Spring系列(五):Spring AOP源码解析
一、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解
在主配置类中添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,开启aop支持,那么@EnableAspectJAutoProxy到底做了什么?接下来分析下:

@EnableAspectJAutoProxy点进去如下:
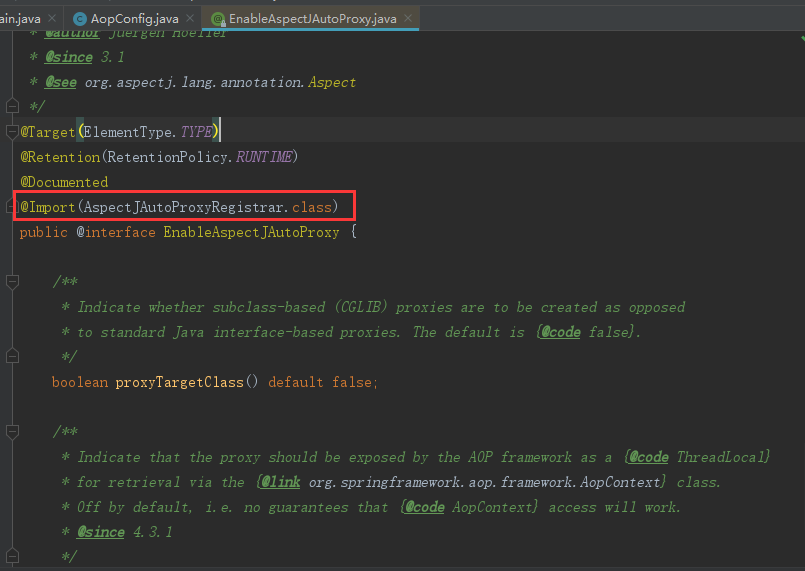
此时看到了我们非常熟悉的@Import注解,@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class),进入到AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar发现实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar如下:
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { /** * Register, escalate, and configure the AspectJ auto proxy creator based on the value * of the @{@link EnableAspectJAutoProxy#proxyTargetClass()} attribute on the importing * {@code @Configuration} class. */ @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions( AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry); AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class); if (enableAspectJAutoProxy != null) { if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry); } if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry); } } } }
会调用registerBeanDefinitions方法,跟进到这个方法里面,主要作用就是往Spring容器中注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的Bean的定义信息:
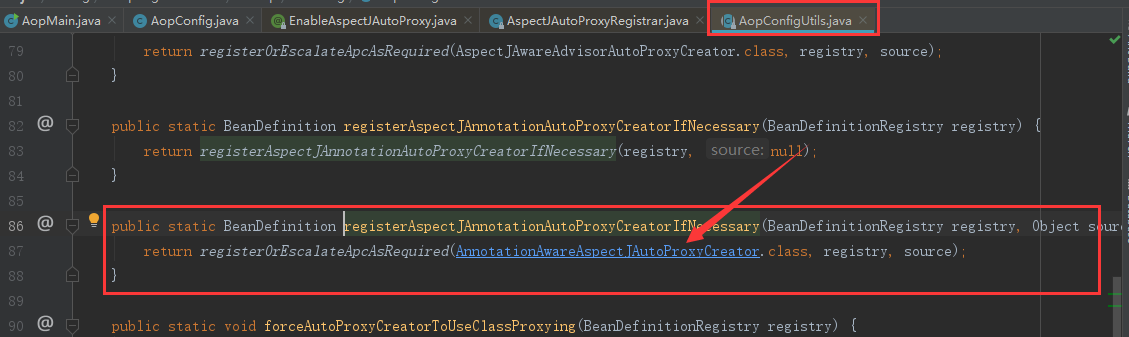
二、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承图
三、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator创建代理
首先AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了BeanFactoryAware接口:
所以在创建AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreatorBean的过程中初始化方法里面会调用setBeanFactory方法:
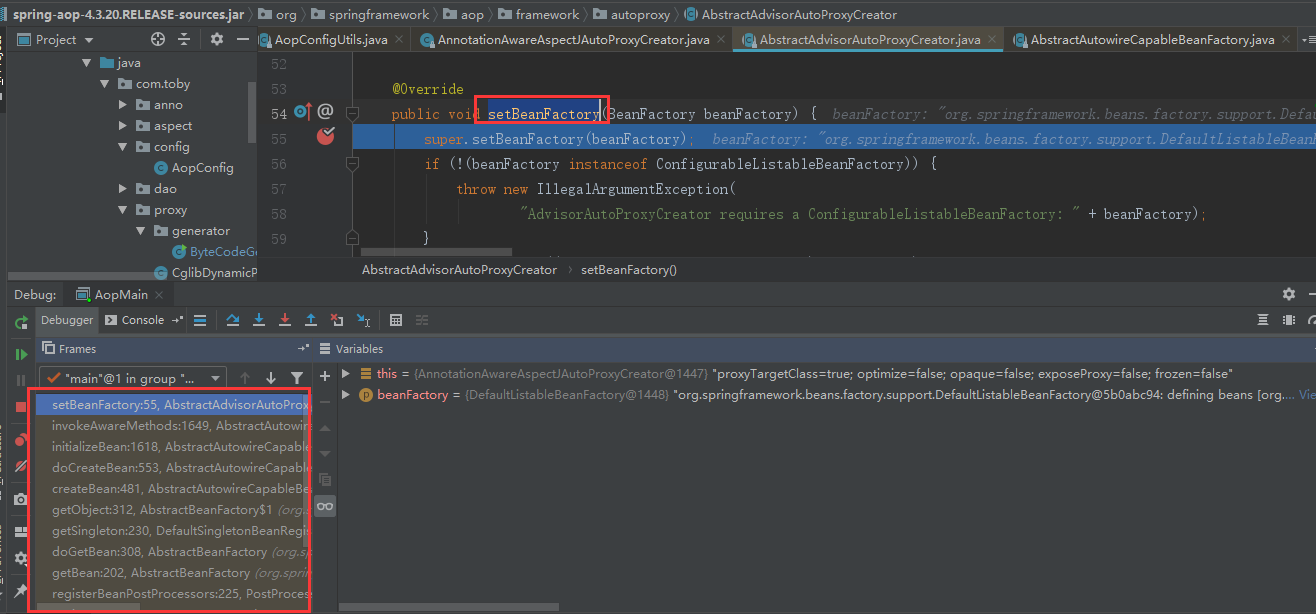
在setBeanFactory方法里面调用initBeanFactory来初始化通知者检索帮助类,后面检索通知会用到。
protected void initBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { this.advisorRetrievalHelper = new BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelperAdapter(beanFactory); }
其次AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口:
该接口定义了2个方法:postProcessBeforeInstantiation和postProcessAfterInstantiation,所以AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了这2个方法;还记得我们在Spring IoC源码解析篇分析到如下代码:
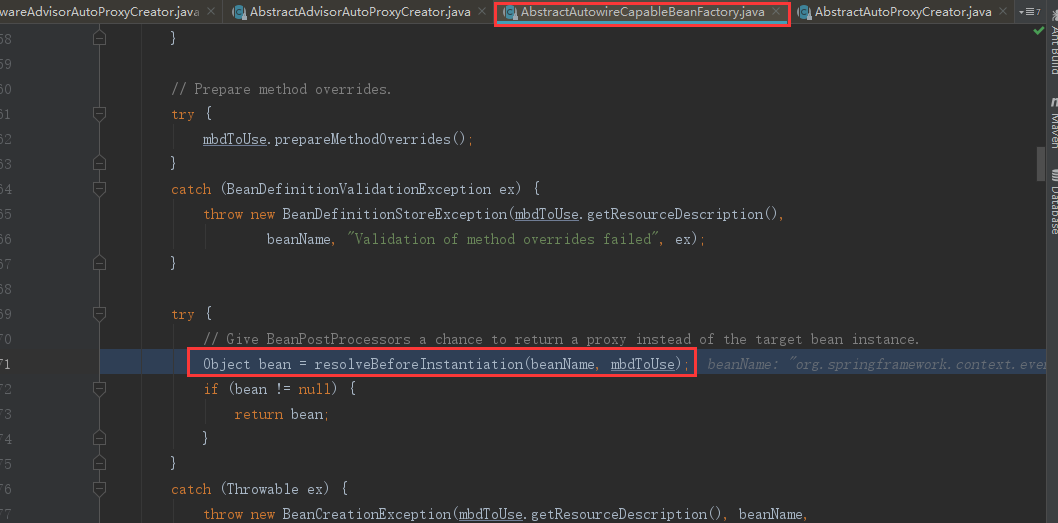
resolveBeforeInstantiation方法进去就会调到AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
/** * 在创建Bean的流程中还没调用构造器来实例化Bean的时候进行调用(实例化前后) * AOP解析切面以及事务解析事务注解都是在这里完成的 * @param beanClass 当前正在创建的Bean的Class对象 * @param beanName beanName * @return * @throws BeansException */ @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException { //构建我们的缓存key Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName); if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { //如果被解析过直接返回 if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) { return null; } /** * 判断是不是基础的Bean(Advice、PointCut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean)是就直接跳过 * 判断是不是应该跳过 (AOP解析直接解析出我们的切面信息(并且把我们的切面信息进行缓存),而事务在这里是不会解析的) */ if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return null; } } TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName); if (targetSource != null) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) { this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName); } Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource); Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } return null; }
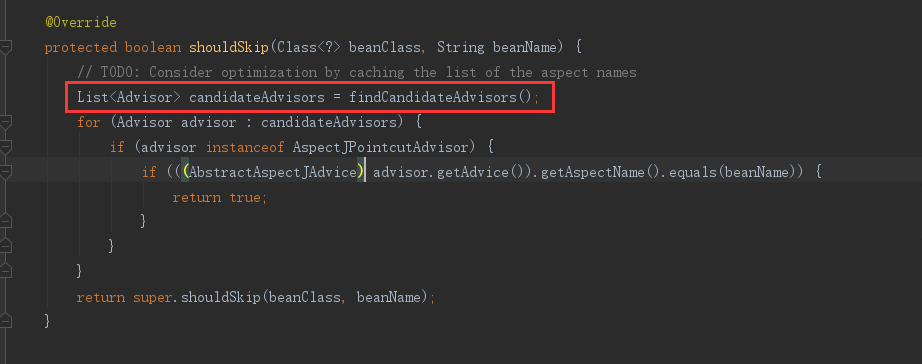
接下来进入到shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)方法(很重要):
