datawhale爬虫task02
2.1 学习beautifulsoup
-
学习beautifulsoup,并使用beautifulsoup提取内容。
-
使用beautifulsoup提取丁香园论坛的回复内容。
2.2学习xpath
-
学习xpath,使用lxml+xpath提取内容。
-
使用xpath提取丁香园论坛的回复内容。
一、学习beautifulsoup:
1.简介:
BeautifulSoup是一个Python的HTML和XML的解析库,用来从网页中提取数据。
BeautifulSoup会自动将文档转换为Unicode编码,输出文档转换为UTF-8编码。
导入BeautifulSoup方法:from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
中文文档地址:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html
2.解析器:
推荐使用lxml解析器,如果使用lxml解析器,则在创建BeautifulSoup对象的时候,第二个参数填:lxml
eg:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup('<p>Hello</p>', 'lxml')
3.基本使用:
1 html = """
2 <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
3 <body>
4 <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
5 <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
6 <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
7 <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
8 <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
9 and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
10 <p class="story">...</p>
11 """
12 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
13 soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
14 print(soup.prettify())
15 print(soup.title.string)
输出结果:
1 <html>
2 <head>
3 <title>
4 The Dormouse's story
5 </title>
6 </head>
7 <body>
8 <p class="title" name="dromouse">
9 <b>
10 The Dormouse's story
11 </b>
12 </p>
13 <p class="story">
14 Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
15 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
16 <!-- Elsie -->
17 </a>
18 ,
19 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">
20 Lacie
21 </a>
22 and
23 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">
24 Tillie
25 </a>
26 ;
27 and they lived at the bottom of a well.
28 </p>
29 <p class="story">
30 ...
31 </p>
32 </body>
33 </html>
34 The Dormouse's story
- BeautifulSoup会自动更正格式。给出的HTML代码不完整,它的html标签和body标签都没有闭合。BeautifulSoup会在初始化创建BeautifulSoup对象的时候,就自动更正格式,将html标签和body标签补充完整
- prettify()方法:可以将要解析的字符串以标准格式输出
- soup.title:选择出HTML中的title节点
- soup.title.string:调用string属性,可以得到节点内部的文本
选择器:BeautifulSoup有3种选择器:1)节点选择器 2)方法选择器 3)CSS选择器
4.节点选择器:
4.1选择元素:
BeautifulSoup对象.节点的名称
eg:soup.title
- 得到的结果为:节点+其内容的全部内容:<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
- 返回的结果类型永远为:bs4.element.Tag类型。经过选择器选择后,结果都是Tag类型,Tag类型有name、attr、string属性,可以调用属性
- 注意:当有多个节点的时候,这种选择方式只会选择到第一个匹配到的节点,其他的后面的节点都会被自动忽略
1 html = """
2 <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
3 <body>
4 <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
5 <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were</p>
6 """
7 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
8 soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
9 print(soup.title)
10 print(type(soup.title))
11 print(soup.title.string)
12 print(soup.head)
13 print(soup.p)
运行结果:
1 <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
2 <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
3 The Dormouse's story
4 <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
5 <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
4.2Tag对象节点属性:
节点Tag对象具有三大属性:name、attr、string
1)name:
用来获取节点的名称
先选择节点,然后调用name属性就可以得到节点名称
print(soup.title.name)
运行结果:title
先选择title节点,然后调用name属性,得到title节点的名称:title
2)attrs:
用来获取节点的属性值
- 调用attrs,获取节点的所有的属性值。返回的字典形式的{'属性1':'属性值1','属性2':'属性值2'}
- 调用attrs['属性名'],得到节点相应的属性值。attrs['属性1']
- 节点元素['属性名'],得到节点相应的属性值。
- 注意:返回结果,有的是字符串,有的是字符串组成的列表
1 print(soup.p.attrs)
2 print(soup.p.attrs['name'])
3 print(soup.p['name'])
4 print(soup.p['class'])
运行结果:
1 {'class': ['title'], 'name': 'dromouse'}
2 dromouse
3 dromouse
4 ['title']
3)string:
用来获取节点元素包含的文本内容
print(soup.title.string)
运行结果:The Dormouse's story
注意:string只适用于节点元素内部,没有子节点、或者只有一个子节点。当存在多个子节点时,.string 方法应该调用哪个子节点的内容, .string 的输出结果是 None
提取节点内部文本,不建议使用string属性,建议使用get_text()方法
4.3 嵌套选择:
选择节点元素里面的节点元素
1 html = """
2 <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
3 <body>
4 """
5
6 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
7 soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
8 print(soup.head)
9 print(type(soup.head))
10 print(soup.head.title))
11 print(type(soup.head.title))
12 print(soup.head.title.string)
运行结果:
1 <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
2 <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
3 <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
4 <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
5 The Dormouse's story
4.4 关联选择:
根据基准节点,查找它的子节点、孙节点、父节点、祖先节点、兄弟节点
1)子节点、孙节点:
- contents
得到直接子节点(既包含文本,也包含节点)列表,返回结果是列表形式
- children
得到直接子节点(既包含文本,也包含节点),返回类型是生成器类型,可以用for循环输出需要内容
- descendants
得到所有的子孙节点(既包含文本,也包含节点),返回结果是生成器类型
2)父节点、祖先节点(直接父节点、爷爷节点、太爷爷节点.....)
