201271050130-滕江南-《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十四周学习总结
201271050130-滕江南-《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十四周学习总结
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
<任课教师博客主页链接> https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
<作业链接地址> https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11953993.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
(1)掌握GUI布局管理器用法; (2)掌握Java Swing文本输入组件用途及常用API; (3)掌握Java Swing选择输入组件用途及常用API;
|
第一部分:总结第十二章本周理论知识(25分)
12.1.Swing和MVC设计模式
a 设计模式初识
b 模型—视图—控制器模式
c Swing组件的模型—视图—控制器分析
12.2布局管理器
a 布局管理器是一组类。
b 实现java.awt.LayoutManager接口
c 决定容器中组件的位置和大小
d Java.awt包中定义了5种布局管理类,每一种布 局管理类对应一种布局策略。
e 每个容器都有与之相关的默认布局管理器。
f 当一个容器选定一种布局策略时,它应该创建该 策略对应的布局管理器对象,并将此对象设置为 自己的布局管理器。
g 5种布局管理器
(1)FlowLayout:流布局(Applet和Panel的默认 布局管理器)
(2)BorderLayout:边框布局(Window、Frame和 Dialog的默认布局管理器)
(3)GridLayout:网格布局
(4)GridBagLayout:网格组布局
(5)CardLayout:卡片布局
12.3文本输入
a 域
b 文本区
c 标签与标签组件
d 密码域
e 滚动窗格
12.4选择组件
a 复选框
b 单选按钮
c 边框
d 组合框
e 滑动条
12.5菜单
a 菜单创建
b 菜单项中的图标
c 复选框和单选按钮菜单项
d 弹出菜单
e 快捷键和加速器
f 启用和禁用菜单项
g工具栏
h 工具提示
12.5对话框
a 选项对话框
b 创建对话框
c 数据选择
d 文件对话框 e 颜色选择器
第二部分:实验部分
实验1:测试程序1(5分)
1.在elipse IDE中运行教材479页程序12-1,结合运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握各种布局管理器的用法;
3.理解GUI界面中事件处理技术的用途。
4.在布局管理应用代码处添加注释;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Calculator
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
CalculatorFrame frame = new CalculatorFrame();
frame.setTitle("Calculator");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package calculator;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* 一个带有计算器面板的框架。
*/
public class CalculatorFrame extends JFrame
{
public CalculatorFrame()
{
add(new CalculatorPanel());
pack();
}
}
package calculator;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* 具有计算器按钮和结果显示的面板。
*/
public class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel
{
private JButton display;
private JPanel panel;
private double result;
private String lastCommand;
private boolean start;
public CalculatorPanel()
{
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
result = 0;
lastCommand = "=";
start = true;
// 添加显示
display = new JButton("0");
display.setEnabled(false);
add(display, BorderLayout.NORTH);
ActionListener insert = new InsertAction();
ActionListener command = new CommandAction();
// 在4×4网格中添加按钮
panel = new JPanel();
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 4));
addButton("0", insert);
addButton("1", insert);
addButton("2", insert);
addButton("3", command);
addButton("4", insert);
addButton("5", insert);
addButton("6", insert);
addButton("7", command);
addButton("8", insert);
addButton("9", insert);
addButton("3", insert);
addButton("/", command);
addButton("*", insert);
addButton(".", insert);
addButton("=", command);
addButton("+", command);
add(panel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
// display = new JButton("验证");
// display.setEnabled(true);
// add(display, BorderLayout.CENTER);
//
// display = new JButton("验证1");
// display.setEnabled(true);
// add(display, BorderLayout.WEST);
//
// display = new JButton("验证2");
// display.setEnabled(true);
// add(display, BorderLayout.EAST);
}
/**
* 向中心面板添加一个按钮。
* @param 标签的按钮标签
* @param 监听器按钮侦听器
*/
private void addButton(String label, ActionListener listener)
{
JButton button = new JButton(label);
button.addActionListener(listener);
panel.add(button);
}
/**
* 此操作将按钮操作字符串插入到显示文本的末尾
*/
private class InsertAction implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
String input = event.getActionCommand();
if (start)
{
display.setText("");
start = false;
}
display.setText(display.getText() + input);
}
}
/**
* 此操作执行按钮操作字符串所表示的命令。
*/
private class CommandAction implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
String command = event.getActionCommand();
if (start)
{
if (command.equals("-"))
{
display.setText(command);
start = false;
}
else lastCommand = command;
}
else
{
calculate(Double.parseDouble(display.getText()));
lastCommand = command;
start = true;
}
}
}
/**
* 执行悬而未决的计算。
* @param x值与先前结果一起累积。
*/
public void calculate(double x)
{
if (lastCommand.equals("+")) result += x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("-")) result -= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("*")) result *= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("/")) result /= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("=")) result = x;
display.setText("" + result);
}
}

实验1:测试程序2(5分)
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材486页程序12-2,结合运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握各种文本组件的用法;
3.记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
package text;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.41 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class TextComponentTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new TextComponentFrame();
frame.setTitle("TextComponentTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package text;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JPasswordField;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTextArea;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.SwingConstants;
/**
* 具有文本文本组件的框架.
