ABP 数据访问 - IRepository 仓储
ABP系列,这个系列来的比较晚,很多大佬其实已经分析过,为什么现在我又来一轮呢?
1.想自己来完整的学习一轮ABP
2.公司目前正在使用ABP,准备迁移Core
基于以上的目的,开始这个系列 😁
ABP IRepository
先上 IRepository 类图结构
只是描述了类的关联关系,很多成员并不准确 😄
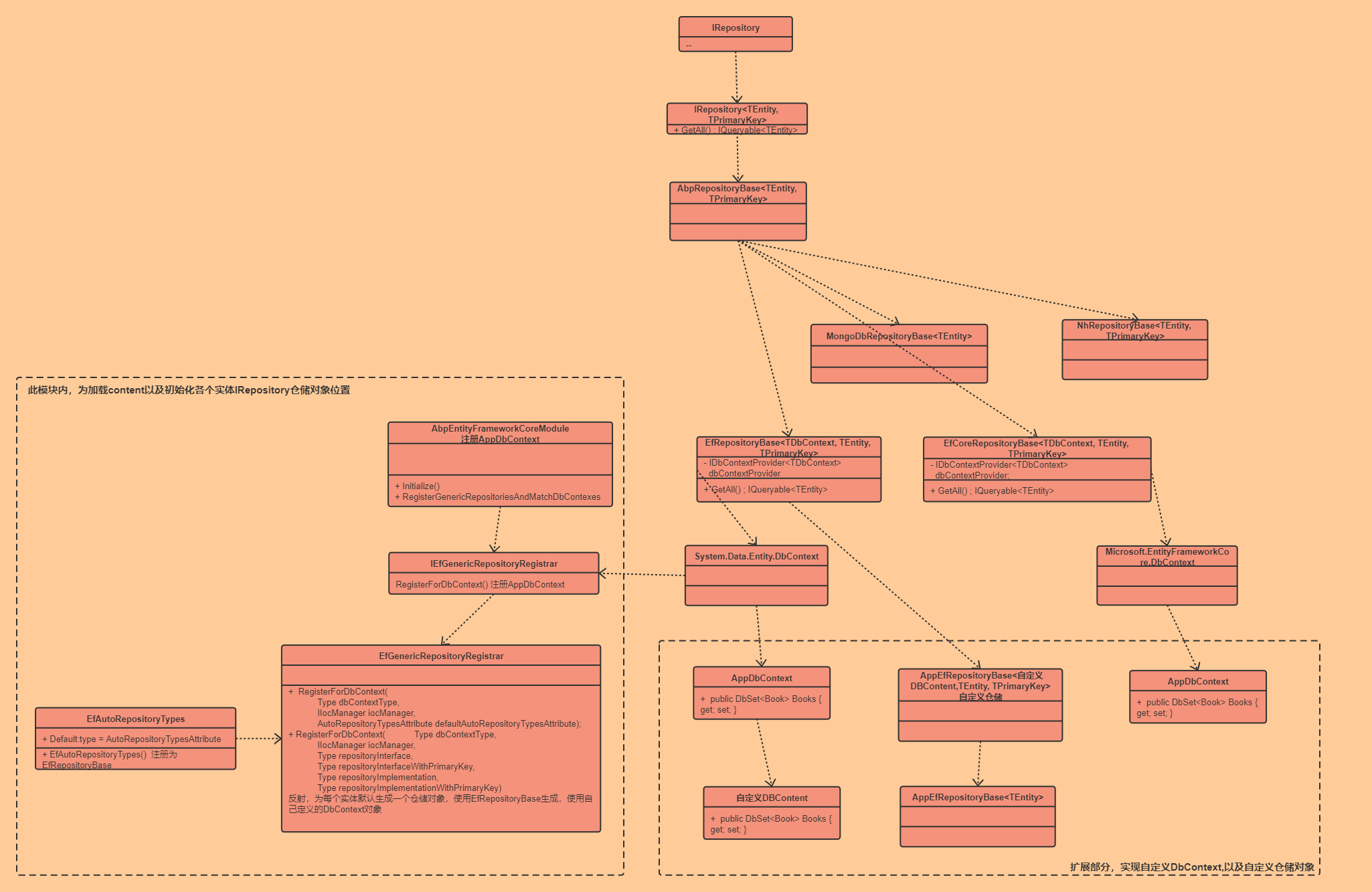
基于这个类图,我们再来分析下ABP的仓储访问;
1.IRepository 整体结构
按照我的理解,可以简单分为三部分;
1.整体接口以及抽象父类定义
2.自定义DbContext,Repository,实体
3.自动注册实体仓储
1.整体接口以及抽象父类定义
这部分内容整体包含在IRepository,IRepository<TEntity,TprimaryKey>,AbpRepositoryBase中,也就是图中为包含在虚线框的内容;
IRepository:仓储的接口,接口中未定义方方法
IRepository<TEntity, TPrimaryKey> :定义仓储对象的相关查询方法,GetAll(),Get()等方法
AbpRepositoryBase<TEntity, TPrimaryKey> :抽象类,封装了一些公共方法但是并未有具体实现,实现留在了具体的调用层,例如 EF,EfCore,Dapper等
接口实现
EfCoreRepositoryBase<TDbContext, TEntity, TPrimaryKey> :
实现AbpRepositoryBase<TEntity, TPrimaryKey>
1.EFCore的内部核心查询全部就依赖于 DbContext,DbSet来操作数据;
2.EFCore的DbContext引用来源Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContext,而Ef的DbContext依赖引用System.Data.Entity.DbContext,Core的底层依赖就全部替换了
AbpDbContext :ABP默认的EFCore的DBContext封装,包含一些公共方法,要在ABP框架下使用DbContext,需要继承 AbpDbContext
2.自定义DbContext,Repository,实体
实现DBContext:
public class SampleAppDbContext : AbpZeroDbContext<Tenant, Role, User, SampleAppDbContext>, IAbpPersistedGrantDbContext
{
public DbSet<PersistedGrantEntity> PersistedGrants { get; set; }
public DbSet<Advertisement> Advertisements { get; set; }
public DbSet<Blog> Blogs { get; set; }
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
public DbSet<Category> Categories { get; set; }
public DbSet<Comment> Comments { get; set; }
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
public DbSet<ProductTranslation> ProductTranslations { get; set; }
public DbSet<Author> Authors { get; set; }
public DbSet<Store> Stores { get; set; }
public DbSet<Order> Orders { get; set; }
public DbSet<OrderTranslation> OrderTranslations { get; set; }
public DbSet<UserTestEntity> UserTestEntities { get; set; }
public DbSet<Country> Countries { get; set; }
