Nordic Collegiate Programming Contest 2015 B. Bell Ringing
Method ringing is used to ring bells in churches, particularly in England. Suppose there are 6 bells that have 6 different pitches. We assign the number 1 to the bell highest in pitch, 2 to the second highest, and so on. When the 6 bells are rung in some order—each of them exactly once—it is called a row. For example, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 6, 3, 2, 4, 1, 5 are two different rows.
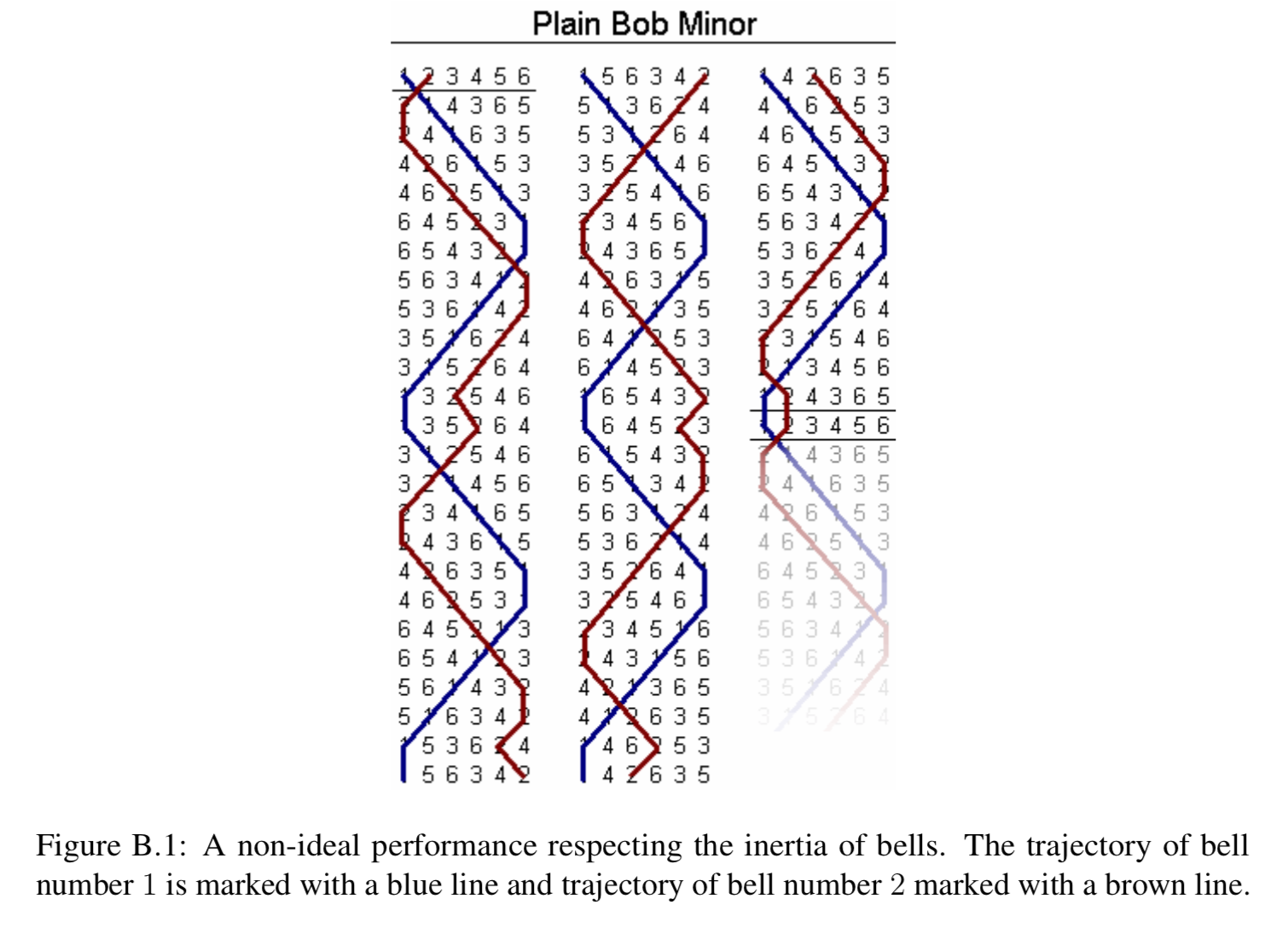
An ideal performance contains all possible rows, each played exactly once. Unfortunately, the laws of physics place a limitation on any two consecutive rows; when a bell is rung, it has considerable inertia and the ringer has only a limited ability to accelerate or retard its cycle. Therefore, the position of each bell can change by at most one between two consecutive rows.
In Figure ??, you can see the pattern of a non-ideal performance, where bells only change position by at most one.
Given nn, the number of bells, output an ideal performance. All possible rows must be present exactly once, and the first row should be 1, 2, \cdots , n1,2,⋯,n.
Input Format
The first and only line of input contains an integer nn such that 1 \le n \le 81≤n≤8.
Output Format
Output an ideal sequence of rows, each on a separate line. The first line should contain the row 1, 2, \cdots, n1,2,⋯,n and each two consecutive lines should be at most 11 step away from each other. Each row should occur exactly once in the output.(No extra space at the end of each line)
样例输入
2
样例输出
1 2 2 1
题目来源
Nordic Collegiate Programming Contest 2015
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <set> 8 #include <map> 9 #include <string> 10 #include <cmath> 11 #include <cstdlib> 12 #include <ctime> 13 using namespace std; 14 typedef long long ll; 15 int n; 16 const int N=5e5+3; 17 int a[N][10]; 18 int x,y; 19 void solve() 20 { 21 a[0][0]=1; 22 int s=0,end=0; 23 for(int i=2;i<=8;i++) 24 { 25 int len=end; 26 for(int j=s;j<=end;j++) 27 { 28 if((j-s)%2)//从左往右 29 { 30 for(int k=0;k<i;k++) 31 { 32 len+=1; 33 for(int l=0;l<k;l++)//前面的直接复制下来 34 { 35 a[len][l]=a[j][l]; 36 } 37 a[len][k]=i;//插到a[len][k] 38 for(int m=k+1;m<i;m++)//后面的与J行错一复制下来 39 { 40 a[len][m]=a[j][m-1]; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 else//从右到左 45 { 46 for(int k=i-1;k>=0;k--) 47 { 48 len+=1; 49 for(int l=0;l<k;l++) 50 { 51 a[len][l]=a[j][l]; 52 } 53 a[len][k]=i; 54 for(int m=k+1;m<i;m++) 55 { 56 a[len][m]=a[j][m-1]; 57 } 58 } 59 60 } 61 } 62 s=end+1;//更新s,end. 63 end=len; 64 } 65 } 66 int jie(int n) 67 { 68 int ans=1; 69 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 70 ans*=i; 71 } 72 return ans; 73 } 74 int main() 75 { 76 solve(); 77 scanf("%d",&n); 78 for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++) 79 { 80 x+=jie(i); 81 } 82 y=x+jie(n)-1; 83 for(int i=x;i<=y;i++) 84 { 85 for(int j=0;j<n;j++) 86 { 87 printf("%d%c",a[i][j],j==n-1?'\n':' '); 88 } 89 } 90 return 0; 91 }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号