1 function g = sigmoidGradient(z)
2 %SIGMOIDGRADIENT returns the gradient of the sigmoid function
3 %evaluated at z
4 % g = SIGMOIDGRADIENT(z) computes the gradient of the sigmoid function
5 % evaluated at z. This should work regardless if z is a matrix or a
6 % vector. In particular, if z is a vector or matrix, you should return
7 % the gradient for each element.
8 g = zeros(size(z));
9
10 % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
11 % Instructions: Compute the gradient of the sigmoid function evaluated at
12 % each value of z (z can be a matrix, vector or scalar).
13
14 g=sigmoid(z).*(1-sigmoid(z));%g'(z)
15
16 % =============================================================
17
18 end
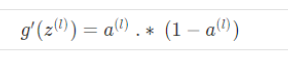
function W = randInitializeWeights(L_in, L_out)
%RANDINITIALIZEWEIGHTS Randomly initialize the weights of a layer with L_in
%incoming connections and L_out outgoing connections
% W = RANDINITIALIZEWEIGHTS(L_in, L_out) randomly initializes the weights
% of a layer with L_in incoming connections and L_out outgoing
% connections.
% Note that W should be set to a matrix of size(L_out, 1 + L_in) as
% the first column of W handles the "bias" terms
% You need to return the following variables correctly
W = zeros(L_out, 1 + L_in);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Initialize W randomly so that we break the symmetry while
% training the neural network.
%
% Note: The first column of W corresponds to the parameters for the bias unit
%
eps=0.12;
W=rand(L_out,1+L_in)*2*eps-eps;
% =========================================================================
end

1 function [J grad] = nnCostFunction(nn_params, ...
2 input_layer_size, ...
3 hidden_layer_size, ...
4 num_labels, ...
5 X, y, lambda)
6 %NNCOSTFUNCTION Implements the neural network cost function for a two layer
7 %neural network which performs classification
8 % [J grad] = NNCOSTFUNCTON(nn_params, hidden_layer_size, num_labels, ...
9 % X, y, lambda) computes the cost and gradient of the neural network. The
10 % parameters for the neural network are "unrolled" into the vector
11 % nn_params and need to be converted back into the weight matrices.
12 %
13 % The returned parameter grad should be a "unrolled" vector of the
14 % partial derivatives of the neural network.
15 %
16
17 % Reshape nn_params back into the parameters Theta1 and Theta2, the weight matrices
18 % for our 2 layer neural network
19 Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
20 hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1));
21
22 Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
23 num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1));
24
25 % Setup some useful variables
26 m = size(X, 1);
27
28 % You need to return the following variables correctly
29 J = 0;
30 Theta1_grad = zeros(size(Theta1));
31 Theta2_grad = zeros(size(Theta2));
32
33 % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
34 % Instructions: You should complete the code by working through the
35 % following parts.
36 %
37 % Part 1: Feedforward the neural network and return the cost in the
38 % variable J. After implementing Part 1, you can verify that your
39 % cost function computation is correct by verifying the cost
40 % computed in ex4.m
41 %
42 % Part 2: Implement the backpropagation algorithm to compute the gradients
43 % Theta1_grad and Theta2_grad. You should return the partial derivatives of
44 % the cost function with respect to Theta1 and Theta2 in Theta1_grad and
45 % Theta2_grad, respectively. After implementing Part 2, you can check
46 % that your implementation is correct by running checkNNGradients
47 %
48 % Note: The vector y passed into the function is a vector of labels
49 % containing values from 1..K. You need to map this vector into a
50 % binary vector of 1's and 0's to be used with the neural network
51 % cost function.
52 %
53 % Hint: We recommend implementing backpropagation using a for-loop
54 % over the training examples if you are implementing it for the
55 % first time.
56 %
57 % Part 3: Implement regularization with the cost function and gradients.
58 %
59 % Hint: You can implement this around the code for
60 % backpropagation. That is, you can compute the gradients for
61 % the regularization separately and then add them to Theta1_grad
62 % and Theta2_grad from Part 2.
