Elasticsearch-Kibana-Beats-Logstash入门、Elasticsearch操作汇总 、ELK概念
ElasticSearch基础概念
近实时,两个意思,从写入数据到数据可以被搜索到有一个小延迟(大概1秒);基于es执行搜索和分析可以达到秒级。
1)可以作为一个大型分布式集群(数百台服务器)技术,处理PB级数据,服务大公司;也可以运行在单机上,服务小公司。
2)Elasticsearch不是什么新技术,主要是将全文检索、数据分析以及分布式技术,合并在了一起,才形成了独一无二的ES;lucene(全文检索),商用的数据分析软件(也是有的),分布式数据库(mycat)。
3)对用户而言,是开箱即用的,非常简单,作为中小型的应用,直接3分钟部署一下ES,就可以作为生产环境的系统来使用了,数据量不大,操作不是太复杂。
4)数据库的功能面对很多领域是不够用的(事务,还有各种联机事务型的操作);特殊的功能,比如全文检索,同义词处理,相关度排名,复杂数据分析,海量数据的近实时处理;Elasticsearch作为传统数据库的一个补充,提供了数据库所不能提供的很多功能。
1、Index(索引-数据库)
ElasticSearch将数据存储在一个或多个索引(index)中,这里的索引就像SQL领域的数据库,例如:MySQL里的一个database。
索引包含一堆有相似结构的文档数据,比如可以有一个客户索引,商品分类索引,订单索引,索引有一个名称。一个index包含很多document,一个index就代表了一类类似的或者相同的document。比如说建立一个product index,商品索引,里面可能就存放了所有的商品数据,所有的商品document。
ElasticSearch内部使用Apache Lucenu将数据写入索引或从索引中读取数据。需要注意的是,ElasticSearch中的索引可能有一个或多个Lucene索引构成,具体由索引分片(shard)、复制(replica)机制及其配置决定。
2、Type(类型-表)
ElasticSearch中每个文档都有自己的类型(type)定义。一个索引中允许存储多种类型的文档,并为不同文档类型提供不同的映射。类型就像SQL数据库中的一个数据表。
每个索引里都可以有一个或多个type,type是index中的一个逻辑数据分类,一个type下的document,都有相同的field,比如博客系统,有一个索引,可以定义用户数据type,博客数据type,评论数据type。
商品index,里面存放了所有的商品数据,商品document
但是商品分很多种类,每个种类的document的field可能不太一样,比如说电器商品,可能还包含一些诸如售后时间范围这样的特殊field;生鲜商品,还包含一些诸如生鲜保质期之类的特殊field
type,日化商品type,电器商品type,生鲜商品type
日化商品type:product_id,product_name,product_desc,category_id,category_name
电器商品type:product_id,product_name,product_desc,category_id,category_name,service_period
生鲜商品type:product_id,product_name,product_desc,category_id,category_name,eat_period
每一个type里面,都会包含一堆document
{
"product_id": "1",
"product_name": "长虹电视机",
"product_desc": "4k高清",
"category_id": "3",
"category_name": "电器",
"service_period": "1年"
}
{
"product_id": "2",
"product_name": "基围虾",
"product_desc": "纯天然,冰岛产",
"category_id": "4",
"category_name": "生鲜",
"eat_period": "7天"
}
3、Document(文档-行)
文档(document)是ElasticSearch中的主要实体。对于所有使用ElasticSearch的场景,最终都会归结到对文档的搜索之上。
文档由字段构成,每个字段包含字段和一个或多个字段值(这种情况下,该字段被称为是多值的,即文档中有多个同名字段)。文档之间可能有各自不同的字段集合,文档没有固定的结构或模式。
从客户端的视角来看,文档就是一个json对象。
文档是es中的最小数据单元,一个document可以是一条客户数据,一条商品分类数据,一条订单数据,通常用JSON数据结构表示,每个index下的type中,都可以去存储多个document。
4、Field(字段-列)
Field是Elasticsearch的最小单位。一个document里面有多个field,每个field就是一个数据字段。
product document
{
"product_id": "1",
"product_name": "高露洁牙膏",
"product_desc": "高效美白",
"category_id": "2",
"category_name": "日化用品"
}
字段类型
字符串类型
- text
当一个字段是要被全文搜索的,比如Email内容、产品描述,应该使用text类型。设置text类型以后,字段内容会被分析,在生成倒排索引以前,字符串会被分析器分成一个一个词项。text类型的字段不用于排序,很少用于聚合。 - keyword
keyword类型适用于索引结构化的字段,比如email地址、主机名、状态码和标签。如果字段需要进行过滤(比如查找已发布博客中status属性为published的文章)、排序、聚合。keyword类型的字段只能通过精确值搜索到。
整数类型
| 类型 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|
| byte | -128~127 |
| short | -32768~32767 |
| integer | -231~231-1 |
| long | -263~263-1 |
在满足需求的情况下,尽可能选择范围小的数据类型。比如,某个字段的取值最大值不会超过100,那么选择byte类型即可。迄今为止吉尼斯记录的人类的年龄的最大值为134岁,对于年龄字段,short足矣。字段的长度越短,索引和搜索的效率越高。
浮点类型
| 类型 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|
| doule | 64位双精度IEEE 754浮点类型 |
| float | 32位单精度IEEE 754浮点类型 |
| half_float | 16位半精度IEEE 754浮点类型 |
| scaled_float | 缩放类型的的浮点数 |
对于float、half_float和scaled_float,-0.0和+0.0是不同的值,使用term查询查找-0.0不会匹配+0.0,同样range查询中上边界是-0.0不会匹配+0.0,下边界是+0.0不会匹配-0.0。
其中scaled_float,比如价格只需要精确到分,price为57.34的字段缩放因子为100,存起来就是5734 优先考虑使用带缩放因子的scaled_float浮点类型。
date类型
我们人类使用的计时系统是相当复杂的:秒是基本单位, 60秒为1分钟, 60分钟为1小时, 24小时是一天……如果计算机也使用相同的方式来计时, 那显然就要用多个变量来分别存放年月日时分秒, 不停的进行进位运算, 而且还要处理偶尔的闰年和闰秒以及协调不同的时区. 基于”追求简单”的设计理念, UNIX在内部采用了一种最简单的计时方式:
-
计算从UNIX诞生的UTC时间1970年1月1日0时0分0秒起, 流逝的秒数. -
UTC时间1970年1月1日0时0分0秒就是UNIX时间0, UTC时间1970年1月2日0时0分0秒就是UNIX时间86400. -
这个计时系统被所有的UNIX和类UNIX系统继承了下来, 而且影响了许多非UNIX系统.
