Java排序算法——拓扑排序




课程表
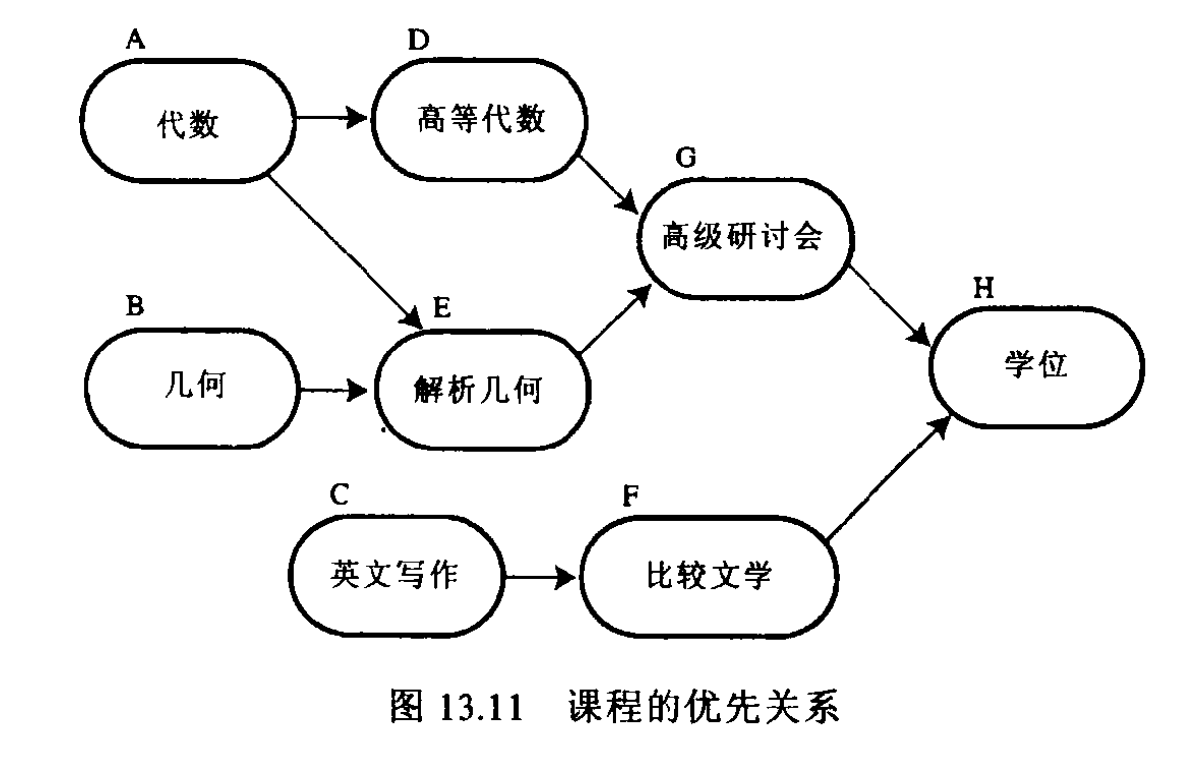
邻接矩阵
package graph;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import thinkinjava.net.mindview.util.Stack;
//类名:Vertex
//属性:
//方法:
class Vertex{
public char label; //点的名称,如A
public boolean wasVisited;
public Vertex(char lab){ //构造函数
label = lab;
wasVisited = false;
}
}
//类名:Graph
//属性:
//方法:
class Graph{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;
private Vertex vertexList[]; //顶点列表数组
private int adjMat[][]; //邻接矩阵
private int nVerts; //当前的顶点
private char sortedArray[];
public Graph(){ //构造函数
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS];
nVerts = 0;
for(int j=0;j<MAX_VERTS;j++){
for(int k=0;k<MAX_VERTS;k++)
adjMat[j][k] = 0;
}
sortedArray = new char[MAX_VERTS];
}
public void addVertex(char lab){ //添加新的顶点,传入顶点的lab,并修改nVerts
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end){ //添加边,这里是无向图
adjMat[start][end] = 1;
//adjMat[end][start] = 1;
}
public void displayVertex(int v){ //显示顶点
System.out.print(vertexList[v].label);
}
public int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int v){ //返回一个和v邻接的未访问顶点
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
if(adjMat[v][j] == 1 && vertexList[j].wasVisited == false){
return j;
}
return -1; //如果没有,返回-1
}
public void dfs(){ //深度搜索
Stack<Integer> theStack = new Stack<Integer>();
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(0);
theStack.push(0); //把根入栈
while(!theStack.empty()){
int v = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(theStack.peek());//取得一个和栈顶元素邻接的未访问元素
if(v == -1) //如果没有和栈顶元素邻接的元素,就弹出这个栈顶
theStack.pop();
else{ //如果有这个元素,则输出这个元素,标记为已访问,并入栈
vertexList[v].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(v);
theStack.push(v);
}
}
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++) //全部置为未访问
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public void bfs(){ //广度搜索
Queue<Integer> theQueue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(0);
theQueue.offer(0); //把根入队列
int v2;
while(!theQueue.isEmpty()){
int v1 = theQueue.remove();//v1记录第1层的元素,然后记录第2层第1个元素...