63 %
64 依据维度来运算
65 %Theta1 25*401
66 %Theta2 10*26
67 %X 5000*400
68 h=eye(num_labels);
69 y=h(y,:);%把y中的值用0-1表示
70 a1=[ones(m,1) X]%5000*401
71 z2=a1*Theta1'%5000*25
72 a2=sigmoid(z2);
73 n=size(a2,1)%5000
74 a2=[ones(n,1) a2]%5000*26
75 z3=a2*Theta2'%5000*10
76 a3=sigmoid(z3);
77 J=sum(sum(-y.*log(a3)-(1-y).*log(1-a3)))/m;%要用点乘
78 reg=lambda/(2*m)*(sum(sum(Theta1(:,2:end).^2))+sum(sum(Theta2(:,2:end).^2)));%第一列不需要正则化
79 J=J+reg;
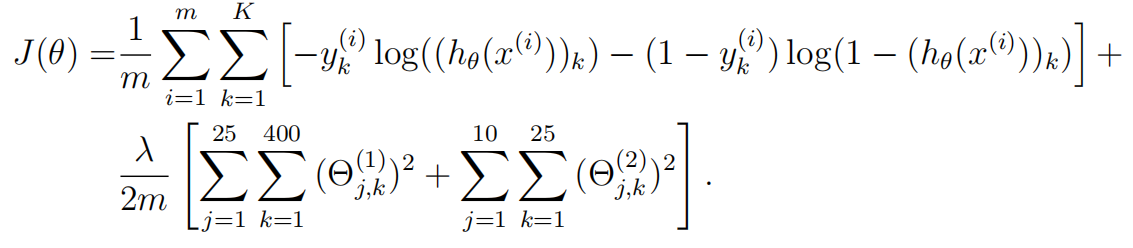
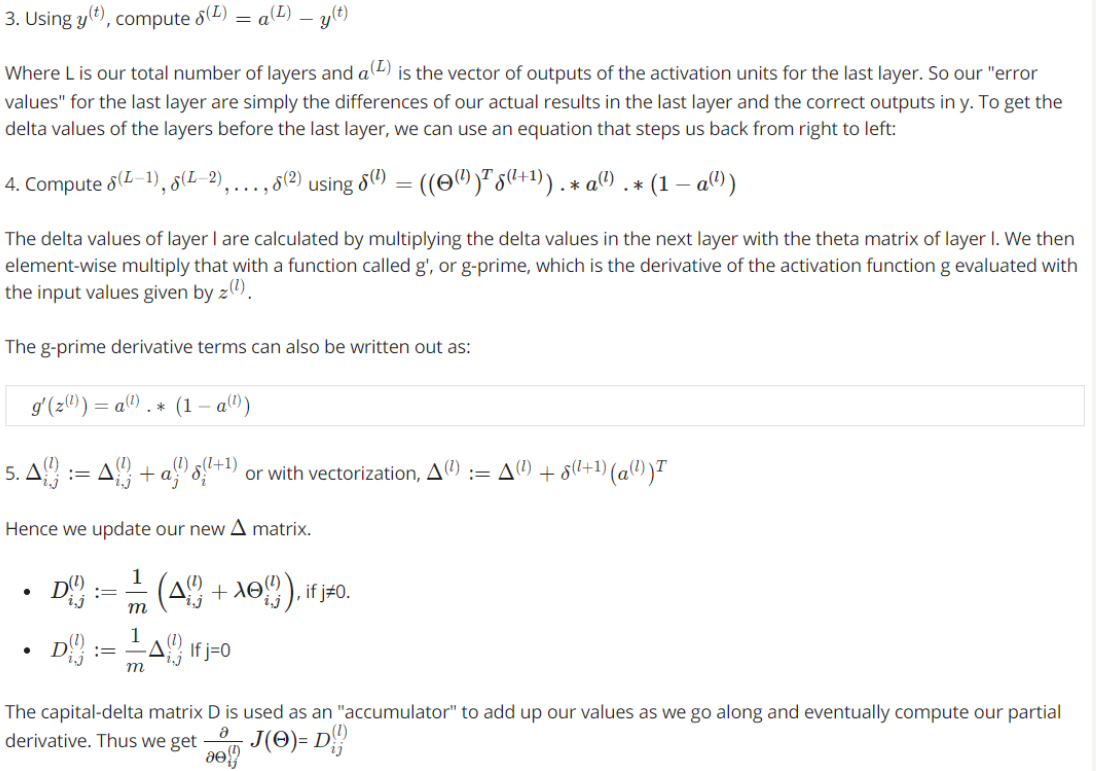
82 delta3=a3-y;%5000*10
83 delta2=delta3*Theta2;%5000*26
84 delta2=delta2(:,2:end);%5000*25
85 delta2=delta2.*sigmoidGradient(z2);%z2--> 5000*25
86
87 Delta1=zeros(size(Theta1));
88 Delta2=zeros(size(Theta2));
89
90 Delta1 =Delta1+delta2'*a1;%25*401
91 Delta2 =Delta2+delta3'*a2;%10*26
92 Theta1_grad =((1/m)*Delta1)+((lambda/m)*Theta1);%Theta1_grad和Theta1维度一样
93 Theta2_grad =((1/m)*Delta2)+((lambda/m)*Theta2);
94 %第一列不需要正则化
95 Theta1_grad(:,1)=Theta1_grad(:,1)-((lambda/m)*(Theta1(:,1)));
96 Theta2_grad(:,1)=Theta2_grad(:,1)-((lambda/m)*(Theta2(:,1)));
97
110 % -------------------------------------------------------------
111
112 % =========================================================================
113
114 % Unroll gradients
115 grad = [Theta1_grad(:) ; Theta2_grad(:)];%展开成一列(向量)
116
117
118 end
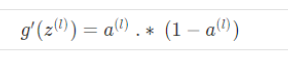
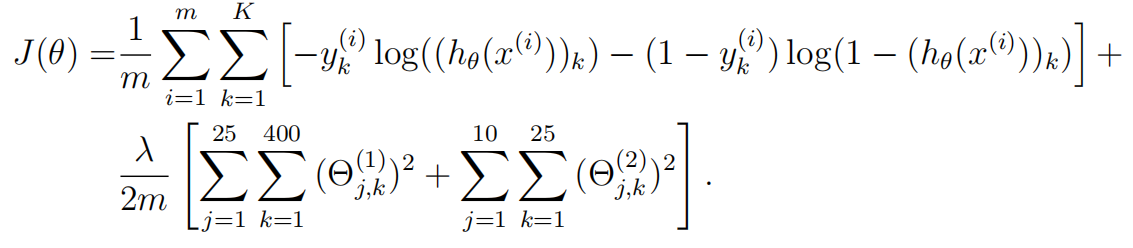







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现