*/
public class TextComponentFrame extends JFrame
{
public static final int TEXTAREA_ROWS = 8;
public static final int TEXTAREA_COLUMNS = 20;
public TextComponentFrame()
{
JTextField textField = new JTextField();
JPasswordField passwordField = new JPasswordField();
JPanel northPanel = new JPanel();
northPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2));
northPanel.add(new JLabel("User name: ", SwingConstants.RIGHT));
northPanel.add(textField);
northPanel.add(new JLabel("Password: ", SwingConstants.RIGHT));
northPanel.add(passwordField);
add(northPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea(TEXTAREA_ROWS, TEXTAREA_COLUMNS);
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea);
add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
// 添加按钮将文本追加到文本区域
JPanel southPanel = new JPanel();
JButton insertButton = new JButton("Insert");
southPanel.add(insertButton);
insertButton.addActionListener(event ->
textArea.append("User name: " + textField.getText() + " Password: "
+ new String(passwordField.getPassword()) + "\n"));
add(southPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
}
}

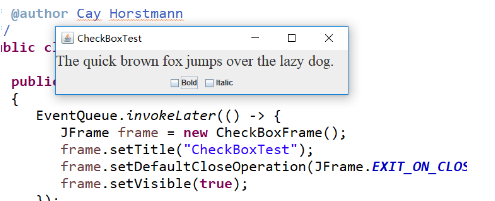
实验1:测试程序3(5分)
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材489页程序12-3,结合运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握复选框组件的用法;
3.记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
package checkBox;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class CheckBoxTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new CheckBoxFrame();
frame.setTitle("CheckBoxTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package checkBox;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* 带有样本文本标签的框和用于选择字体的复选框
* attributes.
*/
public class CheckBoxFrame extends JFrame
{
private JLabel label;
private JCheckBox bold;
private JCheckBox italic;
private static final int FONTSIZE = 24;
public CheckBoxFrame()
{
// 添加示例文本标签
label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.");
label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, FONTSIZE));
add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER);
// 此侦听器设置字体属性
// 到复选框状态的标签
ActionListener listener = event -> {
int mode = 0;
if (bold.isSelected()) mode += Font.BOLD;
if (italic.isSelected()) mode += Font.ITALIC;
label.setFont(new Font("Serif", mode, FONTSIZE));
};
// 添加复选框
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
bold = new JCheckBox("Bold");
bold.addActionListener(listener);
bold.setSelected(true);
buttonPanel.add(bold);
italic = new JCheckBox("Italic");
italic.addActionListener(listener);
buttonPanel.add(italic);
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
}
}
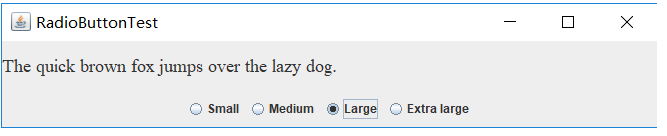
实验1:测试程序4(5分)
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材491页程序12-4,运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握单选按钮组件的用法;
3.记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
package radioButton;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class RadioButtonTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new RadioButtonFrame();
frame.setTitle("RadioButtonTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package radioButton;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* 带有样本文本标签和单选按钮以选择字体大小的框架。
*/
public class RadioButtonFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private ButtonGroup group;
private JLabel label;
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 36;
public RadioButtonFrame()
{
// 添加示例文本标签
label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.");
label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE));
add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER);
// 添加单选按钮
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
group = new ButtonGroup();
addRadioButton("Small", 8);
addRadioButton("Medium", 12);
addRadioButton("Large", 18);
addRadioButton("Extra large", 36);
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
}
/**
* 添加一个设置示例文本字体大小的单选按钮。
* @param 命名按钮上出现的字符串
* @param 设置此按钮设置的字体大小
*/
public void addRadioButton(String name, int size)
{
boolean selected = size == DEFAULT_SIZE;
JRadioButton button = new JRadioButton(name, selected);
group.add(button);
buttonPanel.add(button);
// 此侦听器设置标签字体大小。
ActionListener listener = event -> label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, size));
button.addActionListener(listener);
}
}
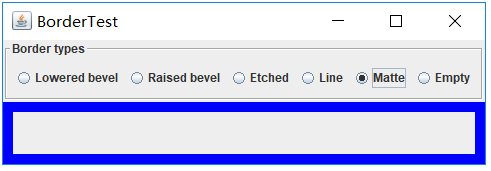
实验1:测试程序5(5分)
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材494页程序12-5,结合运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握边框的用法;
