JAVA 容器
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Pandafz1997/article/details/120558429
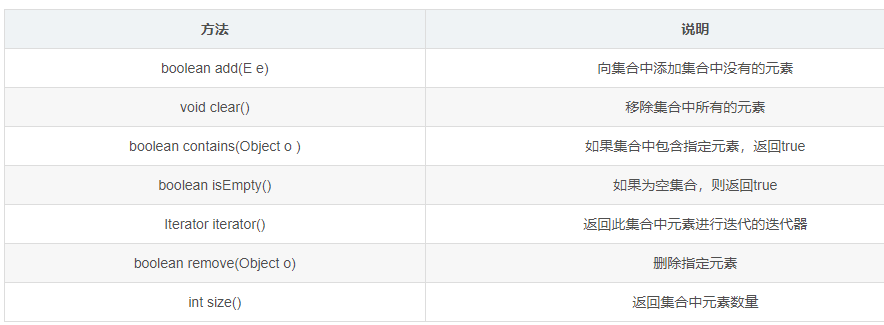
List add remove get set Iterator size Map put remove get containsKey/Value keySet() size Stack push pop/clear/isEmpty() search peek size Set add remove/clear/isEmpty() contains Iterator size set可以删除指定元素 que offer poll/clearList add remove get set Iterator size
HashMap 和HashSet 都不能保证元素顺序
注意 迭代时 // for (int x : list/map.keySet()/stack/set/que) // System.out.println(x); 都可以迭代 顺序 FIFO Iterator接口 Iterator通过遍历(迭代访问)集合中的元素来获取或删除某元素 import java.util.*; public class RongQi { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList(); arrayList.add("ab"); arrayList.add("cd"); arrayList.add("df"); System.out.println("集合内容如下: "); Iterator iterator = arrayList.iterator();// iterator()方法返回一个Iterator对象 while (iterator.hasNext()) { Object o = iterator.next(); System.out.println(o); if (o.equals("df")) { iterator.remove(); } } System.out.println("删除df之后 " + arrayList); } } 集合内容如下: ab cd df 删除df之后 [ab, cd] List List中元素可以重复,并且是有序的(这里的有序指的是按照放入的顺序进行存储。如按照顺序把1,2,3存入List,那么,从List中遍历出来的顺序也是1,2,3) List可以将元素维持在特定序列中,常见的子类实现有 ArrayList 快速查询,插入删除效率低 底层 Object[] 数组 ArrayList底层是用数组实现的,可以认为ArrayList是一个可改变大小的数组。随着越来越多的元素被添加到ArrayList中,其规模是动态增加的。ArrayList 实现了 RandomAccess 接口,就表明了他具有快速随机访问功能。 RandomAccess 接口只是标识,并不是说 ArrayList 实现 RandomAccess 接口才具有快速随机访问功能的! LinkedList 快速插入删除、查询效率低 LinkedList底层是通过双向链表实现的 更占内存 为每个节点存储直接后继和直接前驱 ArrayList、 LinkedList 和 Vector都实现了List接口,是List的三种实现 vector Object[ ] 存储 线程安全 List 方法 Collections.reverse(l); // list 反转
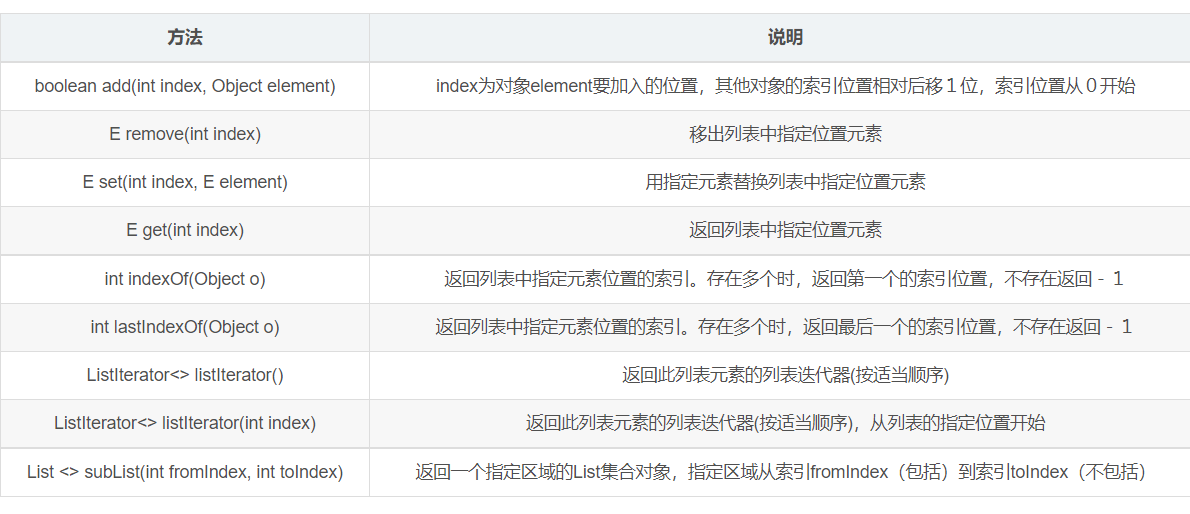
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } arrayList.size() System.out.println("arrayList的指定区域为"+arrayList.subList(1,2));//返回列表中指返回一个指定区域的List集合对象[1,2)
LinkedList类的常用方法
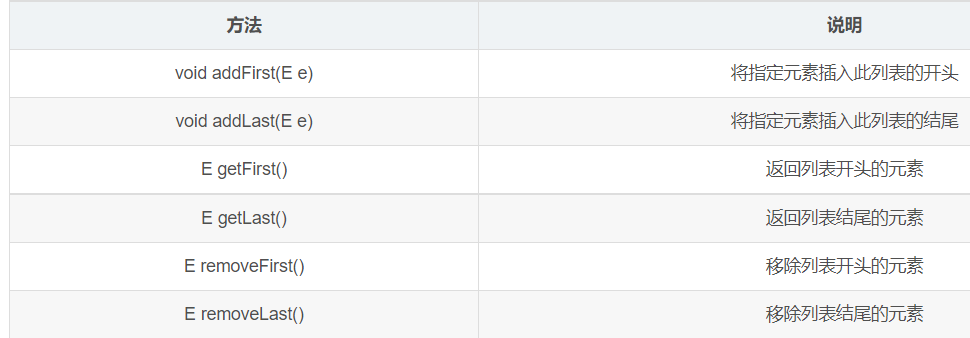
用上面方法必须 LinkedList<Integer> l = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> l = new LinkedList<>(); 会报错
static List<List> a = new ArrayList<List>(); static List b = new ArrayList<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { b.add(i); } System.out.println("b" + b); a.add(b); System.out.println("a" + a); b.clear(); System.out.println("b clear: " + a); for (int i = 2; i < 6; i++) { b.add(i); } System.out.println("b" + b); a.add(b); System.out.println("a" + a); }
b[0, 1, 2]
