C语言讲义——链表的实现
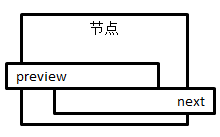
节点(结构体描述)
struct Node {
int _id;
char s[50];
struct Node* pre;// 指向前一个节点的地址
struct Node* next;// 指向下一个节点的地址
};
新建节点(开辟内存空间)
参数: 为新节点id字段赋值
返回值:新节点的地址(指针)
struct Node* node_new(int id) {
struct Node* q = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
memset(q, 0, sizeof(struct Node));
q->_id = id;
return q;
}
添加节点
如果只有一个节点,不用添加
在最后追加节点
/*
* 为链表追加节点(加在最后)
* 参数:头节点,需要追加的节点
* 返回值:无
*/
void chain_add(struct Node* qFirst, struct Node* qAdd) {
// 定位到链表头
struct Node* q = qFirst;
// 只要后面(next)有节点,往后找;直到没有next的节点(最后一个)
for(q; q->next != NULL; q=q->next ) {
node_print(q);
}
// 此时定位在最后一个节点,下图1
// 将新节点加在最后节点的后面(next)
q->next = qAdd;// 下图2
qAdd->pre = q;//下图3
}
图1 定位到最后的节点:
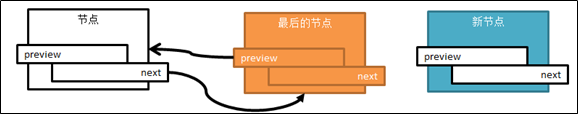
图2 最后节点的next指向新节点:
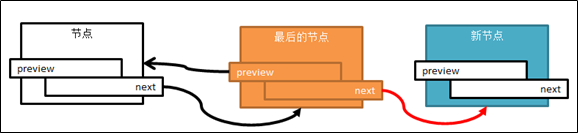
图3 新节点的preview指针指向(前)最后节点:

计算链表中节点的个数
/*
* 获取链表长度(即节点的个数)
* 参数:头节点
* 返回值:链表长度
*/
int chain_count(struct Node* qFirst) {
if (qFirst == NULL) {
// 头节点都没有,长度为0
return 0;
}
int i = 0;
// 遍历链表
struct Node* q = qFirst;
for(q; q != NULL; q=q->next) {
// 顺藤摸瓜,直到最后一个节点
i++;// 找到一个就+1
}
return i;
}
获取节点(仿数组按序号查找,从0开始)
struct Node* chain_get(struct Node* qFirst, int index) {
printf("---获取index = %d的节点:", index);
int i = 0;
// 遍历链表
struct Node* q = qFirst;
for(q; q!= NULL; q=q->next,i++ ) {
if (index == i) {
return q;
}
}
return NULL;
}
打印节点
void node_print(struct Node* q) {
if (NULL == q) {
puts("节点打印:空节点,无可打印");
return;
}
printf("---id = %2d---", q->_id);
printf("preview = %10d ", q->pre);
printf("【address = %10d】 ", q);
printf("next = %10d\n", q->next);
}
打印链表
void chain_print(struct Node* qFirst) {
if (qFirst == NULL) {
puts("没有元素可以打印");
return;
}
puts("----------↓↓↓打印链表------------");
// 遍历链表
struct Node* q;
for(q = qFirst; q != NULL; q=q->next ) {
node_print(q);
}
puts("----------↑↑↑打印链表------------");
}
删除节点
自定义函数:释放空间
节点指针是要置空的,在函数中改指针的指向,需要使用二级指针
void node_free(struct Node** q) {
if( *q != NULL) {
printf("free %d\n",(*q)->_id);
free(*q);
*q = NULL;
}
}
删除节点
图4 删除头结点
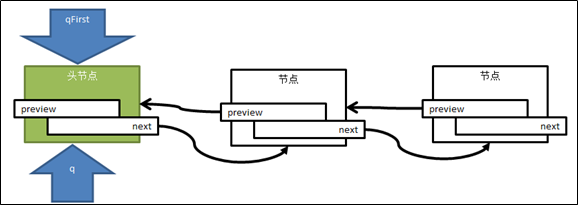
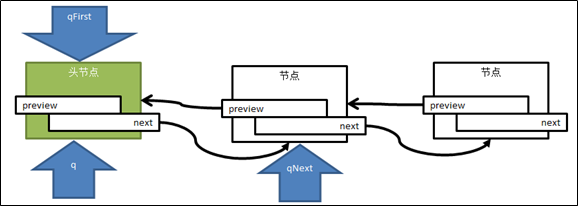
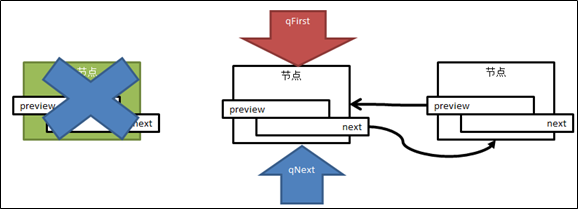
图5 删除中间节点