日期类型表示格式可以是以下几种:
(1)日期格式的字符串,比如 “2018-01-13” 或 “2018-01-13 12:10:30”
(2)long类型的毫秒数( milliseconds-since-the-epoch,epoch就是指UNIX诞生的UTC时间1970年1月1日0时0分0秒)
(3)integer的秒数(seconds-since-the-epoch)
ElasticSearch 内部会将日期数据转换为UTC,并存储为milliseconds-since-the-epoch的long型整数。
实例 日期格式数据
创建索引
DELETE test
PUT test
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"postdate": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}
写入文档
PUT test/my/1
{
"postdate":"2018-01-13"
}
PUT test/my/2
{
"postdate":"2018-01-01 00:01:05"
}
PUT test/my/3
{
"postdate":"1420077400001"
}
批量查询
GET test/my/_mget
{
"ids":["1","2","3"]
}
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "my",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"postdate": "2018-01-13"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "my",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"postdate": "2018-01-01 00:01:05"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "my",
"_id": "3",
"_version": 2,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"postdate": "1420077400001"
}
}
]
}
boolean类型
逻辑类型(布尔类型)可以接受true/false/”true”/”false”值
- 先删除已经存在的索引,再创建
DELETE test
PUT test
{
"mappings":{
"properties": {
"empty":{"type":"boolean"}
}
}
}
- 添加文档
PUT test/my/1
{
"empty":"true"
}
PUT test/my/2
{
"empty":false
}
- 查看文档
GET test/my/_mget
{
"ids":["1","2"]
}
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "my",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"empty": "true"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "my",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"empty": false
}
}
]
}
binary类型
二进制字段是指用base64来表示索引中存储的二进制数据,可用来存储二进制形式的数据,例如图像。默认情况下,该类型的字段只存储不索引。二进制类型只支持index_name属性。
array类型
在ElasticSearch中,没有专门的数组(Array)数据类型,但是,在默认情况下,任意一个字段都可以包含0或多个值,这意味着每个字段默认都是数组类型,只不过,数组类型的各个元素值的数据类型必须相同。在ElasticSearch中,数组是开箱即用的(out of box),不需要进行任何配置,就可以直接使用。
在同一个数组中,数组元素的数据类型是相同的,ElasticSearch不支持元素为多个数据类型:[ 10, “some string” ],常用的数组类型是:
- 字符数组: [ “one”, “two” ]
- 整数数组: productid:[ 1, 2 ]
- 对象(文档)数组: “user”:[ { “name”: “Mary”, “age”: 12 }, { “name”: “John”, “age”: 10 }],ElasticSearch内部把对象数组展开为
object类型
JSON天生具有层级关系,文档会包含嵌套的对象
DELETE test
PUT test/test
PUT test/my/1
{
"employee":{
"age":30,
"fullname":{
"first":"hadron",
"last":"cheng"
}
}
}
上面文档整体是一个JSON,JSON中包含一个employee,employee又包含一个fullname。
GET test/_mapping
{
"test": {
"mappings": {
"my": {
"properties": {
"employee": {
"properties": {
"age": { "type": "long"},
"fullname": {
"properties": {
"first": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"last": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
ip类型
ip类型的字段用于存储IPv4或者IPv6的地址
(1)创建索引
DELETE test
PUT test
{
"mappings": {
"my":{
"properties": {
"nodeIP":{
"type": "ip"
}
}
}
}
}
查询字段
GET test/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"nodeIP": "192.168.0.0/16"
}
}
}
{
"took": 111,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "my",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"nodeIP": "192.168.1.2"
}
}
]
}
}
5、mapping(映射-约束)
所有文档在写入索引前都将被分析,而映射则存储着所有分析链所需要的全部信息。例如,如何将输入文本分割为词条,哪些词条应该被过滤掉,或哪些附加处理有必要被调用(例如处理HTML标签)等。
数据如何存放到索引对象上,需要有一个映射配置,包括:数据类型、是否存储、是否分词等。
这样就创建了一个名为blog的Index。Type不用单独创建,在创建Mapping 时指定就可以。Mapping用来定义Document中每个字段的类型,即所使用的 analyzer、是否索引等属性,非常关键等。
创建Mapping 的代码示例如下:
client.indices.putMapping({
index : 'blog',
type : 'article',
body : {
article: {
properties: {
id: {
type: 'string',
analyzer: 'ik',
store: 'yes',
},
title: {
type: 'string',
analyzer: 'ik',
store: 'no',
},
content: {
type: 'string',
analyzer: 'ik',
store: 'yes',
}
}
}
}
});
6、Node(节点)
单个的ElasticSearch服务实例被称为节点(node)。大多数情况下,一个ElasticSearch节点就能够满足我们大多数的需求,但是考虑到容错性和数据快速膨胀,我们需要搭建ElasticSearch集群。
ElasticSearch节点可以按用途分为3类。
数据(data)节点:用来存放数据,提供数据的搜索能力。主(master)节点:作为监控节点负责控制其他节点的工作。部落(tribe)节点:负责串联起多个集群,使得我们在多个集群上执行几乎所有可以在单集群ElasticSearch上执行的功能。
7、 Cluster(集群)
多个协同工作的ElasticSearch节点的集合被称为集群(cluster)。
ElasticSearch的分布式属性使得我们可以轻松处理超过单机负载能力的数据量。同时,集群也是一种无间断提供服务的一种解决方案,即便当某些节点因为宕机或执行管理任务(例如升级)不可用时,ElasticSearch几乎是无缝继承了集群功能。
8、分片
ElasticSearch集群允许系统存储的数据总量超过单机容量,为了实现这个功能,ES将数据散布到多个物理的Lucene索引上去,这些Lucene索引被称为分片(shard),散布这些分片的过程叫做分片处理(sharding)。ElasticSearch会自动完成分片工作,对用户来说分片更像是一个大的索引。
当然,除了ElasticSearch自动进行分片处理外,用户为具体的应用进行参数调优也至关重要,因为分片的数量在索引创建时就被配置好了,之后无法改变,除非创建一个新索引并重新索引全部数据。
9、副本
分片处理允许用户推送超过单机容量的数据至ElasticSearch集群。副本(replica)则解决了访问压力过大时单机无法处理所有请求的问题。
实现方法很简单,为每个分片创建冗余的副本,处理查询时可以把这些副本当做最初的主分片(primary shard)使用。
如果主分片所在的主机宕机了,ElasticSearch会自动从该分片的副本中选出一个当做新的主分片,不会中断索引和搜索服务,并且可以在任意时间节点添加或删除副本,可随时调整副本的数量。
重要特性:
-
分布式的实时文件存储,每个字段都被索引并可被搜索
-
实时分析的分布式搜索引擎
-
可以扩展到上百台服务器,处理PB级结构化或非结构化数据

集群(cluster): 由一个或多个节点组成, 并通过集群名称与其他集群进行区分
节点(node): 单个 ElasticSearch 实例. 通常一个节点运行在一个隔离的容器或虚拟机中
索引(index): 在 ES 中, 索引是一组文档的集合
分片(shard): 因为 ES 是个分布式的搜索引擎, 所以索引通常都会分解成不同部分, 而这些分布在不同节点的数据就是分片. ES自动管理和组织分片, 并在必要的时候对分片数据进行再平衡分配, 所以用户基本上不用担心分片的处理细节.
副本(replica): ES 默认为一个索引创建 5 个主分片, 并分别为其创建一个副本分片. 也就是说每个索引都由 5 个主分片成本, 而每个主分片都相应的有一个 copy。对于分布式搜索引擎来说, 分片及副本的分配将是高可用及快速搜索响应的设计核心.主分片与副本都能处理查询请求,它们的唯一区别在于只有主分片才能处理索引请求.副本对搜索性能非常重要,同时用户也可在任何时候添加或删除副本。额外的副本能给带来更大的容量, 更高的呑吐能力及更强的故障恢复能力。
如上图,有集群两个节点,并使用了默认的分片配置. ES自动把这5个主分片分配到2个节点上, 而它们分别对应的副本则在完全不同的节点上。其中 node1 有某个索引的分片1、2、3和副本分片4、5,node2 有该索引的分片4、5和副本分片1、2、3。
索引
基本概念:
索引(indices)-------------------Databases 数据库
类型(type)----------------------Table 数据表
文档(Document)---------------Row 行
字段(Field)---------------------Columns 列
详细说明:
| 概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 索引库(indices) | indices是index的复数,代表许多的索引 |
| 类型(type) | 类型是模拟mysql中的table概念,一个索引库下可以有不同类型的索引,比如商品索引,订单索引,其数据格式不同。不过这会导致索引库混乱,现有最新版本中已经移除这个概念 |
| 文档(document) | 存入索引库原始的数据。比如每一条商品信息,就是一个文档 |
| 字段(field) | 文档中的属性 |
| 映射配置(mappings) | 字段的数据类型、属性、是否索引、是否存储等特性 |
要注意的是:Elasticsearch 本身就是分布式的,因此即便你只有一个节点,Elasticsearch 默认也会对你的数据进行分片和副本操作,当你向集群添加新数据时,数据也会在新加入的节点中进行平衡。
一线公司ES使用场景:
1)新浪ES 如何分析处理32亿条实时日志 http://dockone.io/article/505
2)阿里ES 构建挖财自己的日志采集和分析体系 http://afoo.me/columns/tec/logging-platform-spec.html
3)有赞ES 业务日志处理 http://tech.youzan.com/you-zan-tong-ri-zhi-ping-tai-chu-tan/
4)ES实现站内搜索 http://www.wtoutiao.com/p/13bkqiZ.html
6.2 ES必要的插件
必要的Head、kibana、IK(中文分词)、graph等插件的详细安装和使用。
http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/deep-elasticsearch.html
2)RESTful API接口
常见的增、删、改、查操作实现:
http://blog.csdn.net/laoyang360/article/details/51931981
8.ES遇到问题怎么办?
1)国外:https://discuss.elastic.co/
2)国内:http://elasticsearch.cn/
9、还有吗?
