强化学习笔记6:值函数估计Value function Approximation
introduction
v、q表的问题
- 解决离散化的s,a,导致q-table存储量、运算量大
- 解决连续s、a的表示问题
solution
用带权重估计函数,估计v or q
\[
\begin{aligned}
\hat{v}(s, \mathbf{w}) & \approx v_{\pi}(s) \\
\text { or } \hat{q}(s, a, \mathbf{w}) & \approx q_{\pi}(s, a)
\end{aligned}
\]
函数估计器
可谓函数逼近,需要函数式可微分的
- 线性组合
- 神经网络
这些不可微
- 决策树 decision tree
- 领域Nearest neighbour
- 傅里叶/ 小波Fourier/ wavelet bases
incremental methods 递增方法
Gradient descent 梯度下降
值函数估计:随机梯度下降法SGD
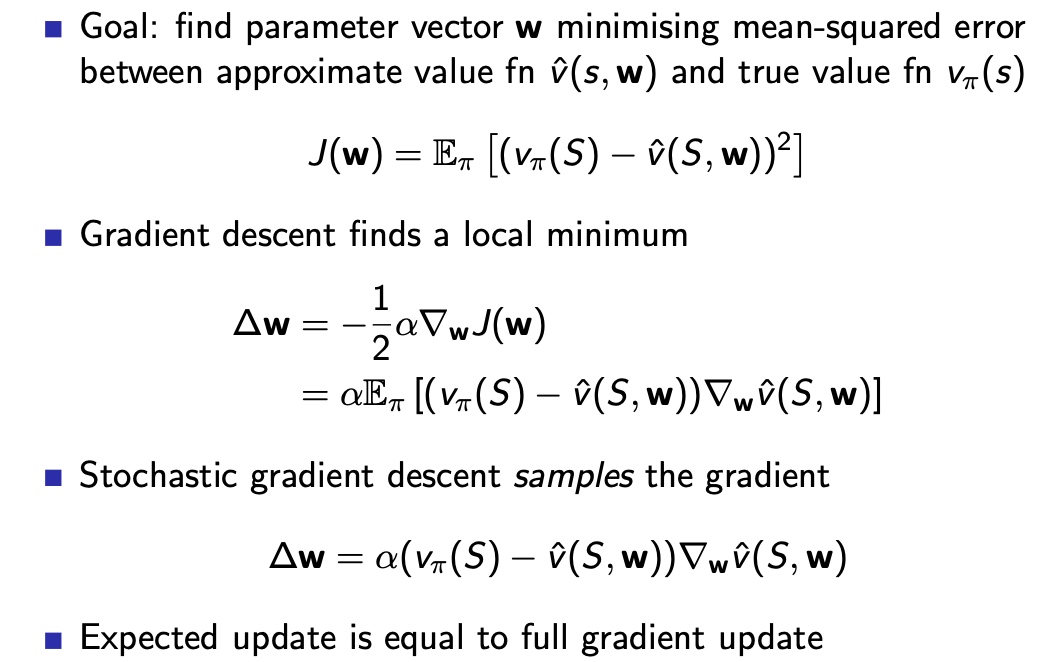
Table lookup 是 GD的一种特例
类似于机器学习的分类问题,将状态值写成0、1向量
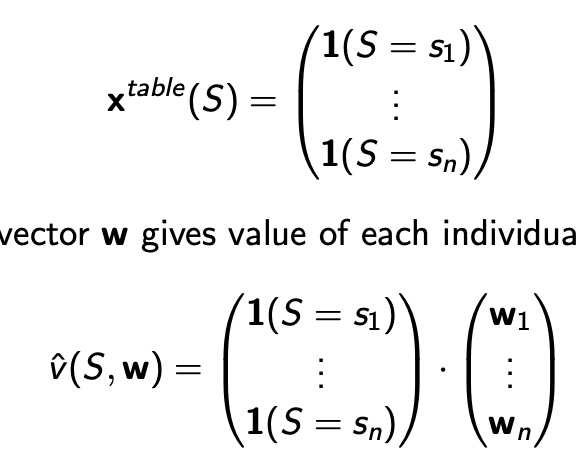
Find a target for value function approximation
把估计函数作为一个监督学习
目标是谁呢,通过MC、TD方法,设定目标

生成训练集
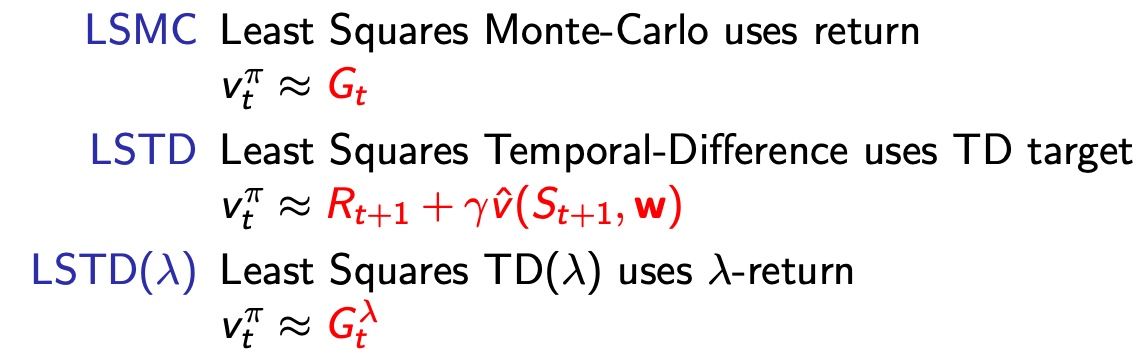
For linear MC

- 无偏目标估计
- 局部最优
For linear TD(0)

- 收敛趋向全局最优
For linear TD(\(\lambda\))

\(\delta\) scalar number
\(E_t\) 维度和s维度一致
- 前后向 相等
Incremental Control Algorithms
用q函数,替代v函数
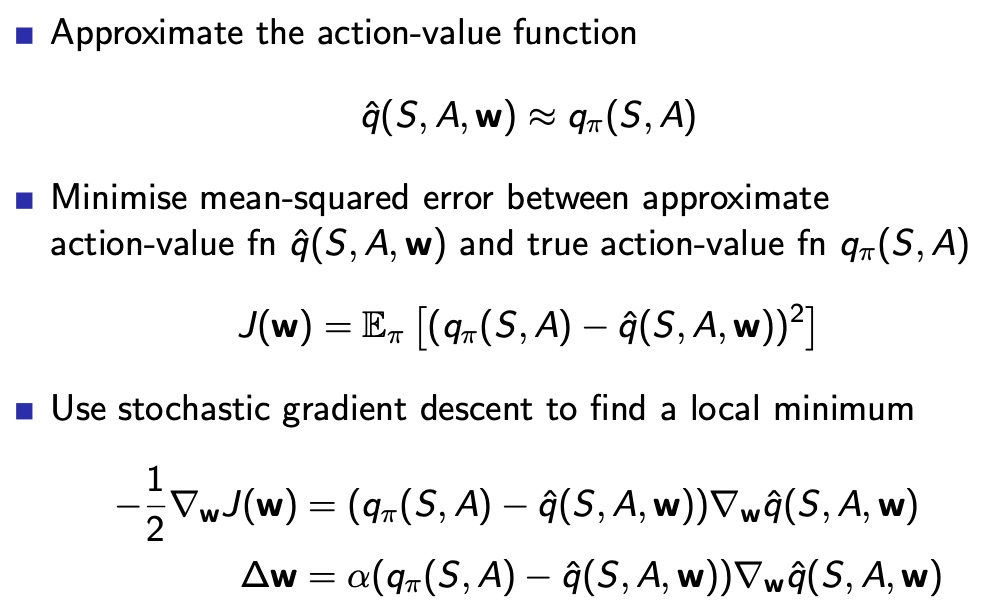