a[[0, 1, 2]]
b clear: [[]]
b[2, 3, 4, 5]
a[[2, 3, 4, 5], [2, 3, 4, 5]]
public static void main(String[] args) { List<List<Integer>> a=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); for(int i=0;i<3:i++) { List<Integer> b=new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int j=0;j<=i;j++) { b.add(j); } a.add(b); } System.out.println(a); }
[[0], [0, 1], [0, 1, 2]]
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; import javax.swing.border.LineBorder; import java.util.*; public class Main { static class Node { int key, value; public Node(int key, int value) { this.key = key; this.value = value; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<Node> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add(new Node(1, 10)); list.add(new Node(2, 20)); list.add(new Node(3, 30)); System.out.println(list.size()); Iterator<Node> ite = list.iterator(); while (ite.hasNext()) { Node tmp = ite.next(); if (tmp.key == 2) { list.remove(tmp); } } Iterator<Node> itee = list.iterator(); while (itee.hasNext()) { Node tmp = itee.next(); System.out.println(tmp.key + " " + tmp.value); } } } // 操作系统的上下文切换 内存管理 // 一些容器的实现
3
1 10
3 30
ArrayList的扩容机制

jdk 1.8 , new 一个 arraylist ,初始化的容量是 0 .
如何实现扩容
如果之前ArrayList,添加新元素后的存储空间不够,ArrayList会采用扩容机制,即在内存中申请原空间的1.5倍空间,并把原数组的值复制到新数组上,以此完成扩容。
最后使用 Arrays.copyOf 方法直接把原数组中的数组 copy 过来,需要注意的是,Arrays.copyOf 方法会创建一个新数组然后再进行拷贝
minCapacity :当前的size
// 扩容一个 private Object[] grow() { return grow(size + 1); } // 保证扩容到期望容量minCapacity及以上 private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) { return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity(minCapacity)); } // 根据期望容量minCapacity计算实际需要扩容的容量 private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 得到旧容量 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 设置新容量为旧容量的1.5倍 if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) { // 如果新容量仍然小于期望容量 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) // 如果是使用的默认容量 return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); // 取默认容量和期望容量较大值返回 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow // 检查期望容量是否越界(int 的范围) throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return minCapacity; // 返回期望容量 } // 如果新容量大于期望容量,判断一下新容量是否越界 return (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE <= 0) ? newCapacity : hugeCapacity(minCapacity); }
ArrayList有缩容吗?