《死磕 Elasticsearch 方法论》:普通程序员高效精进的 10 大狠招!(免费完整版)
https://blog.csdn.net/laoyang360/article/details/79293493
索引 (index)的基本操作
| PUT /dangdang/ | 创建索引 |
|---|---|
| DELETE /dangdang | 删除索引 |
| DELETE /* | 删除所有索引 |
| GET /_cat/indices?v | 查看索引信息 |
创建类型
1 .创建/ddemo 索引并创建(product)类型
curl -X PUT localhost:9200/ddemo -H 'Content-Type:application/json' -d '
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"created": {
"type": "date",
"format": "strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}'
注意:这种方式创建类型要求索引不能存在 否则报错
{"error":{"root_cause":[{"type":"resource_already_exists_exception","reason":"index [ddemo/hzr40uVGQMq2Rbte15uMiw] already exists","index_uuid":"hzr40uVGQMq2Rbte15uMiw","index":"ddemo"}],"type":"resource_already_exists_exception","reason":"index [ddemo/hzr40uVGQMq2Rbte15uMiw] already exists","index_uuid":"hzr40uVGQMq2Rbte15uMiw","index":"ddemo"},
2、添加映射
$ curl -X PUT localhost:9200/demo -H 'Content-Type:application/json' -d '
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"created": {
"type": "date"
}
}
}
}'
Mapping Type: text, keyword, date,integer, long, double, boolean or ip
查看映射:
~$ curl -X GET localhost:9200/weather/_mapping?pretty=true -H 'Content-Type:application/json'
{
"demo" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"created" : {
"type" : "date"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"title" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
}
}
3、索引已存在
增加映射并新增字段create_time:
请求:
PUT secisland3/_mappings
{
"properties": {
"message":{
"type": "text"
},
"city":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"create_time":{
"type": "date"
}
}
}
4、获取映射字段
GET secisland3/_mapping/field/city
{
"secisland3" : {
"mappings" : {
"city" : {
"full_name" : "city",
"mapping" : {
"city" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
创建文档
POST weather/_doc
{
"age":18,
"created_at":"2018 02-12",
"name":"赵形状",
"title":"测试"
}
创建文档 指定 _id
PUT weather/_doc/1
{
"age": 18,
"created_at": "2018 02-12",
"name": "赵形状",
"title": "测试1"
}
获取指定 id 值
GET weather/_doc/1
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 2,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"age": 18,
"created_at": "2018 02-12",
"name": "赵形状",
"title": "测试1"
}
}
查询index全部文档
GET weather/_doc/_search
{
"took": 3,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "0Q2nV3EBML6KlP1euqbR",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"age": 18,
"created_at": "2018 02-12",
"name": "赵形状",
"title": "测试"
}
},
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"age": 18,
"created_at": "2018 02-12",
"name": "赵形状",
"title": "测试1"
}
}
]
}
}
删除操作:
DELETE weather/_doc/1
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 3,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 3,
"_primary_term": 1
}
查看删除之后结果
GET weather/_doc/_search
{
"took": 438,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "0Q2nV3EBML6KlP1euqbR",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"age": 18,
"created_at": "2018 02-12",