- parent
得到直接父节点(父节点及其内部全部内容),不再向外寻找父节点的祖先节点
- parents
得到所有的祖先节点(直接父节点、爷爷节点、太爷爷节点.....),返回类型是生成器类型
注意:这里会除了父节点以外,会将整个文档的信息最后在放进去一遍,最后一个元素的类型为BeautifulSoup对象
3)兄弟节点(同级节点):
- next_sibling
获取基准节点的下一个兄弟节点
- previous_sibling
获取基准节点的上一个兄弟节点元素
- next_siblings
获取基准节点的后面的所有的兄弟节点元素
- previous_siblings
获取基准节点的前面的所有的兄弟节点元素
5.方法选择器:
5.1 find_all(name, attrs, recursive, text, **kwargs)
查询所有符合条件的元素,返回结果是列表类型,每个元素依然都是bs4.element.Tag类型
支持嵌套查询
参数:
- name
根据节点的名字来查询元素。节点的名字:a、p、ul、li、div、title.........
- attrs
根据节点的属性查询元素
注意:传入的attrs参数类型是字典类型
- text
根据节点内部文本,来查询元素。传入的text参数形式可以是字符串,也可以是正则表达式对象
5.2 find()
同find_all(),只不过返回的是单个元素,即第一个匹配到的元素
5.3 find_parents()、find_parent():
前者返回所有的祖先节点,后者返回直接的父节点
5.4 find_next_siblings()、find_next_siblings():
前者返回后面所有的兄弟节点,后者返回后面的第一个兄弟节点
5.5 find_previous_siblings()、find_previous_siblings():
前者返回前面所有的兄弟节点,后者返回前面的第一个兄弟节点
5.6 find_all_next()、find_next():
前者返回当前节点的后面的所有符合条件的节点,后者返回当前节点后面的第一个符合条件的节点
5.7 find_all_previous()、find_previous():
前者返回当前节点的前面的所有符合条件的节点,后者返回当前节点前面的第一个符合条件的节点
6.CSS选择器:
7.爬取丁香园的帖子回复内容
# 使用beautifulsoup提取丁香园论坛的回复内容。
# 丁香园直通点:http://www.dxy.cn/bbs/thread/626626#626626 。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
class dingxiangyuan():
#1.发送请求
def send_request(self):
#1.1添加请求头:
headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.100 Safari/537.36"}
#1.2 url
url = 'http://www.dxy.cn/bbs/thread/626626#626626'
#发送请求
response = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers)
return response
#2.解析数据
def parse(self,response):
#读取response数据
response_data = response.content.decode()
