Spring注解(赋值相关)
上面是与生命周期有关的内容,下面是属性赋值相关的:
@Configuration public class ProperTyValueConfig { @Bean public Person person() { return new Person(); } }
测试:
public class test { private void printBeans(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for(String name : beanDefinitionNames) { System.out.println(name); } Object p = applicationContext.getBean("person"); System.out.println(p); } @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); System.out.println("容器创建完成"); printBeans(applicationContext); //关闭容器 applicationContext.close(); } }
看看容器有哪些Bean
除了容器自带的,还有就是我们配置的person,还没有赋值哦

xml:
<baen id = "person" class = "com.toov5.Person">
<property name = "age" value= 12> </property>
<property name="name" value = "jack"> </property>
</bean>
注解:
@Value() boolean
Spel 基本数值都可以写 #{}
${} 取出配置文件中的值 在运行环境中的变量值
Bean类及其赋值:
package com.toov5.Bean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; public class Person { @Value("#{20-1}") int age; @Value("MaYun") String name; public Person() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Person(int age, String name) { super(); this.age = age; this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [age=" + age + ", name=" + name + "]"; } }
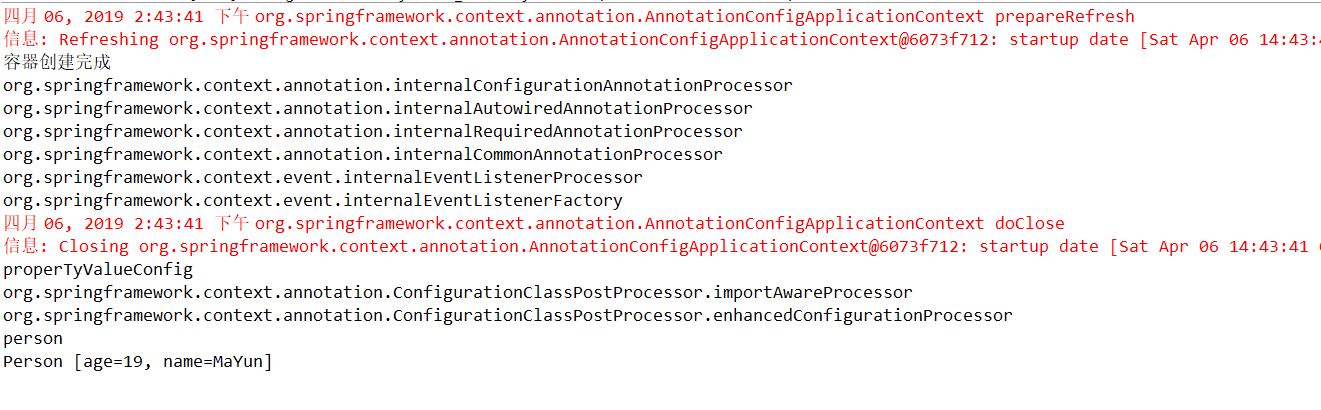
注意赋值 @Value 类型要匹配
下面介绍使用properties文件的:
如果用xml形式的读取:
xml中需要有命名空间: <context: property-placeholder location=“xxxxxx/xxx” /> 用其导入外部的配置文件
如果用注解的方式读取:
config:
@Configuration @PropertySource(value= {"classpath"/person.properties"}) public class ProperTyValueConfig { @Bean public Person person() { return new Person(); } }
Bean类:
public class Person { @Value("#{20-1}") int age; @Value("MaYun") String name; @Value("${person.addr}") String addr; public Person() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Person(int age, String name) { super(); this.age = age; this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAddr() { return addr; } public void setAddr(String addr) { this.addr = addr; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [age=" + age + ", name=" + name + ", addr=" + addr + "]"; } }
properties:

person.addr=beijing
测试:
public class test { private void printBeans(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for(String name : beanDefinitionNames) { System.out.println(name); } Object p = applicationContext.getBean("person"); System.out.println(p); } @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); System.out.println("容器创建完成"); printBeans(applicationContext); //关闭容器 applicationContext.close(); } }
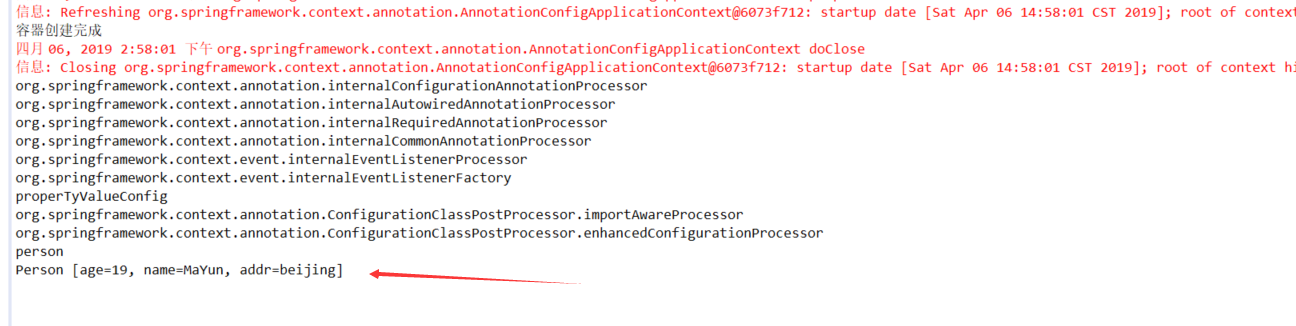
一旦properties文件被加载,还可以使用如下方式获取:
public class test { private void printBeans(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for(String name : beanDefinitionNames) { System.out.println(name); } Object p = applicationContext.getBean("person"); System.out.println(p); //运行时环境变量 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment(); String property = environment.getProperty("person.addr"); System.out.println(property); } @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); System.out.println("容器创建完成"); printBeans(applicationContext); //关闭容器 applicationContext.close(); } }
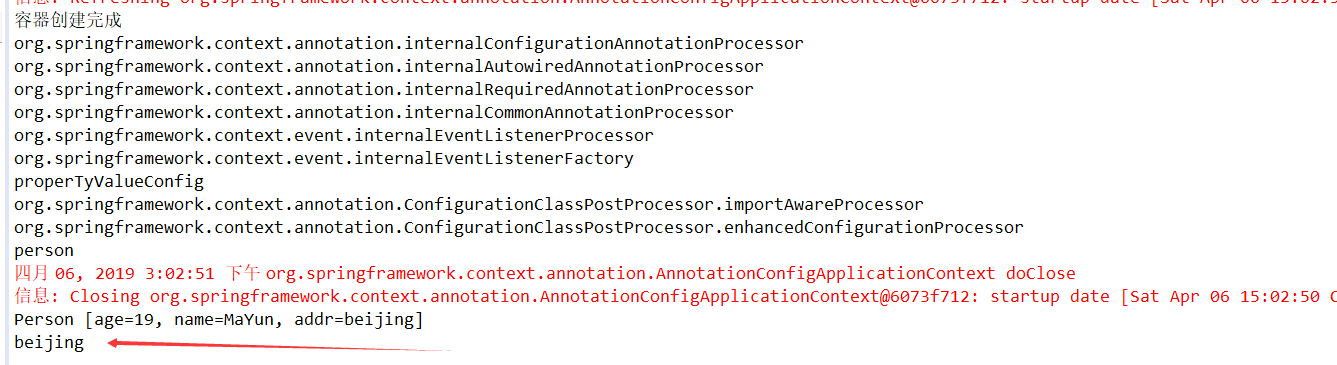
自动装配:
Spring 利用依赖注入(DI),完成IOC容器中格个组件的依赖关系赋值
Service
@Service public class BookService { @Autowired private BookDao bookDao; public void print() { System.out.println(bookDao); } @Override public String toString() { return "BookService"+bookDao; } }
config:
@Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.toov5.dao","com.toov5.service","com.toov5.controller"}) public class ProperTyValueConfig { }
test:
public class test { @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext =new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); BookService bookService =(BookService) applicationContext.getBean(BookService.class); //按照类型去拿 System.out.println(bookService); applicationContext.close(); } }

有了dao哦
其实就是容器中的到哦:

@Autowired 自动注入
默认优先按照类型去容器找对应的组件: applicationContext.getBean(BookService.class);
找到则赋值
如果这个类型的组件在IOC中有多个,怎么处理?
容器中有两个类型相同 名字不同的bean
如果找到多个相同类型的组件,再将属性名作为组件的id 去容器中查找。applicationContext.getBean("bookDao")
在装配时候:
名字是bookDao2
@Service public class BookService { @Autowired private BookDao bookDao2; public void print() { System.out.println(bookDao2); } @Override public String toString() { return "BookService"+bookDao2.getFlag(); } }
config注入的是 bookDao2
@Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.toov5.dao","com.toov5.service","com.toov5.controller"}) public class ProperTyValueConfig { @Bean(name="bookDao2") public BookDao bookDao() { BookDao bookDao = new BookDao(); bookDao.setFlag("2"); return bookDao; } }
测试:
public class test { @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext =new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); BookService bookService =(BookService) applicationContext.getBean(BookService.class); //按照类型去拿 System.out.println(bookService); BookDao bookDao = applicationContext.getBean(BookDao.class); System.out.println(bookDao.getFlag()); applicationContext.close(); } }
可以在装配时候这么玩儿
@Qualifier("bookDao") 指定需要抓给你配的组件的id 而不是属性名
@Service public class BookService { @Qualifier("bookDao") @Autowired private BookDao bookDao2; public void print() { System.out.println(bookDao2); } @Override public String toString() { return "BookService"+bookDao2.getFlag(); } }
打印:

