scrapy_redis之官网列子domz
一. domz.py
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule class DmozSpider(CrawlSpider): """Follow categories and extract links.""" name = 'dmoz' #gihtub上面给的举例网址挂了,换成这个 allowed_domains = ['dmoztools.net'] start_urls = ['http://dmoztools.net/'] #这个链接提取器秩序要定位到标签,他会自动提取链接 rules = [ Rule(LinkExtractor( restrict_css=('.top-cat', '.sub-cat', '.cat-item') ), callback='parse_directory', follow=True), ] #解析过程 def parse_directory(self, response): for div in response.css('.title-and-desc'): yield { 'name': div.css('.site-title::text').extract_first(), 'description': div.css('.site-descr::text').extract_first().strip(), 'link': div.css('a::attr(href)').extract_first(), }
看一下和scapy的主要区别:

二. settings.py
# Scrapy settings for example project # # For simplicity, this file contains only the most important settings by # default. All the other settings are documented here: # # http://doc.scrapy.org/topics/settings.html # SPIDER_MODULES = ['example.spiders'] NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'example.spiders' #ua不同 USER_AGENT = 'scrapy-redis (+https://github.com/rolando/scrapy-redis)' #比scrappy多了这三行 DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter" #指定去重方法给requests对象去重 SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler" #指定scheduler队列 SCHEDULER_PERSIST = True #队列中的内容是否持久化保存,如果为False会在会在关闭redis的时候清空redis #SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.queue.SpiderPriorityQueue" #SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.queue.SpiderQueue" #SCHEDULER_QUEUE_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.queue.SpiderStack" #pipline多了下面一行,并且打开的 ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'example.pipelines.ExamplePipeline': 300, 'scrapy_redis.pipelines.RedisPipeline': 400, #scrapy_redis实现item保存到redis的pipline } LOG_LEVEL = 'DEBUG' # 这个需要自己添加 #链接数据库,只要pipline开启,并且'scrapy_redis.pipelines.RedisPipeline': 400, #那么数据就会保存到数据库,并且我们并不需要去pipline写保存的函数 REDIS_URL='redis://127.0.0.1:6379' #redis也可以这么写: # REDIS_HOST='127.0.0.1' # REDIS_PORT=6379 # Introduce an artifical delay to make use of parallelism. to speed up the # crawl. DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 1
三.运行爬虫后的的结果
进入项目文件夹,执行:
scrapy crawl domz
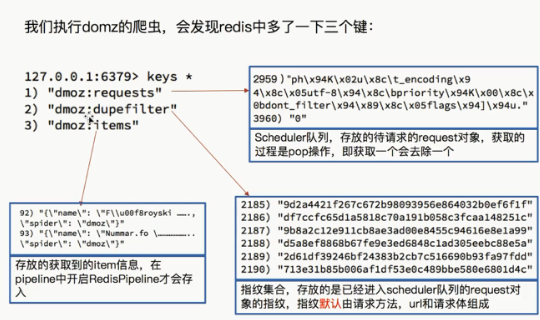
再看一下数据库:
·
注意:
1.这个并没有用到items和pipline所以我们先研究这两个文件
四.注释掉写入reid的语句,在运行一下看下结果
在settings.py 注释这一句
ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'example.pipelines.ExamplePipeline': 300, # 'scrapy_redis.pipelines.RedisPipeline': 400, }
运行爬虫,发现
爬虫正常运行,但是items的数量并没有增多,说明RedisPipeline只是实现了item出具存储到redis的过程,
我们可以新建一个pipeline(或者修改example的的examplepipinne),让数据存储到任意地方
分类:
爬虫




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器