#初始化BeautifulSoup,使用BeautifulSoup解析response数据,使用lxml解析器
bsoup = BeautifulSoup(response_data, 'lxml')
#获取所有回复节点
replies = bsoup.find_all(name='td', attrs={'class': 'postbody'})
#print(replies)
for reply in replies:
reply_content = reply.get_text().strip()
print(reply_content)
#3.存储数据
#4.运行
def run(self):
response = self.send_request()
self.parse(response)
pass
dingxiangyuan().run()
二、学习xpath:
xpath文档:https://www.w3.org/TR/xpath/
1.准备工作:
- 导入lxml库的etree模块
注意:在pycharm中,导入该模块虽然会显示为红色,但是实际上是导入成功的,不影响后续调用etree模块的方法。
- 调用HTML()方法构造Xpath解析对象——使用Xpath之前,一定要将要解析的数据,转换成Xpath对象
其中,etree模块的HTML()方法会自动修正HTML文本(就如之前BeautifulSoup那样补全html、body标签等)
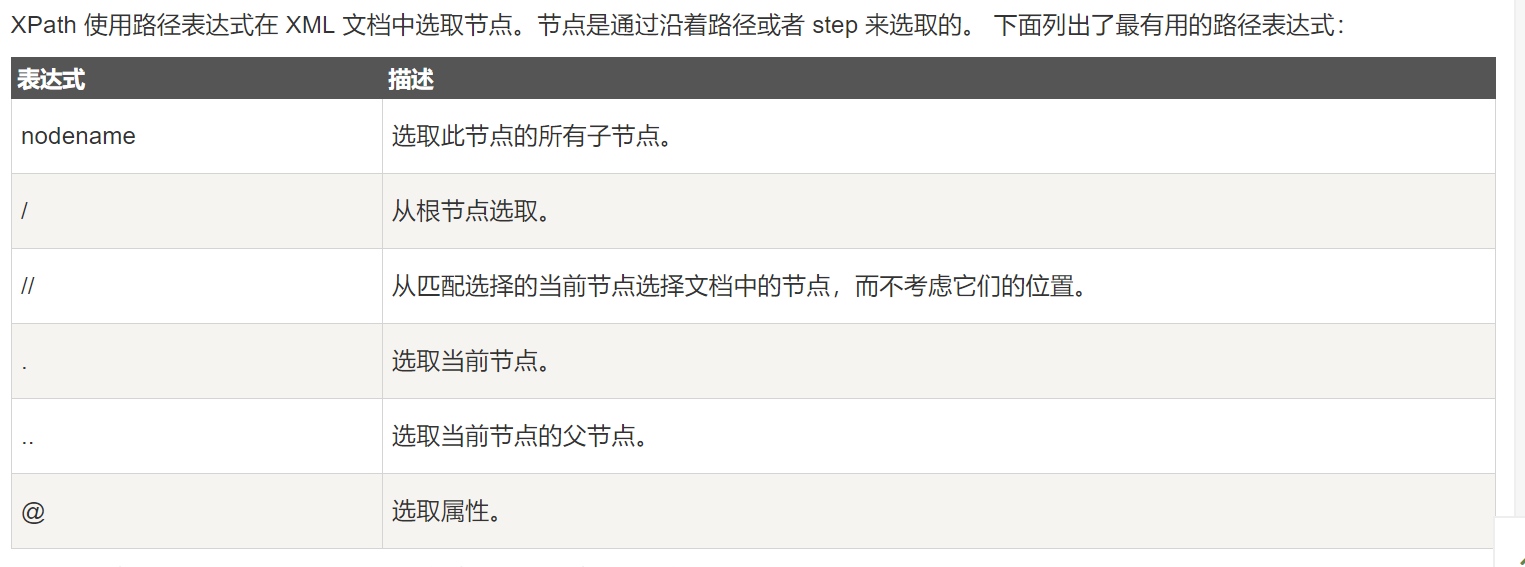
2. 选取节点:
使用Xpath规则选取符合条件匹配到的节点。
- 返回的结果为列表类型
[<Element li at 0x105849208>, <Element li at 0x105849248>]
- 每个节点元素:
<Element li at 0x105849208>
节点元素为Element类型,后面跟了节点的名称
2.1 子节点、子孙节点:
(1)使用“/”,可以获取节点的直接子节点
xpath_data.xpath('//li/a')
——获取li节点的直接子节点中的a节点
(2)使用“//”可以获取节点的子孙节点
xpath_data.xpath('//li//a')
——获取li节点的所有a子孙节点
2.2 父节点:
(1)使用“..”获取节点的父节点
xpath_data.xpath('//a(@href="link4.html")/../@class')
——先选中href属性为link4.html的a节点,然后再获取该节点的父节点的class属性
(2)使用“parent::”获取节点的父节点
xpath_data.xpath('//a(@href="link4.html")/parent::*/@class')
——先选中href属性为link4.html的a节点,然后再获取该节点的父节点的class属性
2.3 获取节点文本内容:
- 使用/text()方法获取节点中的文本内容
xpath_data.xpath('//a(@href="link4.html")/text()')
——获取href属性为link4.html的a节点中的文本内容
2.4 获取节点属性值:
使用“@属性名”,获取节点相应的属性值
xpath_data.xpath('//a(@href="link4.html")/@class')
——获取href属性为link4.html的a节点的class的属性值
2.5 属性匹配:
使用“@属性名=属性值”,来进行属性过滤,筛选到符合条件的节点
