C语言讲义——文件操作
fopen( ) 函数:创建一个新的文件或者打开一个已有的文件
FILE *fopen( const char * filename, const char * mode );
关于参数mode的取值
| r | 读 |
|---|---|
| w | 写(无文件则创建)(从头写) |
| a | 写(无文件则创建)(追加) |
| r+ | 读写 |
| w+ | 读写。如果文件存在,则截断为零长度,如果文件不存在,则创建一个新文件。 |
| a+ | 从头读,追加写(无文件则创建) |
| 读 | 写 | 新建 | 从头 | 追加 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | ○ | ○ | |||
| w | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||
| a | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||
| r+ | ○ | ○ | |||
| w+ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| a+ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
写文件示例
#include <stdio.h>
int fileWrite() {
FILE *fp = NULL;
fp = fopen("test.txt", "a+");
if(NULL == fp) {
// 将文件设为"只读",可测此处代码
puts("fopen出错");
// 使用perror()显示错误信息
perror("fopen() Err");
return -1;
}
fprintf(fp, "云想衣裳花想容,春风拂槛露华浓。\n");
fputs("若非群玉山头见,会向瑶台月下逢。\n", fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
main() {
fileWrite();
}
读文件示例
#include <stdio.h>
int fileRead() {
FILE *fp = NULL;
char buff[255];
fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if(NULL == fp) {
perror("fopen Error");
return -1;
}
fscanf(fp, "%s", buff);
printf("读取到空白字符: %s\n", buff );
fgets(buff, 255, (FILE*)fp);
printf("读取一行: %s\n", buff );
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
main() {
fileRead();
}
偏移
fp = fopen(g_sFile, "r");
// int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int fromwhere);
// 第一个参数stream为文件指针
// 第二个参数offset为偏移量,整数表示正向偏移,负数表示负向偏移
// 第三个参数origin设定从文件的哪里开始偏移,可能取值为:SEEK_CUR、 SEEK_END 或 SEEK_SET
// SEEK_SET:文件开头(0)
// SEEK_CUR:当前位置(1)
// SEEK_END:文件结尾(2)
// 定位成功:返回0
// 定位失败:返回非0
fseek(fp,1,SEEK_CUR);
示例:修改指定人员的成绩记录
现有成绩文件: data.dat
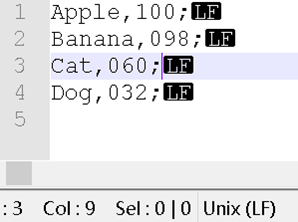
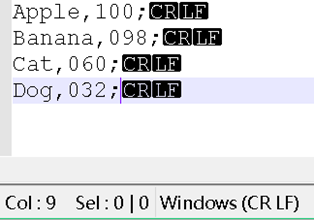
Apple,100;
Banana,098;
Cat,060;
Dog,032;
修改Cat的成绩为59分,即[Cat,060;]→[Cat,059;]前后内容都不变
为了方便定位,约定成绩都是3位字符表示
SEEK_CUR版
偏移数值问题——Unix和Windows不同
Unix(不算LF):fseek(fp, -4, SEEK_CUR)
Windows(算CR LF):fseek(fp, -6, SEEK_CUR)
SEEK_SET版
即使使用SEEK_SET从头找,找到上一行尾,再加,也有区别:
Unix:fseek(fp, nCurLen+4, SEEK_SET);
WIndows:fseek(fp, nCurLen+6, SEEK_SET);
结论:CRLF在内存中是不同的,所以fseek的参数有差别;但是反映在字符串上,都是一个\n(ASCII 10),比如第一行,strlen都是11
参考代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int updateFile() {
int nRet = 0;
FILE * fp = NULL;
fp = fopen("data.dat", "r+");// r+:读写
if (NULL == fp) {
perror("fopen() Err");
return 0;
}
// 读取文件
char buff[1024]= {0};
while(fgets(buff, 1024, fp)) {
// char *strstr(char *str1, const char *str2);
// 判断字符串str2是否是str1的子串。
// 是:返回str2在str1中首次出现的地址;
// 否:返回NULL
if(strstr(buff, "Cat") != NULL) {
//此时"光标"在读到的内容后面
int nSeek = fseek(fp, -6, SEEK_CUR);
if(nSeek != 0) {
perror("fseek");
break;
} else {
// 修改文件
fprintf(fp, "%s", "059");
nRet = 1;
break;
}
}
}
// 无果:关闭文件
fclose(fp);
return nRet;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
updateFile();
return 0;
}
应用:读写log
#include <stdio.h>
#include <io.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <direct.h>
enum Level { DEBUG, INFO, WARING, ERROR};
const char* g_sDir = "temp";
const char* g_sFile = "temp/info.txt";
void getTime(char* sTime_o) {
time_t _time;
time(&_time);
struct tm *p =localtime(&_time);
// 格式化,并写入到字符串中
sprintf(sTime_o, "%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
p->tm_year+1900,
p->tm_mon + 1,
p->tm_mday,
p->tm_hour,
p->tm_min,
p->tm_sec);
}
int makeDir() {
// access:判断文件或文件夹是否存在
// <io.h>
// F_OK:判断是否存在
// success:0
// fault:-1
if (access(g_sDir, F_OK ) == 0) {
// 文件夹存在
} else {
// _mkdir:创建文件夹
// <direct.h>
// success:0
// fault:-1
if (_mkdir(g_sDir) == -1) {
printf("创建文件夹失败");
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int logWrite(Level lvl, char*msg) {
// 获取时间
char sTime_o[200];
getTime(sTime_o);
//-------------------------
// 创建log文件夹
if(makeDir() == -1) {
return -1;
}
// 打开文件
FILE *fp = NULL;
fp = fopen(g_sFile, "a+");
if(NULL == fp) {
printf("无法打开文件%s\n", g_sFile);
return -1;
}
// 根据log级别,写入log
if (lvl == DEBUG) {
fprintf(fp, "%s [DEBUG] %s\n",sTime_o,msg);
} else if(lvl == INFO) {
fprintf(fp, "%s [INFO] %s\n",sTime_o,msg);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
int logRead() {
FILE *fp = NULL;
fp = fopen(g_sFile, "r");
if(NULL == fp) {
puts("文件读取失败");
return -1;
}
//TEST: 当前位置右移1
fseek(fp,1,SEEK_CUR);
// 读取文件
char buff[255] = {0};
while(fgets(buff, 255, (FILE*)fp)!=NULL) {
printf("> %s", buff );
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
main() {
// 能写,才读;不写,不读
if (logWrite(INFO,"郭德纲") == 0) {
logRead();
}
}