ArrayList没有缩容。无论是remove方法还是clear方法,它们都不会改变现有数组elementData的长度。但是它们都会把相应位置的元素设置为null,以便垃圾收集器回收掉不使用的元素,节省内存
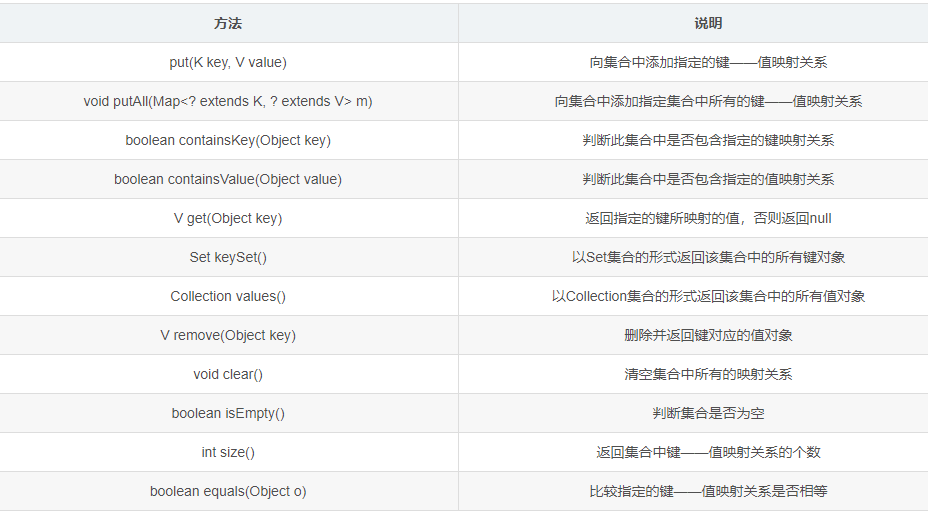
Map
Map集合用于保存具有映射关系的数据,在Map集合中保存着两组值,一组值是key键,另一组值是value值。key和value之间存在一对一的关系,
通过指定的key键就能找到唯一的value值。Map中的key键不允许重复(key键唯一),value值可以重复。
在JDK8之后,对map新增了getOrDefault()方法
Map.getOrDefault(key,默认值);
Map中会存储一一对应的key和value。
如果 在Map中存在key,则返回key所对应的的value。
如果 在Map中不存在key,则返回默认值。

和为1 的分数对
public static int solution(int[] X, int[] Y) { // write your code in Java 8 (Java SE 8) int mod = (int) (1e9 + 7); int n = X.length; long res = 0; Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Integer>> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int gcg = gcd(X[i], Y[i]); int up = X[i] / gcg; int down = Y[i] / gcg; Map<Integer, Integer> curMap = map.computeIfAbsent(down, k -> new HashMap<>()); res = (res + curMap.getOrDefault(down - up, 0)) % mod; 只和该值前面的配对 curMap.put(up, curMap.getOrDefault(up, 0) + 1); } return (int) res; }
Map map1 = new HashMap<>(); Map map2 = new HashMap<>(); Map map3 = new HashMap<>(); map1.put(1001, "bc"); map1.put(1002, "ab"); map1.put(null, null); map2.put(1003, "B"); map2.put(100, "C"); map3.put(100, "C"); map3.put(1003, "B"); System.out.println("map1: " + map1); System.out.println("map2: " + map2); map1.putAll(map2); System.out.println("map1: " + map1); // map1: {null=null, 1001=bc, 1002=ab} // map2: {100=C, 1003=B} // map1: {null=null, 100=C, 1001=bc, 1002=ab, 1003=B} // 如果把map2.put(1003, "B")改为map2.put(1001, "B"); // map1: {null=null, 1001=bc, 1002=ab} // map2: {100=C, 1001=B} // map1: {null=null, 100=C, 1001=B, 1002=ab},1001唯一,value值被覆盖 System.out.println("map1是否包含键对象null: " + map1.containsKey(null)); System.out.println("map1是否包含\"a\"值 :" + map1.containsValue("a")); System.out.println("map1的键1001的对象为 :" + map1.get(1001)); System.out.println("map1的键对象为 :" + map1.keySet()); System.out.println("map1的值对象为 :" + map1.values()); System.out.println("删除1003键对象后,map1的值对象为 :" + map1.remove(1003) + "," + map1); // map1是否包含键对象null: true // map1是否包含"a"值 :false // map1的键1001的对象为 :bc // map1的键对象为 :[null, 100, 1001, 1002, 1003] // map1的值对象为 :[null, C, bc, ab, B] // 删除1003键对象后,map1的值对象为 :B,{null=null, 100=C, 1001=bc, 1002=ab} map1.clear(); System.out.println("map1的值对象为 " + map1); System.out.println("map1是否为null" + map1.isEmpty()); System.out.println("map2的大小" + map2.size()); System.out.println("map2和map3是否是一个对象" + map2.equals(map3)); // map1的值对象为 {} // map1是否为nulltrue // map2的大小2 // map2和map3是否是一个对象true
HashMap类
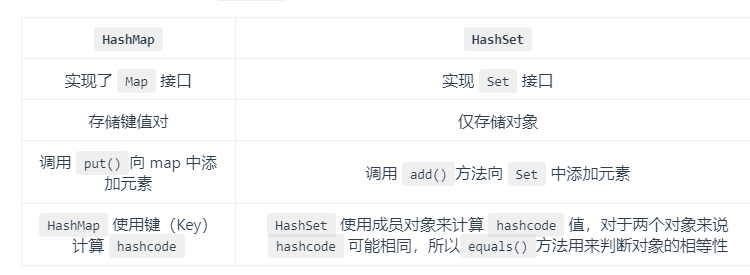
HashMap实现了Map接口,因此HashMap有Map接口提供的所有常用方法。同HashSet类似,HashMap不能保证元素的顺序。
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Integer,Integer>map =new HashMap<>(); map.put(1,3); map.put(8,3); map.put(0,3); for(int x:map.keySet()){ System.out.println(x+" "+map.get(x)); } } }
0 3 1 3 8 3
HashMap的底层实现采用了哈希表,JDK1.8之前,HashMap的底层是采用数组+链表的方法,即用链表处理哈希冲突。
HashMap允许有一个键为null,允许多个值为null
HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("asd", 1); map.put("2das", 2); map.put("3das", 3); map.put("4das", 4); map.put("4das", 5);// 存在相同的key时,后插入的会被覆盖 System.out.println(map);// 不能保证有序 System.out.println(map.containsKey(99));// for (Object o : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(o + "-->" + map.get(o)); }