xpath_data.xpath('//a(@href="link4.html")')
——匹配到href属性值为link4.html的a节点
2.6 一个属性有多个值匹配:某个节点的某个属性可能有多个值
使用contains()函数。
xpath_data.xpath('//a[contains(@href, "li")]')
——寻找href属性的属性值为li的a节点
——contains(参数1, 参数2)方法:第一个参数传:属性名称、第二个参数:传相应的属性值
2.7 多属性匹配:根据多个属性确定一个节点,即同时匹配多个属性
使用“and”运算符
xpath_data.xpath('//a[contains(@href, "li")] and @name="item"')
——选择href属性的属性值为:li,同时,name属性为item的a节点
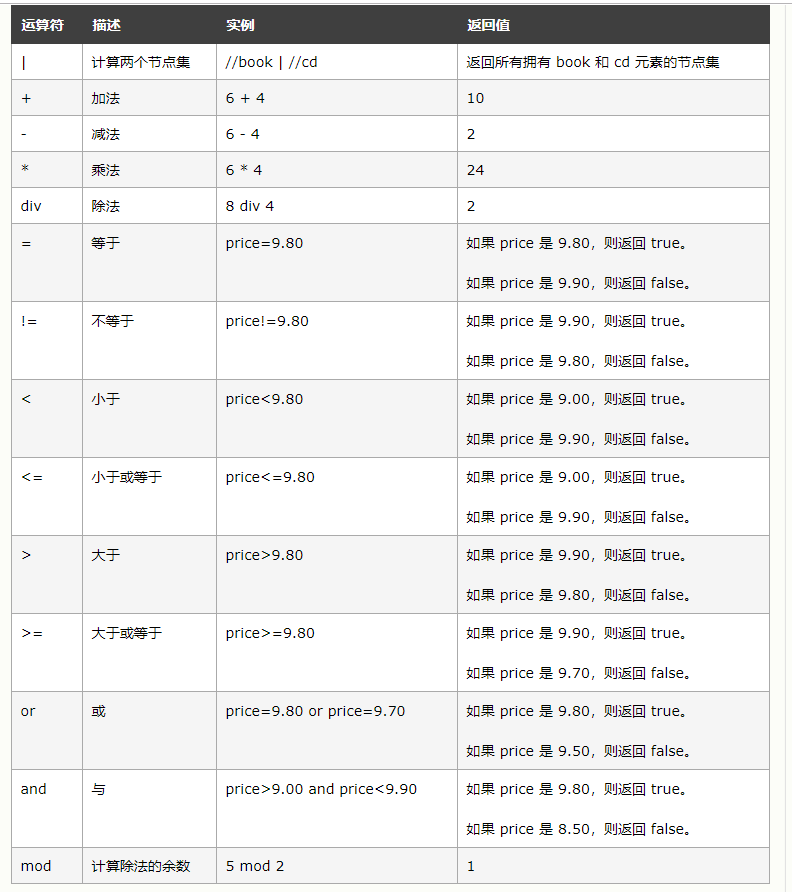
Xpath的运算符如下:
2.8 按序选择:
(1)按照序号选择:
xpath_data.xpath('//li[1]')
xpath_data.xpath('//li[2]')
——分别选择了第1个li节点、第2个li节点。
注意:这里和代码中list不同,序号以0开头,不是以1开头。所以li[1]是第1个节点,li[0]无效
(2)last():选择最后一个节点
xpath_data.xpath('//li[last()]')
——选择了最后一个li节点
xpath_data.xpath('//li[last()-1]')
——倒数第2个li节点
(3)position():
xpath_data.xpath('//li[position()<3]')
——选择了位置小于3的节点,即li[1]、li[2]
2.9 节点轴选择:
(1)格式: 基准节点 / 节点轴 :: 节点选择器
(2)节点轴:

(3)
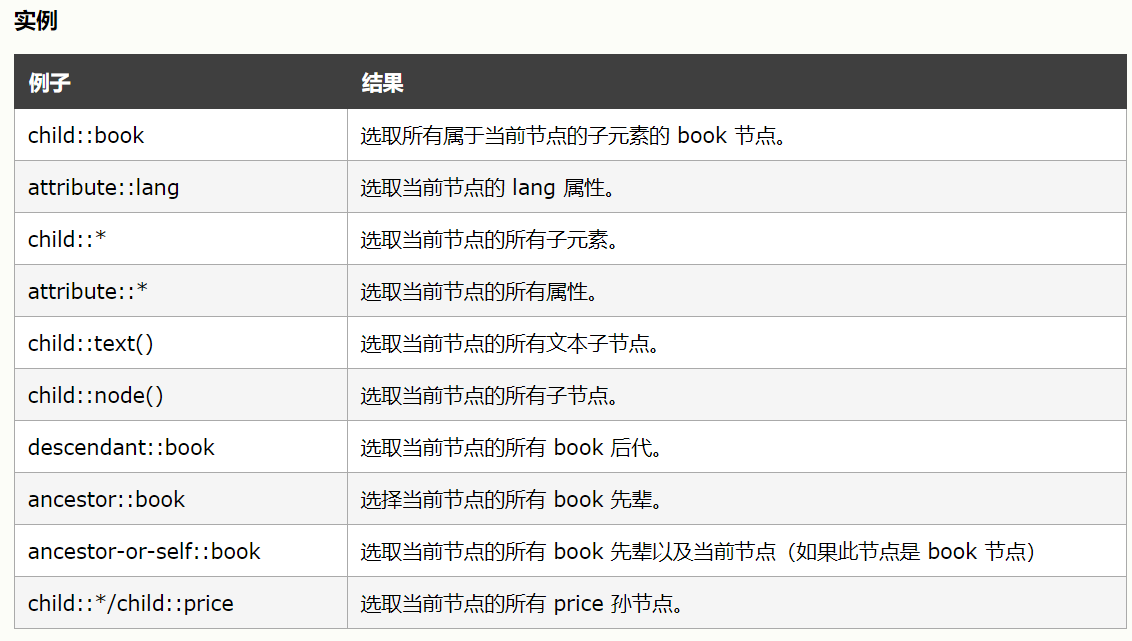
xpath_data.xpath('//li[1]/ancestor::div')
——获取第1个li节点的div祖先节点
3. 爬取代码:
1 # 使用beautifulsoup提取丁香园论坛的回复内容。
2 # 丁香园直通点:http://www.dxy.cn/bbs/thread/626626#626626 。
3
4 import requests
5 from lxml import etree
6 class dingxiangyuan():
7 reply_list = []
8 #1.发送请求
9 def send_request(self):
10 #1.1添加请求头:
11 headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.100 Safari/537.36"}
12 #1.2 url
13 url = 'http://www.dxy.cn/bbs/thread/626626#626626'
14 #发送请求
15 response = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers)
16 return response
17 #2.解析数据
18 def parse(self,response):
19 #读取response数据
20 response_data = response.content.decode('utf-8')
21 #初始化Xpath,转换HTML