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { /** * 找到候选的Advisors(通知者或者增强器对象) */ List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) { if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor && ((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) { return true; } } return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName); }
接下来看如何找候选的Advisors,findCandidateAdvisors()方法如下:
@Override protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() { //找出事务相关的advisor List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors(); //找出Aspect相关的信息之后封装为一个advisor if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) { advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors()); } //返回我们所有的通知 return advisors; }
第一步找事务相关的Advisor:
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() { Assert.state(this.advisorRetrievalHelper != null, "No BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper available"); /** * 通过通知者检测帮助类来帮助我们找到通知 * */ return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans(); }
第二步找构建AspectJAdvisors:
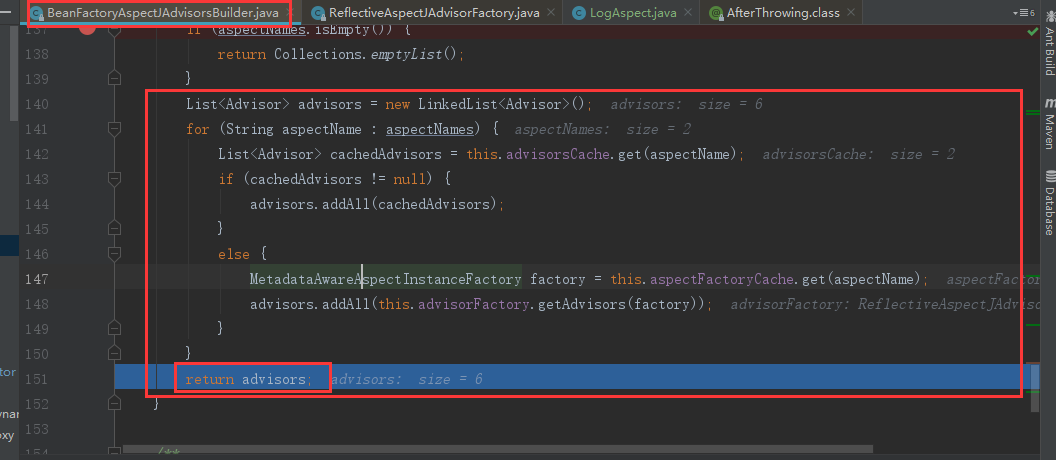
/** * 去容器中获取到所有的切面信息保存到缓存中 */ public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() { List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames; //缓存字段aspectNames没有值 注意实例化第一个单实例bean的时候就会触发解析切面 if (aspectNames == null) { synchronized (this) { aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames; if (aspectNames == null) { //用于保存所有解析出来的Advisors集合对象 List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>(); //用于保存切面的名称的集合 aspectNames = new ArrayList<>(); /** * AOP功能中在这里传入的是Object对象,代表去容器中获取到所有的组件的名称,然后再 * 进行遍历,这个过程是十分的消耗性能的,所以说Spring会再这里加入了保存切面信息的缓存。 * 但是事务功能不一样,事务模块的功能是直接去容器中获取Advisor类型的,选择范围小,且不消耗性能。 * 所以Spring在事务模块中没有加入缓存来保存我们的事务相关的advisor */ String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false); //遍历我们从IOC容器中获取处的所有Bean的名称 for (String beanName : beanNames) { if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) { continue; } //通过beanName去容器中获取到对应class对象 Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName); if (beanType == null) { continue; } //根据class对象判断是不是切面 @Aspect if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) { //是切面类 //加入到缓存中 aspectNames.add(beanName); //把beanName和class对象构建成为一个AspectMetadata AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName); if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) { //构建切面注解的实例工厂 MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName); //真正的去获取我们的Advisor List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory); //加入到缓存中 if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) { this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors); } else { this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory); } advisors.addAll(classAdvisors); } else { // Per target or per this. if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName + "' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton"); } MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName); this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory); advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory)); } } } this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames; return advisors; } } } if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptyList(); }
