6.2 Examples 示例
Examples 示例
This section contains some Application Service and Domain Service examples to discuss how to decide to place business logic inside these services.
本节包含一些应用服务和领域服务的例子,讨论如何决定将业务逻辑放在这些服务中。
Example: Creating a new Organization in a Domain Service 示例:在一个领域服务中创建一个新的Organization
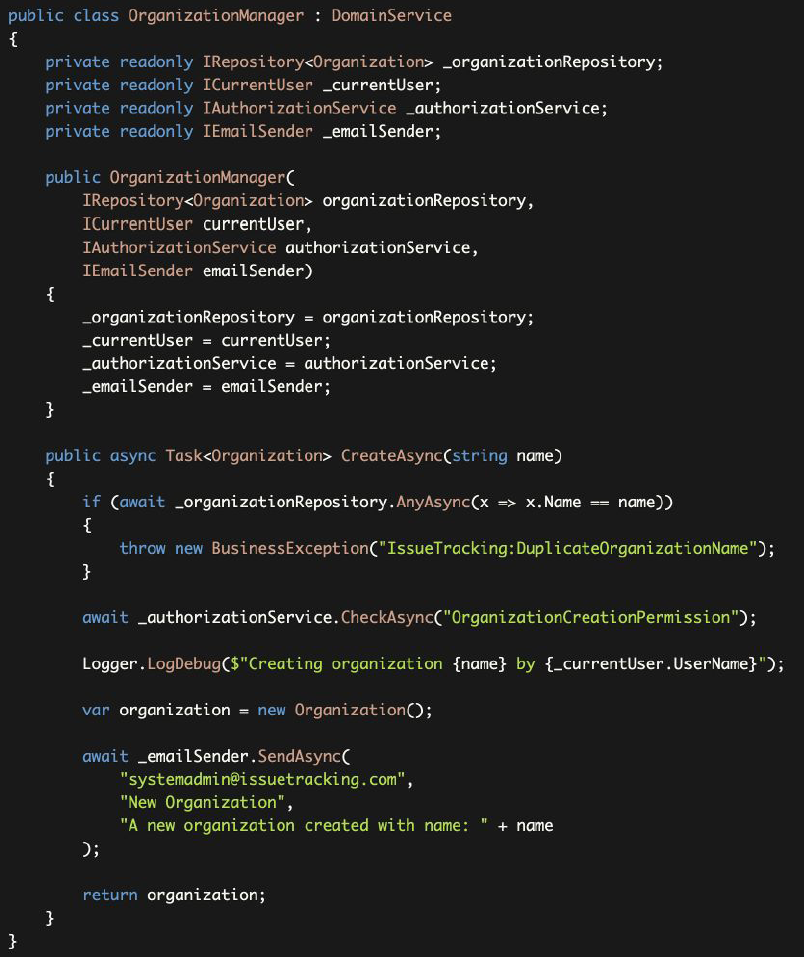
Let's see the CreateAsync method step by step to discuss if the code part should be in the Domain Service, or not;
让我们来看看CreateAsync方法的步骤,讨论一下代码部分是否应该在领域服务中,或者不应该。
- CORRECT: It first checks for duplicate organization name and and throws exception in this case. This is something related to core domain rule and we never allow duplicated names.
- 正确:它首先检查
Organization的名称是否重复,并在这种情况下抛出异常。这与核心领域规则有关,我们从不允许重复的名字。 - WRONG: Domain Services should not perform authorization. Authorization should be done in the Application Layer.
- 错误:领域服务不应该执行授权检查。授权应该在应用层完成。
- WRONG: It logs a message with including the Current User's
UserName. Domain service should not be depend on the Current User. Domain Services should be usable even if there is no user in the system. Current User (Session) should be a Presentation/Application Layer related concept. - 错误:它记录了一条包括当前用户的
UserName。领域服务不应该依赖于当前用户。即便是系统中没有用户,域服务也应该是可用的。当前用户(会话)应该是一个与表现/应用层相关的概念。 - WRONG: It sends an email about this new organization creation. We think this is also a use case specific business logic. You may want to create different type of emails in different use cases or don't need to send emails in some cases.