22 xpath_data = etree.HTML(response_data)
23 print(xpath_data)
24 #获取所有回复节点
25 #starts-with(@title,"注册时间")
26 replies = xpath_data.xpath('//div[starts-with(@id, "post_")]')
27 print("replies: " + str(replies))
28 #print(replies)
29 for reply in replies:
30 reply_dict = {}
31 print('reply: ' + str(reply))
32 #回复人姓名:
33 auth_name = reply.xpath('.//div[@class="auth"]')[0].xpath('string(.)')
34 # print('auth_name: ' + str(auth_name))
35 #级别
36 auth_rank = reply.xpath('.//div[@class="info clearfix"]')[0].xpath('string(.)').strip()
37 print("auth_rank: " + str(auth_rank))
38 #回复内容
39 reply_content = reply.xpath('.//td[@class="postbody"]')[0].xpath('string(.)').strip()
40 print('reply_content: ' + str(reply_content))
41 reply_dict['auth_name'] = auth_name
42 reply_dict['auth_rank'] = auth_rank
43 reply_dict['reply_content'] = reply_content
44 self.reply_list.append(reply_dict)
45 #3.存储数据
46 #4.运行
47 def run(self):
48 response = self.send_request()
49 self.parse(response)
50 print(self.reply_list)
51 pass
52
53 dingxiangyuan().run()
遇到的坑:
(1)嵌套选取节点:
- 首先,Xpath选取到的节点,返回一定是列表类型,需要获取到列表里面的节点元素,再嵌套进行xpath,如果只选取到一个节点,记得一定要加序号[0]
- 其次,从基准节点,再Xpath选取节点,一定要以“.//”或者“./”开头
replies = xpath_data.xpath('//div[starts-with(@id, "post_")]')
auth_name = reply.xpath('.//div[@class="auth"]')[0].xpath('string(.)')
(2)Xpath模糊查询:
以....为开头:starts-with(参数1,参数2)
replies = xpath_data.xpath('//div[starts-with(@id, "post_")]')
——获取id以“post_”为开头的div节点
以....为结尾:ends-with(参数1,参数2)
(3)text()、String()的区别:
- text():获取节点内的直接文本内容
- string():获取节点内部的所有文本内容


