spring ioc
Spring IoC容器的设计
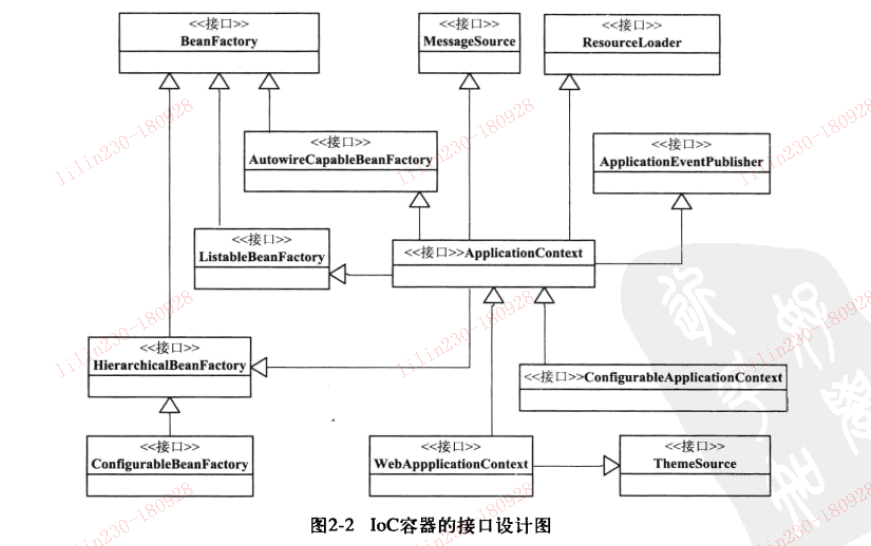
一)从接口BeanFactory到HierarchicalBeanFactory,再到ConfigurableBeanFactory,是一条主要的BeanFactory
设计路径。在这条接口设计路径中,BeanFactory接口定义了基本的IoC容器的规范。在这个接口定义中,包
括了getBean()这样的IoC容器的基本方法。而HierarchicalBeanFactory接口在继承了BeanFactory的基本接口
之后,增加了getParentBeanFactory()的接口功能,使BeanFactory具备了双亲IoC容器的管理功能。在接下来
的ConfigurableBeanFactory接口中,主要定义了一些对BeanFactory的配置功能,比如
通过setParentBeanFactory( )设置双亲IoC容器,通过addBeanPostProcessor( )配置Bean后置处理器,
等等。通过这些接口设计的叠加,定义了BeanFactory就是简单IoC容器的基本功能
二)第二条接口设计主线是,以ApplicationContext应用上下文接口为核心的接口设计,这里涉及的主要接口
设计有,从BenaFactory到ListableBeanFactory,再到ApplicationContext,再到我们常用的WebApplicationContext或者ConfigurableApplicationContext接口。
在这个接口体系中,ListableBeanFactory和HierarchicalBeanFactory两个接口,连接BeanFactory接口定义和ApplicationContext应用上下文的接口定义。
在ListableBeanFactory接口中,细化了许多BeanFactory的接口功能,比如定义了getBeanDefinitionNames()接口方法;对于HierarchicalBeanFactory接口,
我们在前文中已经提到过;对于ApplicationContext接口,它通过继承MessageSource、ResourceLoader、
ApplicationEventPublisher接口,在BeanFactory简单IoC容器的基础上添加了许多对高级容器的特性的支持。
1. BeanFactory
以XmlBeanFactory为例
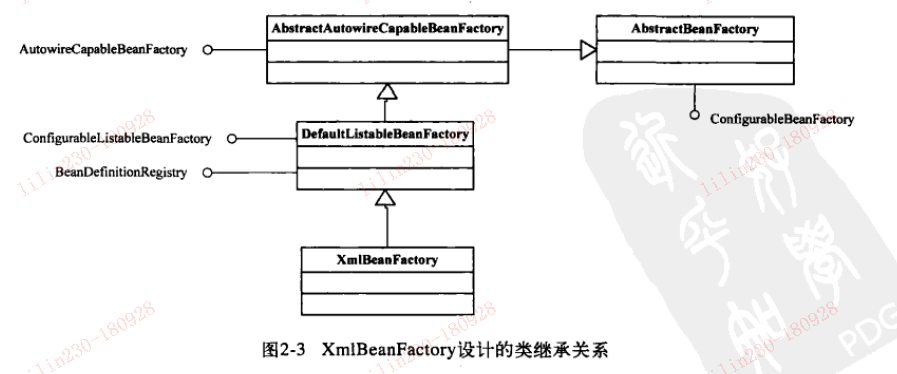
XmlBeanFactory中
1 @Deprecated 2 @SuppressWarnings({"serial", "all"}) 3 public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory { 4 5 private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this); 6 7 8 /** 9 * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource, 10 * which must be parsable using DOM. 11 * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from 12 * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors 13 */ 14 public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException { 15 this(resource, null); 16 } 17 18 /** 19 * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream, 20 * which must be parsable using DOM. 21 * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from 22 * @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory 23 * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors 24 */ 25 public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException { 26 super(parentBeanFactory); 27 this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 28 } 29 30 }
参考XmlBeanFactory 编程式使用IoC容器
1 ClassPathResource res = new ClassPathResource("bean.xml"); 2 DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); 3 XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); 4 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res);
这样,我们就可以通过factory对象来使用DefaultListableBeanFactory这个IoC容器了。
在使用IoC容器时,需要如下几个步骤:
1)创建IoC配置文件的抽象资源,这个抽象资源包含了BeanDefinition的定义信息。
2)创建一个BeanFactory,这里使用DefaultListableBeanFactory。
3)创建一个载入BeanDefinition的读取器,这里使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader来载入XML文件形式的
BeanDefinition,通过一个回调配置给BeanFactory。
4)从定义好的资源位置读入配置信息,具体的解析过程由XmlBeanDefinitionReader来完成。完成整个载入
和注册Bean定义之后,需要的IoC容器就建立起来了。这个时候就可以直接使用IoC容器了。
2. ApplicationContext
在ApplicationContext容器中,以常用的FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的实现为例
来说明ApplicationContext容器的设计原理。
在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的设计中,我们看到ApplicationContext应用上下文的主要功能是在
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的基类AbstractXmlApplicationContext中实现了,
在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext中,作为一个具体的应用上下文,只需要实现和它自身设计相关的
两个功能。
一个功能是,如果应用直接使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,对于实例化这个应用上下文的
支持,同时启动IoC容器的refresh( )过程。