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String aspectName : aspectNames) { List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName); if (cachedAdvisors != null) { advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors); } else { MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName); advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory)); } } return advisors; }
① org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory#isAspect:
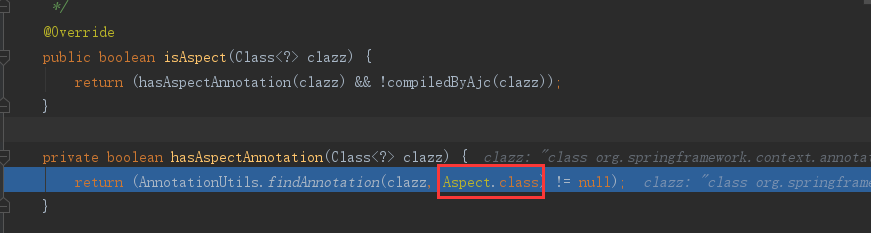
② 真正的去获取我们的Advisor,this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory)方法如下:
@Override public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) { //获取我们的标记为Aspect的类 Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass(); //获取我们的切面类的名称 String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName(); //校验我们的切面类 validate(aspectClass); //我们使用的是包装模式来包装我们的MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory构建为MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory = new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory); List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>(); //获取到切面类中的所有方法,但是该方法不会解析到标注了@PointCut注解的方法 for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) { //循环解析我们切面中的方法 Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName); if (advisor != null) { advisors.add(advisor); } } if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) { Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory); advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor); } for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) { Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field); if (advisor != null) { advisors.add(advisor); } } return advisors; }
获取切面上的通知方法,并按照规则排序,getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass):
private List<Method> getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass) { final List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>(); ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, method -> { if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) { methods.add(method); } }); methods.sort(METHOD_COMPARATOR); return methods; }
排序(该顺序在代理调用的时候会用到)规则如下:
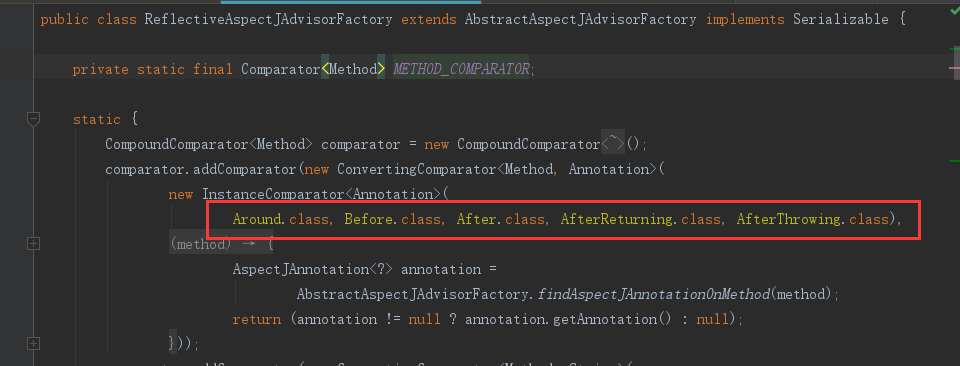
根据通知的方法创建增强器:getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName)如下:
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) { validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass()); //切面的方法上构建切点表达式 AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut( candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass()); if (expressionPointcut == null) { return null; } //实例化我们的切面通知对象 return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod, this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName); }
实例化我们的切面通知对象,new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName):
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut, Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) { //当前的切点表达式 this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut; //切面的class对象 this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass(); //切面方法的名称 this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName(); //切面方法的参数类型 this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes(); //切面方法对象 this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod; //aspectj的通知工厂 this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory; //aspect的实例工厂 this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory; //切面的顺序 