while((v2=getAdjUnvisitedVertex(v1)) != -1){//输出所有和第1层邻接的元素,输出和第2层第1个元素邻接的元素...
vertexList[v2].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(v2);
theQueue.offer(v2);
}
}
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++) //全部置为未访问
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public void mst(){ //基于深度搜索的最小生成树
Stack<Integer> theStack = new Stack<Integer>();
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
theStack.push(0); //把根入栈
while(!theStack.empty()){
int currentVertex = theStack.peek(); //记录栈顶元素,当有为邻接元素的时候,才会输出
int v = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(theStack.peek());//取得一个和栈顶元素邻接的未访问元素
if(v == -1) //如果没有和栈顶元素邻接的元素,就弹出这个栈顶
theStack.pop();
else{ //如果有这个元素,则输出这个元素,标记为已访问,并入栈
vertexList[v].wasVisited = true;
theStack.push(v);
displayVertex(currentVertex);
displayVertex(v);
System.out.println();
}
}
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++) //全部置为未访问
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public int noSuccessors(){ //使用邻接矩阵找到没有后继的顶点,有后继顶点返回行数,没有返回-1
boolean isEdge;
for(int row=0;row<nVerts;row++){//从第1行开始
isEdge = false;
for(int col=0;col<nVerts;col++){//如果某一行某一列为1,返回这个行的行数
if(adjMat[row][col] > 0){
isEdge = true;
break;
}
}
if(!isEdge)
return row;
}
return -1;
}
public void moveRowUp(int row,int length){
for(int col=0;col<length;col++)
adjMat[row][col] = adjMat[row+1][col];
}
public void moveColLeft(int col,int length){
for(int row=0;row<length;row++)
adjMat[row][col] = adjMat[row][col+1];
}
public void deleteVertex(int delVert){
if(delVert != nVerts-1){
for(int j=delVert;j<nVerts-1;j++)//在数组中去掉这个顶点
vertexList[j] = vertexList[j+1];
for(int row=delVert;row<nVerts-1;row++)//在邻接矩阵中把删除的这一行下的所有行上移
moveRowUp(row,nVerts);
for(int col=delVert;col<nVerts-1;col++)//在邻接矩阵中把删除的这一列下的所有列左移
moveColLeft(col,nVerts-1);
}
nVerts--;
}
public void topo(){ //拓扑排序,必须在无环的有向图中进行,必须在有向图中
int orig_nVerts = nVerts; //记录有多少个顶点
while(nVerts > 0){
int currentVertex = noSuccessors();
if(currentVertex == -1){
System.out.println("错误:图含有环!");
return;
}
sortedArray[nVerts-1] = vertexList[currentVertex].label;
deleteVertex(currentVertex);
}
System.out.println("拓扑排序结果:");
for(int j=0;j<orig_nVerts;j++)
System.out.println(sortedArray[j]);
}
}
public class graph_demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Graph theGraph = new Graph();
theGraph.addVertex('A'); //数组元素0
theGraph.addVertex('B'); //数组元素1
theGraph.addVertex('C'); //数组元素2
theGraph.addVertex('D'); //数组元素3
theGraph.addVertex('E'); //数组元素4
// theGraph.addEdge(0, 1); //AB
// theGraph.addEdge(1, 2); //BC
// theGraph.addEdge(0, 3); //AD
// theGraph.addEdge(3, 4); //DE
// System.out.println("dfs访问的顺序:");
// theGraph.dfs();
// System.out.println();
//
// System.out.println("bfs访问的顺序:");
// theGraph.bfs();
// theGraph.addEdge(0, 1); //AB
// theGraph.addEdge(0, 2); //AC
// theGraph.addEdge(0, 3); //AD
// theGraph.addEdge(0, 4); //AE
// theGraph.addEdge(1, 2); //BC
// theGraph.addEdge(1, 3); //BD
// theGraph.addEdge(1, 4); //BE
// //theGraph.addEdge(2, 3); //CD
// //theGraph.addEdge(2, 4); //CE
// theGraph.addEdge(3, 4); //DE
// System.out.println("最小生成树:");
// theGraph.mst();
theGraph.addVertex('F'); //数组元素5
theGraph.addVertex('G'); //数组元素6
theGraph.addVertex('H'); //数组元素6
theGraph.addEdge(0, 3); //AD
theGraph.addEdge(0, 4); //AE
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4); //BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 5); //CF
theGraph.addEdge(3, 6); //DG
theGraph.addEdge(4, 6); //EG
theGraph.addEdge(5, 7); //FH
theGraph.addEdge(6, 7); //GH
theGraph.topo();
}
}
本文只发表于博客园和tonglin0325的博客,作者:tonglin0325,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tonglin0325/p/5837877.html