1 /** 2 * Create a new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext with the given parent, 3 * loading the definitions from the given XML files. 4 * @param configLocations array of file paths 5 * @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context, 6 * loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons. 7 * Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context. 8 * @param parent the parent context 9 * @throws BeansException if context creation failed 10 * @see #refresh() 11 */ 12 public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) 13 throws BeansException { 14 15 super(parent); 16 setConfigLocations(configLocations); 17 if (refresh) { 18 refresh(); 19 } 20 }
另一个功能是与FileSystemXmlApplicationContext设计具体相关的功能,这部分与怎样从文件系统
中加载XML的Bean定义资源有关。
通过这个过程,可以为在文件系统中读取以XML形式存在的BeanDefinition做准备,因为不同的
应用上下文实现对应着不同的读取BeanDefinition的方式,在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext中的
实现代码如下:
1 /** 2 * Resolve resource paths as file system paths. 3 * <p>Note: Even if a given path starts with a slash, it will get 4 * interpreted as relative to the current VM working directory. 5 * This is consistent with the semantics in a Servlet container. 6 * @param path path to the resource 7 * @return Resource handle 8 * @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext#getResourceByPath 9 */ 10 @Override 11 protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { 12 if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) { 13 path = path.substring(1); 14 } 15 return new FileSystemResource(path); 16 }
可以看到,调用这个方法,可以得到FileSystemResource的资源定位。
IoC容器的初始化过程
简单来说,IoC容器的初始化是由前面介绍的refresh( )方法来启动的,具体来说,这个启动包括
BeanDefinition的Resource定位、载入和注册三个基本过程。
Spring把这三个过程分开,并使用不同的模块来完成,如使用相应的ResourceLoader、
BeanDefinitionReader、BeanDefinitionRegistry等模块,通过这样的设计方式,可以让用户更加灵活
的对这三个过程进行剪裁或扩展,定义出最合适自己的IoC容器的初始化过程。
第一个过程是Resource定位过程。这个Resource定位指的是BeanDefinition的资源定位,它由
ResourceLoader通过统一的Resource接口来完成,这个Resource对这种形式的BeanDefinition的使用
都提供了统一接口。比如,在文件系统中的Bean定义信息可以使用FileSystemResource来进行抽象;
在类路径中的Bean定义信息可以使用前面提到的ClassPathResource来使用。
第二个过程是BeanDefinition的载入。这个过程是把用户定义好的Bean表示成IoC容器内部的数据结构,
而这个容器内部的数据结构就是BeanDefinition。
第三个过程是向IoC容器注册这些BeanDefinition的过程。是通过调用BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的
实现来完成的。这个注册过程把载入过程中解析得到的BeanDefinition向IoC容器进行注册。通过分析,可以
看到,在IoC容器内部将BeanDefinition注入到一个HashMap中,通过HashMap来管理这些BeanDefinition
数据的。
IoC容器的依赖注入
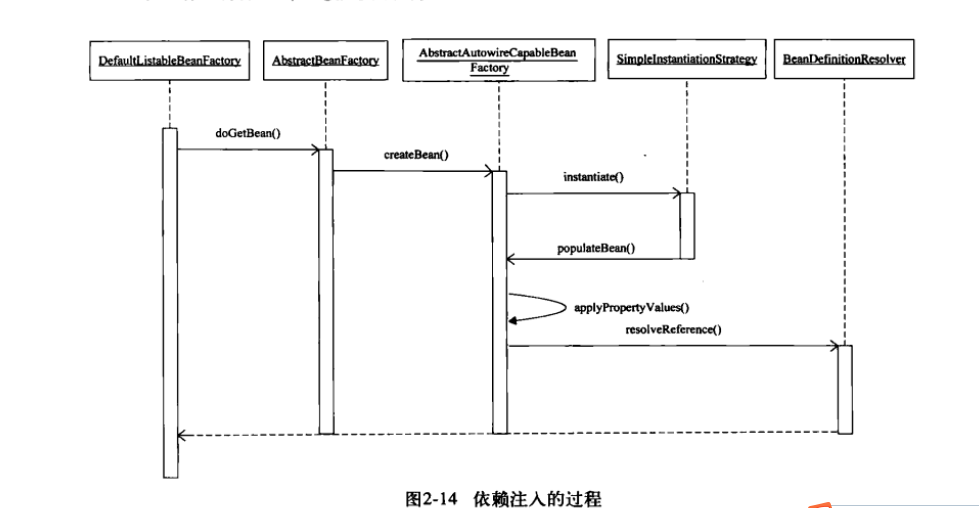
当前IoC容器已经载入了用户定义的Bean信息,开始分析依赖注入的原理。首先,注意到依赖注入的过程是
用户第一次向IoC容器索要Bean时触发的,当然也有例外,也就是我们可以在BeanDefinition信息中通过控制
lazy-init属性来让容器完成对Bean的预实例化。下面从DefaultListableBeanFactory的基类AastractBeanFactory
入手去看看getBean的实现
1 public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException { 2 return doGetBean(name, null, null, false); 3 } 4 5 /** 6 * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean. 7 * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve 8 * @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve 9 * @param args arguments to use if creating a prototype using explicit arguments to a 10 * static factory method. It is invalid to use a non-null args value in any other case. 11 * @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check, 12 * not for actual use 13 * @return an instance of the bean 14 * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created 15 */ 16 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 17 protected <T> T doGetBean( 18 final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) 19 throws BeansException { 20 21 final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); 22 Object bean; 23 24 // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons. 25 Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); 26 if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { 27 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 28 if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { 29 logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + 30 "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); 31 } 32 else { 33 logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); 34 } 35 } 36 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null); 37 } 38 39 else { 40 // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance: 41 // We're assumably within a circular reference. 