"name": "赵形状",
"title": "测试"
}
}
]
}
}
更新文档:
更新文档id 为1的字段 内容
PUT weather/_doc/1
{
"age": 11,
"name": "赵形状1",
"title": "赵形状测试",
"created_at": "2018 02-12"
}
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 7,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 11,
"_primary_term": 1
}
保护已经存在的字段防止覆盖
POST weather/_doc/1/_create
{
"age": 11,
"name": "赵形状1",
"title": "赵形状测试",
"created_at": "2018 02-12"
}
防止字段覆盖
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[1]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [7])",
"index_uuid": "qioxGcVVQIKDDliy72HAdg",
"shard": "0",
"index": "weather"
}
],
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[1]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [7])",
"index_uuid": "qioxGcVVQIKDDliy72HAdg",
"shard": "0",
"index": "weather"
},
"status": 409
}
更新文档的字段
通过脚本更新制定字段,其中ctx是脚本语言中的一个执行对象,先获取_source,再修改content字段
POST weather/_doc/1/_update
{
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.title=\"从官网下载VMware-workstation,双击可执行文件进行安装...\""
}
}
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 8,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 12,
"_primary_term": 1
}
GET weather/_doc/1/
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 8,
"_seq_no": 12,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"age": 11,
"name": "赵形状1",
"title": "从官网下载VMware-workstation,双击可执行文件进行安装...",
"created_at": "2018 02-12"
}
}
添加字段:
POST weather/_doc/1/_update
{
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.title=\"chengyuqiang\""
}
}
删除字段:
POST blog/_doc/1/_update
{
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.remove(\"title\")"
}
}
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 14,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 18,
"_primary_term": 1
}
新获取title已经删除掉
GET weather/_doc/1/
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 14,
"_seq_no": 18,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"age": 11,
"name": "赵形状1",
"created_at": "2018 02-12"
}
}
删除文档
DELETE weather/_doc/1
{
"_index": "weather",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 15,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 19,
"_primary_term": 1
}
bulk 操作
bulk.json
{"index":{}}
{"name":"⼩⿊","age":23,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"为开发团队选择⼀款优秀的MVC框架是件难事⼉,在>众多可⾏的⽅案中决择需要很⾼的经验和⽔平","address":"北 京"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"王⼩⿊","age":24,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"Spring 框架是⼀个分层架构,由 7 个定义良好的
模块组成。Spring 模块构建在核⼼容器之上,核⼼容器定义了创建、配置和管理 bean 的⽅式","address":"上海
"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"张⼩五","age":8,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"Spring Cloud 作为Java 语⾔的微服务框架,它依>赖于Spring Boot,有快速开发、持续交付和容易部署等特点。Spring Cloud 的组件⾮常多,涉及微服务的⽅⽅⾯
