6.1 Multiple Application Layers 多种应用层
Multiple Application Layers 多种应用层
DDD helps to deal with complexity when your system is large. Especially, if there are multiple applications are being developed in a single domain, then the Domain Logic vs Application Logic separation becomes much more important.
当你的系统很大时,DDD有助于处理复杂性问题。特别是,如果在一个领域中开发了多个应用程序,那么领域逻辑与应用逻辑的分离就变得更加重要。
Assume that you are building a system that has multiple applications; 假设你正在建立一个有多个应用程序的系统:
- A Public Web Site Application, built with ASP.NET Core MVC, to show your products to users. Such a web site doesn't require authentication to see the products. The users login to the web site, only if they are performing some actions (like adding a product to the basket).
- 一个是用ASP.NET Core MVC构建的公共网站应用程序,向用户展示你的产品。这样的网站不需要认证就可以看到产品。用户只有在执行某些操作(如将产品添加到购物篮)时才会登录到网站。
- A Back Office Application, built with Angular UI (that uses REST APIs). This application used by office workers of the company to manage the system (like editing product descriptions).
- 一个是用Angular UI构建(使用REST APIs)的后台应用程序。这个应用程序由公司的办公人员用来管理系统(如编辑产品描述)。
- A Mobile Application that has much simpler UI compared to the Public Web Site. It may communicate to the server via REST APIs or another technology (like TCP sockets).
- 一个是移动端应用程序,与公共网站相比,它的用户界面要简单得多。它可以通过REST APIs或其他技术(如TCP套接字)与服务器通信。
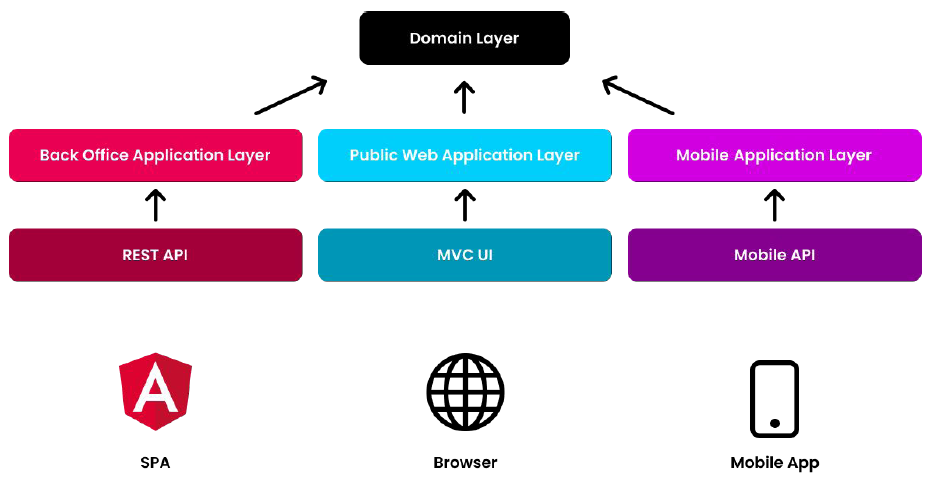
Every application will have different requirements, different use cases (Application Service methods), different DTOs, different validation and authorization rules... etc.
每个应用都会有不同的要求,不同的用例(应用服务方法),不同的DTO,不同的验证和授权规则...等等。
Mixing all these logics into a single application layer makes your services contain too many if conditions with complicated business logic makes your code harder to develop, maintain and test and leads to potential bugs.
将所有这些逻辑混合到一个应用层中,会使你的服务包含太多的如果条件与复杂的业务逻辑,还使你的代码更难开发、维护和测试并导致潜在的错误。
If you've multiple applications with a single domain; 如果你有多个应用程序用一个领域。
- Create separate application layers for each application/client type and implement application specific business logic in these separate layers.
- 为每个应用/客户类型创建独立的应用层,并在这些独立的应用层中实现特定的业务逻辑。
- Use a single domain layer to share the core domain logic.
- 使用单一的领域层来共享核心领域逻辑。
Such a design makes it even more important to distinguish between Domain logic and Application Logic.
这样的设计使得区分领域逻辑和应用逻辑变得更加重要。
To be more clear about the implementation, you can create different projects (.csproj) for each application types. For example;
为了更清楚地了解如何实现,你可以为每种应用类型创建不同的项目(.csproj)。比如说。
IssueTracker.Admin.Application&IssueTracker.Admin.Application.Contractsprojects for the Back Office (admin) Application.IssueTracker.Admin.Application&IssueTracker.Admin.Application.Contracts项目用于后台(管理)应用程序。IssueTracker.Public.Application&IssueTracker.Public.Application.Contractsprojects for the Public Web Application.IssueTracker.Public.Application&IssueTracker.Public.Application.Contracts项目用于公共Web应用。IssueTracker.Mobile.Application&IssueTracker.Mobile.Application.Contractsprojects for the Mobile Application.IssueTracker.Mobile.Application&IssueTracker.Mobile.Application.Contracts项目用于移动应用程序。
本文来自博客园,作者:草叶睡蜢,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tjubuntu/p/15687470.html