public SampleAppDbContext(DbContextOptions<SampleAppDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.ConfigurePersistedGrantEntity();
modelBuilder.Entity<Blog>().OwnsOne(x => x.More);
modelBuilder.Entity<Blog>().OwnsMany(x => x.Promotions, b =>
{
b.WithOwner().HasForeignKey(bp => bp.BlogId);
b.Property<int>("Id");
b.HasKey("Id");
b.HasOne<Blog>()
.WithOne()
.HasForeignKey<BlogPromotion>(bp => bp.AdvertisementId)
.IsRequired();
});
modelBuilder.Entity<Advertisement>().OwnsMany(a => a.Feedbacks, b =>
{
b.WithOwner().HasForeignKey(af => af.AdvertisementId);
b.Property<int>("Id");
b.HasKey("Id");
b.HasOne<Comment>()
.WithOne()
.HasForeignKey<AdvertisementFeedback>(af => af.CommentId);
});
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().ToTable("Books");
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().Property(e => e.Id).ValueGeneratedNever();
modelBuilder.Entity<Store>().Property(e => e.Id).HasColumnName("StoreId");
}
}
}
DbContext中需要定义实体的DBSet,因为数据操作都是基于DbSet来完成
个性化仓储:
第一步,设置自定义仓储接口
public interface IPostRepository : IRepository<Post, Guid>
{
}
这里继承IRepository<Entity,PrimaryKey>,说明实体主键并非Int类型,所以需要重新实现
第二步,继承 EfCoreRepositoryBase,实现自定义仓储方法
public class PostRepository : EfCoreRepositoryBase<BloggingDbContext, Post, Guid>,
IPostRepository
{
public PostRepository(IDbContextProvider<BloggingDbContext> dbContextProvider)
: base(dbContextProvider)
{
}
public override int Count()
{
throw new Exception("can not get count of posts");
}
}
第三步,注册自定义仓储,注册代码写在自定义模块中
注意:自定义模块的注册必须依赖 AbpEntityFrameworkCoreModule 模块先注册 ❓ 这里留着后面来解释,为什么一定要依赖
//Custom repository
Configuration.ReplaceService<IRepository<Post, Guid>>(() =>
{
IocManager.IocContainer.Register(
Component.For<IRepository<Post, Guid>, IPostRepository,
PostRepository>()
.ImplementedBy<PostRepository>()
.LifestyleTransient()
);
});
3.自动注册实体仓储
首先来看下,我们定义好DbContext后,如果使用自己的仓储服务呢?