{asd=1, 3das=3, 4das=5, 2das=2}
false
asd-->1
3das-->3
4das-->5
2das-->2
HashMap 的 7 种遍历方式与性能分析
HashMap 遍历从大的方向来说,可分为以下 4 类:
- 迭代器(Iterator)方式遍历;
- For Each 方式遍历;
- Lambda 表达式遍历(JDK 1.8+);
- Streams API 遍历(JDK 1.8+)。
但每种类型下又有不同的实现方式,因此具体的遍历方式又可以分为以下 7 种:
- 使用迭代器(Iterator)EntrySet 的方式进行遍历;
- 使用迭代器(Iterator)KeySet 的方式进行遍历;
- 使用 For Each EntrySet 的方式进行遍历;
- 使用 For Each KeySet 的方式进行遍历;
- 使用 Lambda 表达式的方式进行遍历;
- 使用 Streams API 单线程的方式进行遍历;
- 使用 Streams API 多线程的方式进行遍历
entrySet 的性能比 keySet 的性能高出了一倍之多,因此我们应该尽量使用 entrySet 来实现 Map 集合的遍历TreeMap类
TreeMap是Map接口的主要实现类,TreeMap存放的是有序数据,按照key进行排序。
TreeMap底层采用红黑树(红黑树的每个节点就是一个key-value对)对key-value进行排序。
import java.util.*; public class Main { static class Student { // public class Student{ private String name; private int age; private int id; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age, int id) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", id=" + id + '}'; } } static class Studenco implements Comparator<Student>{ public int compare(Student s1,Student s2) { // int cmp = age - s1.age;//按age从小到大 // bb-->Student{name='Allen', age=10} // aa-->Student{name='Allen', age=20} // dd-->Student{name='Diana', age=30} // cc-->Student{name='Catalina', age=40} // int cmp = name.compareTo(s1.name); // cmp = cmp != 0 ? cmp : age - s1.age; // bb-->Student{name='Allen', age=10} // aa-->Student{name='Allen', age=20} // cc-->Student{name='Catalina', age=40} // dd-->Student{name='Diana', age=30} // int cmp = s1.name.compareTo(name); // cmp = cmp != 0 ? cmp : s1.age - age;// 先按name大到小,然后age大到小 // dd-->Student{name='Diana', age=30} // cc-->Student{name='Catalina', age=40} // aa-->Student{name='Allen', age=20} // bb-->Student{name='Allen', age=10} int cmp = s1.name.compareTo(s2.name);//继续加入ID if (cmp != 0) { return cmp; } else { int cmp1 = s1.age - s2.age; if (cmp1 != 0) { return cmp1; } else { return s1.id - s2.id; } } // aa-->Student{name='Allen', age=20, id=1} // bb-->Student{name='Allen', age=20, id=45} // cc-->Student{name='Catalina', age=40, id=2} // dd-->Student{name='Diana', age=30, id=0} } } public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student("Allen", 20, 1); Student s2 = new Student("Allen", 20, 45); Student s3 = new Student("Catalina", 40, 2); Student s4 = new Student("Diana", 30, 0); // 无参的构造方法 TreeMap<Student, String> map = new TreeMap<>(new Studenco());// 对key 排序,不然没有意义 map.put(s2, "bb"); map.put(s1, "aa"); map.put(s4, "dd"); map.put(s3, "cc"); for (Object o : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(map.get(o) + "-->" + o); } } }
import java.util.*; Student s1 = new Student("Allen", 20, 1); Student s2 = new Student("Allen", 20, 45); Student s3 = new Student("Catalina", 40, 2); Student s4 = new Student("Diana", 30, 0); // 无参的构造方法 TreeMap<Student, String> map = new TreeMap<>();// 对key 排序,不然没有意义 map.put(s2, "bb"); map.put(s1, "aa"); map.put(s4, "dd"); map.put(s3, "cc"); for (Object o : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(map.get(o) + "-->" + o); } } static class Student implements Comparable<Student> { // public class Student{ private String name; private int age; private int id; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age, int id) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", id=" + id + '}'; } @Override public int compareTo(Student s1) { // int cmp = age - s1.age;//按age从小到大 // bb-->Student{name='Allen', age=10} // aa-->Student{name='Allen', age=20} // dd-->Student{name='Diana', age=30} // cc-->Student{name='Catalina', age=40} // int cmp = name.compareTo(s1.name); // cmp = cmp != 0 ? cmp : age - s1.age; // bb-->Student{name='Allen', age=10} // aa-->Student{name='Allen', age=20} // cc-->Student{name='Catalina', age=40} // dd-->Student{name='Diana', age=30} // int cmp = s1.name.compareTo(name); // cmp = cmp != 0 ? cmp : s1.age - age;// 先按name大到小,然后age大到小 // dd-->Student{name='Diana', age=30} // cc-->Student{name='Catalina', age=40} // aa-->Student{name='Allen', age=20} // bb-->Student{name='Allen', age=10} int cmp = name.compareTo(s1.name);//继续加入ID if (cmp != 0) { return cmp; } else { int cmp1 = age - s1.age; if (cmp1 != 0) { return cmp1; } else { return id - s1.id; } } // aa-->Student{name='Allen', age=20, id=1} // bb-->Student{name='Allen', age=20, id=45} // cc-->Student{name='Catalina', age=40, id=2} // dd-->Student{name='Diana', age=30, id=0} } } }
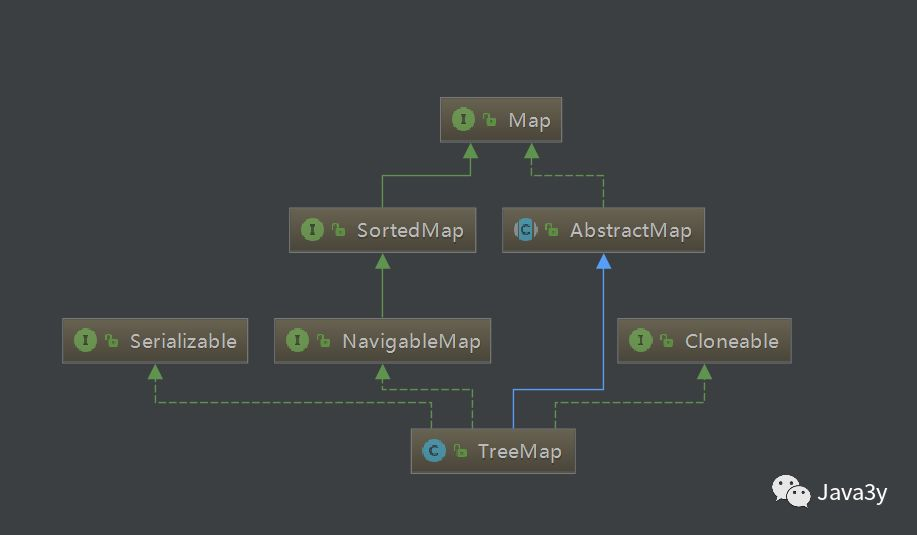
(1)TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,而AbstractMap实现了Map接口,并实现了Map接口中定义的方法,减少了其子类继承的复杂度;
(2)TreeMap 实现了Map接口,成为Map框架中的一员,可以包含着key-value形式的元素;
(3)TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着拥有了更强的元素搜索能力; 而NavigableMap接口继承着SortedMap接口,致使我们的TreeMap是有序的!
(4)TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,实现了clone()方法,可以被克隆;
(5)TreeMap 实现了Java.io.Serializable接口,支持序列化操作;
常用的接口方法
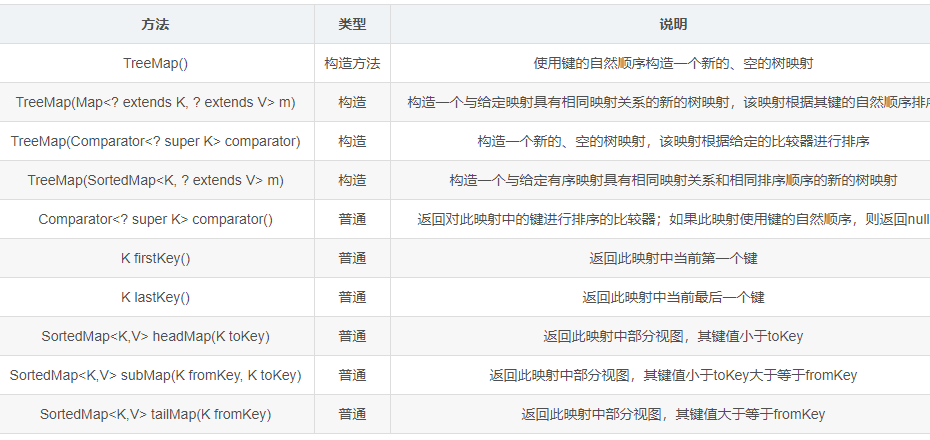
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap<>();//构造方法1 treeMap.put(10, "a"); treeMap.put(1, "a"); treeMap.put(9, null); treeMap.put(5, "c"); treeMap.put(3, null); System.out.println(treeMap); System.out.println("first key " + treeMap.firstKey()); System.out.println("last key " + treeMap.lastKey()); System.out.println(treeMap.headMap(3)); System.out.println(treeMap.subMap(3, 7)); System.out.println(treeMap.tailMap(5)); TreeMap treeMap1 = new TreeMap(treeMap);//构造方法2
System.out.println(treeMap1);
{1=a, 3=null, 5=c, 9=null, 10=a}
first key 1
last key 10
{1=a}
{3=null, 5=c}
{5=c, 9=null, 10=a}
{1=a, 3=null, 5=c, 9=null, 10=a}
TreeMap和HashMap, HashTable性能比较
排序:TreeMap按照键值大小输出,,针对需要排序的Map,优先使用TreeMap。
线程安全:HashTable是线程安全的类,很多方法都是用synchronized修饰,但同时因为加锁导致并发效率低下,单线程环境效率也十分低;
对 Null key 和 Null value 的支持 :HashMap 可以存储 null 的 key 和 value,但 null 作为键只能有一个,null 作为值可以有多个;Hashtable 不允许有 null 键和 null 值,否则会抛出 NullPointerException。
ConcurrentHashMap 和 Hashtable 的区别

Map bug
import java.util.*; import javax.swing.plaf.synth.SynthSplitPaneUI; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Map<StringBuilder, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); int nums[] = { 1, 7, 4, 0 }; StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (int x : nums) { s.append(x); } map.put(s, 15); for (Object o : map.keySet()) { System.out.println("yiyoude " + o + " " + map.get(o)); } System.out.println("........."); s.append("5"); map.put(new StringBuilder(s), 56); // StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder(s); // s1.append("5"); // map.put(s1, 56); for (Object o : map.keySet()) { System.out.println("yiyoude " + o + " " + map.get(o)); } } }
yiyoude 1740 15
.........
yiyoude 17405 56
yiyoude 17405 15
key重复
解决 import java.util.*; import javax.swing.plaf.synth.SynthSplitPaneUI; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Map<StringBuilder, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); int nums[] = { 1, 7, 4, 0 }; StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (int x : nums) { s.append(x); } map.put(s, 15); for (Object o : map.keySet()) { System.out.println("yiyoude " + o + " " + map.get(o)); } System.out.println("........."); map.put(s, 56); StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder(s); s1.append("5"); map.put(s1, 56); for (Object o : map.keySet()) { System.out.println("yiyoude " + o + " " + map.get(o)); } } }
yiyoude 1740 15
.........
yiyoude 17405 56
yiyoude 1740 56
HashMap和Hashtable有什么区别?
- HashMap是Hashtable的轻量级实现,HashMap允许key和value为null,但最多允许一条记录的key为null.而HashTable不允许。
- HashTable中的方法是线程安全的,而HashMap不是。在多线程访问HashMap需要提供额外的同步机制。
- Hashtable使用Enumeration进行遍历,HashMap使用Iterator进行遍历。
Stack
栈是Vector的一个子类,它实现了一个标准的后进先出的栈。
Stack stack = new Stack(); System.out.println(stack.empty()); stack.push(1); stack.push("aj"); stack.push('A'); System.out.println(stack.search("aj"));// 从1开始 System.out.println(stack.peek());// 查看堆栈顶部的对象,但不从堆栈中移除它。 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Object o = stack.pop();// 移除堆栈顶部的对象,并作为此函数的值返回该对象。 System.out.println(o); }
true
2
A
A
aj
1
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如,序列 {1,2,3,4,5} 是某栈的压栈序列,序列 {4,5,3,2,1} 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 {4,3,5,1,2} 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
示例 1:
输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,5,3,2,1] 输出:true 解释:我们可以按以下顺序执行: push(1), push(2), push(3), push(4), pop() -> 4, push(5), pop() -> 5, pop() -> 3, pop() -> 2, pop() -> 1
class Solution { public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) { Stack<Integer>sta =new Stack(); int i =0; for(int num:pushed){ sta.push(num); while(!sta.isEmpty()&&sta.peek()==popped[i]) { sta.pop(); i++; } } return sta.isEmpty(); } }
DFS 指定入栈顺序输出所有出栈顺序
import java.util.*; public class Main { static int cnt = 0; static char in[] = { '1', '2', '3', '4' }; static String tmp; static void dfs(int num, Stack sta, String sout) {// num:当前压入栈的数目 if (num == in.length && sta.isEmpty()) { System.out.println(sout); cnt++; return; } else { Stack sta1 = (Stack) sta.clone(); Stack sta2 = (Stack) sta.clone();//要新建,因为对象传的是地址 if (num < in.length) { sta1.push(in[num]); dfs(num + 1, sta1, sout); } if (!sta2.isEmpty()) {//必须if tmp = sout + sta2.pop(); dfs(num, sta2, tmp); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { dfs(0, new Stack(), ""); System.out.println(cnt); } }
Queue
Queue接口是一个先入先出(FIFO)的数据结构,继承Collection接口,LinkedList(双向链表)实现了List和Deque接口。
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>(); queue.offer("a"); queue.offer("b"); queue.offer("c"); queue.offer("d"); // offer,add 区别: // 一些队列有大小限制,因此如果想在一个满的队列中加入一个新项,多出的项就会被拒绝。 // 这时新的 offer 方法就可以起作用了。它不是对调用 add() 方法抛出一个 unchecked 异常,而只是得到由 offer() 返回的 // false。 for (String x : queue) { System.out.println(x); } System.out.println("____"); System.out.println(queue.poll());// 返回第一个元素,并在队列中删除 System.out.println("____"); // poll,remove 区别: // remove() 和 poll() 方法都是从队列中删除第一个元素。 // remove() 的行为与 Collection 接口的版本相似, 但是新的 poll() 方法在用空集合调用时不是抛出异常,只是返回 // null。因此新的方法更适合容易出现异常条件的情况。 for (String x : queue) { System.out.println(x); } System.out.println("____"); System.out.println(queue.peek());// 返回第一个元素 System.out.println("____"); // peek,element区别: // element() 和 peek() 用于在队列的头部查询元素。与 remove() 方法类似,在队列为空时, element() 抛出一个异常,而 // peek() 返回 null for (String x : queue) { System.out.println(x); }
a
b
c
d
____
a
____
b
c
d
____
b
____
b
c
d
PriorityQueue
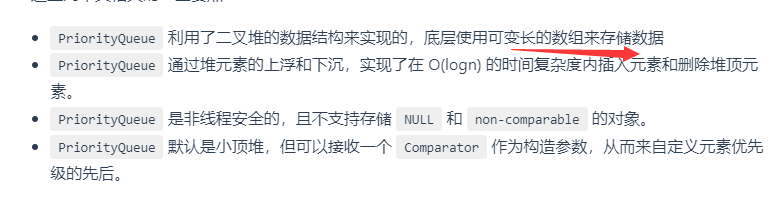
class IntegerComparator implements Comparator<Integer> { @Override public int compare(Integer s1, Integer s2) { return s2 - s1; } } Queue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();//默认升序 queue.offer(2); queue.offer(1); queue.offer(6); queue.offer(0); queue.offer(9); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { System.out.println(queue.poll() + " "); } System.out.println("______"); Queue<Integer> queu = new PriorityQueue<>(new IntegerComparator());//逆序 queu.offer(2); queu.offer(1); queu.offer(6); queu.offer(0); queu.offer(9); while (!queu.isEmpty()) { System.out.println(queu.poll() + " "); }
0
1
2
6
9
______
9
6
2
1
0
class Node { int x, y; public Node(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } } public class RongQi { static int[] nums = { 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 5, 5, 5 }; static class Icompator implements Comparator<Node> { @Override public int compare(Node s1, Node s2) { // 操作 if (s1.x == s2.x) { return s1.y - s2.y; } return s1.x - s2.x; } } public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>(new Icompator()); Node n1 = new Node(1, 2); Node n2 = new Node(2, 5); Node n3 = new Node(2, 3); q.offer(n1); q.offer(n2); q.offer(n3); Node n; while (!q.isEmpty()) { n = q.poll(); System.out.println("x: " + n.x + " y: " + n.y); }
x: 1 y: 2
x: 2 y: 3
x: 2 y: 5
如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。
例如,
[2,3,4] 的中位数是 3
[2,3] 的中位数是 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5
设计一个支持以下两种操作的数据结构:
- void addNum(int num) - 从数据流中添加一个整数到数据结构中。
- double findMedian() - 返回目前所有元素的中位数。
class MedianFinder { Queue<Integer>minheap,maxheap; /** initialize your data structure here. */ public MedianFinder() { minheap =new PriorityQueue<Integer>();//维护大的一半 maxheap =new PriorityQueue<Integer>((x,y)->(y-x));//(y-x)维护小的一半 } public void addNum(int num) { //先往minheap 装,保证元素个数为奇数时中位数为minheap.peek(); 也就是minheap中元素数目始终多一个 //装时注意:需要向minheap装, 先装入maxheap,将maxheap的顶部元素弹出并装入minheap.这样可保证minheap始终维护大的一半 //需要向maxheap装,类似 if(minheap.size()!=maxheap.size()){ minheap.offer(num); maxheap.offer(minheap.poll()); } else{ maxheap.offer(num); minheap.offer(maxheap.poll()); } } public double findMedian() { return maxheap.size()==minheap.size()? (minheap.peek()+maxheap.peek())*0.5:minheap.peek(); } } /** * Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such: * MedianFinder obj = new MedianFinder(); * obj.addNum(num); * double param_2 = obj.findMedian(); */
时间复杂度 :优先队列的弹出,压入 O(logn) 中位数查找 O(1)
空间复杂度: O(n)
双端队列 Deque
在队列的两端均可以插入或删除元素。
Deque<Integer> que = new LinkedList(); que.offerFirst(1); que.offerLast(2); que.offerFirst(3); que.offerLast(4); for (int x : que) { System.out.println(x);// 3 1 2 4 } que.pollFirst(); for (int x : que) { System.out.println(x);// 1 2 4 } que.pollLast(); for (int x : que) { System.out.println(x);// 1 2 } System.out.println(que.peekFirst());// 1 System.out.println(que.peekLast());// 2
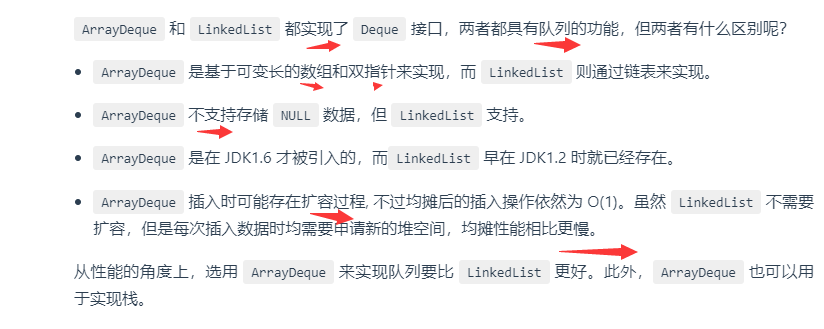
ArrayDeque 与 LinkedList 的区别
Set
List集合按照对象的插入顺序保存对象,Set集合的对象不按照顺序保存对象,可以说是不完全无序状态。
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Integer>set =new HashSet<>(); set.add(1); set.add(0); set.add(10); for(int x:set){ System.out.println(x); } } }
0 1 10
Set集合中的对象没有按照特定的方式排序,仅仅简单地将对象加入其中,但是集合中不能存放重复对象。由于Set接口实现了Collection接口,所以Set接口有Collection接口提供的所有常用方法
HashSet类
可以add null
Set集合中不允许重复的元素存在,当向集合中插入对象时,如何判别在集合中是否已经存在该对象?