this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder; //切面的名称 this.aspectName = aspectName; /** * 判断当前的切面对象是否需要延时加载 */ if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) { // Static part of the pointcut is a lazy type. Pointcut preInstantiationPointcut = Pointcuts.union( aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), this.declaredPointcut); // Make it dynamic: must mutate from pre-instantiation to post-instantiation state. // If it's not a dynamic pointcut, it may be optimized out // by the Spring AOP infrastructure after the first evaluation. this.pointcut = new PerTargetInstantiationModelPointcut( this.declaredPointcut, preInstantiationPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); this.lazy = true; } else { // A singleton aspect. this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut; this.lazy = false; //将切面中的通知构造为advice通知对象 this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut); } }
将切面中的通知构造为advice通知对象,instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut):

获取通知getAdvice方法如下:
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) { //获取我们的切面类的class对象 Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass(); validate(candidateAspectClass); //获取切面方法上的注解 AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation = AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod); //解析出来的注解信息是否为null if (aspectJAnnotation == null) { return null; } //再次判断是否是切面对象 if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) { throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " + "Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" + candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]"); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod); } AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice; //判断标注在方法上的注解类型 switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) { //是PointCut注解 那么就抛出异常 因为在外面传递进来的方法已经排除了Pointcut的方法 case AtPointcut: if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'"); } return null; //环绕通知 构建AspectJAroundAdvice case AtAround: springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break; //前置通知 构建AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice case AtBefore: springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break; //后置通知 AspectJAfterAdvice case AtAfter: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break; //返回通知 AspectJAfterReturningAdvice case AtAfterReturning: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation(); if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) { springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning()); } break; //异常通知 AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice case AtAfterThrowing: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice( candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation(); if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) { springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing()); } break; default: throw new UnsupportedOperationException( "Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod); } //设置我们构建出来的通知对象的相关属性比如DeclarationOrder,在代理调用的时候,责任链顺序上会用到 springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName); springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder); String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod); if (argNames != null) { springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames); } springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings(); return springAdvice; }
