IOC容器中Bean的生命周期
Spring IOC容器可以管理Bean的生命周期,Spring 允许在Bean生命周期的特定执行定制的任务
Spring IOC容器对Bean的声明周佳琪进行管理的过程:
1.通过构造器或工厂方法创建Bean实例
2.为Bean的属性设置值和其他Bean的引用
(将Bean实例传递给Bean后置处理器的方法)
3.调用Bean的初始化方法
(将Bean实例传递给Bean后置处理器的方法)
4.Bean可以使用
5.当容器关闭时候,调用Bean销毁方法
在Bean的生命力设置init-method和destory-method属性,为Bean指定初始化和销毁方法
Spring Boot项目中对Bean生命周期的使用
当前bean需要实现接口 InitializingBean
class Bean implements InitializingBean 然重写 @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { if (cloudAccount != null) { Properties mnsProperties = PropertiesReader.getProperties("mns.properties"); consultMsgQueue = cloudAccount.getMNSClient().getQueueRef(mnsProperties.getProperty("consult.msg.queue")); downloadFileQueue = cloudAccount.getMNSClient().getQueueRef(mnsProperties.getProperty("call.recordfile.download.queue")); } else { log.warn("init cloud account error."); } }
补充:
创建Bean后置处理器
Bean后置处理器允许在调用初始化方法前后对Bean进行额外的处理
Bean后置处理器对IOC容器里所有的Bean实例逐一处理,而非单一实例。典型应用是:检查Bean属性的正确性根据特定的标注能更改Bean的属性
对Bean后置处理器而言,需要实现interface BeanPostProcessor接口。在初始化方法被调用前后,Spring 将把每个Bean实例分别传递给上述接口的一下两个方法
一个是在init-method之前被调用 另一个是init-method之后被调用
Bean生命周期分析
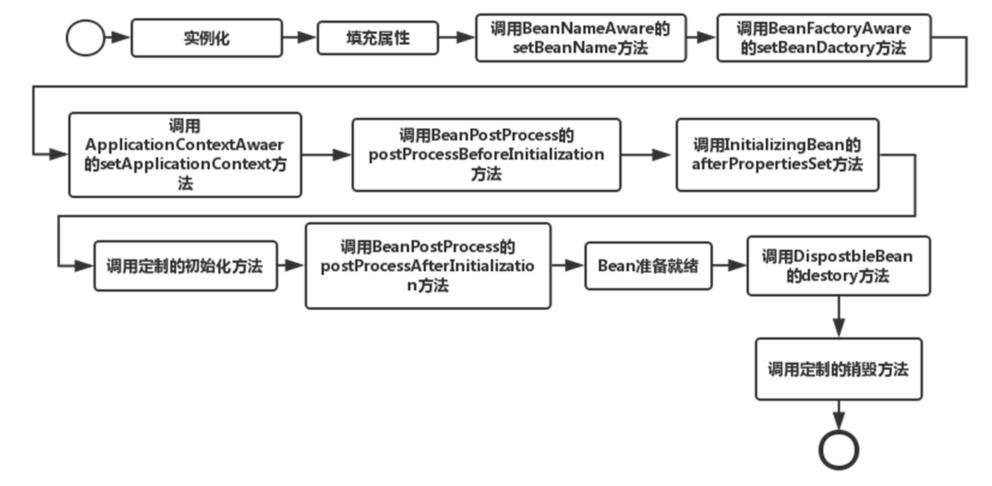
1) spring对bean进行实例化,默认bean是单例
2)spring对bean进行依赖注入
3)如果bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,spring将bean的id传给setBeanName()方法
4)如果bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,spring将调用setBeanFactory方法,将BeanFactory实例传进来
5)如果bean实现了ApplicationContextAware()接口,spring将调用setApplicationContext()方法将应用上下文的引用传入
6) 如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,spring将调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization接口方法
7) 如果bean实现了InitializingBean接口,spring将调用它们的afterPropertiesSet接口方法,类似的如果bean使用了init-method属性声明了初始化方法,改方法也会被调用
8)如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,spring将调用它们的postProcessAfterInitialization接口方法
9)此时bean已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了,他们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到该应用上下文被销毁
10)若bean实现了DisposableBean接口,spring将调用它的distroy()接口方法。同样的,如果bean使用了destroy-method属性声明了销毁方法,则该方法被调用
小结:
1 创建对象(实例化),反射机制
2 初始化属性
3 BeanNameAware 获取查找beanName
4 BeanFactoryAware 获取BeanFactory 就有了ioc的基本操作
5 获取上下文
6 BeanPostProcess
7 销毁Bean --web开发
过滤器Filter 不在扫包范围之内的 Filter中的属性没法使用 @Autowried 所以使用Spring 上下文。不能通过注解了
大家可以写一个Bean 去实现BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware ,InitializingBean, DisposableBean
Bean:
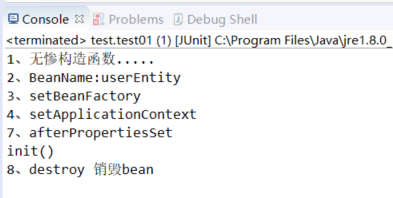
package com.toov5.bean; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class UserEntity implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean,DisposableBean { private String userName; private Integer age = null; public UserEntity() { System.out.println("1、无惨构造函数....."); } public UserEntity(String userName, Integer age) { System.out.println("我是有参构造函数 userName:" + userName + ",age:" + age); this.userName = userName; this.age = age; } public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "UserEntity [userName=" + userName + ", age=" + age + "]"; } public void setBeanName(String name) { System.out.println("2、BeanName:" + name); } public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("3、setBeanFactory"); } public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("4、setApplicationContext"); } public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("5、postProcessBeforeInitialization bean初始化之前" + beanName); return bean; } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("6、postProcessAfterInitialization bean初始化之后" + beanName); return bean; } public void init(){ System.out.println("init()"); } public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("7、afterPropertiesSet"); } public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("8、destroy 销毁bean"); } }
Config:
@Configuration @ComponentScan(value="com.toov5") public class Config { @Bean(initMethod="init") UserEntity userEntity() { return new UserEntity(); } }
Test:
public class test { @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class); UserEntity user = (UserEntity) applicationContext.getBean("userEntity"); applicationContext.destroy(); } }
结果: