JAVA 排序
简述稳定排序和非稳定排序的区别
稳定排序:排序前后两个相等的数相对位置不变,则算法稳定 非稳定排序:排序前后两个相等的数相对位置发生了变化,则算法不稳定
稳定:插入 冒泡 归并
堆排序
什么是最大堆和最小堆?
二叉堆是一种特殊的堆,二叉堆是完全二叉树。二叉堆有两种:最大堆和最小堆。最大堆:父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值;最小堆:父结点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值[百度百科]。在最大堆中任意子堆都满足父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值这一性质。如下图即为一个最大堆。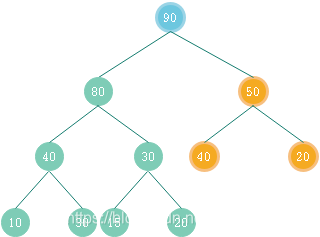
堆排序
import java.util.*; public class Main { // static int[] a = { 9, 5, 3, 2, 2, 2, 6, 1, 0 }; static int[] a = { 3, 2, 6, 1, 0 }; void downAdjust(int[] arr, int parentIndex, int length) { // temp保存父节点的值,用于最后赋值 int temp = arr[parentIndex]; int childrenIndex = 2 * parentIndex + 1; while (childrenIndex < length) { // 如果有右孩子,且右孩子大于左孩子的值,则定位到右孩子 // 这里其实是比较左、右子树的大小,选择更大的 if (childrenIndex + 1 < length && arr[childrenIndex + 1] > arr[childrenIndex]) { childrenIndex++; } // 如果父节点大于任何一个孩子得值,则直接跳出 if (temp >= arr[childrenIndex]) { break; } // 当左、右子树比父节点更大,进行交换 arr[parentIndex] = arr[childrenIndex]; parentIndex = childrenIndex; childrenIndex = 2 * childrenIndex + 1; } arr[parentIndex] = temp; } void swap(int a, int b) { int tmp = a; a = b; b = tmp; } /** * 堆排序(升序) * * @param {array} arr 待调整的堆 */ int[] heapSort(int[] arr) { // 把无序数组构建成最大堆, 这里-2,是因为从索引0开始、另外就是叶子节点【最后一层是不需要堆化的】 for (int i = (arr.length - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {// (arr.length-2)/2:最后一个父节点 downAdjust(arr, i, arr.length); } // 循环删除堆顶元素,并且移到集合尾部,调整堆产生新的堆顶 for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) { // 交换最后一个元素与第一个元素 // swap(arr[0], arr[i]); int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[0]; arr[0] = temp; // swap(arr[0],arr[i])错误,无法交换 // 下沉调整最大堆 // downAdjust(arr, 0, i - 1);// 1 0 2 3 6 i-1的话 i==2时,无法重新更细为最大堆 downAdjust(arr, 0, i);// 0 1 2 3 6 } return arr; } public static void main(String agrs[]) { Main ma = new Main(); ma.heapSort(a); for (int x : a) { System.out.print(x + " "); } } }
输入整数数组 arr ,找出其中最小的 k 个数。例如,输入4、5、1、6、2、7、3、8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1、2、3、4。
class Solution { public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) { if(arr.length==0 ||k==0){ return new int[0]; } PriorityQueue<Integer>que =new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new acomparator());//PriorityQueue默认最小堆,这里改为最大堆 for(int a:arr){ if(que.size()<k) que.offer(a); else if(a<que.peek()){ que.poll(); que.offer(a); } } int n =que.size(); int []b =new int[n]; // for(int i=0;i<que.size();i++) {//这里不能用que.size(),因为que.size()在变化 // b[i] =que.poll(); // } for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { b[i] =que.poll(); } return b; } } class acomparator implements Comparator<Integer>{ public int compare(Integer a,Integer b){ return b-a; } }
最大的K个数,需要修改如下:
归并排序
把两个有序的序列归并成一个序列
当小组只有一个数据时,可以认为这个小组组内已经达到了有序,然后再合并相邻的二个小组就可以了
import java.util.*; public class Main { int[] a = new int[5]; int[] b = new int[5]; int ans; void merge(int[] a, int l, int r) { if (l == r) return; int m = (l + r) >> 1; merge(a, l, m); merge(a, m + 1, r); int i = l, j = m + 1, k = l; while (i <= m && j <= r) { if (a[i] <= a[j])//= b[k++] = a[i++]; else { b[k++] = a[j++]; ans += (m - i + 1);//逆序对数目 左边比我大 } } while (i <= m) b[k++] = a[i++]; while (j <= r) b[k++] = a[j++]; for (int p = l; p <= r; p++) a[p] = b[p]; } public static void main(String args[]) { Main ma = new Main(); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { ma.a[i] = input.nextInt(); } ma.merge(ma.a, 0, 4); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.print(ma.a[i] + " "); } System.out.println(" "); System.out.println(ma.ans); } }
小数和,一个数组,每个数字左边所有小于该数字的和 为这个是的小数和。每一个数的小数和加起来为这个数组的小数和
while (i <= m && j <= r) { if (a[i] < a[j]) {//没有= ret += (a[i] * (r - j + 1));//a[i]出现r-j+1次 一定在b[k++] = a[i++]之前执行 System.out.println(a[i] + " " + r + " " + j); b[k++] = a[i++]; } else { b[k++] = a[j++]; } }
链表归并
归并1 package lianbaio; import lianbaio.归并排序链表1.ListNode.Node; public class 归并排序链表1 { // 数组归并排序 // static void guisort(int a[], int l, int r) { // if (l == r)// 不然会一直递归 // return; // int b[] = new int[a.length]; // int m = (l + r) >> 1; // guisort(a, l, m); // guisort(a, m + 1, r); // int i = l, j = m + 1, k = l; // while (i <= m && j <= r) { // if (a[i] <= a[j]) { // b[k++] = a[i++]; // } else { // b[k++] = a[j++]; // } // } // while (i <= m) // b[k++] = a[i++]; // while (j <= r) // b[k++] = a[j++]; // for (int p = l; p <= r; p++) // a[p] = b[p]; // } // public static void main(String[] args) { // int a[] = { -2, 1, 0, 8, -3, 52 }; // guisort(a, 0, a.length - 1); // for (int x : a) { // System.out.println(x); // } // } static class ListNode { static class Node { int val; Node next; Node() { } Node(int val) { this.val = val; } } Node head, first; public void init() { head = new Node(); head.next = first; } } static void touinsert(ListNode list, int val) { Node newnode = new Node(val); if (list.first != null) { newnode.next = list.first; } list.first = newnode; list.head.next = list.first; } static void printlist(ListNode list) { Node first = list.first; while (first != null) { System.out.print(first.val + " "); first = first.next; } System.out.println(); } // 时间 O(nlogn) 空间O(logn) static public Node list_guisort1(Node first) { if (first == null || first.next == null) return first; Node m = getmid(first); Node r = m.next; m.next = null; return merge(list_guisort1(first), list_guisort1(r)); } static public Node getmid(Node first) { if (first == null || first.next == null) return first; Node sl = first, fa = first; while (fa.next != null && fa.next.next != null) { sl = sl.next; fa = fa.next.next; } return sl; } static public Node merge(Node first1, Node first2) { Node p1 = first1, p2 = first2; Node dumpy = new Node(-1); Node tmp = dumpy; while (p1 != null && p2 != null) { if (p1.val <= p2.val) { tmp.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; } else { tmp.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } tmp = tmp.next; } if (p1 != null) tmp.next = p1; if (p2 != null) tmp.next = p2; return dumpy.next; } public static void main(String[] args) { ListNode l1 = new ListNode(); l1.init(); int a[] = { 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 }; for (int x : a) { touinsert(l1, x); } printlist(l1); l1.first = list_guisort1(l1.first); printlist(l1); } }
归并2 package lianbaio; import lianbaio.归并排序链表2.ListNode.Node; public class 归并排序链表2 { static class ListNode { static class Node { int val; Node next; Node() { } Node(int val) { this.val = val; } } Node head, first; public void init() { head = new Node(); head.next = first; } } static void touinsert(ListNode list, int val) { Node newnode = new Node(val); if (list.first != null) { newnode.next = list.first; } list.first = newnode; list.head.next = list.first; } static void printlist(ListNode list) { Node first = list.first; while (first != null) { System.out.print(first.val + " "); first = first.next; } System.out.println(); } static public int len(Node first) { int l = 0; Node p = first; while (p != null) { l++; p = p.next; } return l; } // 时间 O(nlogn) 空间O(1) static public Node list_guisort2(Node first) { int l = len(first); Node dumpy = new Node(-1); dumpy.next = first; for (int i = 1; i < l; i <<= 1) { Node pre = dumpy, cur = dumpy.next; while (cur != null) { Node h1 = cur; for (int j = 1; j < i && cur.next != null; j++) {// cur.next!=null 例如l=7 i=8 cur = cur.next; } Node h2 = cur.next; cur.next = null;// h1 链表独立 cur = h2;// 始终是cur在移动 for (int j = 1; j < i && cur != null && cur.next != null; j++) {// cur!=null 例如i=2 但只还剩下1个 cur = cur.next; } Node next = null; if (cur != null) { next = cur.next; cur.next = null; } Node mer = merge(h1, h2); pre.next = mer; while (pre.next != null) { pre = pre.next;// 指向当前的最后一个节点 } cur = next;// cur继续 } } return dumpy.next; } static public Node merge(Node first1, Node first2) { Node p1 = first1, p2 = first2; Node dumpy = new Node(-1); Node tmp = dumpy; while (p1 != null && p2 != null) { if (p1.val <= p2.val) { tmp.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; } else { tmp.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } tmp = tmp.next; } if (p1 != null) tmp.next = p1; if (p2 != null) tmp.next = p2; return dumpy.next; } public static void main(String[] args) { ListNode l1 = new ListNode(); l1.init(); int a[] = { 0, -2, 34, -12, 91, -789 }; for (int x : a) { touinsert(l1, x); } printlist(l1); l1.first = list_guisort2(l1.first);//