42 if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { 43 throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); 44 } 45 46 // Check if bean definition exists in this factory. 47 BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); 48 if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { 49 // Not found -> check parent. 50 String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); 51 if (args != null) { 52 // Delegation to parent with explicit args. 53 return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); 54 } 55 else { 56 // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. 57 return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); 58 } 59 } 60 61 if (!typeCheckOnly) { 62 markBeanAsCreated(beanName); 63 } 64 65 try { 66 final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); 67 checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); 68 69 // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on. 70 String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); 71 if (dependsOn != null) { 72 for (String dependsOnBean : dependsOn) { 73 getBean(dependsOnBean); 74 registerDependentBean(dependsOnBean, beanName); 75 } 76 } 77 78 // Create bean instance. 79 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { 80 sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { 81 public Object getObject() throws BeansException { 82 try { 83 return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); 84 } 85 catch (BeansException ex) { 86 // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there 87 // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. 88 // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. 89 destroySingleton(beanName); 90 throw ex; 91 } 92 } 93 }); 94 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); 95 } 96 97 else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { 98 // It's a prototype -> create a new instance. 99 Object prototypeInstance = null; 100 try { 101 beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); 102 prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); 103 } 104 finally { 105 afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); 106 } 107 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); 108 } 109 110 else { 111 String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); 112 final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); 113 if (scope == null) { 114 throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope '" + scopeName + "'"); 115 } 116 try { 117 Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { 118 public Object getObject() throws BeansException { 119 beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); 120 try { 121 return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); 122 } 123 finally { 124 afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); 125 } 126 } 127 }); 128 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); 129 } 130 catch (IllegalStateException ex) { 131 throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, 132 "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; " + 133 "consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", 134 ex); 135 } 136 } 137 } 138 catch (BeansException ex) { 139 cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); 140 throw