自动装配默认一定要将属性赋值好,没有就会报错
如果:
@Service public class BookService { @Qualifier("bookDao") @Autowired(required=false) private BookDao bookDao2; public void print() { System.out.println(bookDao2); } @Override public String toString() { return "BookService"+bookDao2.getFlag(); } }
如果没有的情况下,不报错:
@Service public class BookService { @Qualifier("bookDao666") @Autowired(required=false) private BookDao bookDao2; public void print() { System.out.println(bookDao2); } }
测试:
public class test { @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext =new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); BookService bookService =(BookService) applicationContext.getBean(BookService.class); //按照类型去拿 bookService.print(); applicationContext.close(); } }
打印:
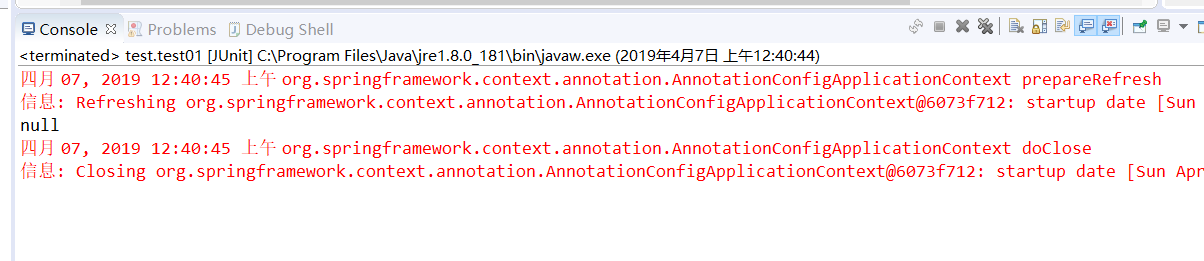
容器中没有的情况 会null
还有一个spring的牛逼的注解 @Primary 让spring自动装配的时候 默认使用首选bean
@Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.toov5.dao","com.toov5.service","com.toov5.controller"}) public class ProperTyValueConfig { @Primary @Bean(name="bookDao2") public BookDao bookDao() { BookDao bookDao = new BookDao(); bookDao.setFlag("2"); return bookDao; } }
每次首选装配的是加了 @Primary的
既然已经在容器中声明了 在装配时候 @Qualifier 就不需要了
使用首选来装配
如果加了@Qualifier 那就是明确指定的了
service:
@Service public class BookService { @Autowired(required=false) private BookDao bookDao; public void print() { System.out.println(bookDao.getFlag()); } }
config 明确了优先装配的bean
@Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.toov5.dao","com.toov5.service","com.toov5.controller"}) public class ProperTyValueConfig { @Primary @Bean(name="bookDao2") public BookDao bookDao() { BookDao bookDao = new BookDao(); bookDao.setFlag("2"); return bookDao; } }
测试:
public class test { @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext =new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); BookService bookService =(BookService) applicationContext.getBean(BookService.class); //按照类型去拿 bookService.print(); applicationContext.close(); } }
Spring还支持使用 @Resource(JSR250) java 规范的注释 @Qualifier+ @Autowired = @Resource 或者 @Resource(name="bookDao2") 否则就默认当前的属性名字
和 @Inject(JSP330) 需要额外导入依赖 (maven仓库搜索inject) Autowried可以设置required属性
@Autowried构造器 参数 方法 属性 都可以标注使用
CarBean:
@Component public class Car { public Car() { System.out.println("无参构造初始化"); } public void init() { System.out.println("CarBean---init"); } public void destory() { System.out.println("CarBean---destory"); } }
BossBean: 默认加载IOC容器中的组件,容器会调用无参构造器创建对象,在进行初始化赋值等操作。
@Component public class Boss { private Car car; public Car getCar() { return car; } @Autowired //标注在方法上 spring容器创建对象时候 调用方法 完成赋值。方法使用的参数,自定义类型的值 从IOC获取值 public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } }
config:
@Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.toov5.Bean"}) public class ProperTyValueConfig { @Primary @Bean(name="bookDao2") public BookDao bookDao() { BookDao bookDao = new BookDao(); bookDao.setFlag("2"); return bookDao; } }
测试:
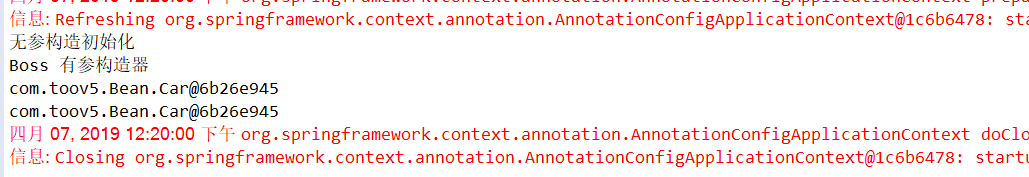
public class test { @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext =new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); Boss boss =(Boss) applicationContext.getBean(Boss.class); //按照类型去拿 System.out.println(boss.getCar()); //再从容器中获取car 进行比对 Car carBean =applicationContext.getBean(Car.class); System.out.println(carBean); applicationContext.close(); } }
打印:

来个有参构造器: 标注在有参构造器上面: Spring启动时候 调用有参构造器
@Component public class Boss { private Car car; @Autowired public Boss(Car car) { this.car=car; System.out.println("Boss 有参构造器 "); } public Car getCar() { return car; } // @Autowired //标注在方法上 spring容器创建对象时候 调用方法 完成赋值。方法使用的参数,自定义类型的值 从IOC获取值 public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } }
当然也可以放在参数位置:
public Boss(@Autowired Car car) { this.car=car; System.out.println("Boss 有参构造器 "); }
如果只有一个有参构造器,注解可以省略。建议平时大家开发时候还是不要省略了吧
也可以在config里面这么玩儿
@Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.toov5.Bean"}) public class ProperTyValueConfig { @Primary @Bean(name="boss") public Boss boss(Car car) { Boss boss =new Boss(); boss.setCar(car); return boss; } }
Bean标注的方法创建对象的时候,方法参数的值从容器中获取!
原理可以看Aware接口

可以看下这个:

启动容器后,创建对象,需要的其他组件都会以接口方法回调的方式引入进来
bean:
@Component public class Animal implements ApplicationContextAware,BeanNameAware,EmbeddedValueResolverAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; String color ; String name; public Animal() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Animal(String color, String name) { super(); this.color = color; this.name = name; } //第一个接口 public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("传入IOC:"+applicationContext); this.applicationContext=applicationContext; } //第二个接口 public void setBeanName(String name) { //传入bean名字 通过名字去容器查找bean System.out.println("当前bean的名字"+name); } //第三个接口 //容器启动时候 创建对象 然后把resolver对象传递进来 public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) { //解析字符串 # {} 等等 // TODO Auto-generated method stub String resolveStringValue = resolver.resolveStringValue("你好${os.name} 我是#{30*1}"); System.out.println("解析的字符串"+resolveStringValue); } }
config:
@Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.toov5.Bean"}) public class ProperTyValueConfig { @Primary @Bean(name="boss") public Boss boss(Car car) { Boss boss =new Boss(); boss.setCar(car); return boss; } }
测试:
public class test { @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext =new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ProperTyValueConfig.class); Boss boss =(Boss) applicationContext.getBean(Boss.class); //按照类型去拿 System.out.println(boss.getCar()); //再从容器中获取car 进行比对 Car carBean =applicationContext.getBean(Car.class); System.out.println(carBean); applicationContext.close(); } }
打印:
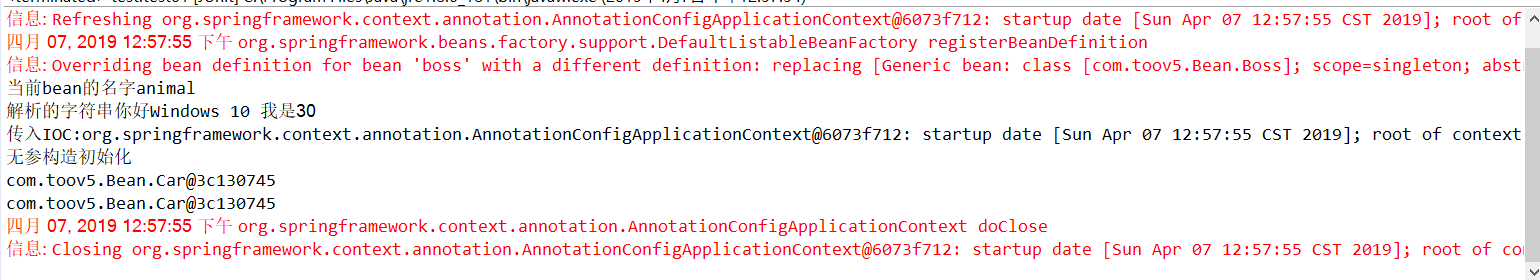
自定义组件想要使用Spring容器底层的一些组件 (ApplicationContext BeanFactory...)
自定义组件实现xxxAware; 在创建对象的时候,会调用接口规定的方法注入相关组件; Aware; 把Spring 底层一些组件注入到自定义的Bean
每个xxxAware 都会有相关的 xxxAwareProcessor 后置处理器




