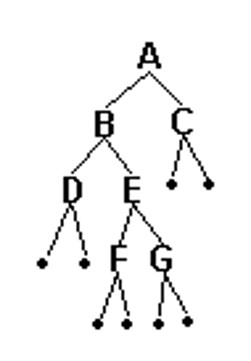
树的建立及遍历
内容简介
本次作业在建立二叉树方面,使用了先序输入建立的方法(递归实现)。在遍历输出方面,有先序/中序/后序遍历三种。
其中,本次建立二叉树时,输入结束的条件为输入数据为'.'。
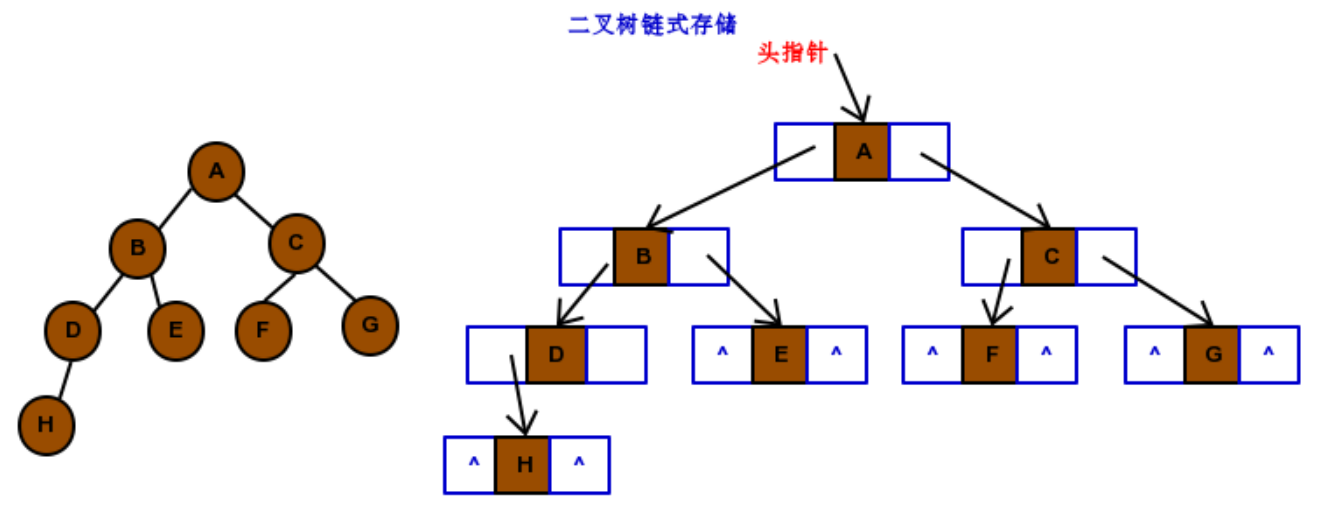
用链式结构存储,生成的树大体如上图
二叉树的建立
树的结构体
typedef struct dfs *tree;
struct dfs
{
tree lchild ,rchild;
char data;
};
按先序输入建立二叉树
tree DFS()
{
char m;
cin>>m;
tree father;
father=new struct dfs;
if(m=='.')
father = NULL;
else
{
father->data=m;
father->lchild=DFS();
father->rchild=DFS();
}
return father;
}
这里用递归法创建树,每次递归返回父节点指针,当碰到表示为空的'.'时,使父节点为空。先序输入建立二叉树是从根节点出发,
先建立每个父节点的左孩子,当没有左孩子时依次返回建立每个父节点右孩子,直至最后一个右孩子被创建,返回所有父节点,
生成一棵二叉树。
二叉树的遍历
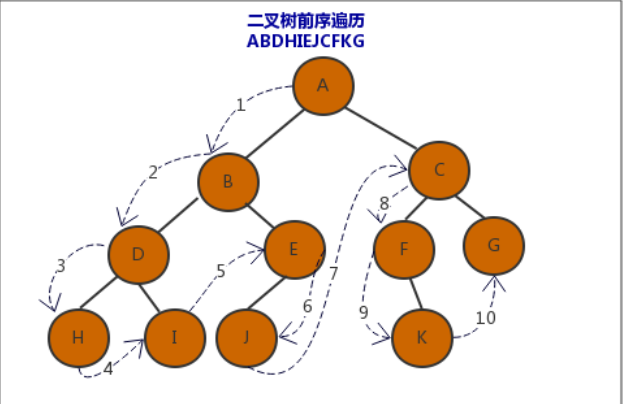
1.先序遍历
思路:先访问根结点 -> 遍历左子树 -> 遍历右子树;先访问根结点
void frontorder(tree root)
{
if(root)
{
cout<<root->data;
frontorder(root->lchild);
frontorder(root->rchild);
}
}
如图
2.中序遍历
思路:遍历左子树 -> 访问根结点 -> 遍历右子树;中间访问根结点
void inorder(tree root)
{
if(root)
{
inorder(root->lchild);
cout<<root->data;
inorder(root->rchild);
}
}
如图

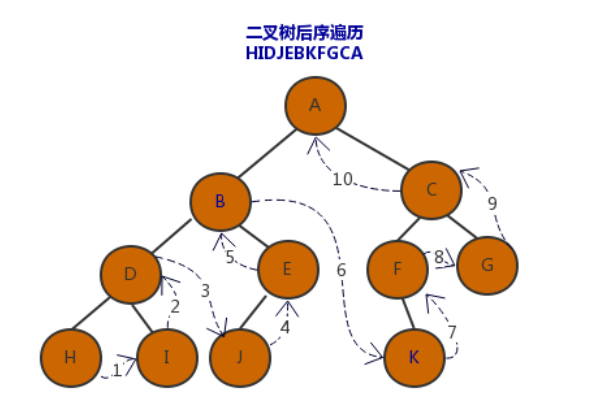
3.后序遍历
思路:遍历左子树 -> 遍历右子树 -> 后访问根结点;后访问根结点
void postorder(tree root)
{
if(root)
{
postorder(root->lchild);
postorder(root->rchild);
cout<<root->data;
}
}
如图
运行结果
因为是先序输入,先序遍历的结果应与输入一致

该数据的生成的树