收敛性分析
预测学习
- On-policy:一般边训练,边执行,(s,a)是当前policy产生的
- off-policy:离线训练,通过训练其他策略或者agent产生的(s,a)训练集
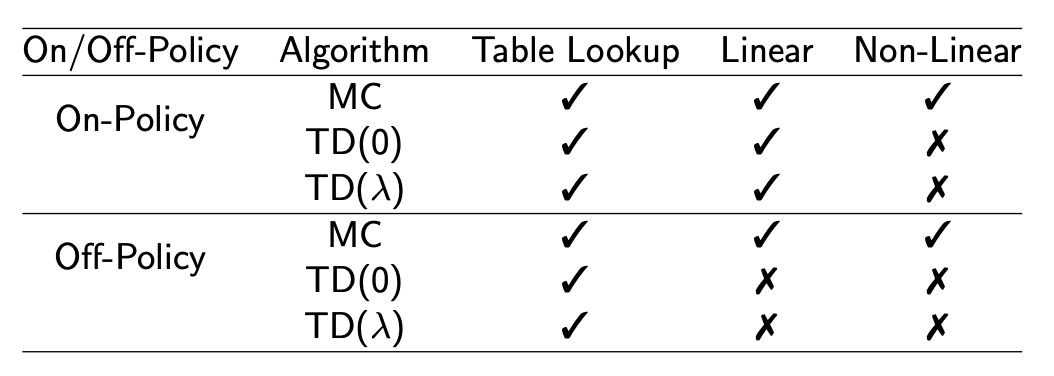
引入Gradient TD,完全满足贝尔曼方程,无差
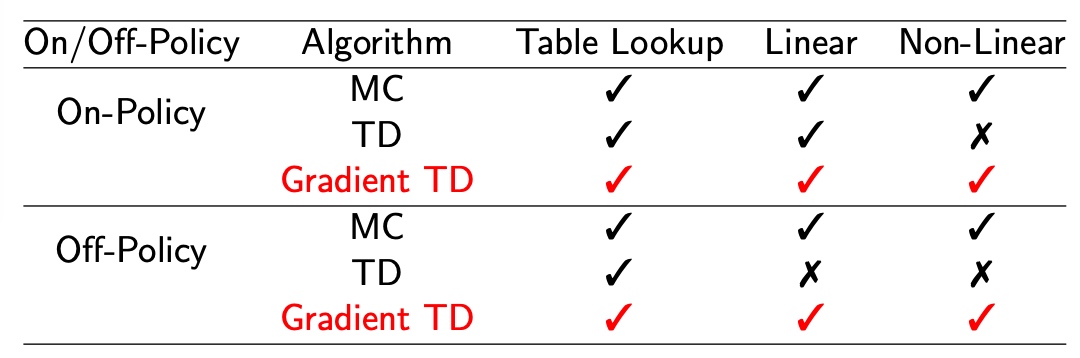
- 控制学习
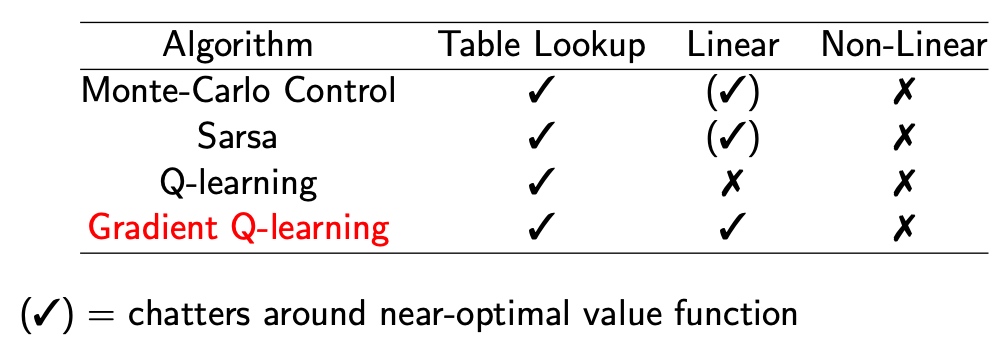
(√)表示在最优值函数附近振荡
batch methods
For least squares prediction
LS定义,估计误差平方,求和

相当于经历重现(experience replay)
- 从history中sample一个batch
- 用SGD更新参数w
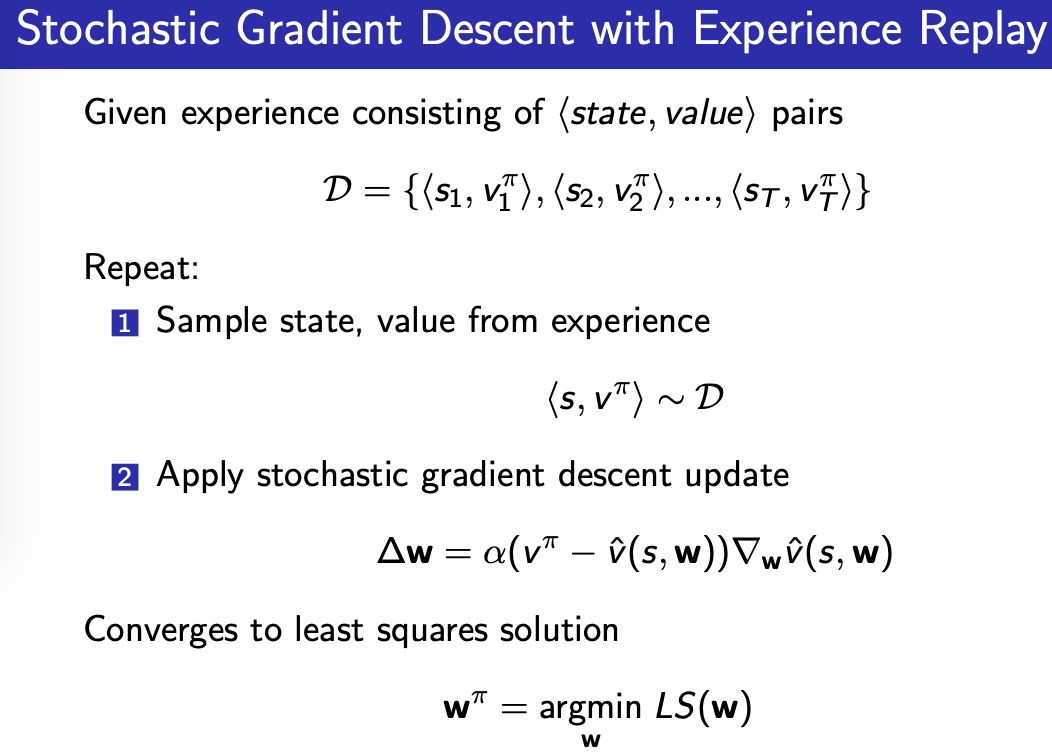
找到使LS最小的权重\(w^\pi\)
