Java基础教程——String类
String类
Java程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 "abc" )都是String的实例
字符串是常量(因为 String 对象是不可变的,所以可以共享)
字符串的本质是字符数组:private final char value[];
创建字符串常用的方式
public class CreateString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 直接定义字符串
String str1 = "虎老狮";
// new 字符串
String str2 = new String("Java");
// 字符数组→字符串
char[] arrChar = { 'A', 'n', 'd', 'y' };
String str3 = new String(arrChar);
// 字节数组→字符串
byte[] arrByte = { 97, 98 };
String str4 = new String(arrByte);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println(str3);
System.out.println(str4);
}
}
字符串的比较
public class 字符串比较 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "奎木狼";
String s2 = "奎木狼";
String s3 = new String("奎木狼");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s1 == s3);
}
}
解析:
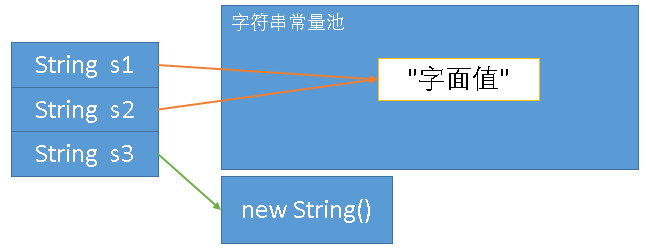
采用字面值创建的字符串存放在常量池中(constant pool),同样内容的字符串对象指向同一个字符串对象。
常量池中的字符串,无则创建,有则直接使用。
字符串常量池:
相当于缓存,可以使得程序运行更快
以前在方法区,JDK 1.7之后,移到堆内存区(暂时不理解Java虚拟机内存知识的话,这句话直接无视)
new String()在运行时创建字符串对象,不在常量池中,因此s3和s1、s2不是同一个对象。
关于使用==进行比较判断:
|--基本类型,数值比较(只要求值相等,类型可以不同)
|--引用类型,地址比较(只有指向同一个对象才返回true)
public class 双等号基本类型 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 97;
double b = 97.0;
char c = 'a';
System.out.println(a == b);// true
System.out.println(c == b);// true
}
}
equals方法
String类提供equals方法进行字符串比较。
看下这个方法的源码:
地址相等的时候,直接就判为相等。地址不相等时,长度不等的直接判为不相等;长度相等时,一个一个字符比较。
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
应用:
public class 字符串比较 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "奎木狼";
String s2 = "奎木狼";
String s3 = new String("奎木狼");
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println(s3.equals("奎木狼"));// 不推荐,可能空指针异常
System.out.println("奎木狼".equals(s3));// 推荐
}
}
推荐使用字符串字面值调用equals方法,即使用"...".equals(...),因为引号中的字符串字面值一定不会为null,调用方法不会出现空指针异常。
但是很多时候,无法确定其是否为null(比如调用equals方法的对象是从别处传入的参数)。
如果不能确定调用equals的对象必不为null,就需要在调用之前先做null判断。
if (s3 != null) {
boolean equals = s3.equals(s2);
System.out.println(equals);
}
或者使用Objects类提供的equals方法进行比较。Objects类从JAVA 1.7开始提供,可以防止空指针异常。
String s1 = "奎木狼";
String s2 = "奎木狼";
String s3 = new String("奎木狼");
boolean equals = Objects.equals(s2, s3);
System.out.println(equals);// true
更多字符串比较方法:
| boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) | 判断字符串anotherString是否与当前字符串相等,忽略大小写形式 |
| int compareTo(String anotherString) | 根据ASCII码比较字符串anoterString和当前字符串的大小,比较方式类似于C语言中的strcmp函数 |
| boolean startsWith(String prefix) | 判断当前字符串是否以字符串prefix为开头 |
| boolean endsWith(String suffix) | 判断当前字符串是否以字符串suffix为后缀 |
public class Test字符串比较 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "ABC";
System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase("abc"));// equalsIgnoreCase比较重要
System.out.println(str1.compareTo("ABB"));// 1
System.out.println(str1.compareTo("ABC"));// 0
System.out.println(str1.compareTo("ABD"));// -1
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("AB"));// T
System.out.println(str1.endsWith("C"));// T
}
}
字符串变量重新赋值,其实原字符串内容不变,只是变量中引用的地址变了。
因此,后面讲的字符串拼接、替换、去空格等操作都会得到新的字符串。
public class 字符串变内容不变 {
// 说明:System.identityHashCode(Onject):不同对象,此结果必不同
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "黄袍怪";
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s1));
s1 = "奎木狼";// s1保存的是地址值,之前的字符串对象没变,只是s1的地址变了
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s1));
String s2 = "黄袍怪";
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s2));
}
}
字符串提取
| char charAt(int index) | 从指定位置提取单个字符,该位置由index(索引值)指定 |
| String substring(int index) | 提取从index指定的位置开始的部分字符串 |
| String substring(int begin, int end) | 提取 begin 和 end 位置之间的部分字符串 |
| String concat(String str) | 连接两个字符串,并新建一个包含调用字符串的字符串对象 |
| String replace (char oldChar, char newChar) | 将字符串中出现oldChar指定的字符全部替换为newChar指定的字符 |
| replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | 将字符串中匹配regex的字符串全部都替换为replacement指定的字符 |
| String trim() | 去除字符串前后的空格,得到的是一个新的字符串。 |
public class Test提取字符串 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "《西游记》中,如来为什么要传经?";
String str2 = new String("普度众生,一个都不能放过!");
System.out.println("------------查找--------------");
int _index = 2;
char _c = str1.charAt(_index);
System.out.println("charAt " + _index + ":" + _c);
System.out.println("------------substring--------------");
String _subStr = str1.substring(_index);
System.out.println("substring(" + _index + "):" + _subStr);
int _begin = 2, _end = 9;
_subStr = str1.substring(_begin, _end);
System.out.println("substring(" + _begin + "," + _end + "):" + _subStr);
System.out.println("------------拼接--------------");
