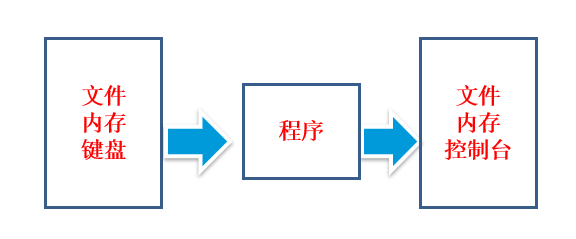
JAVA IO流的概念
java的io流是实现输入和输出的基础,可以方便的实现数据的输入和输出操作。
在java中把不同的输入/输出源(键盘,文件,网络连接等)抽象表述为“流”(stream)。
通过流的形式允许java程序使用相同的方式来访问不同的输入/输出源。stram是从起源(source)到接收的(sink)的有序数据。
File类
File file = new File( String pathname );//这就是创建了一个File对象
注意:地址格式书写有两种方法("c:\\test .txt")或("c:/test .txt")
File常用方法
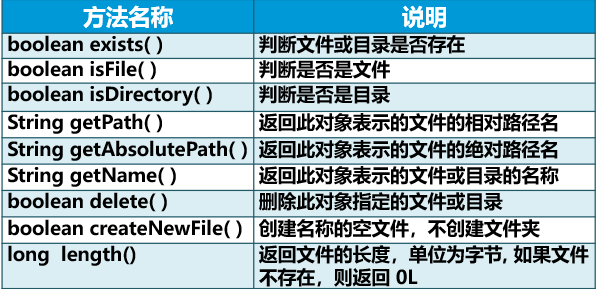
//判断文件是否存在 System.out.println("文件存在吗?"+file.exists()); //判断文件|目录 System.out.println("这个是文件吗?"+file.isFile()); System.out.println("这个是目录吗?"+file.isDirectory()); //获取文件的相对路径和绝对路径 //相对路径:指当前程序的位置到目标文件的路径 //绝对路径:系统的根目录到目标文件的路径 System.out.println("相对路径:"+file.getPath()); System.out.println("绝对路径:"+file.getAbsolutePath()); //获取文件的有效字节数 System.out.println("字节数:"+file.length()); file.delete();//删除文件 在文件不存在时,没有异常抛出 file.createNewFile();//创建新文件 当文件存在时 不会抛出异常也不会创建新文件
JAVA流的分类
一、流向区分

注意:输入输出流是相对于计算机内存来说的
二、处理数据单元

注意:字节流是 8 位通用字节流,字符流是 16 位 Unicode 字符流
IO流具体使用方法
一、字节流
字节输入流(读)
InputStream
read()
read(byte[])
read(byte[],off,len)
close()
FileInputStream
new FileInputStream(File file)
new FileInputStream(String path)
字节输出流(写)
OutputStream
write(int)
write(byte[])
write(byte[],off,len)
close()
flush():强制将缓冲区清空
FileOutputStream
new FileOutputStream(Filefile)
new FileOutputStream(String path)
new FileOutputStream(String path,boolean append):可以指定覆盖或追加文件内容
二、字符流
字符输入流(读)
Reader
read()
read(char [])
read(char[], off, len)
close()
InputStreamReader
new InputStreamReader(InputStream)
new InputStreamReader(InputStream, String)
FileReader
new FileReader(File file)
new FileReader(String path)
中文乱码原因:文件编码格式 和 程序环境的编码格式不一致
解决方案:字符流去读的时候,指定字符流的编码格式
FileReader(无法指定编码格式,会按照文件系统默认编码格式读)
System.out. println(System. getproperty("file.encoding"))://显示当前系统编码格式(必须按照这种书写否则错误)
所以使用 InputsStreamReader
BufferedReader(缓冲流)
readLine()
字符输出流(写)
Writer
write(String)
close()
flush():清空缓存
OutputStreamReader:可以指定字符编码格式
new InputStreamReader(InputStream)
new InputStreamReader(InputStream, String charSetName)
FileWriter
new FileWriter(File file)
new FileWriter(String path)
BufferedWrite:带缓冲区的输出流
PrintWriter什么类型都可以传
println(Object)
三 、二进制文件的读写
DataInputStream
DataOutputStream
方法与上面相同这里就不一一书写了
四 序列化和反序列化
ObjectInputStream 反序列化 readObject() 类型转换
ObjectOutputStream 序列化 writeObject(Object)
常见异常:
NotSerializableException:类没有实现Serializab接口,不可被序列化
transient屏蔽某些敏感字段的序列化
IO流实现读取写入代码
File
//创建文件 public void create(File file){ if(!file.exists()){//判断文件是否存在 try { file.createNewFile();//创建文件 不是文件夹 System.out.println("文件已创建"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
//查看文件 public void showFile(File file){ if(file.exists()){//判断文件是否存在 if(file.isFile()){//判断是否是文件 System.out.println("该文件名为:"+file.getName());//获得文件的名称 System.out.println("绝对路径:"+file.getAbsolutePath());//绝对路径(从根盘开始) System.out.println("相对路径:"+file.getPath());//相对路径 System.out.println("文件大小为:"+file.length());//返回文件的长度,单位为字节, 如果文件不存在,则返回 0L } if(file.isDirectory()){//判断是否是目录 System.out.println("此文件是目录"); } }else { System.out.println("文件不存在"); } }
//删除文件 public void delete(File file){ if(file.exists()){ file.delete();//删除文件 System.out.println("您已删除文件"); } }
public static void main(String[] args) { FileTest fi=new FileTest();//实例化类 File file=new File("d:/test/1.txt");//创建文件 括号里的是路径还可以写成(d:\\大数据\\1.txt) //调用方法 fi.create(file); fi.showFile(file); fi.delete(file); }
FileReader