Experience Replay in Deep Q-Networks (DQN)
Two features
- Experience Relpay:minibatch的数据采样自memory-D
- Fixed Q-targets:\(w^-\) 在一个更新batch内 ,保持不变,让更新过程更稳定
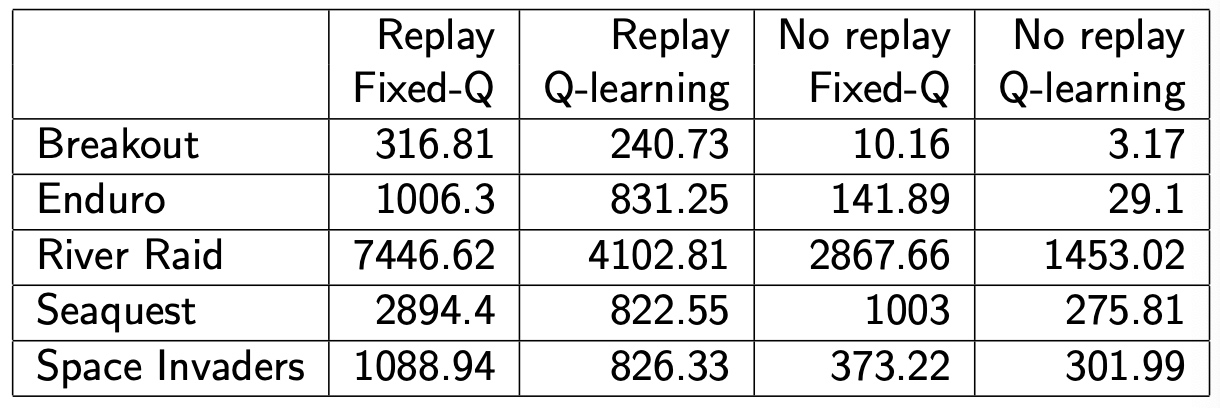
算法流程
- Take action at according to ε-greedy policy
- Store transition (st,at,rt+1,st+1) in replay memory D
- Sample random mini-batch of transitions (s,a,r,s′) from D
- Compute Q-learning targets w.r.t. old, fixed parameters \(w^− \)
- Optimise MSE between Q-network and Q-learning targets