⾯,井在开源社区Spring 和Netflix 、Pivotal 两⼤公司的推动下越来越完善","address":"⽆锡"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"win7","age":9,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"Spring的⽬标是致⼒于全⽅位的简化Java开发。这势>必引出更多的解释, Spring是如何简化Java开发的?","address":"南京"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"梅超⻛","age":43,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"Redis是⼀个开源的使⽤ANSI C语⾔编写、⽀持⽹>络、可基于内存亦可持久化的⽇志型、Key-Value数据库,并提供多种语⾔的API","address":"杭州"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"张⽆忌","age":59,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"ElasticSearch是⼀个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。>它提供了⼀个分布式多⽤户能⼒的全⽂搜索引擎,基于RESTfulweb接⼝","address":"北京"}
curl -X PUT localhost:9200/ems/_doc/_bulk -H 'Content-Type:application/json' --data-binary '@bulk.json'
查询字段:
POST ems/emp/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"age": 23
}
}
}

参考该 文件
https://blog.csdn.net/shenkeding9350/article/details/90904908
高级检索:
查询所有
POST ems/emp/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": "desc"
}
]
}
执行结果
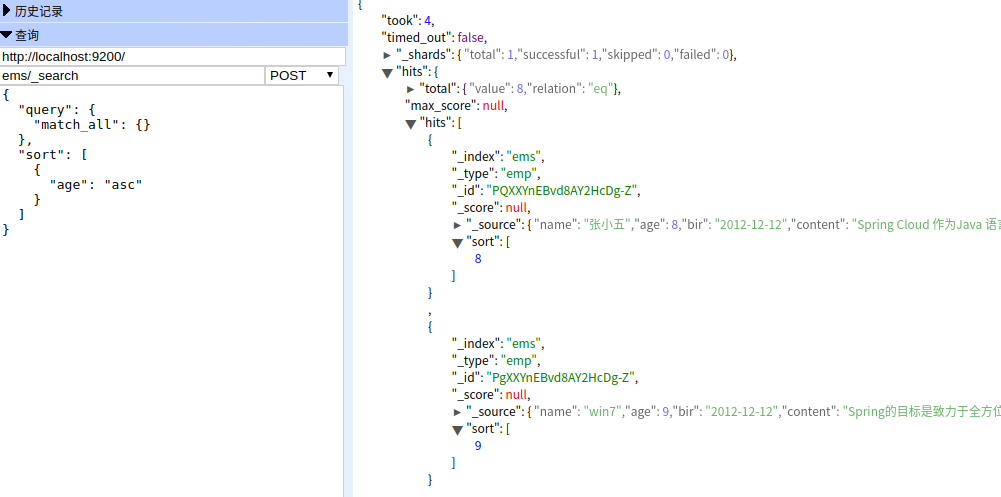
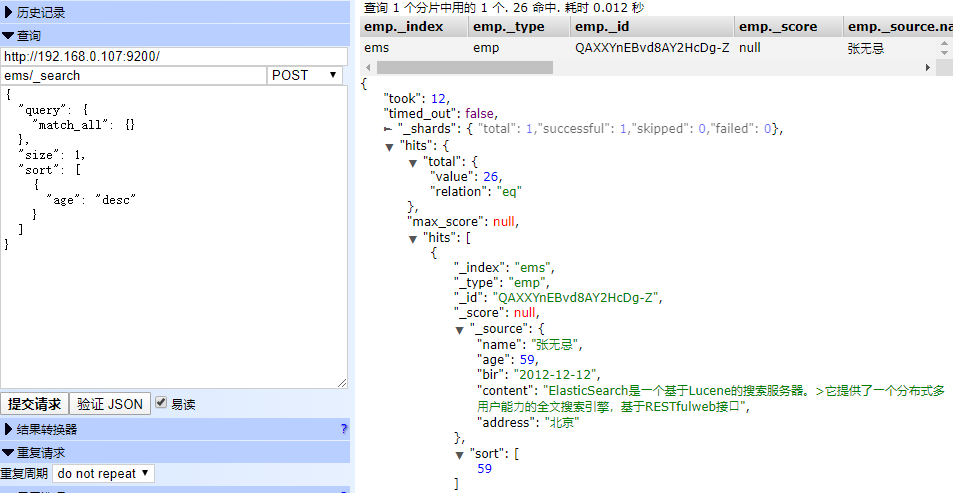
返回指定条数
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 1,
"sort": [
{
"age": "desc"
}
]
}
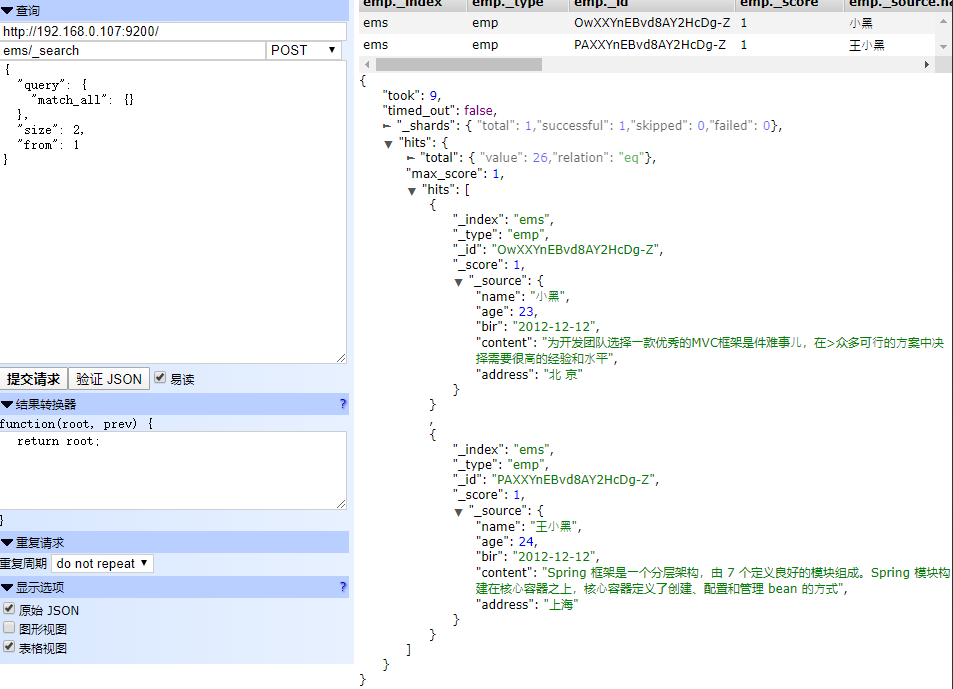
分页查询
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 2,
"from": 1
}
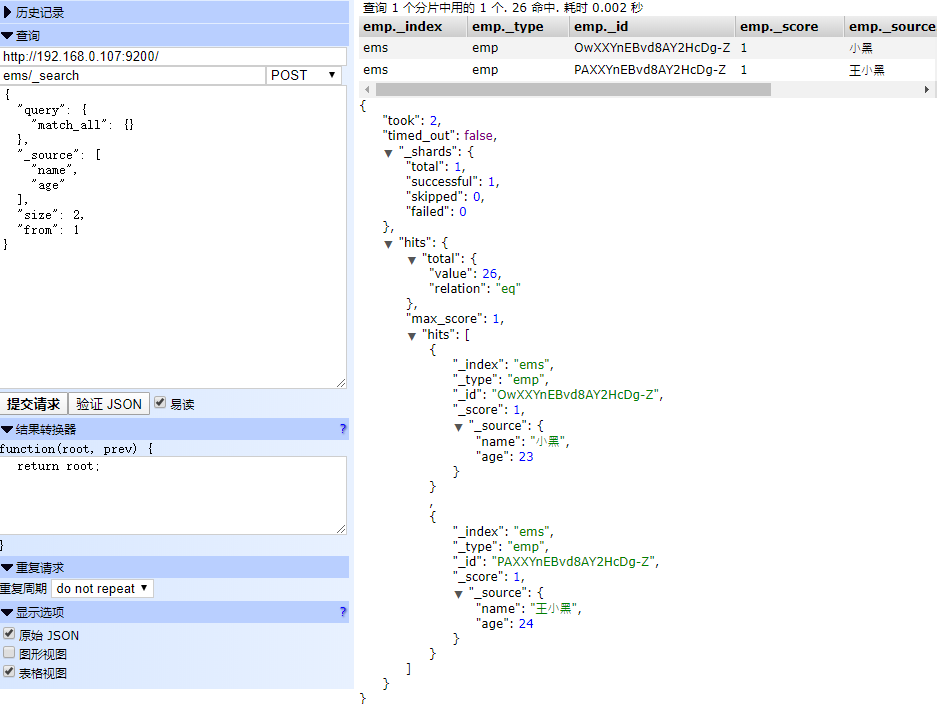
返回指定字段
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": [
"name",
"age"
],
"size": 2,
"from": 1
}
关键词查询 term
NOTE1: 通过使⽤term查询得知ES中默认使⽤分词器为标准分词器(StandardAnalyzer),标准分词器对于英⽂单词分词,对于中⽂单字分词。
NOTE2: 通过使⽤term查询得知,在ES的Mapping Type 中 keyword , date ,integer, long , double , boolean or ip 这些类型不分词,只有text类型分词。
term是代表完全匹配,也就是精确查询,搜索前不会再对搜索词进行分词,所以我们的搜索词必须是文档分词集合中的一个。比如说我们要查找年龄为39的所有文档
关于term
POST ems/_analyze
{
"field": "address",
"text": "baidu info"
}
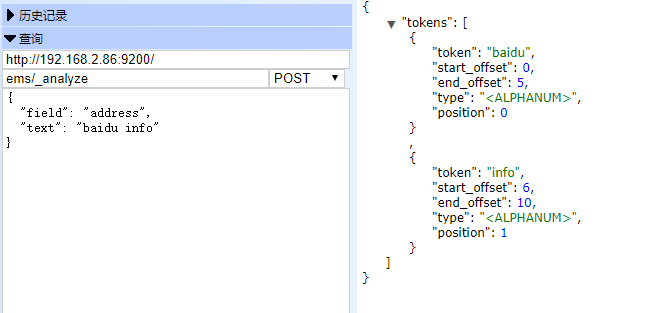
查看分词
POST ems/_analyze
{
"field": "content",
"text": "111赵兴壮 info"
}
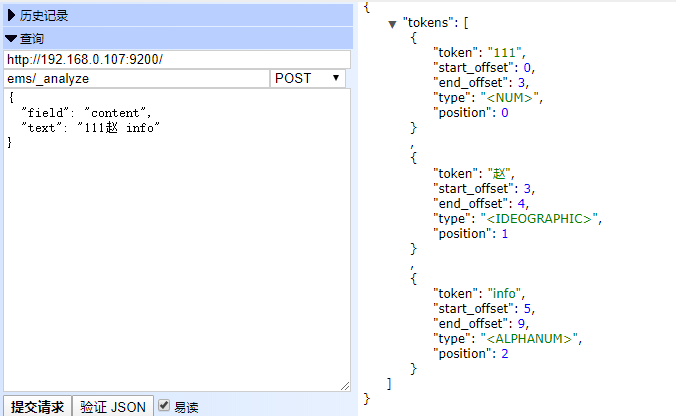
分析原因:
字符串字段可以是文本类型(视为全文,如电子邮件正文)或关键字(视为精确值,如电子邮件地址或邮政编码)。精确值(如数字,日期和关键字) 具有在添加到倒排索引的字段中指定的确切值,以使其可被搜索。
但是,分析文本字段。这意味着它们的值首先通过一个分析器产生一个项目列表,然后将其添加到倒排索引中。
分析文本的方法有很多种:默认的标准分析器会删除大部分的标点符号,将文本分解为单个的单词,并将其分解为小写字母。例如,标准分析仪会将字符串“Quick Brown Fox!”变成[quick,brown,fox]。
text 类型字段会被倒排索引,keyword或精确值 则不会。
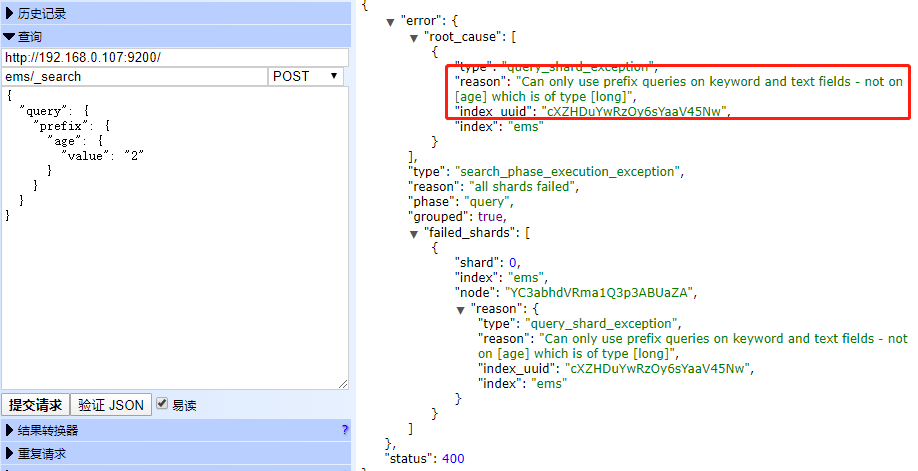
前缀查询
用来检索关键词前缀
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"age": {
"value": "2"
}
}
}
}
尝试在age字段上执行前缀查询报错:前缀查询只能用在 字段类型 和 关键词类型 字段上
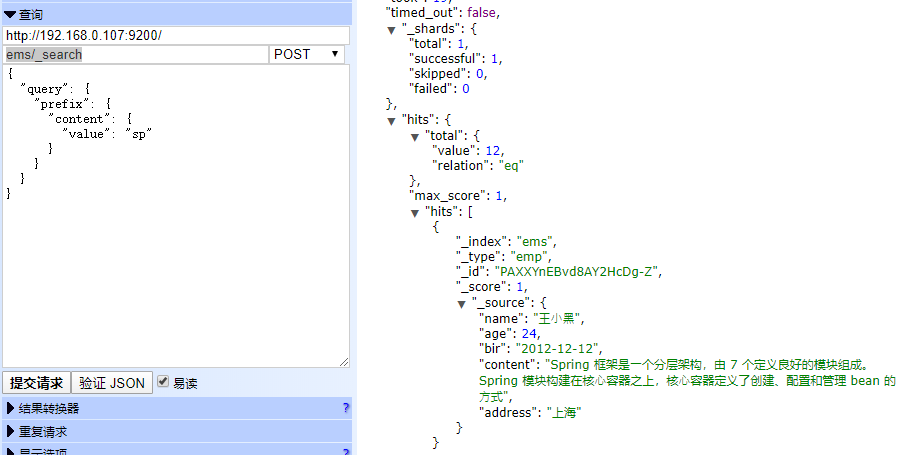
执行以下正确查询
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"content": {
"value": "sp"
}
}
}
}
通配符查询(wildcard)
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"content": {
"value": "re*"
}
}
}
}
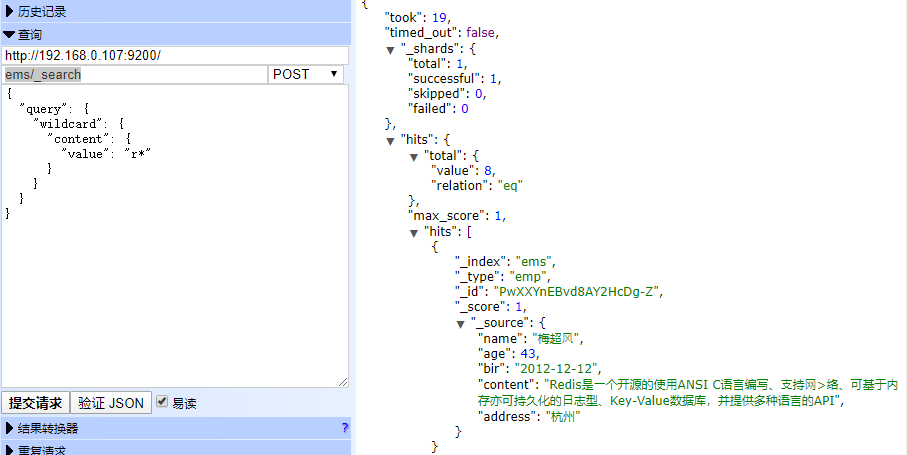
多id查询(ids)
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [
"PwXXYnEBvd8AY2HcDg-Z",
"QAXXYnEBvd8AY2HcDg-Z"
]
}
}
}
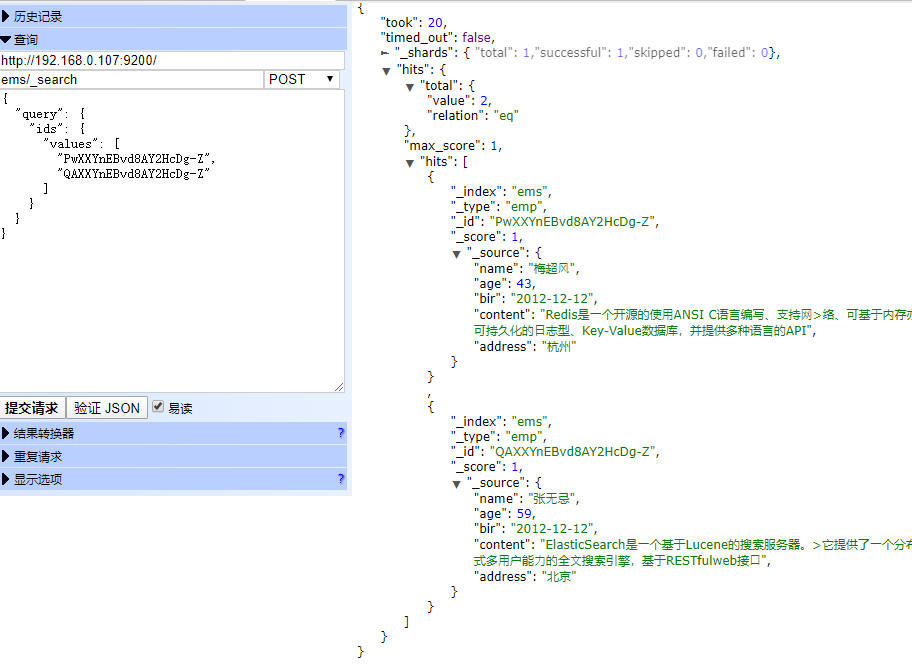
布尔查询(bool)
bool 关键字: ⽤来组合多个条件实现复杂查询 boolb
表达式查询
must: 相当于&& 同时成⽴
should: 相当于|| 成⽴⼀个就⾏
must_not: 相当于! 不能满⾜任何⼀个
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 0,
"lte": 30
}
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"wildcard": {
"content": {
"value": "redi?"