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { FileReader reader=new FileReader("file/test.txt");//创建FileReader对象 StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();//可变字符串 char chars[]=new char[1024];//每次缓冲1024个字符 int data=0; while((data=reader.read(chars))!=-1){//用read方法把读取到的字节放到数组中去 String str=new String(chars);//把数组中的字节强转成String sb.append(str);//每循环一次添加一次 } System.out.println(sb); //不要忘记关闭流 reader.close(); }
FileWriter
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("file/test.txt"); String str="啊哈哈哈哈"; fw.write(str); fw.close(); }
FileInputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建流对象 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("file/test.txt"); //声明字节类型的数组 byte bytes[]=new byte[1024]; //处理业务逻辑 StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(); int data=bytes.length;//read方法的返回值如果不为-1的情况下 证明有内容可读 while(fis.available()!=0){ //avaiables:代表着输入流中可读字节数 data=fis.read(bytes, 0, data);//避免读取到空字符 String str=new String(bytes); sb.append(str); } System.out.println(sb); //关闭流,释放文件资源 fis.close(); }
FileOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) { FileOutputStream fos=null; //默认会把文件的内容清空并重新写入 try { fos=new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.txt",true); String word="好好学习 天天向上"; fos.write(word.getBytes()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream并用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String oldFile="D:\\test.txt"; String newFile="D:\\ts.txt"; FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(oldFile); //输入流对象 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(newFile);//输出流对象 int data=0; byte bytes[]=new byte[1024]; while((data=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ fos.write(bytes,0,data); } //流关闭的顺序是先开的后关,后开的先关 fos.close(); fis.close(); }
DataInputStream和DataOutputStream(二进制)
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //分别实例化输入流和输出流对象 DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("file/强哥.jpg")); DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\山间的风.jpg")); byte bytes[]=new byte[1024]; int data=0; while((data=dis.read(bytes))!=-1){ dos.write(bytes, 0, data); } dos.close(); dis.close(); }
BufferedReader
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //无需用户手动声明缓冲区数组,在BufferedXXX中自带缓冲区 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("file/wode.txt"))); //按照行的终止符:换行符 String readLine = br.readLine(); System.out.println(readLine); }
PrintWriter(这里不说BufferedWrite介绍一个更实用的)
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("file/强哥.txt")); pw.println("我叫强哥"); pw.println("我叫程程"); pw.flush();//强制刷新缓冲区中的字符或字节 pw.close(); }
//如果想用BufferedWrite跟上面FileWrite用法一样
序列化跟反序列化(ObjectInputStream跟ObjectOutputStream)
public class Student implements Serializable{//继承了Serializable接口,代表可以序列化 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;//序列化的版本号(不是必须的) private transient String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Student(String name, int age) {//重写构造方法 super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Student() { super(); } public String toString() {//重写String方法 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
//这里我们拥有了一个Student类(可序列化的),接下来我们去实现
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Student stu=new Student("小明",18);//创建Student对象
//反序列化 ObjectOutputStream ois=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("file/Test.txt")); ois.writeObject(stu);//可以传入一个对象 ois.close(); //序列化 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("file/强哥.txt")); Student stu=(Student)ois.readObject();//传入一个对象,强转成Student System.out.println(stu); }
以上是我所介绍的关于IO流常用方法,到这里就结束了。。。