3。记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
package border;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-13
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class BorderTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new BorderFrame();
frame.setTitle("BorderTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package border;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.*;
/**
* 用单选按钮选择边框样式的框架
*/
public class BorderFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel demoPanel;
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private ButtonGroup group;
public BorderFrame()
{
demoPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
group = new ButtonGroup();
addRadioButton("Lowered bevel", BorderFactory.createLoweredBevelBorder());
addRadioButton("Raised bevel", BorderFactory.createRaisedBevelBorder());
addRadioButton("Etched", BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());
addRadioButton("Line", BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.BLUE));
addRadioButton("Matte", BorderFactory.createMatteBorder(10, 10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE));
addRadioButton("Empty", BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder());
Border etched = BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder();
Border titled = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched, "Border types");
buttonPanel.setBorder(titled);
setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));
add(buttonPanel);
add(demoPanel);
pack();
}
public void addRadioButton(String buttonName, Border b)
{
JRadioButton button = new JRadioButton(buttonName);
button.addActionListener(event -> demoPanel.setBorder(b));
group.add(button);
buttonPanel.add(button);
}
}
实验1:测试程序6(5分)
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材498页程序12-6,结合运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握组合框组件的用法;
3.记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
package comboBox;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.35 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ComboBoxTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ComboBoxFrame();
frame.setTitle("ComboBoxTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package comboBox;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Font;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
/**
* 具有样本文本标签和选择字体面的组合框的框架。
*/
public class ComboBoxFrame extends JFrame
{
private JComboBox<String> faceCombo;
private JLabel label;
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 24;
public ComboBoxFrame()
{
// 添加示例文本标签
label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.");
label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE));
add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER);
// 制作组合框并添加面部名称
faceCombo = new JComboBox<>();
faceCombo.addItem("Serif");
faceCombo.addItem("SansSerif");
faceCombo.addItem("Monospaced");
faceCombo.addItem("Dialog");
faceCombo.addItem("DialogInput");
// 组合框侦听器将标签字体更改为选定的面部名称。
faceCombo.addActionListener(event ->
label.setFont(
new Font(faceCombo.getItemAt(faceCombo.getSelectedIndex()),
Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE)));
// 将组合框添加到框架的南部边界的面板上
JPanel comboPanel = new JPanel();
comboPanel.add(faceCombo);
add(comboPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
}
}

实验2:结对编程练习包含以下4部分:(30分)
1) 程序设计思路简述;
2) 符合编程规范的程序代码;
3) 程序运行功能界面截图;
4) 结对过程描述,提供两人在讨论、细化和编程时的结对照片(非摆拍)。
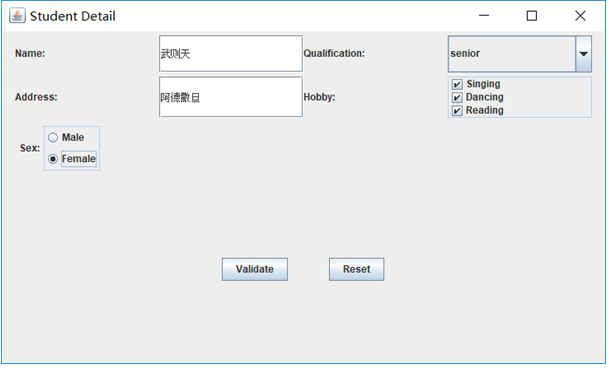
1.设计一个用户信息采集程序,要求如下:
(1) 用户信息输入界面如下图所示:
(2) 用户点击提交按钮时,用户输入信息显示在录入信息显示区;
(3) 用户点击重置按钮后,清空用户已输入信息;
(4) 点击窗口关闭,程序退出。
package 程序一;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class First_exercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
DemoJFrame JFrame = new DemoJFrame();
});
}
}
First_exercise
package 程序一;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.awt.LayoutManager;
import java.awt.Panel;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import javax.swing.BorderFactory;
import javax.swing.ButtonGroup;
import javax.swing.ButtonModel;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JCheckBox;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JRadioButton;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class DemoJFrame extends JFrame {
private JPanel jPanel1;
private JPanel jPanel2;
private JPanel jPanel3;
private JPanel jPanel4;
private JTextField fieldname;
private JComboBox comboBox;
private JTextField fieldadress;
private ButtonGroup Button;
private JRadioButton Male;
private JRadioButton Female;