printlist(l1);
}
}
快速排序
最坏的情况:每次找的pivot将数组分成两部分,其中有一部分是空,这样递归树就变成了一棵倾斜的树。树的深度为n-1,这样时间复杂度就变成了O(N^2). 一般当数据有序或者局部有序的时候会出现这种坏的情况,比如数组正序或者逆序
import java.util.*; public class Main { private static void sort(int[] arr, int l, int r) { int i = l; int j = r; if (l < r) { while (l < r) { while (l < r && arr[r] >= arr[l]) { r--; } int tmp = arr[l]; arr[l] = arr[r]; arr[r] = tmp; while (l < r && arr[l] <= arr[r]) { l++; } tmp = arr[l]; arr[l] = arr[r]; arr[r] = tmp; } sort(arr, i, l - 1);// 递归左边,此时l=5 sort(arr, l + 1, j);// 递归右边,此时l=5 } } public static void main(String agrs[]) { int[] arr = { -5, 1, 1, 8, 7, 300, 7, 0, 0, 6 }; sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); for (int i : arr) { System.out.print(i + " "); } } }
链表快排 https://www.cnblogs.com/morethink/p/8452914.html
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { quicksort(head,null); return head; } public void quicksort(ListNode head,ListNode end){ if(head!=end){//注意边界 ListNode node =partion(head,end); quicksort(head,node); quicksort(node.next,end); } } public ListNode partion(ListNode head,ListNode end){//p1前面的都小于key,p1,p2之间的都大于key,p2=end时交换p1 head,p1就是partion ListNode p1 =head,p2 =head.next; while(p2!=end){ if(p2.val<head.val){ p1 = p1.next; int tmp = p1.val; p1.val =p2.val; p2.val =tmp; } p2 =p2.next; } if(p1!=head){//已经有序不需要交换 int tmp = p1.val; p1.val =head.val; head.val =tmp; } return p1; } }
剑指 Offer 40. 最小的k个数
输入整数数组 arr ,找出其中最小的 k 个数。例如,输入4、5、1、6、2、7、3、8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1、2、3、4。
class Solution { public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) { if (k == 0 || arr.length == 0) { return new int[0]; } // 最后一个参数表示我们要找的是下标为k-1的数 return quickSearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, k - 1); } private int[] quickSearch(int[] nums, int lo, int hi, int k) { // 每快排切分1次,找到排序后下标为j的元素,如果j恰好等于k就返回j以及j左边所有的数; int j = partition(nums, lo, hi); if (j == k) { return Arrays.copyOfRange(nums,0, j + 1); } // 否则根据下标j与k的大小关系来决定继续切分左段还是右段。 return j > k? quickSearch(nums, lo, j - 1, k): quickSearch(nums, j + 1, hi, k); } private int partition(int[] arr, int l, int r) { int i = l; int j = r; if (l < r) { while (l < r) { while (l < r && arr[r] >= arr[l]) { r--; } int tmp = arr[l]; arr[l] = arr[r]; arr[r] = tmp; while (l < r && arr[l] <= arr[r]) { l++; } tmp = arr[l]; arr[l] = arr[r]; arr[r] = tmp; } } return r; //arr[r]左边不大于他,右边不小于他 } }
选择排序
最小的往前放
static void selectsort(int a[]) { int n = a.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int min = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (a[j] < a[min]) min = j; } if (a[i] != a[min]) { int tmp = a[i]; a[i] = a[min]; a[min] = tmp; } } }
冒泡排序
最大的往后放
static void paosort(int a[]) { boolean flag = true; int n = a.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { flag = true; for (int j = 0; j + 1 < n - i; j++) { if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) { flag = false; int tmp = a[j]; a[j] = a[j + 1]; a[j + 1] = tmp; } } if (flag == true)//改进 break; for (int x : a) { System.out.print(x + " "); } System.out.println(); } }
插入排序
public static void InsertSort(int[] arr) { int i, j; int n = arr.Length; int target; //假定第一个元素被放到了正确的位置上 //这样,仅需遍历1 - n-1 for (i = 1; i < n; i++) { j = i; target = arr[i]; while (j > 0 && target < arr[j - 1]) { arr[j] = arr[j - 1]; j--; } arr[j] = target; } }







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现