至此真正的去获取我们的Advisor方法解析完成,List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);

③ 如果该切面是单实例的就加入到缓存中:
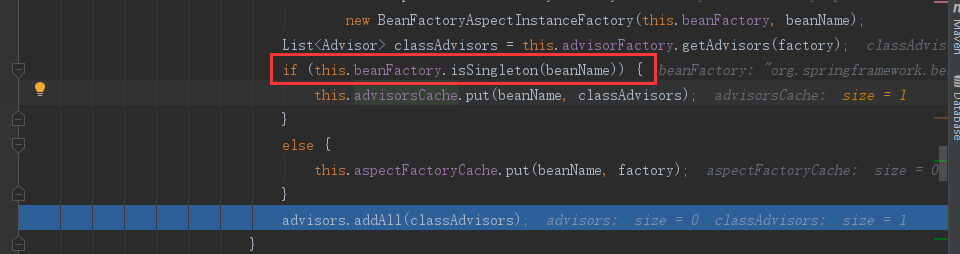
④ 遍历所有的切面,将每个切面的所有的增强器添加在advisors中进行返回:
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.shouldSkip()方法中的List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();返回找到的候选的增强器,然后再调用父类的shouldSkip()返回false,就是不跳过的意思
执行完shouldSkip()返回到AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessBeforeInstantiation的方法,至此postProcessBeforeInstantiation执行完成。
最后AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了Bean的后置处理器BeanPostProcessor接口:
该接口有2个方法:postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization,其中在postProcessAfterInitialization方法主要就是通过前面创建的增强器来创建代理对象
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean != null) { //获取缓存key Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) { //如果有必要就代理 return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
进入如果必要就代理方法,wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey):
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { //已经被处理过 if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } //不需要增强的 if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } //是不是基础的bean 是不是需要跳过的 if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } //如果有匹配的通知,就创建代理对象 Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); //如果不为空,表述需要代理 if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { //设置当前的对象已处理 this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); //创建我们的真正的代理对象 Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); //加入到缓存 this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
① 获取匹配的通知方法,getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null):
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) { //找合适的增强器对象 List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); //若为空表示没找到 if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); }
跟进到找合适的增强器对象方法,findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName):
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { //找到Spring IoC容器中所有的候选通知 List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); //判断找到的通知能不能作用到当前的类上 List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); //对我们的advisor进行排序 if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
跟进到判断找到的通知能不能作用到当前的类上方法,findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName):
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply( List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName); try { //从候选的通知器中找到合适正在创建的实例对象的通知器 return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass); } finally { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null); } }
跟进到从候选的通知器中找到合适正在创建的实例对象的通知器方法,AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass):
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) { //若候选的增强器集合为空 直接返回 if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) { return candidateAdvisors; } //定义一个合适的增强器集合对象 List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>(); //循环我们候选的增强器对象 for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { //判断我们的增强器对象是不是实现了IntroductionAdvisor (很明显我们事务的没有实现 所以不会走下面的逻辑) if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } //不为空 boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { //判断我们的增强器对象是不是实现了IntroductionAdvisor (很明显我们事务的没有实现 所以不会走下面的逻辑) if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { //在上面已经处理过 ,不需要处理 continue; } /** * 真正的判断增强器是否合适当前类型 */ if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors; }