查看源码可知:当向HashSet对象添加新对象时,Java系统先调用对象的hashCode()方法来获取该对象的哈希码,如何根据哈希码找到对应的存储区域。如果该存储区域已经有了对象,则调用equals()方法与新元素进行比较,相同就不保存,
如果不同的话,就会插入元素。这样我们就大大减少了 equals 的次数,相应就大大提高了执行速度。
针对用户自行定义的对象,需要重写hashCode()和equals()方法才能避免重复添加对象,保证程序的正常运行。
HashMap 和 HashSet 区别
TreeSet类
TreeSet集合中的元素处于排序状态,主要按照红黑树的数据结构来存储对象。TreeSet提供了一些额外的方法。
HashSet、LinkedHashSet 和 TreeSet

无序性和不可重复性的含义

为什么重写 equals() 时必须重写 hashCode() 方法?
因为两个相等的对象的 hashCode 值必须是相等。也就是说如果 equals 方法判断两个对象是相等的,那这两个对象的 hashCode 值也要相等。
如果重写 equals() 时没有重写 hashCode() 方法的话就可能会导致 equals 方法判断是相等的两个对象,hashCode 值却不相等。
set调用equals方法验证没有问题,但是有个前提条件。正确的验证流程应该是:
比较对象的hashCode是否相同,若相同,再进行equals方法的判断,true认为元素重复,反之元素不重复。若hashCode不相同,则直接返回元素不重复并将元素插入。
static class Node1 { int x, y; public Node1() { } public Node1(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(x, y); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { // 判断一下如果是同一个对象直接返回true,提高效率 return true; } if (obj == null || obj.getClass() != this.getClass()) { // 如果传进来的对象为null或者二者为不同类,直接返回false return false; } Node1 node1 = (Node1) obj; // 向下转型 return x == node1.x && y == node1.y; // 注意:浮点数的比较不能简单地用==,会有精度的误差,用Math.abs或者Double.compare // return Double.compare(rectangle.length, length) == 0 && // Double.compare(rectangle.wide, wide) == 0; } }
Set<Node1> set = new HashSet<>(); for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) { set.add(new Node1(1, 4)); } for (Node1 sd : set) {// 只有(1,4) System.out.println(sd.x + " " + sd.y); System.out.println(sd.hashCode());// 996 } System.out.println(set.contains(new Node1(1, 4)));// true
Java中线程安全的基本数据结构有哪些
线程安全 :一段操纵共享数据的代码能够保证在同一时间内被多个线程执行而仍然保持其正确性的,就被称为是线程安全的。
HashTable: 哈希表的线程安全版,效率低
HashTable使用synchronized来修饰方法函数来保证线程安全,但是在多线程运行环境下效率表现非常低下。
因为当一个线程访问HashTable的同步方法时,其他线程也访问同步方法就会出现阻塞状态。
比如当一个线程在添加数据时候,另外一个线程即使执行获取其他数据的操作也必须被阻塞,大大降低了程序的运行效率。
ConcurrentHashMap:哈希表的线程安全版,效率高,用于替代HashTable
ConcurrentHashMap是HashMap的线程安全版。
ConcurrentHashMap允许多个修改操作并发运行,其原因在于使用了锁分段技术:首先讲Map存放的数据分成一段一段的存储方式,然后给每一段数据分配一把锁,
当一个线程占用锁访问其中一个段的数据时,其他段的数据也能被其他线程访问。这样就保证了每一把锁只是用于锁住一部分数据,那么当多线程访问Map里的不同数据段的数据时,线程间就不会存在锁竞争,从而可以有效提高并发访问效率。
上述的处理机制明显区别于HashTable是给整体数据分配了一把锁的处理方法。为此,在多线程环境下,常用ConcurrentHashMap在需要保证数据安全的场景中去替换HashMap,而不会去使用HashTable,同时在最新版的JDK中已经推荐废弃使用HashTable。
Vector:线程安全版Arraylist
利用synchronized同步锁机制进行实现,其实现方式与HashTable类似
Stack:线程安全版栈
BlockingQueue及其子类:线程安全版队列
https://www.jianshu.com/p/b1408e3e3bb4
StringBuffer
synchronized修饰实现其线程安全特性






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
2019-12-14 第二周 第五部分