ex; 141 } 142 } 143 144 // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance. 145 if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) { 146 try { 147 return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); 148 } 149 catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { 150 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 151 logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type [" + 152 ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "]", ex); 153 } 154 throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); 155 } 156 } 157 return (T) bean; 158 }
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory中的createBean
1 /** 2 * Central method of this class: creates a bean instance, 3 * populates the bean instance, applies post-processors, etc. 4 * @see #doCreateBean 5 */ 6 @Override 7 protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { 8 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 9 logger.debug("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); 10 } 11 // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point. 12 resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); 13 14 // Prepare method overrides. 15 try { 16 mbd.prepareMethodOverrides(); 17 } 18 catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { 19 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), 20 beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex); 21 } 22 23 try { 24 // Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance. 25 Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbd); 26 if (bean != null) { 27 return bean; 28 } 29 } 30 catch (Throwable ex) { 31 throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 32 "BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex); 33 } 34 35 Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbd, args); 36 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 37 logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); 38 } 39 return beanInstance; 40 }
/** * Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened * at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks. * <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a * factory method, and autowiring a constructor. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean * @param args arguments to use if creating a prototype using explicit arguments to a * static factory method. This parameter must be {@code null} except in this case. * @return a new instance of the bean * @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created * @see #instantiateBean * @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod * @see #autowireConstructor */ protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) { // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null); Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null); // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition. synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { public Object getObject() throws BeansException { return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean); } }); } // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); if (exposedObject != null) { exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } if (earlySingletonExposure) { Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); if (earlySingletonReference != null) { if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); } } } } // Register bean as disposable. try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; }
在这里我们看到,与依赖注入关键的方法有createBeanInstance和populateBean,
在createBeanInstance中生成了Bean所包含的Java对象


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号