读书笔记(一)——Element of Financial Risk Management
第一章:Risk Management and Financial Returns(风险控制和金融收益)
Why Should Firms Manage Risk?
a brief taxonomy of risks:Market Risk,Liquidity Risk,Operational Risk,Credit Risk,Business Risk
asset returns:log return(R) and arithmetic return(r)
其他介绍:skew,Autocorrelation,leverage effect
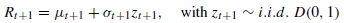 (μ:收益期望,σ:标准差)
(μ:收益期望,σ:标准差)
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
第二章:Volatility Modeling(波动性建模)
建立一个框架来对金融投资组合中大型资产的非正态分布进行建模:
逐步分布建模方法stepwise distribution modeling approach (SDM):1.建立每个资产的方差预测模型(第二章内容)2.将个体方差预测与相关模型联系起来 3.non-normal aspects建模
variance models:
1.simple variance forecasting(RiskMetrics model)(假设平均收益率为0,正态性假设,则收益率模型只需预测方差。方差,用平方回报来衡量,表现出很强的自相关)
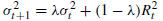 (λ常取0.94)(即:t+1日的方差仅与前一日的方差和收益率有关)
(λ常取0.94)(即:t+1日的方差仅与前一日的方差和收益率有关)
优点:没有未知参数,数据存储少;缺点:正态性假设(实际skew>0,且未考虑杠杆效应)
2.自回归条件异方差模型 GARCH(The generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity) variance model:
GARCH(1,1)(短期):
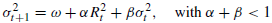 (=1时,w=0,即为RiskMetrics模型)
(=1时,w=0,即为RiskMetrics模型)
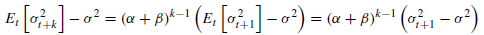 (第k天的方差预测)
(第k天的方差预测)
GARCH(p,q)(GRACH模型扩展):
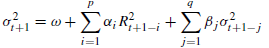 (allows for longer lags)
(allows for longer lags)
NGARCH (nonlinear GARCH) model: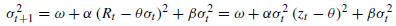
GJR-GARCH model: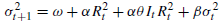 (can capture the leverage effect)
(can capture the leverage effect)
exponential GARCH model(EGARCH):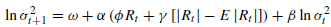 (can capture the leverage effect)
(can capture the leverage effect)
其他:加入其他解释变量:周末or节假日后的交易日
3.最大似然估计(Maximum Likelihood Estimation):
最大似然估计也可以被称为最大可能性估计,即给定x预测y
参考链接:最大似然估计
Standard MLE:
Quasi-MLE:
4.方差模型评估:In-Sample Check on the Autocorrelations;Out-of-Sample Check Using Regression
5.USING INTRADAY INFORMATION:
AR,ARMA
6.Summary:
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
第三章:Correlation Modeling
1.value at risk for simple portfolio
VaR
2.portfolio variance
3.conditional Covariance
4.conditional correlation
想要计算风险度量(如风险价值)的风险经理需要构建包含许多资产的投资组合的方差矩阵和协方差矩阵。如果假设返回值为正态分布且均值为零,则计算VaR所需的就是协方差矩阵
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
第四章: Modeling the Conditional Distribution
第五章:Simulation-Based Methods
第六章:Option Pricing
第七章:Modeling Option Risk
第八章:Backtesting and Stress Testing
未完待续……


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号