}
}
}
]
}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
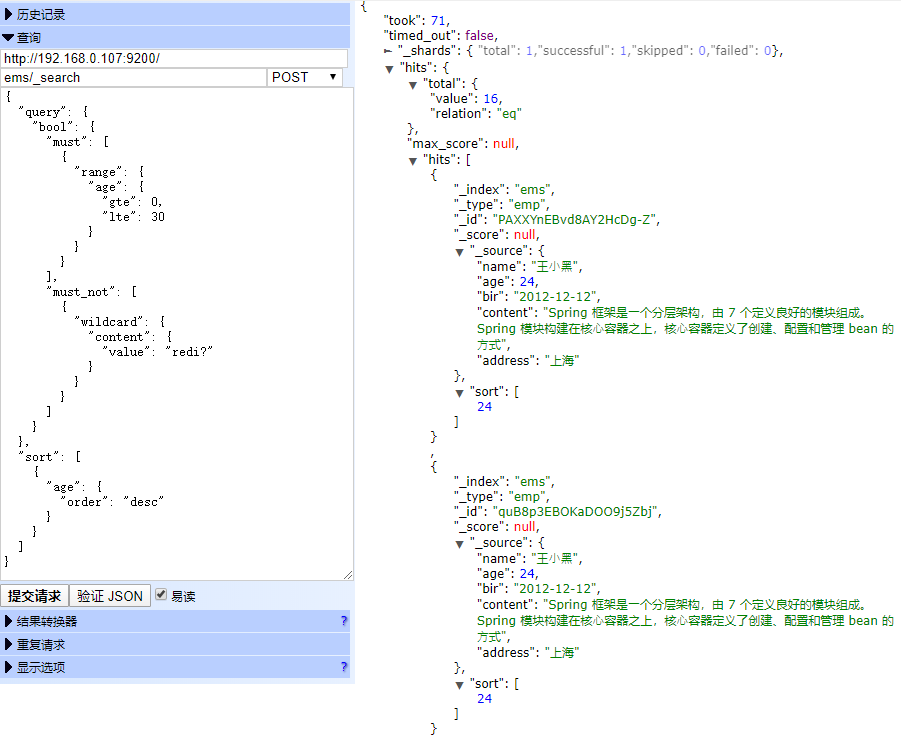
模糊查询(fuzzy)
fuzzy 关键字: ⽤来模糊查询含有指定关键字的⽂档 注 意:允许出现的错误必须在0-2之间
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"content": "开"
}
}
}
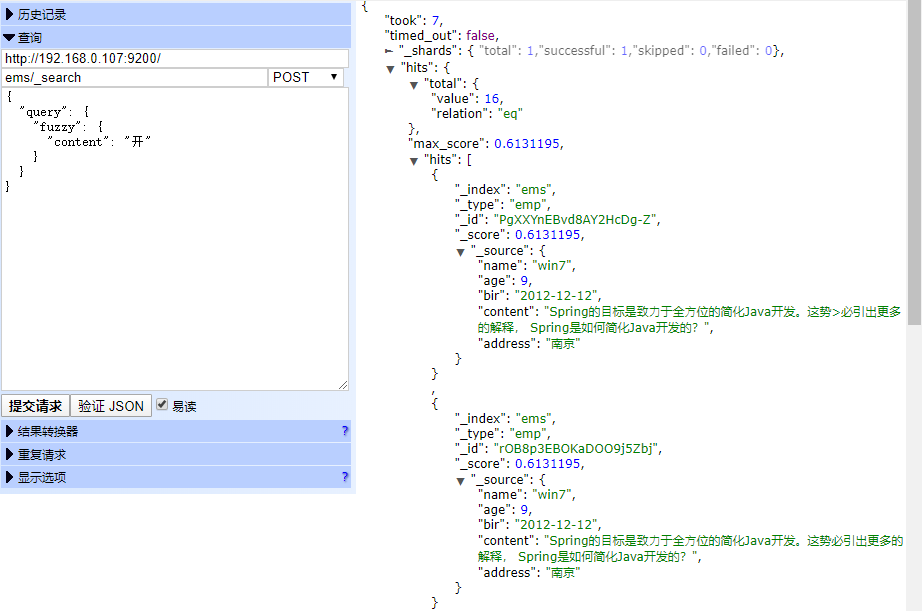
⾼亮查询(highlight)
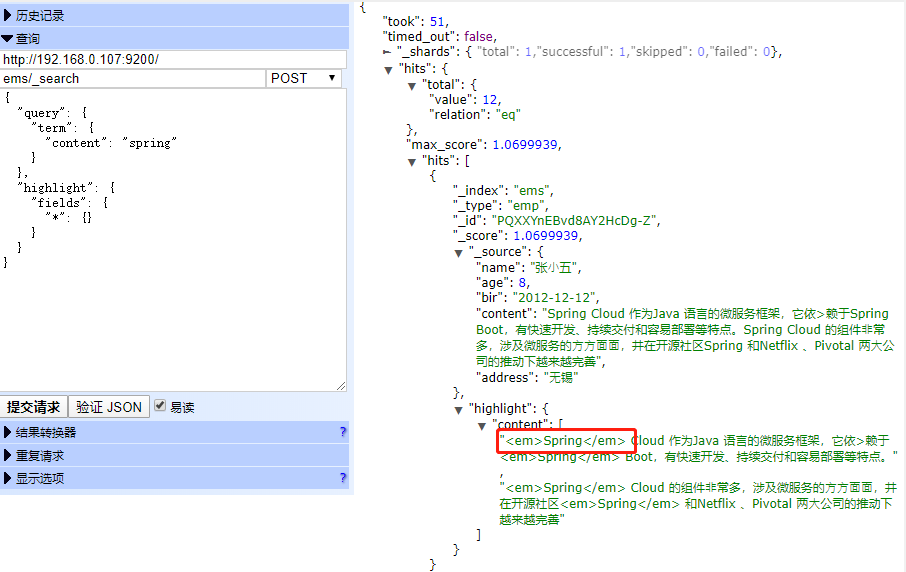
highlight 关键字: 可以让符合条件的⽂档中的关键词⾼亮
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"content": "spring"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"*": {}
}
}
}
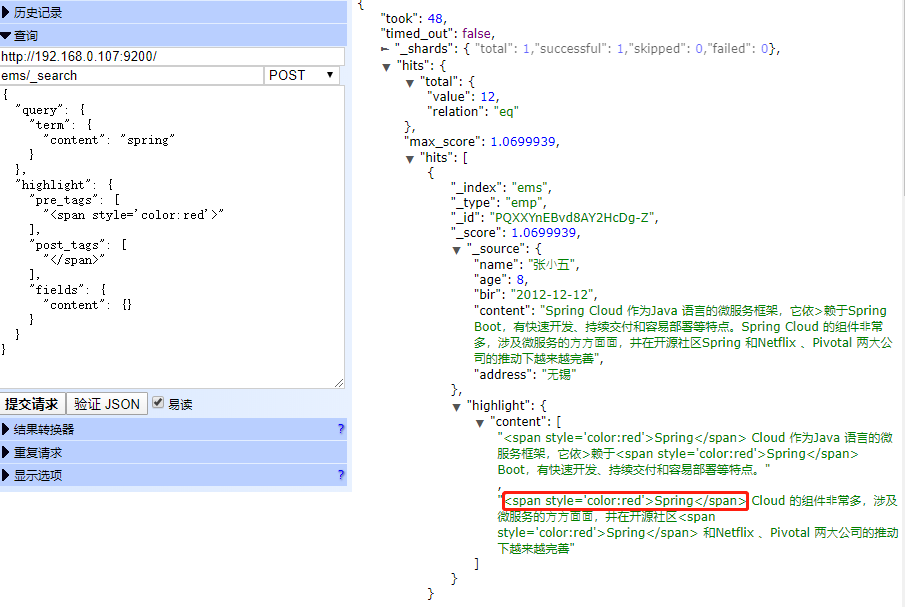
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"content": "spring"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": [
"<span style='color:red'>"
],
"post_tags": [
"</span>"
],
"fields": {
"content": {}
}
}
}
⾃定义⾼亮html标签: 可以在highlight中使⽤ pre_tags 和 post_tags
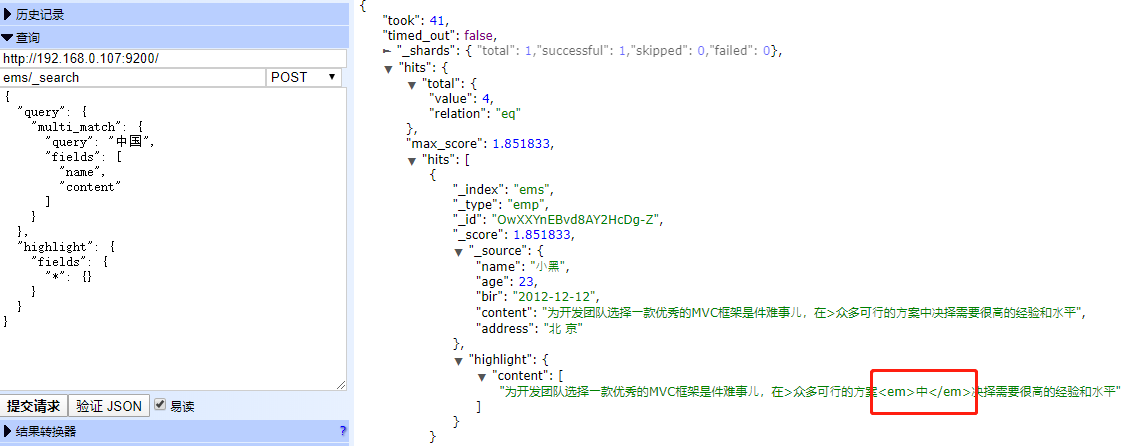
多字段查询(multi_match)
注意:使⽤这种⽅式进⾏查询时,为了更好获取搜索结果,在查询过程中先将查询条件根据当前的分词器分词之后进⾏查询
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "中国",
"fields": [
"name",
"content"
]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"*": {}
}
}
}
多字段分词查询(query_String)
注意:使⽤这种⽅式进⾏查询时,为了更好获取搜索结果,在查询过程中先将查询条件根据当前的分词器分词之后进⾏查询
GET /dangdang/book/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "中国声⾳",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"fields": ["name","content"]
}
}
}
过滤查询 Filter Query
其实准确来说,ES中的查询操作分为2种: 查询(query) 和 过滤(filter) 。 查询即是之前提到的query查询,它 (查询)默认会计算每个返回⽂档的得分,然后根据得分排序 。 ⽽过滤(filter)只会筛选出符合的⽂档,并不计算 得分,且它可以缓存⽂档 。所以,单从性能考虑,过滤⽐查询更快 。
换句话说,过滤适合在⼤范围筛选数据,⽽查询则适合精确匹配数据。⼀般应⽤时, 应先使⽤过滤操作过滤数据, 然后使⽤查询匹配数据。
测试中文分词:
$ curl -X POST 'http://localhost:9200/_analyze?pretty=true' -H 'Content-Type:application/json' -d '
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": [
"我是中国人"
]
}'
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "我",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "是",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "中国人",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
}
]
}
IK分词器
IK 分词
#切换目录
cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.6.2/plugins/
#创建ik文件夹
mkdir ik
#切换到ik文件夹下进行文件上传
cd ik
#对zip进行解压
unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.6.2.zip
NOTE:
IK分词器提供了两种mapping类型⽤来做⽂档的分词分别是 ik_max_word 和 ik_smart ik_smart
ik_max_word 和 ik_smart 什么区别?
- ik_max_word: 会将⽂本做最细粒度的拆分 ,⽐如会将“中华⼈⺠共和国国歌”拆分为“中华⼈⺠共和国,中华⼈⺠,中华,华⼈,⼈⺠共和国,⼈⺠,⼈,⺠,共和国,共和,和,国国,国歌”,会穷尽各种可能的组合;
- ik_smart: 会做最粗粒度的拆分 ,⽐如会将“中华⼈⺠共和国国歌”拆分为“中华⼈⺠共和国,国歌”。
测试数据:
POST ems/emp
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"bir": {
"type": "date"
},
"content": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"address": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
ikdemo.json
{"index":{}}
{"name":"⼩⿊","age":23,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"为开发团队选择⼀款优秀的MVC框架是件难事⼉,在>众多可⾏的⽅案中决择需要很⾼的经验和⽔平","address":"北 京"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"王⼩⿊","age":24,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"Spring 框架是⼀个分层架构,由 7 个定义良好的模块组成。Spring 模块构建在核⼼容器之上,核⼼容器定义了创建、配置和管理 bean 的⽅式","address":"上海"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"张⼩五","age":8,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"Spring Cloud 作为Java 语⾔的微服务框架,它依>赖于Spring Boot,有快速开发、持续交付和容易部署等特点。Spring Cloud 的组件⾮常多,涉及微服务的⽅⽅⾯⾯,井在开源社区Spring 和Netflix 、Pivotal 两⼤公司的推动下越来越完善","address":"⽆锡"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"win7","age":9,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"Spring的⽬标是致⼒于全⽅位的简化Java开发。这势>必引出更多的解释, Spring是如何简化Java开发的?","address":"南京"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"梅超⻛","age":43,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"Redis是⼀个开源的使⽤ANSI C语⾔编写、⽀持⽹>络、可基于内存亦可持久化的⽇志型、Key-Value数据库,并提供多种语⾔的API","address":"杭州"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"张⽆忌","age":59,"bir":"2012-12-12","content":"ElasticSearch是⼀个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。>它提供了⼀个分布式多⽤户能⼒的全⽂搜索引擎,基于RESTfulweb接⼝","address":"北京"}
curl -X PUT localhost:9200/ems/emp/_bulk -H 'Content-Type:application/json' --data-binary '@ikdemo.json'
POST ems/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"content": "框架"
}
}
]
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": [
"<span style='color:red'>"
],
"post_tags": [
"</span>"
],
"fields": {
"content": {}
}
}
}
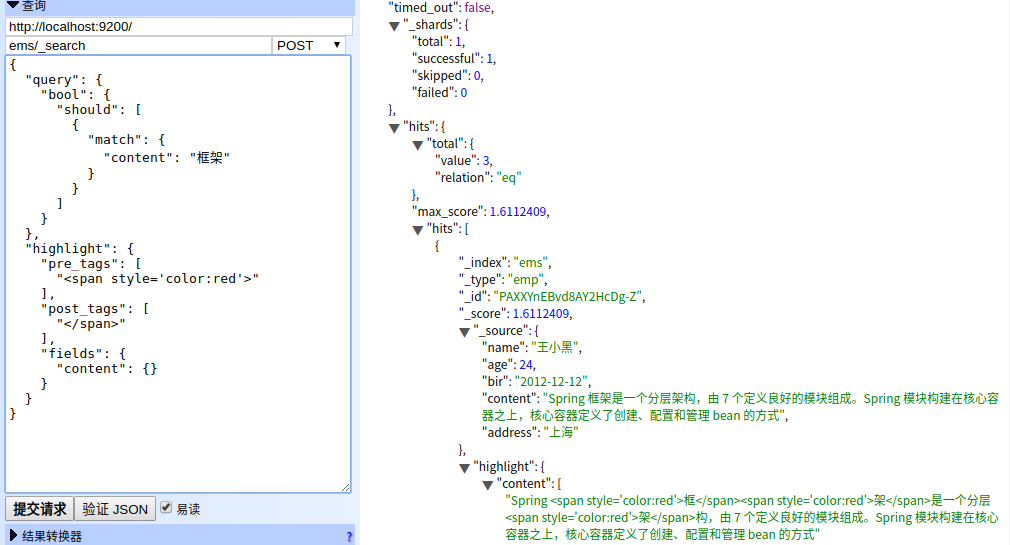
es 聚合:
https://blog.csdn.net/itsoftchenfei/article/details/86100037
命令行操作:
$ curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/weather/person/1' -H 'Content-Type:application/json' -d '{"user":"1","title":"2"}'
$ curl -X POST 'localhost:9200/weather/person/' -H 'Content-Type:application/json' -d '{"user":"1","title":"2"}'
$ curl 'localhost:9200/weather/person/1?pretty=true'
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 197 100 197 0 0 15153 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 15153{
"_index" : "weather",
"_type" : "person",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 3,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"user" : "1",
"title" : "2"
}
}
$ curl 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search?pretty=true'
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 526 100 526 0 0 40461 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 43833{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "index_not_found_exception",
"reason" : "no such index [accounts]",
"resource.type" : "index_or_alias",
"resource.id" : "accounts",
"index_uuid" : "_na_",
"index" : "accounts"
}
],
"type" : "index_not_found_exception",
"reason" : "no such index [accounts]",
"resource.type" : "index_or_alias",
"resource.id" : "accounts",
"index_uuid" : "_na_",
"index" : "accounts"
},
"status" : 404
}
$ curl 'localhost:9200/weather/person/_search?pretty=true' -H 'Content-Type:application/json' -d '
{
"query" : { "match" : { "title" : "2" }}
}'
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 751 100 704 100 47 16761 1119 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 18317{
"took" : 23,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.18232156,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "weather",
"_type" : "person",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.18232156,
"_source" : {
"user" : "1",
"title" : "2"
}
},
{
"_index" : "weather",
"_type" : "person",
"_id" : "i4pOF3EBAViQC_2snA0c",
"_score" : 0.18232156,
"_source" : {
"user" : "1",
"title" : "2"
}
}
]
}
}
知乎专栏 https://www.zhihu.com/people/liang-shen-83-27/posts
开启远程访问:
遇到得问题
http://ip:9200/ 无法访问
vim config/elasticsearch.yml
# 增加
network.host: 0.0.0.0
ERROR: [1] bootstrap checks failed
[1]: the default discovery settings are unsuitable for production use; at least one of [discovery.seed_hosts, discovery.seed_providers, cluster.initial_master_nodes] must be configured
修改
elasticsearch.yml
取消注释保留一个节点
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
beats
beats是一组轻量级采集程序的统称,这些采集程序包括并不限于:
Beats是ELK Stack技术栈中负责单一用途数据采集并推送给Logstash或Elasticsearch的轻量级产品。
- filebeat: 进行文件和目录采集,主要用于收集日志数据。
- metricbeat: 进行指标采集,指标可以是系统的,也可以是众多中间件产品的,主要用于监控系统和软件的性能。
- packetbeat: 通过网络抓包、协议分析,对一些请求响应式的系统通信进行监控和数据收集,可以收集到很多常规方式无法收集到的信息。
- Winlogbeat: 专门针对windows的event log进行的数据采集。
- Heartbeat: 系统间连通性检测,比如icmp, tcp, http等系统的连通性监控。
filebeat
FileBeat是一个轻量级的【日志收集工具】。
官网介绍说,当有几十,几百甚至上千台服务器、容器、虚拟机生成日志时,Filebeat提供一种轻量级简单的方式转发和收集日志。
健壮性
filebeat异常中断重启后会继续上次停止的位置。(通过${filebeat_home}\data\registry文件来记录日志的偏移量)
智能调节传输速度,防止logstash、elasticsearch过载