跟进到是否能用方法,canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions):
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { //判断我们的增强器是否是IntroductionAdvisor if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass); } //判断我们事务的增强器BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor是否实现了PointcutAdvisor else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { //转为PointcutAdvisor类型 PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; //找到真正能用的增强器 return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions); } else { // It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies. return true; } }
跟进到找到真正能用的增强器方法,canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions):
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null"); if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { return false; } /** * 通过切点获取到一个方法匹配器对象 */ MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) { // No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway... return true; } //判断匹配器是不是IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null; if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher; } //创建一个集合用于保存targetClass的class对象 Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>(); //判断当前class是不是代理的class对象 if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { //加入到集合中去 classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass)); } //获取到targetClass所实现的接口的class对象,然后加入到集合中 classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass)); //循环所有的class对象 for (Class<?> clazz : classes) { //通过class获取到所有的方法 Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz); //循环我们的方法 for (Method method : methods) { //通过methodMatcher.matches来匹配我们的方法 if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ? introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) : //通过方法匹配器进行匹配 methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) { return true; } } } return false; }
如果该方法返回true就表示匹配,就添加到合适的集合eligibleAdvisors中,遍历完所有的候选增强器后,debug截图如下:
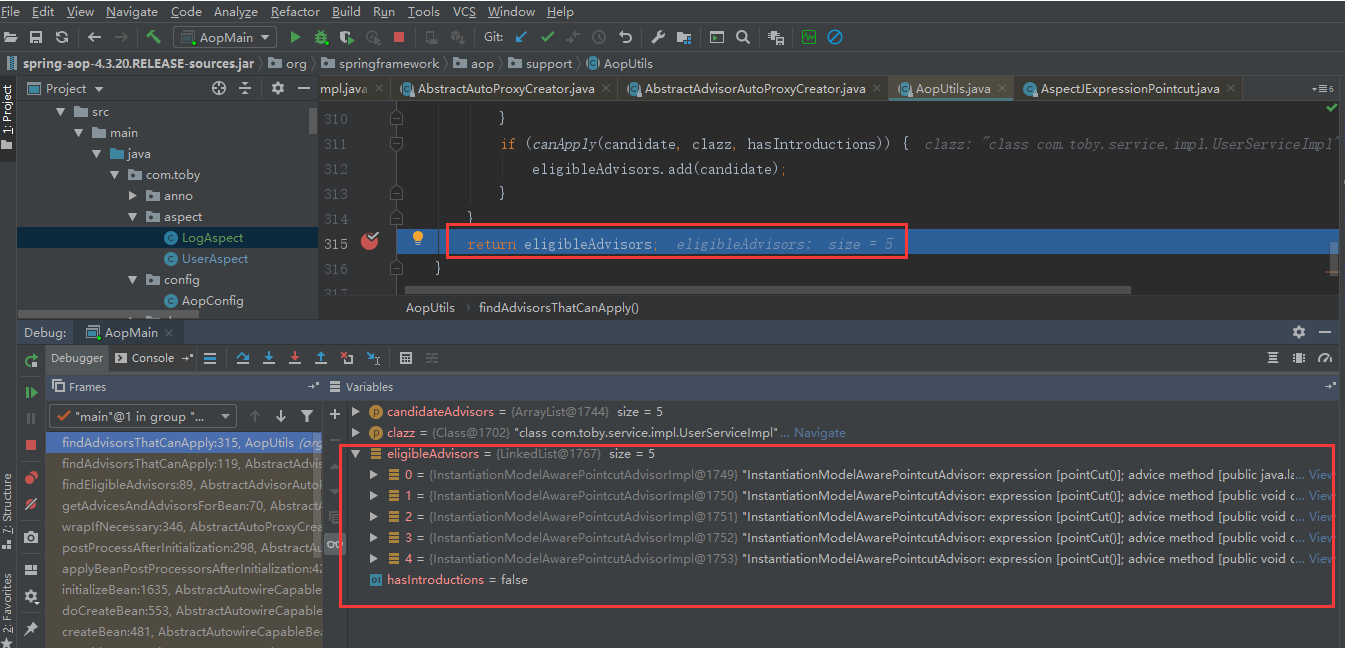
返回到AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.findEligibleAdvisors方法中,然后扩展增强器,如果合适的增强器列表不是空的就排序。
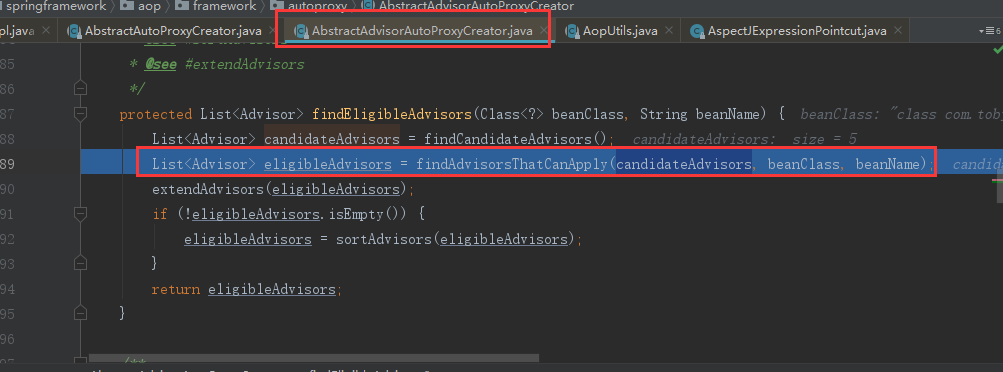
返回到AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean,如果空就表示不需要代理,不为空就表示需要代理。
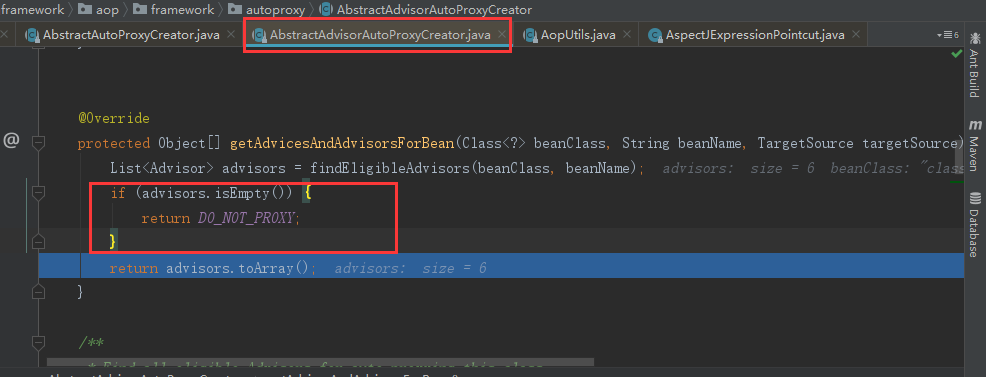
② 真正创建代理对象,Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)):
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) { if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); } //创建一个代理对象工厂 ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this); //为proxyFactory设置创建jdk还是cglib代理 if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); } else { evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } } //把我们的specificInterceptors数组中的Advisor转化为数组形式的 Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); //为我们的代理工加入通知器, proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); //设置targetSource对象 proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true); } //真正创建代理对象 return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()); }