System.out.println("concat:" + str1.concat(str2));
System.out.println("String + String:" + str1 + str2);
System.out.println("------------替换--------------");
char oldC = '西', newC = '东';
String _newString = str1.replace(oldC, newC);
System.out.println("replace(" + oldC + "," + newC + ") :" + _newString);
String _tar = "记", _repl = "释厄转";
_newString = str1.replace(_tar, _repl);
System.out.println("replace(" + _tar + "," + _repl + "):" + _newString);
_newString = "tel:10086".replaceAll("\\d", "*");
System.out.println("replaceAll(数字→*):" + _newString);
System.out.println("------------去空格--------------");
String s = " A B C ".trim();
System.out.println("trim:【" + s + "】");
}
}
字符串转为其它格式
| byte[] getBytes() | 将字符串转为byte数组(即字符串在内存中保存的最原始的二进制形态) |
| char[] toCharArray() | 将字符串转为字符数组,类似于C语言中字符串的保存形式 |
public class Test字符串转化 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] b;
b = "Hello Java".getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
System.out.print("【" + b[i] + " " + (char) b[i] + "】");
}
System.out.println("-------------------------");
char[] c;
c = "Hello Java".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
System.out.print(" " + c[i]);
}
}
}
字符串转为字符串数组形式(.split(...)):
public class StringSplit {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] sArr = "01,天魁星,呼保义,宋江".split(",");
for (String s : sArr) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
StringBuiler和StringBuffer
StringBuiler/StringBuffer表示可变的字符序列(即可变的字符串)
使用“+运算符”连接字符串将创建新的字符串,频繁修改字符串时,一般使用StringBuilerh或StringBuffer类以提高效率。
public class StringB {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("诸");
sb.append("葛");
sb.append("孔");
sb.append("明");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
解析:String的值是final的,因此字符串底层的存储数组是不变的,每次append都创建对象。
private final char value[];
StringBuilder的值不是final的
char[] value;// 在抽象类AbstractStringBuilder中定义
| StringBuilder类 | |
|---|---|
| 构造方法() | 构造方法:创建一个空的StringBuffer对象 |
| 构造方法(String str) | 构造方法:根据字符串str的内容创建StringBuffer对象 |
| append(x) | 添加内容:类型不限 |
| insert(int index, x) | 插入:将x插入到索引为index的位置,x可以为任何类型的数据 |
| delete(int start, int end) | 删除:从start位置开始,直到end指定的索引位置 |
| deleteCharAt(int index) | 删除:index指定的索引处的字符 |
| setCharAt(int index, char ch) | 替换:使用ch指定的新值替换 index指定的位置上的字符 |
| replace(int start, int end, String str) | 替换:从start指定的位置开始替换,直到 end 指定的位置结束 |
| reverse() | 字符序列倒置 |
| length() | 长度 |
| String toString() | 转换为字符串类型 |
public class TestStringBuXXX {
static void m最常用方法() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 【.length()】
System.out.println("length():" + sb.length());
// 【.append()】
sb.append("ABC,");
sb.append(true);
// 【.toString()】
System.out.println("append():" + sb.toString());
// 链式编程:append方法返回的就是自身,可以继续append
sb.append("青狮").append("白象").append("大鹏鸟");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
// 【转置:.reverse()】
sb.reverse();
System.out.println("转置:" + sb.toString());
// 【清空:.setLength(0)】
sb.setLength(0);
System.out.println("清空:" + sb.toString());
}
static void m其它常用方法() {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("ABCDEFGHI");
System.out.println("---插入---");
sb.insert(2, "123");
System.out.println("|--insert():" + sb);
System.out.println("---删除---");
sb.delete(2, 2 + 3);
System.out.println("|--delete():" + sb);
sb.deleteCharAt(2);
System.out.println("|--deleteCharAt():" + sb);
System.out.println("---替换---");
sb.setCharAt(2, '*');
System.out.println("|--setCharAt():" + sb);
sb.replace(1, 1 + 4, "#@");
System.out.println("|--replace():" + sb);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
m最常用方法();
m其它常用方法();
}
}
*StringBuffer和StringBuilder用法上一样,StringBuilder适用于单线程环境,效率较高。
*StringBuffer是JDK 1.5新增的。
例:回文
写一个方法,判断某句话是不是回文(英文不区分大小写)。
如:Able was I ere I saw Elba
如:假似真时真似假
public class 回文 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "Able was I ere I saw Elba";
check(s);
s = "假似真是真似假";
check(s);
}
static void check(String s) {
String sLower = s.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(sLower);
StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer(sLower);
s2.reverse();
System.out.println(s2);
if (sLower.equals(s2.toString())) {
System.out.println("是回文");
} else {
System.out.println("不是回文");
}
}
}
*扩展·MessageFormat
java.text.MessageFormat
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestMessageFormat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String template = "姓名:{0},年龄:{1},时间:{2}";
String s = MessageFormat.format(template, "陈玄奘", 28, new Date());
System.out.println(s);
System.out.printf("姓名:%s,年龄:%d,时间:%s", "陈玄奘", 28, new Date());
}
}