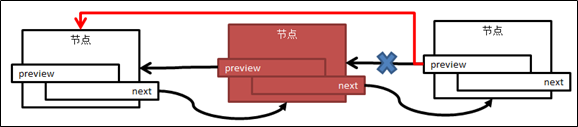
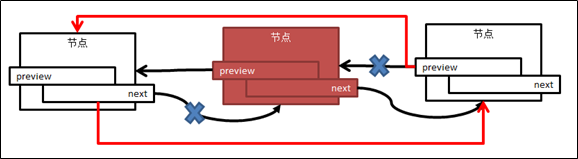

图6 删除尾节点
1.定位到尾节点,找到其前一节点(倒数第二个节点,即将来的尾节点)
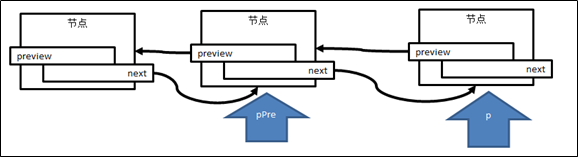
2.倒数第二节点的next节点置空
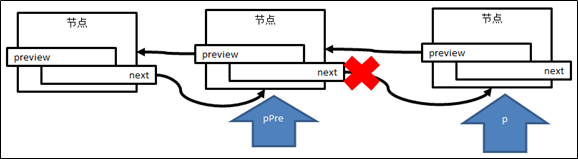
3.释放掉最后的节点
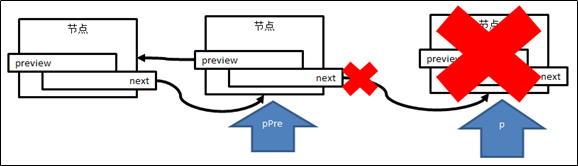
/*
* 删除节点
* 参数:1.头结点 2.待删除的结点
* 因为被删除的结点需要置空,所以需要使用二级指针
* 返回值:-1 删除失败/0 删除成功
*/
int chain_remove(struct Node** qFirst, struct Node** qRemove) {
struct Node* qPre = NULL;
struct Node* qNext = NULL;
struct Node* q = *qFirst;
// 1.输入Check
if(NULL == *qRemove){
puts("删无可删!");
return -1;
}else{
printf("删除节点:id=%d\n", (*qRemove)->_id);
}
// 2.删除头结点,特殊对待
if(*qFirst == *qRemove ) {
if((*qFirst)->next == NULL){
// 就一个头结点的场合
node_free(qFirst);
}else{
qNext = q->next;
node_free(qFirst);
*qFirst = qNext;
}
return 0;
}
// 3.遍历链表
for(q; q != NULL; q=q->next ) {
if (q == *qRemove) {
qPre = q->pre;
qNext = q->next;
if (qNext!=NULL) {
qNext->pre = qPre;
qPre->next= qNext;
} else {
// 尾节点的场合
qPre->next= NULL;
}
node_free(qRemove);
return 0;
}
}
}
清空链表
void chain_clear(struct Node** qFirst) {
puts("\n----------Clear------------");
if (qFirst == NULL) {
puts("已经是空");
return;
}
// 遍历链表
// 不断删除第一个元素
while(*qFirst != NULL) {
chain_remove(qFirst,qFirst);
}
}