Filebeat使用压力敏感协议(backpressure-sensitive)来传输数据,在logstash忙的时候,Filebeat会减慢读取-传输速度,一旦logsta恢复,则Filebeat恢复原来的速度。
filebeats 输出 到logstash 中
logstash中配置
#输入如下内容:
input {
beats {
port => "5044"
}
}
# The filter part of this file is commented out to indicate that it is # optional.
# filter {
# }
output
{
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
启动logstash
bin/logstash -f nginx.conf --config.reload.automatic --path.data=/root/
实例:nginx 访问记录 filebeats采集 到 logstash 过滤处理后输出到 elasticsearch:
filebeats filebeat.exe -c nginx.yml -e
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /home/wwwlogs/access.log
#- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\*
tags: ["log"]
fields:
from: nginx
fields_under_root: false
filebeat.config.modules:
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: false
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 1
setup.kibana:
output.logstash:
hosts: ["localhost:5044"]
processors:
- add_host_metadata: ~
- add_cloud_metadata: ~
- add_docker_metadata: ~
- add_kubernetes_metadata: ~
filebeat.exe -c nginx.yml -e
logstash:
input {
beats {
port => "5044"
}
}
# The filter part of this file is commented out to indicate that it is
# optional.
filter {
grok {
patterns_dir => "/usr/local/src/logstash-7.6.2/nginx-patterns"
match => { "message" => "%{NGINX_ACCESS}"}
remove_tag => [ "_grokparsefailure" ]
add_tag => [ "nginx_access" ]
}
}
#output {
# stdout { codec => rubydebug }
#}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => [ "127.0.0.1:9200"],
}
}
nginx-pattern
NGINX_ACCESS %{IPORHOST:remote_addr} - %{USERNAME:remote_user} \[%{HTTPDATE:time_local}\] \"%{DATA:request}\" %{INT:status} %{NUMBER:bytes_sent} \"%{DATA:http_referer}\" \"%{DATA:http_user_agent}\"
bin/logstash -f nginx.conf --config.test_and_exit 测试配置文件
bin/logstash -f nginx.conf --config.reload.automatic --path.data=/root/
kibana
左下角 management 添加索引模式
logstash输出到logstash中 https://www.jianshu.com/p/0b89c07021f4
logstash
简单来说logstash就是一根具备实时数据传输能力的管道,负责将数据信息从管道的输入端传输到管道的输出端;与此同时这根管道还可以让你根据自己的需求在中间加上滤网,Logstash提供里很多功能强大的滤网以满足你的各种应用场景。
logstash常用于日志系统中做日志采集设备,最常用于ELK中作为日志收集器使用
集中、转换和存储你的数据,是一个开源的服务器端数据处理管道,可以同时从多个数据源获取数据,并对其进行转换,然后将其发送到你最喜欢的“存储
数据往往以各种各样的形式,或分散或集中地存在于很多系统中。Logstash 支持各种输入选择 ,可以在同一时间从众多常用来源捕捉事件。能够以连续的流式传输方式,轻松地从您的日志、指标、Web 应用、数据存储以及各种 AWS 服务采集数据。
input {
beats {
port => "5044"
}
}
# The filter part of this file is commented out to indicate that it is
# optional.
filter {
grok {
patterns_dir => "/usr/local/src/logstash-7.6.2/nginx-patterns"
match => { "message" => "%{NGINX_ACCESS}"}
remove_tag => [ "_grokparsefailure" ]
add_tag => [ "nginx_access" ]
}
}
#output {
# stdout { codec => rubydebug }
#}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => [ "127.0.0.1:9200"],
}
}
logstash 模板
Kibana
kibana 安装: https://juejin.im/entry/59f9220df265da431d3bfdc3
Kibana在6.7版本以上,支持了多种语言。并且自带在安装包里。
vim config/kibana.yml
# 将默认配置改成如下:
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.2.41:9200"
kibana.index: ".kibana"
开启方式:
找到Kibana配置文件所在:/YOUR_KIBANA_PATH/kibana/config/kibana.yml。
找到配置:i18n.locale: "en" 并将en修改为zh-CN(简体中文)。重启即可。
注意版本一致
Kibana是世界上最受欢迎的开源日志分析平台ELK Stack中的“K” ,它为用户提供了一个工具,用于在存储于Elasticsearch集群中的日志数据进行检索,可视化和构建仪表板。
Grafana是一个开源可视化工具,可以在各种不同的数据存储上使用,但最常用的是Graphite,InfluxDB,以及Elasticsearch等.
两个可视化工具之间的关键区别源于它们的目的。Grafana旨在分析和可视化系统CPU,内存,磁盘和I / O利用率等指标。Grafana不允许全文数据查询。另一方面,Kibana运行在Elasticsearch之上,主要 用于分析日志消息。
总结
Kibana和Grafana都是强大的可视化工具。但是,它们的核心是用于不同的数据类型和用例。Grafana与时间序列数据库(如Graphite或InfluxDB)是用于度量分析的组合,而Kibana是流行的ELK Stack的一部分,用于探索日志数据。
这两个平台都是不错的选择,有时甚至可以相互补充。如上所述,大量组织将使用这两种工具作为其整体监控堆栈的一部分。

赞助我写出更好的博客



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
2014-05-13 php 异常捕获
2014-05-13 php 设置报错等级
2014-05-13 php stripslashes() addslashes() 解析
2014-05-13 php中magic_quotes_gpc函数详解