\[
\mathcal{L}_{i}\left(w_{i}\right)=\mathbb{E}_{s, a, r, s^{\prime}} \sim \mathcal{D}_{i}\left[\left(r+\gamma \max _{a^{\prime}} Q\left(s^{\prime}, a^{\prime} ; w_{i}^{-}\right)-Q\left(s, a ; w_{i}\right)\right)^{2}\right]
\]
- 用SGD更新
伪算法: 注意:
注意: - Fixed Q-target \(\theta\),每C steps 更新一次
- Experience Replay: minibatch 从 memory D 采样
Features:
- 随机采样,打破了状态之间的联系
- 冻结参数,增加了算法的稳定性,选q的网络参数回合制更新
- 例子
DQN in Atari(构成)- input: state s (4 frames pictures)
- output: Q(s,a)
- CNN: mapping input(s) to output(Q)
LS 最小二乘法 总结
- Experience replay -> LS solution
- 迭代次数太多
- 用线性估计\(\hat v(s,w) = x(s)^Tw\)
- 直接求解LS
LSP 直接求解
对于线性近似函数:
\[
\hat v(s,w) = x(s)^T w
\]
最终的平衡状态,梯度=0
求解方程,得到w值关于状态s和v真值的函数关系
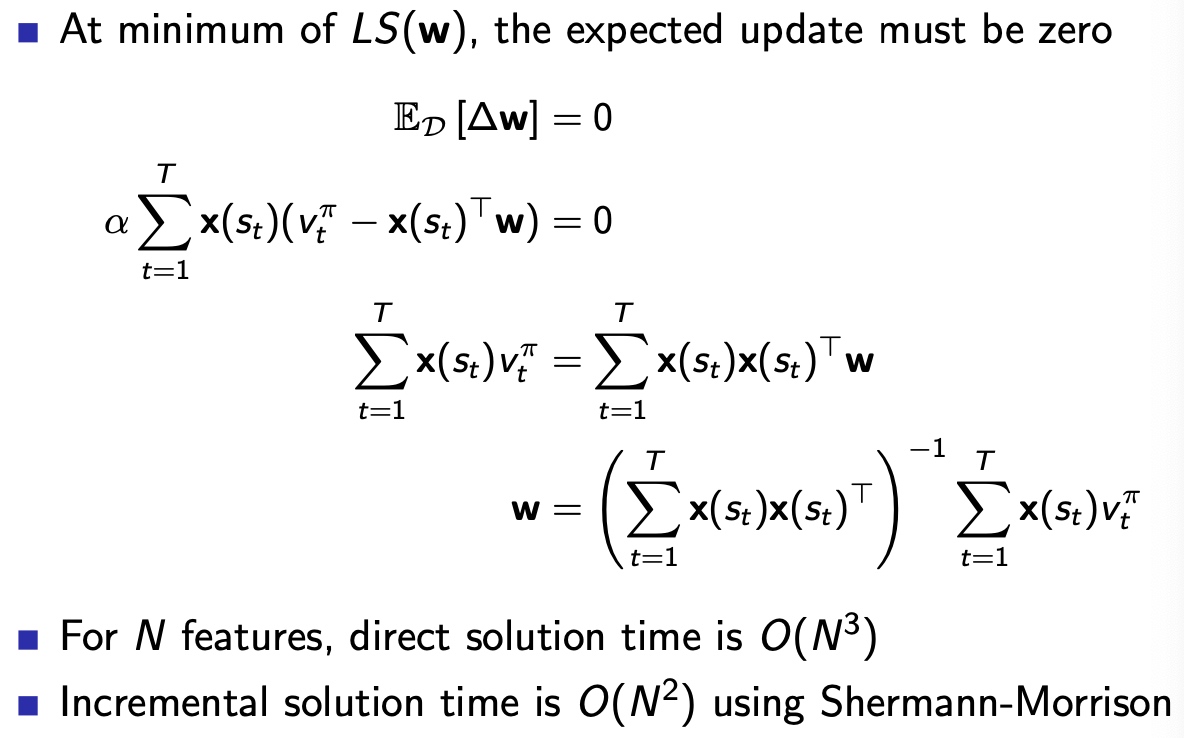
However,真值不知道
缺点是复杂度高,引入了矩阵的逆
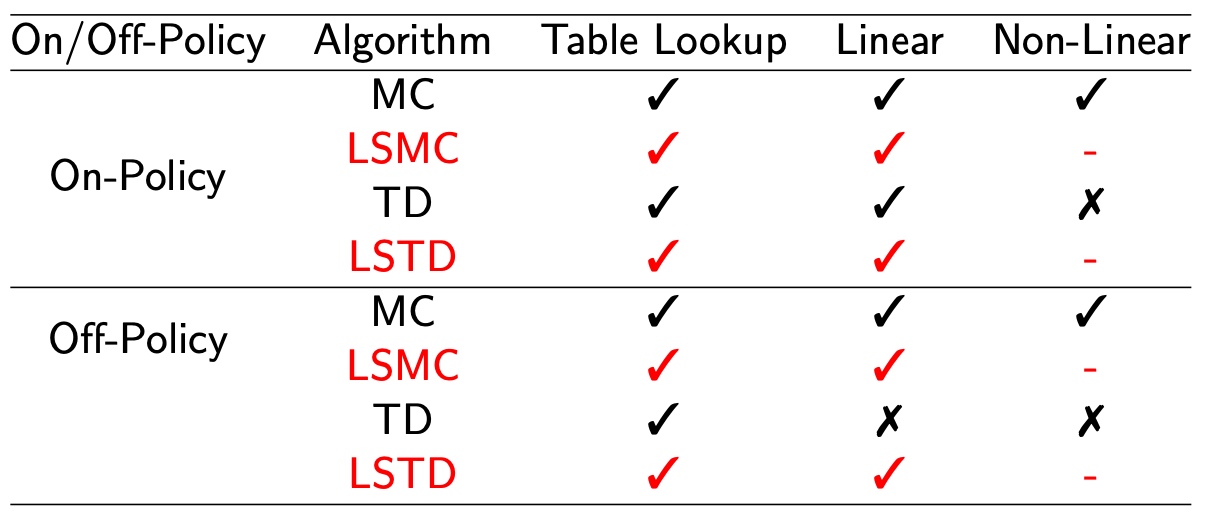
Other algorithms
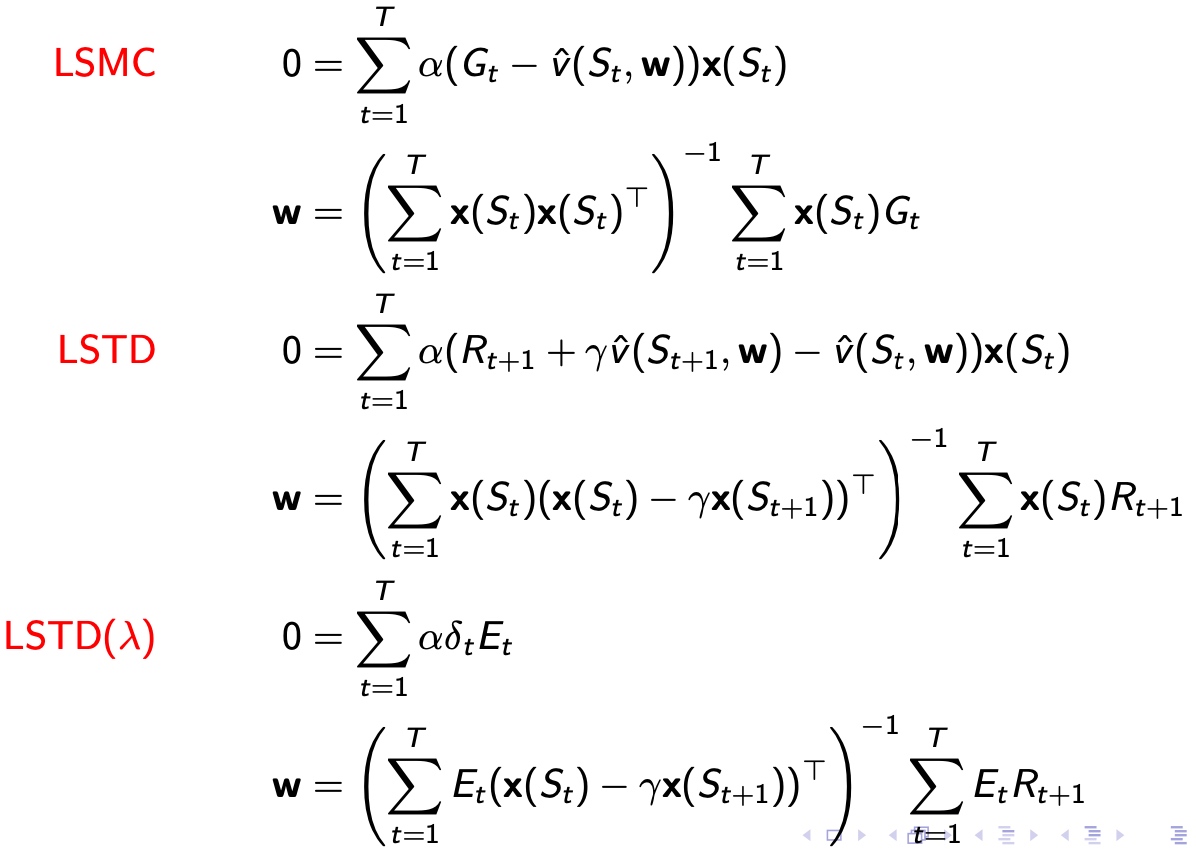


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号