private JCheckBox sing;
private JCheckBox dance;
private JCheckBox draw;
public DemoJFrame() {
this.setSize(750, 450);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setTitle("Student Detail");
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Windows.center(this);
jPanel1 = new JPanel();
setJPanel1(jPanel1);
jPanel2 = new JPanel();
setJPanel2(jPanel2);
jPanel3 = new JPanel();
setJPanel3(jPanel3);
jPanel4 = new JPanel();
setJPanel4(jPanel4);
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout();
this.setLayout(flowLayout);
this.add(jPanel1);
this.add(jPanel2);
this.add(jPanel3);
this.add(jPanel4);
}
private void setJPanel1(JPanel jPanel) {
jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 45));
jPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4));
JLabel name = new JLabel("Name:");
name.setSize(100, 50);
fieldname = new JTextField("");
fieldname.setSize(80, 20);
JLabel study = new JLabel("Qualification:");
comboBox = new JComboBox();
comboBox.addItem("Graduate");
comboBox.addItem("senior");
comboBox.addItem("Undergraduate");
jPanel.add(name);
jPanel.add(fieldname);
jPanel.add(study);
jPanel.add(comboBox);
}
private void setJPanel2(JPanel jPanel) {
jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 50));
jPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4));
JLabel name = new JLabel("Address:");
fieldadress = new JTextField();
fieldadress.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(150, 50));
JLabel study = new JLabel("Hobby:");
JPanel selectBox = new JPanel();
selectBox.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(""));
selectBox.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1));
sing = new JCheckBox("Singing");
dance = new JCheckBox("Dancing");
draw = new JCheckBox("Reading");
selectBox.add(sing);
selectBox.add(dance);
selectBox.add(draw);
jPanel.add(name);
jPanel.add(fieldadress);
jPanel.add(study);
jPanel.add(selectBox);
}
private void setJPanel3(JPanel jPanel) {
jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150));
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout);
JLabel sex = new JLabel("Sex:");
JPanel selectBox = new JPanel();
selectBox.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(""));
selectBox.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));
Button = new ButtonGroup();
Male = new JRadioButton("Male");
Female = new JRadioButton("Female");
Button.add(Male);
Button.add(Female);
selectBox.add(Male);
selectBox.add(Female);
jPanel.add(sex);
jPanel.add(selectBox);
}
private void setJPanel4(JPanel jPanel) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
jPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150));
FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER, 50, 10);
jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout);
jPanel.setLayout(flowLayout);
JButton sublite = new JButton("Validate");
JButton reset = new JButton("Reset");
sublite.addActionListener((e) -> valiData());
reset.addActionListener((e) -> Reset());
jPanel.add(sublite);
jPanel.add(reset);
}
private void valiData() {
String name = fieldname.getText().toString().trim();
String xueli = comboBox.getSelectedItem().toString().trim();
String address = fieldadress.getText().toString().trim();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(xueli);
String hobbystring="";
if (sing.isSelected()) {
hobbystring+="Singing ";
}
if (dance.isSelected()) {
hobbystring+="Dancing ";
}
if (draw.isSelected()) {
hobbystring+="Reading ";
}
System.out.println(address);
if (Male.isSelected()) {
System.out.println("Male");
}
if (Female.isSelected()) {
System.out.println("Female");
}
System.out.println(hobbystring);
}
private void Reset() {
fieldadress.setText(null);
fieldname.setText(null);
comboBox.setSelectedIndex(0);
sing.setSelected(false);
dance.setSelected(false);
draw.setSelected(false);
Button.clearSelection();
}
}
DemoJFrame
package 程序一;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.Window;
public class Windows {
public static void center(Window win){
Toolkit tkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension sSize = tkit.getScreenSize();
Dimension wSize = win.getSize();
if(wSize.height > sSize.height){
wSize.height = sSize.height;
}
if(wSize.width > sSize.width){
wSize.width = sSize.width;
}
win.setLocation((sSize.width - wSize.width)/ 2, (sSize.height - wSize.height)/ 2);
}
}
Windows
实验总结:(10分)
通过本周的学习,掌握了线程概念和线程创建;理解了基础线程的优先级属性及调度方法;学会了Java GUI 编程技术的基础及Swing图形界面组件相关知识。现在掌握的知识内容比之前多,所以容易混淆记不住,在编写程序的时候就经常丢三落四导致浪费了很多时间。在程序编写的条理性方面还有待加强,代码需要更多的自我消化,不然也不是自己的东西。