在类里面定义属性仓储
private readonly IRepository<EntityDynamicParameter> _entityDynamicParameterRepository;
大家有没有考虑过,为什么我们可以直接使用实体的仓储类,在哪里实例化的呢? 这是ABP自动完成的,会反射获取所有的实体服务,并自动为其注册仓储服务,我们一起来分析下自动注册的内容
AbpEntityFrameworkCoreModule.cs
public override void Initialize()
{
IocManager.RegisterAssemblyByConvention(typeof(AbpEntityFrameworkCoreModule).GetAssembly());
IocManager.IocContainer.Register(
Component.For(typeof(IDbContextProvider<>))
.ImplementedBy(typeof(UnitOfWorkDbContextProvider<>))
.LifestyleTransient()
);
RegisterGenericRepositoriesAndMatchDbContexes();
}
调用 RegisterGenericRepositoriesAndMatchDbContexes 方法
private void RegisterGenericRepositoriesAndMatchDbContexes()
{
var dbContextTypes =
_typeFinder.Find(type =>
{
var typeInfo = type.GetTypeInfo();
return typeInfo.IsPublic &&
!typeInfo.IsAbstract &&
typeInfo.IsClass &&
typeof(AbpDbContext).IsAssignableFrom(type);
});
if (dbContextTypes.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
Logger.Warn("No class found derived from AbpDbContext.");
return;
}
using (IScopedIocResolver scope = IocManager.CreateScope())
{
foreach (var dbContextType in dbContextTypes)
{
Logger.Debug("Registering DbContext: " + dbContextType.AssemblyQualifiedName);
scope.Resolve<IEfGenericRepositoryRegistrar>().RegisterForDbContext(dbContextType, IocManager, EfCoreAutoRepositoryTypes.Default);
IocManager.IocContainer.Register(
Component.For<ISecondaryOrmRegistrar>()
.Named(Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N"))
.Instance(new EfCoreBasedSecondaryOrmRegistrar(dbContextType, scope.Resolve<IDbContextEntityFinder>()))
.LifestyleTransient()
);
}
scope.Resolve<IDbContextTypeMatcher>().Populate(dbContextTypes);
}
}
1.首先加载所有的AbpDbContext
2.对AbpDbContext循环进行注册
这里的注册依赖接口
scope.Resolve().RegisterForDbContext(dbContextType, IocManager, EfCoreAutoRepositoryTypes.Default);
我们来看下这个具体实现逻辑,依赖接口 IEfGenericRepositoryRegistrar
EfGenericRepositoryRegistrar.cs
public void RegisterForDbContext(
Type dbContextType,
IIocManager iocManager,
AutoRepositoryTypesAttribute defaultAutoRepositoryTypesAttribute)
{
var autoRepositoryAttr = dbContextType.GetTypeInfo().GetSingleAttributeOrNull<AutoRepositoryTypesAttribute>() ?? defaultAutoRepositoryTypesAttribute;
RegisterForDbContext(
dbContextType,
iocManager,
autoRepositoryAttr.RepositoryInterface,
autoRepositoryAttr.RepositoryInterfaceWithPrimaryKey,
autoRepositoryAttr.RepositoryImplementation,
autoRepositoryAttr.RepositoryImplementationWithPrimaryKey
);
if (autoRepositoryAttr.WithDefaultRepositoryInterfaces)
{
RegisterForDbContext(
dbContextType,
iocManager,
defaultAutoRepositoryTypesAttribute.RepositoryInterface,
defaultAutoRepositoryTypesAttribute.RepositoryInterfaceWithPrimaryKey,
autoRepositoryAttr.RepositoryImplementation,
autoRepositoryAttr.RepositoryImplementationWithPrimaryKey
);
}
}
private void RegisterForDbContext(
Type dbContextType,
IIocManager iocManager,
Type repositoryInterface,
Type repositoryInterfaceWithPrimaryKey,
Type repositoryImplementation,
Type repositoryImplementationWithPrimaryKey)
{
foreach (var entityTypeInfo in _dbContextEntityFinder.GetEntityTypeInfos(dbContextType))
{
var primaryKeyType = EntityHelper.GetPrimaryKeyType(entityTypeInfo.EntityType);
