设计原则-GRASP
GRASP原则
General Responsibility Assignment Software Pattern 通用职责分派软件模式
Information Expert
assign the responsibility to the class that has the information needed to fulfill it.
将职责分配给拥有履行该职责所需信息的类。即某项功能需要某些必要的信息,这些信息在哪个类中就让这个类承担这项职责。
示例:
消费者(Customer)想知道他已经订购了哪些商品(Item),这个功能可以有购物车(ShoppingCart)所实现。

Creater 创建者
Assign class B the responsibility to create an instance of class A if one of these is true;
如果以下情况之一为真,则指定类B负责创建类A的实例:
- B “contains” or completely aggregates A
- B "包含 "或完全聚合了A
- B records A
- B记录A
- B closely uses A
- B紧密使用A
- B has the initializing data for A
- B拥有对A的初始化数据
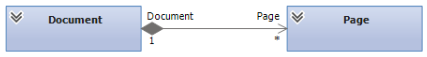
Controller 控制器
Assign the responsibility to an object representing one of these choices:
将责任分配给一个代表以下条件之一的对象:
- Represents the overall “system” – a root object
- 代表整个 "系统"-一个根对象
- Represents a use case scenario within which the system operation occurs.
- 代表一个用例场景,在这个场景中发生系统操作。

- 不要在实现业务逻辑的代码中访问UI控件。
- 不要在UI代码中直接嵌入实现业务逻辑的代码。

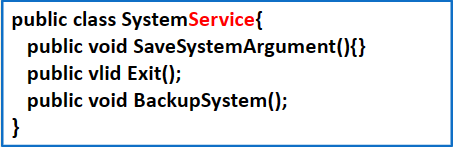
Pure Fabrication 纯功能性类
当某些功能不适合于归属到特定的业务逻辑相关的类时,创建一个新的类,这种类往往叫“XXXService”。
High Cohesion & Low Coupling 高内聚低耦合
-
Coupling(耦合性)用于衡量对象之间依赖性的强弱。
-
Cohesion(内聚性)用于衡量某个类说提供的外部功能及内部代码之间关联的紧密程度。
在设计类时要求高内聚低耦合。
实现方式:组合优先于继承
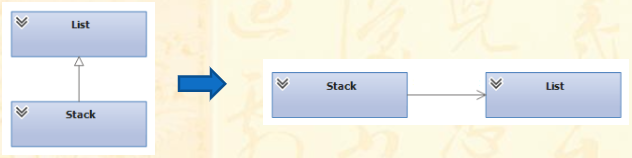
继承在父类与子类之间建立了很强的耦合性,对父类成员的修改有可能会影响到它所有的子类。
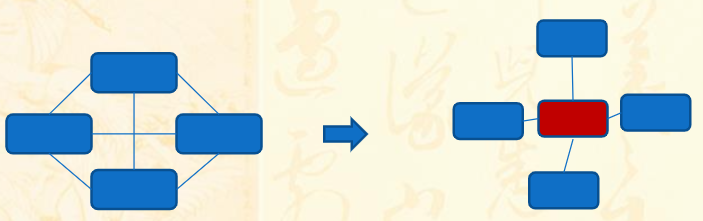
Indirection 中间对象
对象之间相互关联形成了复杂的交互网络,为了减少耦合程度,创建一个中间对象,将多对多关联拆散为一对多关联。
Protected Variations 隔离变化
在设计类时应该尽量让其少受外界的影响。
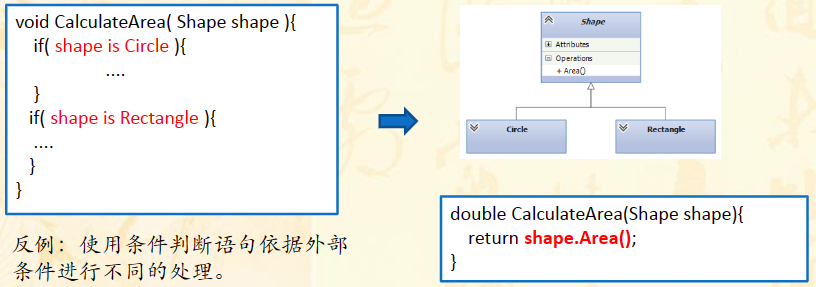
Polymorphism 多态性
利用多态特性把变化封装到子类中。
本文来自博客园,作者:草叶睡蜢,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tjubuntu/p/15481243.html



