
0 | 0
1 | 0
2 | 0
3 | 0
4 | 0
...
从以上很容易看出,单例是线程不安全的,会导致属性的重复性利用。
转载自https://www.cnblogs.com/eric-fang/p/5629892.html
11. 其他问题
Spring MVC如何读取请求参数值?
(1)直接把表单的参数写在Controller相应的方法的形参中,通过url提交的参数名称需要和Controller方法中的参数名称一致
(2)通过HttpServletRequest接收,使用request.getParameter()获得
(3)通过JavaBean,建立一个和表单中参数对应的bean,用这个bean来封装接收的参数
(4)使用@ModelAttribute注解获取POST请求的FORM表单数据
(5)通过@RequestParam注解绑定请求参数到方法入参
spring MVC如何向页面传值?
(1)通过HttpServletRequest,使用request.setAttribute
(2)使用ModelAndView对象,使用model.addObject
(3)使用@ModelAttribute注解
(4)使用session存储
其他见 https://blog.csdn.net/a745233700/article/details/80963758



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号