if (primaryKeyType == typeof(int))
{
var genericRepositoryType = repositoryInterface.MakeGenericType(entityTypeInfo.EntityType);
if (!iocManager.IsRegistered(genericRepositoryType))
{
var implType = repositoryImplementation.GetGenericArguments().Length == 1 ? repositoryImplementation.MakeGenericType(entityTypeInfo.EntityType) : repositoryImplementation.MakeGenericType(entityTypeInfo.DeclaringType,
entityTypeInfo.EntityType);
iocManager.IocContainer.Register(
Component
.For(genericRepositoryType)
.ImplementedBy(implType)
.Named(Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N"))
.LifestyleTransient()
);
}
}
var genericRepositoryTypeWithPrimaryKey =
repositoryInterfaceWithPrimaryKey.MakeGenericType(entityTypeInfo.EntityType,primaryKeyType);
if (!iocManager.IsRegistered(genericRepositoryTypeWithPrimaryKey))
{
var implType =
repositoryImplementationWithPrimaryKey.GetGenericArguments().Length == 2? repositoryImplementationWithPrimaryKey.MakeGenericType(entityTypeInfo.EntityType, primaryKeyType) : repositoryImplementationWithPrimaryKey.MakeGenericType(entityTypeInfo.DeclaringType, entityTypeInfo.EntityType, primaryKeyType);
iocManager.IocContainer.Register(
Component
.For(genericRepositoryTypeWithPrimaryKey)
.ImplementedBy(implType)
.Named(Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N"))
.LifestyleTransient()
);
}
}
}
来分析下具体的实现逻辑
foreach (var entityTypeInfo in _dbContextEntityFinder.GetEntityTypeInfos(dbContextType))
_dbContextEntityFinder.GetEntityTypeInfos(dbContextType) 这里获取的就是DbContext定义的实体DbSet,从而获取到每个实体,用来做后续的仓储注入;例如:获取到了 PersonEntity
var primaryKeyType = EntityHelper.GetPrimaryKeyType(entityTypeInfo.EntityType);
获取实体主键
if (primaryKeyType == typeof(int))
判断主键是否为int,如果是int,则继承 IRepository
那是通过什么类来实现的IRepository呢?
public static AutoRepositoryTypesAttribute Default { get; }
static EfCoreAutoRepositoryTypes()
{
Default = new AutoRepositoryTypesAttribute(
typeof(IRepository<>),
typeof(IRepository<,>),
typeof(EfCoreRepositoryBase<,>),
typeof(EfCoreRepositoryBase<,,>)
);
}
这是默认的实体继承的仓储类,EfCoreRepositoryBase 类
好了,实体的默认仓储就介绍完毕了。。。 😔 不对啊,这里可以满足我们的DbContext里面所有的实体,但是万一有了自定义仓储呢?怎么注册自己的仓储呢?
哈哈,其实还是有个方法的,而且还不只一个。。。
1.DbContext打标记,用来替换默认的AutoRepositoryTypesAttribute
[AutoRepositoryTypes(
typeof(IMyModuleRepository<>),
typeof(IMyModuleRepository<,>),
typeof(MyModuleRepositoryBase<>),
typeof(MyModuleRepositoryBase<,>)
)]
public class SupportDbContext : AbpDbContext
2.第二种就是替换已经注册的实体仓储服务
回到上面问题,AbpEntityFrameworkCoreModule 模块先注册 ? 其实上面写到了,在我们自定义的模块注册时,可以重新注册仓储服务
//Custom repository
Configuration.ReplaceService<IRepository<Post, Guid>>(() =>
{
IocManager.IocContainer.Register(
Component.For<IRepository<Post, Guid>, IPostRepository,
PostRepository>()
.ImplementedBy<PostRepository>()
.LifestyleTransient()
);
});
就是要必须在 AbpEntityFrameworkCoreModule 注册之后,否则就会被覆盖哦,这里也就呼应了上面的问题了
仓储三要素:
- 仓储的生命周期:仓储都是临时性的,需要的时候创建,用完销毁。
- 数据库的连接和管理仓储的方法中,数据库的连接和管理都是由ABP框架自动处理的。当方法被调用的时候,ABP自动开启数据库的连接同时开启事务,当方法结束后,ABP会将实体数据保存,然后断开连接。当在仓储方法中调用仓储方法的时候,此时只会创建一个数据库连接,他们共同享用数据库连接和事务,由最上层的那个仓储方法进行管理。
- 仓储的最佳实践在ABP框架初始化的时候已经为每一个实体类都默认的实现了相应的仓储,这些仓储里的方法基本可以满足日常的开发需求,所以不要自己手动创建仓储





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理