Spring Boot系列(二):Spring Boot自动装配原理解析
一、Spring Boot整合第三方组件(Redis为例)
1、加依赖
<!--redis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
2、加配置
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 spring.redis.password= spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=200 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=1024 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=1000
3、加注解(看各自的组件需要,比如整合Mybatis就需要,Redis不需要)
二、Spring Boot自动装配组件原理
1、@SpringBootApplication注解
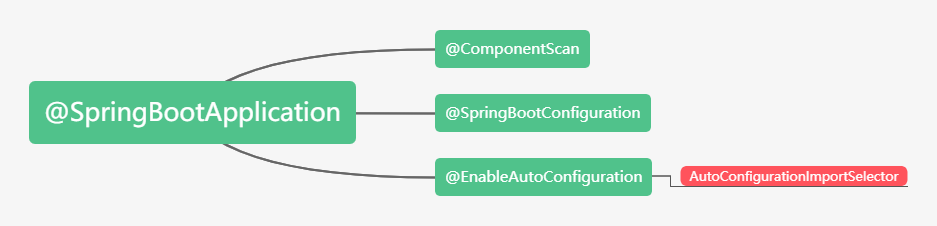
2、AutoConfigurationImportSelector分析
① selectImports方法:
@Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return NO_IMPORTS; } AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader .loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
//获取自动装配的入口 AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata); return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()); }
② getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata,annotationMetadata)方法:
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return EMPTY_ENTRY; } AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata); /** * 获取候选的配置类,主要是到classpath下面的\META-INF\spring.factories中, * 取key为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的配置类 */ List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); /**去除重复的配置类,若我们自己写的starter 可能存主重复的*/ configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations); Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); /**根据maven依赖导入的启动器过滤出需要导入的配置类*/ configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions); }
③ getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)方法:
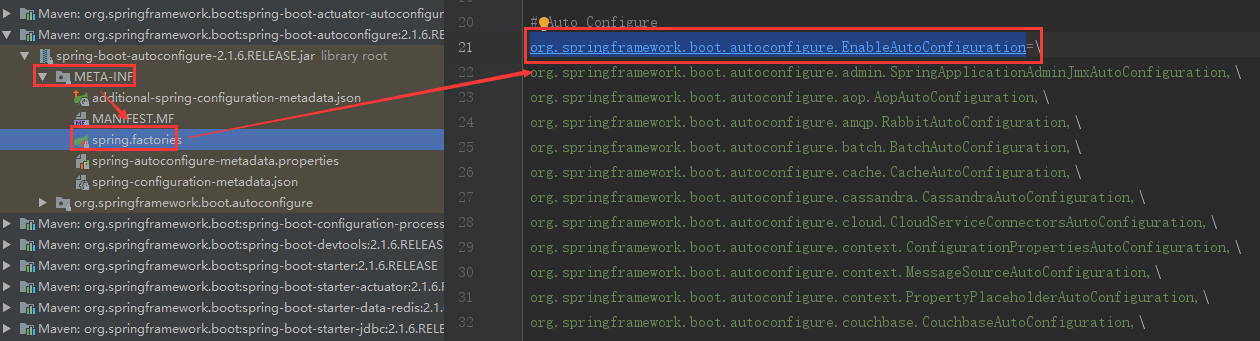
/** * Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default * this method will load candidates using {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with * {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}. * @param metadata the source metadata * @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation * attributes} * @return a list of candidate configurations */ protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { //去spring.factories中去查询EnableAutoConfiguration类 List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }
④ SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法:
/** * Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the * given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given * class loader. * @param factoryClass the interface or abstract class representing the factory * @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading resources; can be * {@code null} to use the default * @throws IllegalArgumentException if an error occurs while loading factory names * @see #loadFactories */ public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); //去spring.factories 中去查询EnableAutoConfiguration类 return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList()); }
⑤ loadSpringFactories(classLoader)方法:
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } try { /** * The location to look for factories. Can be present in multiple JAR files. * FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"; */ Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION)); result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) { String factoryClassName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim(); for (String factoryName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) { result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim()); } } } cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); } }
spring.factories如下:
3、RedisAutoConfiguration分析
导入了三个组件:RedisTemplate,StringRedisTemplate,JedisConnectionConfiguration
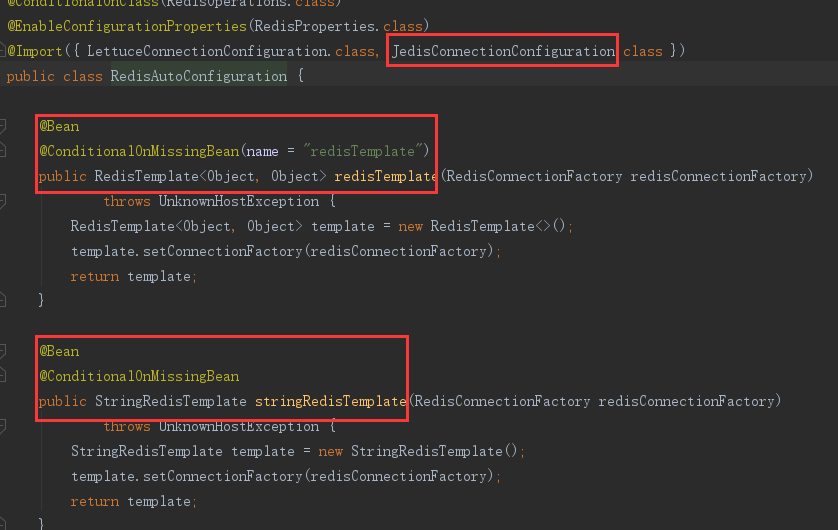
① RedisTemplate组件(默认采用java序列化,所以一般要自定义该组件):
@Bean //当没有Spring容器中没有redisTemplate的Bean的时候才加载 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate") public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); return template; }
自定义RedisTemplate组件,主要修改序列化方式,如下:
@Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setDefaultSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class)); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); return template; }
② StringRedisTemplate(默认采用java序列化,所以一般要自定义该组件):
@Bean //当没有Spring容器中没有StringRedisTemplate类型的Bean的时候才加载 @ConditionalOnMissingBean public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); return template; }
③ JedisConnectionConfiguration组件:
/** * Redis connection configuration using Jedis. */ @Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ GenericObjectPool.class, JedisConnection.class, Jedis.class }) class JedisConnectionConfiguration extends RedisConnectionConfiguration { /** * redis配置 */ private final RedisProperties properties; private final ObjectProvider<JedisClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer> builderCustomizers; JedisConnectionConfiguration(RedisProperties properties, ObjectProvider<RedisSentinelConfiguration> sentinelConfiguration, ObjectProvider<RedisClusterConfiguration> clusterConfiguration, ObjectProvider<JedisClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer> builderCustomizers) { super(properties, sentinelConfiguration, clusterConfiguration); this.properties = properties; this.builderCustomizers = builderCustomizers; } /** * Jedis连接工厂 * @return * @throws UnknownHostException */ @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(RedisConnectionFactory.class) public JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() throws UnknownHostException { return createJedisConnectionFactory(); } /** * Jedis连接工厂 * @return */ private JedisConnectionFactory createJedisConnectionFactory() { JedisClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = getJedisClientConfiguration(); if (getSentinelConfig() != null) { return new JedisConnectionFactory(getSentinelConfig(), clientConfiguration); } if (getClusterConfiguration() != null) { return new JedisConnectionFactory(getClusterConfiguration(), clientConfiguration); } return new JedisConnectionFactory(getStandaloneConfig(), clientConfiguration); } ......