- 错误:它发送了一封关于这个新的
Organization创建的电子邮件。我们认为这也是一个特定用例的业务逻辑。你可能想在不同的用例中创建不同类型的电子邮件,或者在某些情况下不需要发送电子邮件。
Example: Creating a new Organization in an Application Service 示例:在一个应用服务中创建一个新的Organization
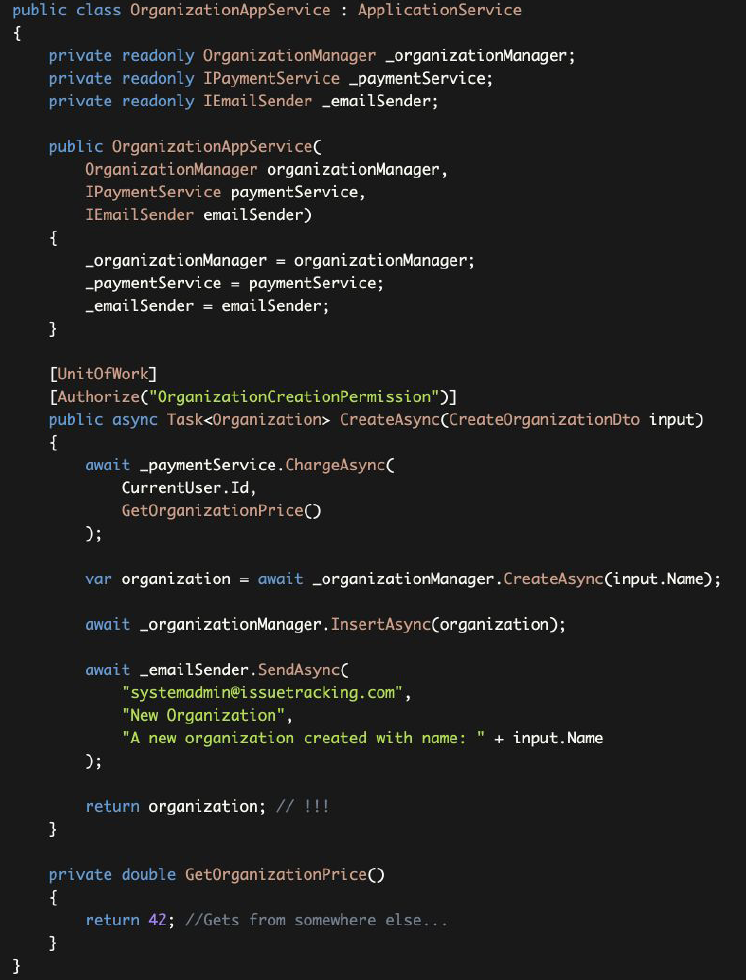
Let's see the CreateAsync method step by step to discuss if the code part should be in the Application Service, or not;
让我们来看看CreateAsync方法的步骤,讨论一下这部分代码是否应该在应用服务中:
- CORRECT: Application Service methods should be unit of work (transactional). ABP's Unit Of Work system makes this automatic (even without need to add
[UnitOfWork]attribute for the Application Services). - 正确:应用服务方法应该是工作单元(事务性的)。ABP的工作单元系统使其自动实现(甚至不需要为应用服务添加
[UnitOfWork]属性)。 - CORRECT: Authorization should be done in the application layer. Here, it is done by using the
[Authorize]attribute. - 正确:授权应该在应用层完成。在这里,它是通过使用
[Authorize]属性完成的。 - CORRECT: Payment (an infrastructure service) is called to charge money for this operation (Creating an Organization is a paid service in our business).
- 正确:支付(一种基础设施服务)被调用,以便为该操作收取费用(在我们的业务中,创建组织是一种付费服务)。
- CORRECT: Application Service method is responsible to save changes to the database.
- 正确:应用服务方法负责将变化保存到数据库。
- CORRECT: We can send email as a notification to the system admin.
- 正确:我们可以发送电子邮件来通知系统管理员。
- WRONG: Do not return entities from the Application Services. Return a DTO instead.
- 错误:不要从应用服务中返回实体。应该返回一个DTO。
Discussion: Why don't we move the payment logic into the domain service? 讨论:我们为什么不把支付逻辑移到领域服务中?