跟进到真正创建代理对象方法,proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()):
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { //createAopProxy() 用来创建我们的代理工厂 return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader); }
跟进到创建AOP代理方法,createAopProxy():
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() { if (!this.active) { activate(); } return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this); }
跟进到getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this):
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { //判断我们是否指定使用cglib代理ProxyTargetClass =true 默认false if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } //targetClass是接口使用的就是jdk代理 if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } //cglib代理 return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { //jdk动态代理 return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } }
跟进到创建动态代理(注意这个是jdk的,cglib同理)方法,getProxy(classLoader):
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true); findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces); //创建jdk动态代理 return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this); }
有没有眼前一亮:该方法用来创建我们的代理对象,如果proxyTargetClass = true,创建cglib代理 ,为false,如果代理类没有实现接口也创建cglib代理,否则创建jdk代理
至此AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator创建动态代理完成!!
四、AOP动态代理invoke
以JdkDynamicAopProxy为例,CGLIB动态代理参照Jdk动态代理自行分析
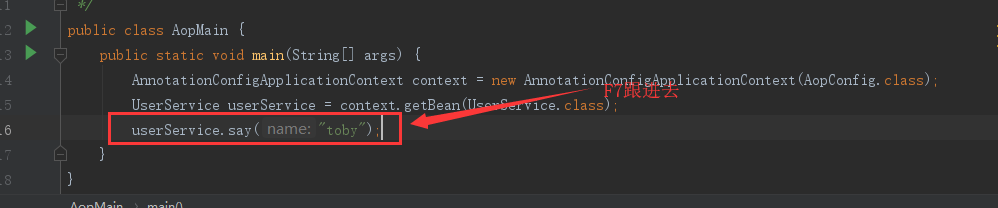
JdkDynamicAopProxy的invole方法:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; //获取到我们的目标对象 TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Object target = null; try { //若是equals方法不需要代理 if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself. return equals(args[0]); } //若是hashCode方法不需要代理 else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself. return hashCode(); } //若是DecoratingProxy也不要拦截器执行 else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) { // There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config. return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised); } else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() && method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) { // Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config... return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args); } Object retVal; /** * 这个配置是暴露我们的代理对象到线程变量中,需要搭配@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)一起使用
* 比如在目标对象方法中再次获取代理对象可以使用这个AopContext.currentProxy() * 还有的就是事务方法调用事务方法的时候也是用到这个 */ if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { //把我们的代理对象暴露到线程变量中 oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } //获取我们的目标对象 target = targetSource.getTarget(); //获取我们目标对象的class Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null); //把aop的advisor转化为拦截器链 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); //如果拦截器链为空 if (chain.isEmpty()) { //通过反射直接调用执行 Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else { //创建一个方法调用对象 MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); //调用执行 retVal = invocation.proceed(); } // Massage return value if necessary. Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method // is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets // a reference to itself in another returned object. retVal = proxy; } else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) { throw new AopInvocationException( "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); } return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { // Must have come from TargetSource. targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } }
跟进到invocation.proceed()方法,该方法的调用用到了递归和责任链设计模式:
public Object proceed() throws Throwable { //从-1开始,下标=拦截器的长度-1的条件满足表示执行到了最后一个拦截器的时候,此时执行目标方法 if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { return invokeJoinpoint(); } //获取第一个方法拦截器使用的是前++ Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) { // Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have // been evaluated and found to match. InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice; if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) { return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); } else { // Dynamic matching failed. // Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain. return proceed(); } } else { return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); } }
跟进到((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this)方法,责任链模式,执行顺序如下:
① ExposeInvocationInterceptor.invoke方法:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get(); invocation.set(mi); try { return mi.proceed(); } finally { invocation.set(oldInvocation); } }
② AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice.invoke方法:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { try { //执行下一个通知/拦截器 return mi.proceed(); } catch (Throwable ex) { //抛出异常 if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) { //执行异常通知 invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex); } throw ex; } }
③ AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor.invoke方法:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { //执行下一个通知/拦截器 Object retVal = mi.proceed(); //返回通知方法 this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); return retVal; }
④ AspectJAfterAdvice.invoke方法:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { try { //执行下一个通知/拦截器 return mi.proceed(); } finally { //后置通知的方法总是会被执行 原因就在这finally invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null); } }
⑤ AspectJAroundAdvice.invoke方法:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) { throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi); } ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi; ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi); JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi); return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null); }
⑥ MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.invoke方法:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { //执行前置通知的方法 this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); //执行下一个通知/拦截器,但是该拦截器是最后一个了,所以会调用目标方法 return mi.proceed(); }
运行的执行顺序如下:
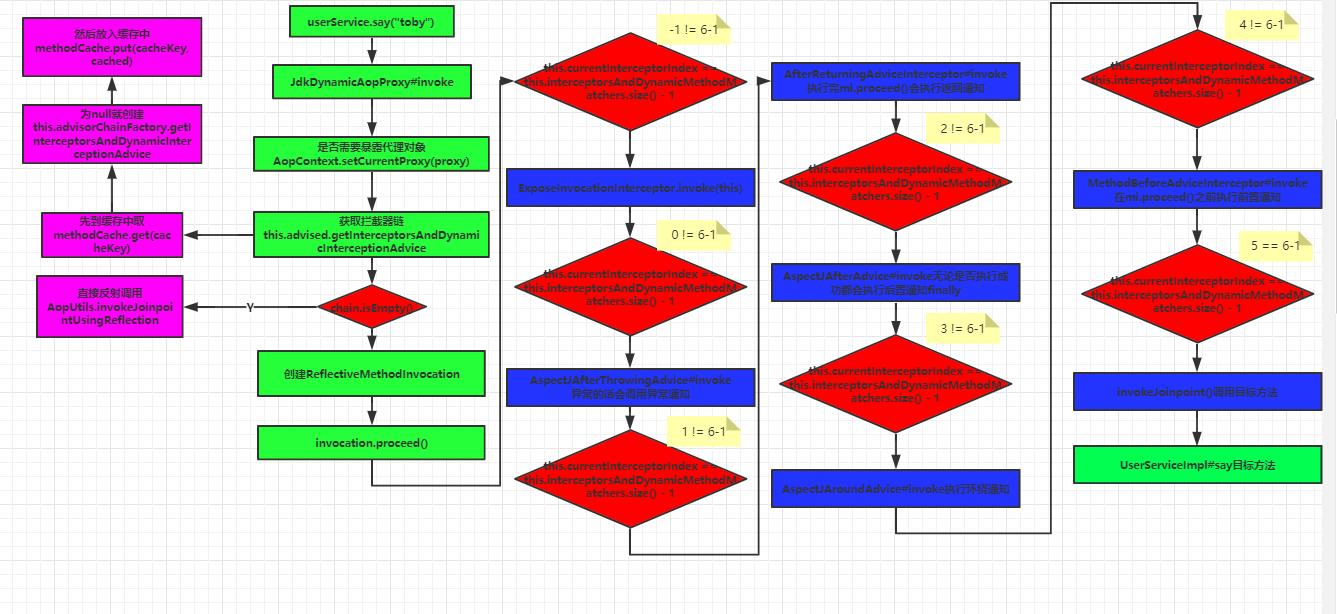
JdkDynamicAopProxy的invole方法流程图如下:
注意:该流程图是以本人的spring系列中的spring-aop模块中的LogAspect为例的。
总结:通过@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解开启AOP功能,该注解为我们Spring容器中注册了AnnotationAwareAspectJAuto ProxyCreator组件,AOP的准备和代理创建都在这个组件中完成,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承AbstractAuto ProxyCreator实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,在方法postProcessBeforeInstantiation中找到Spring容器中所有的增强器,为创建代理做准备;AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了BeanPost Processor接口,在方法postProcessAfterInitialization中通过前面找到的候选增强器中找到合适的增强器来创建代理对象,最后调用目标方法,进去到代理对象的invoke方法中进行调用。