redis对应的属性配置类:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis") public class RedisProperties { /** * Database index used by the connection factory. */ private int database = 0; /** * Connection URL. Overrides host, port, and password. User is ignored. Example: * redis://user:password@example.com:6379 */ private String url; /** * Redis server host. */ private String host = "localhost"; /** * Login password of the redis server. */ private String password; /** * Redis server port. */ private int port = 6379; ...... }
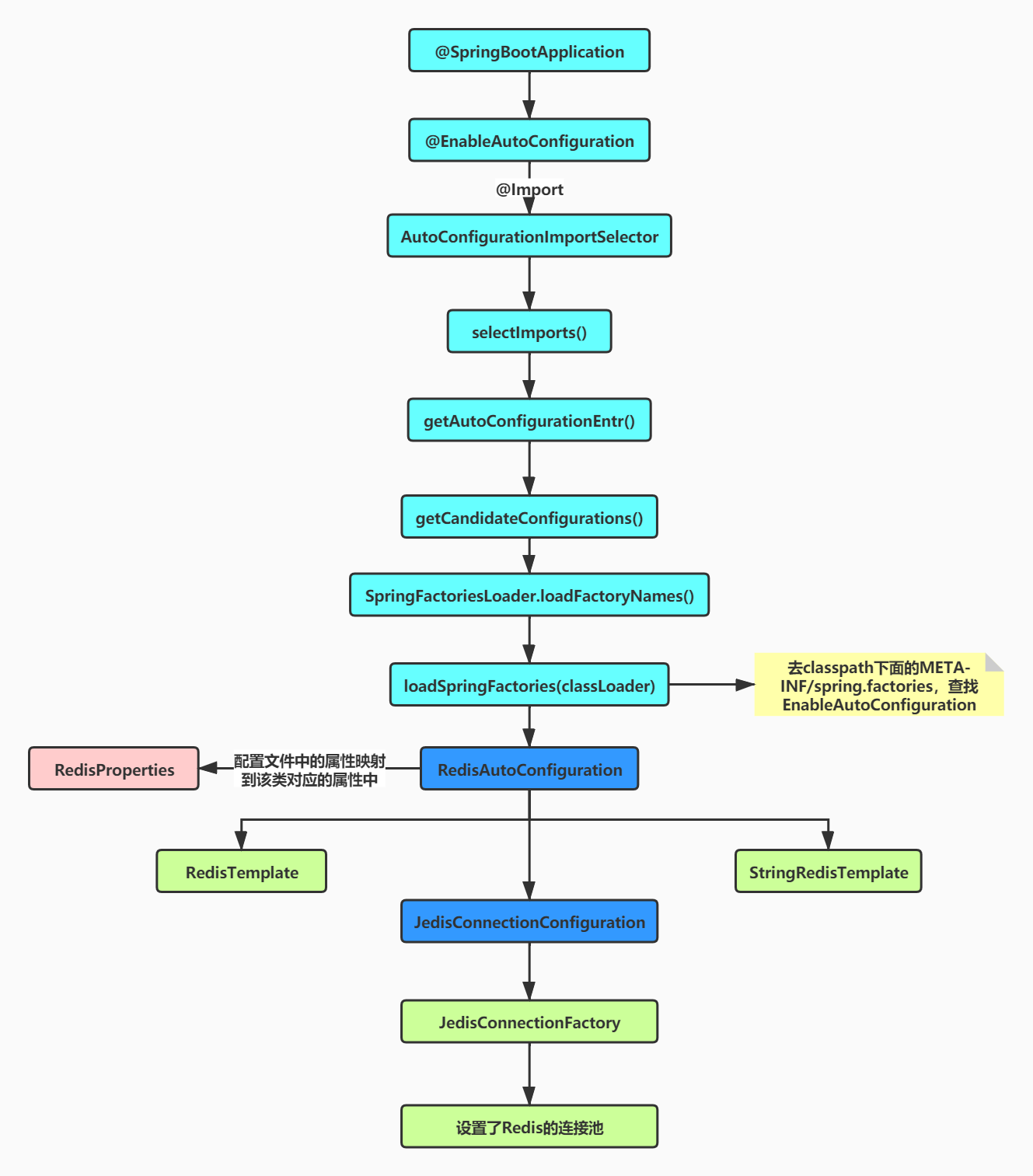
三、Spring Boot自动装配流程图
四、自定义starter启动器
1、创建一个工程toby-spring-boot-autoconfigure,用来编写启动器的核心逻辑
① 在工程的pom.xml中添加依赖:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies>
② 创建一个业务相关类:
/** * @desc: 具体业务bean * @author: toby */ public class TobyBean { /** * 是否开启 */ private Boolean enabled; public TobyBean(Boolean enabled){ this.enabled = enabled; } /** * 检测是否开启toby功能 * @return */ public String checkTobyFunction(){ if(enabled){ return "open toby function"; } return "not open toby function"; } }
③ 创建一个Toby的属性类:
/** * @desc: Configuration properties for Toby. * @author: toby */ @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = TobyProperties.TOBY_PREFIX) @Data public class TobyProperties { public static final String TOBY_PREFIX = "toby"; /** * 是否开启 */ private Boolean enabled = true; }
④ 创建一个Toby自动装配类:
/** * @desc: Toby自动装配 * @author: toby */ @Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties(TobyProperties.class) public class TobyAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean { private final TobyProperties properties; public TobyAutoConfiguration(TobyProperties properties){ this.properties = properties; } @Bean public TobyBean tobyBean(){ TobyBean tobyBean = new TobyBean(properties.getEnabled()); return tobyBean; } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { //TODO 初始化工作 } }
⑤在resources/META-INF下面新建一个spring.factories:
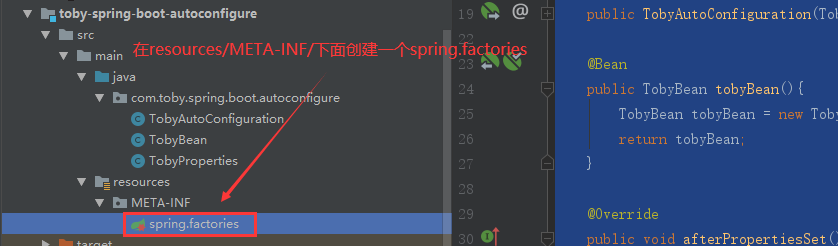
⑥ spring.factories内容如下:
# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ com.toby.spring.boot.autoconfigure.TobyAutoConfiguration
2、创建一个工程toby-spring-boot-starter,里面没有逻辑,就依赖上面的toby-spring-boot-autoconfigure

3、测试自定义的starter启动器
① 在需要用到该starter的工程的pom.xml中引入该starter依赖:
<!--自定义starter--> <dependency> <groupId>com.toby</groupId> <artifactId>toby-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency>
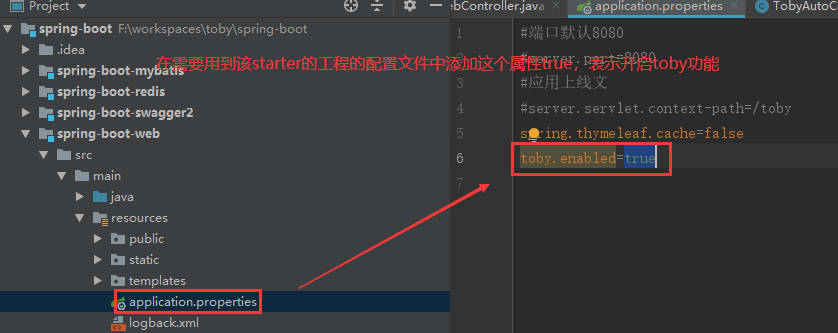
② 需要用到该starter的工程的配置文件中,根据需要设置开启属性值:
③ 使用该starter的业务bean(TobyBean):
@RestController public class WebController { @Autowired private TobyBean tobyBean; /** * 测试toby * @return */ @RequestMapping("/toby") public String toby() { return tobyBean.checkTobyFunction(); } /** * 测试web * @return */ @RequestMapping("/web") public String web() { return "this is spring boot web"; } }
④ 启动工程,访问http://localhost:8080/toby,显示如下:
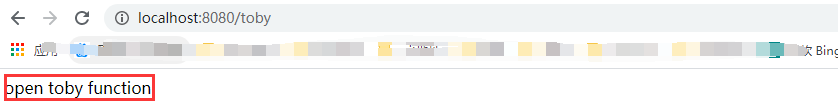
自此自定义Spring Boot Starter启动器完成!!!
五、总结
本文以Spring Boot整合Redis为例,把Spring Boot整合第三方组件的自动装配原理进行了解析,对应其他的第三方组件,比如整合Mybatis,套路是一样的,根据自动装配原理自定义了一个Spring Boot Starter启动器。