You may wonder why the payment code is not inside the OrganizationManager. It is an important thing and we never want to miss the payment.
你可能想知道为什么支付逻辑代码不在OrganizationManager里面。这是一件很重要的事情,我们绝不希望错过付款。
However, being important is not sufficient to consider a code as a Core Business Logic. We may have other use cases where we don't charge money to create a new Organization. Examples;
然而,重要并不是将一段代码视为核心商业逻辑的依据。我们可能有其他的用例,在这些用例中,我们不收取金钱来创建一个新的Organization。例如:
- An admin user can use a Back Office Application to create a new organization without any payment.
- 管理员用户可以使用后台应用程序来创建一个新的
Organization,而不需要支付任何费用。 - A background-working data import/integration/synchronization system may also need to create organizations without any payment operation.
- 一个后台工作的数据导入/整合/同步系统也可能需要在没有任何支付操作的情况下创建
Organization。
As you see, payment is not a necessary operation to create a valid organization. It is a use-case specific application logic.
正如你所看到的,支付并不是创建一个有效Organization的必要操作。它是一个特定用途的应用逻辑。
Example: CRUD Operations 示例:CRUD操作
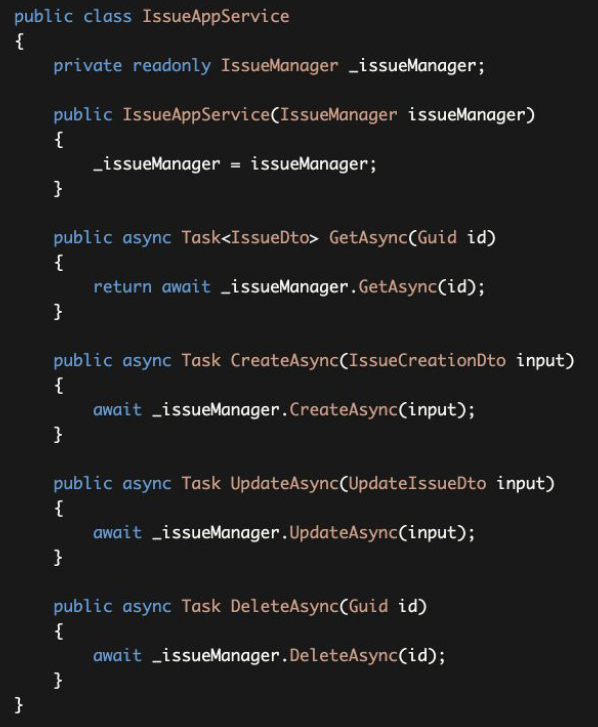
This Application Service does nothing itself and delegates all the work to the Domain Service. It even passes the DTOs to the IssueManager.
这个应用服务本身不做任何事情,而是将所有的工作委托给域服务。它甚至将DTOs传递给IssueManager。
- Do not create Domain Service methods just for simple CRUD operations without any domain logic.
- 不要为没有任何领域逻辑的简单CRUD操作创建领域服务方法。
- Never pass DTOs to or return DTOs from the Domain Services.
- 永远不要把DTO传给领域服务或从领域服务返回DTO。
Application Services can directly work with repositories to query, create, update or delete data unless there are some domain logics should be performed during these operations. In such cases, create Domain Service methods, but only for those really necessary.
应用服务可以直接与存储库一起工作,以查询、创建、更新或删除数据,除非在这些操作中应该执行一些领域逻辑。在这种情况下,创建领域服务方法,但只针对那些真正必要的方法。
Do not create such CRUD domain service methods just by thinking that they may be needed in the future (YAGNI)! Do it when you need and refactor the existing code. Since the Application Layer gracefully abstracts the Domain Layer, the refactoring process doesn't effect the UI Layer and other clients.
不要以为将来可能会需要这些CRUD领域的服务方法,就去创建这些方法(YAGNI)! 当你需要时再去做,并重构现有的代码。因为应用层优雅地抽象了领域层,所以重构过程不会影响UI层和其他客户端。
本文来自博客园,作者:草叶睡蜢,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tjubuntu/p/15687715.html



