栈和队列的一些练习

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<stack>//pop,top,push #include<vector> using namespace std; class TwoStacks { public: vector<int> twoStacksSort(vector<int> numbers) { stack<int> sta; for(vector<int>::reverse_iterator riter=numbers.rbegin();riter!=numbers.rend();riter++) { //cout<<*riter<<endl; sta.push(*riter); } StackSort(sta); vector<int> res; while(!sta.empty()) { res.push_back(sta.top()); sta.pop(); } return res; } void StackSort(stack<int> &sta) { //help从栈低到栈顶始终保持升序 stack<int> help; while(!sta.empty()) { int res=sta.top(); sta.pop(); if(help.empty()||res<=help.top()) help.push(res); else { while(!help.empty()&&res>help.top()) { sta.push(help.top()); help.pop(); } help.push(res); } } while(!help.empty()) { sta.push(help.top()); help.pop(); } } }; int main() { int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5}; TwoStacks A; vector<int> arr(a,a+5),res; res=A.twoStacksSort(arr); for(vector<int>::iterator iter=res.begin();iter!=res.end();iter++) cout<<*iter<<" "; return 0; }

思路:


#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<stack>//pop,top,push #include<vector> using namespace std; class StackReverse { public: vector<int> reverseStack(vector<int> A, int n) { stack<int> sta; int i; for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--) sta.push(A[i]); revStack(sta); vector<int> res; while(!sta.empty()) { res.push_back(sta.top()); sta.pop(); } return res; } void revStack(stack<int> &A) { if(A.empty()) return; int res1=Get(A); revStack(A); A.push(res1); } int Get(stack<int> &A) { if(A.empty()) exit(-1); int res1=A.top(); A.pop(); if(A.empty()) return res1; else { int res2=Get(A); A.push(res1); return res2; } } }; int main() { int a[4]={4,3,2,1}; vector<int> arr(a,a+4),res; StackReverse A; res=A.reverseStack(arr,4); for(vector<int>::iterator iter=res.begin();iter!=res.end();iter++) cout<<*iter<<" "; return 0; }

思路:


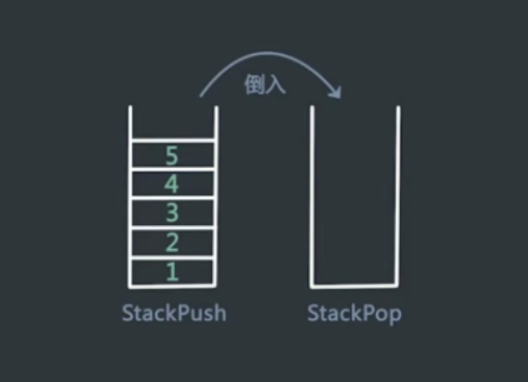
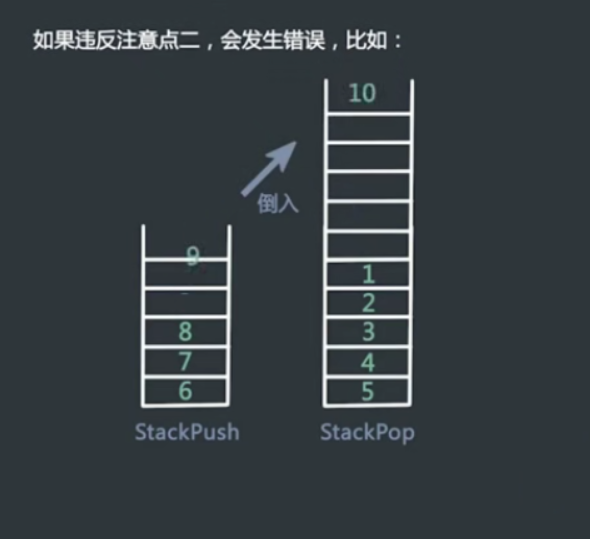
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<stack>//pop,top,push #include<vector> using namespace std; class TwoStack { public: stack<int> stack_push,stack_pop; vector<int> twoStack(vector<int> ope, int n) { vector<int> res; int i; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { if(ope[i]>0) push(ope[i]); if(ope[i]==0) res.push_back(pop()); if(ope[i]<0) exit(-1); } return res; } void push(int value) { stack_push.push(value); } int pop() { if(stack_pop.empty()) while(!stack_push.empty()) { stack_pop.push(stack_push.top()); stack_push.pop(); } int res=stack_pop.top(); stack_pop.pop(); return res; } }; int main() { int a[6]={1,2,3,0,4,0}; vector<int> arr(a,a+6); TwoStack A; vector<int> res=A.twoStack(arr,6); for(vector<int>::iterator iter=res.begin();iter!=res.end();iter++) cout<<*iter<<" "; return 0; }

思路:

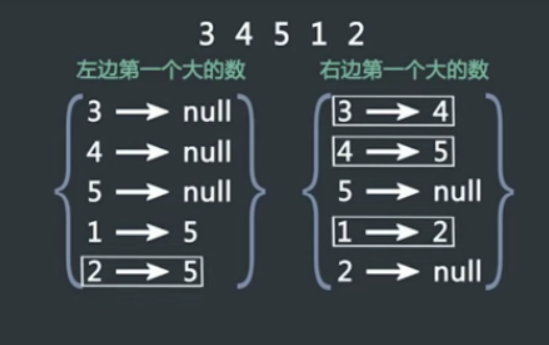



#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<stack>//pop,top,push #include<vector> using namespace std; class MaxTree { public: vector<int> buildMaxTree(vector<int> A, int n) { stack<int> sta; vector<int> left,res; int i; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { while(!sta.empty()&&A[sta.top()]<=A[i]) sta.pop(); if(sta.empty()) left.push_back(-1); else left.push_back(sta.top()); sta.push(i); } stack<int> st; vector<int> right(n,0); for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--) { while(!st.empty()&&A[st.top()]<=A[i]) st.pop(); if(st.empty()) right[i]=-1; else right[i]=st.top(); st.push(i); } for(i=0;i<n;i++) { if(right[i]==-1&&left[i]==-1) res.push_back(-1); else if(right[i]==-1||left[i]==-1) res.push_back(right[i]>left[i]?right[i]:left[i]); else { if(A[right[i]]>A[left[i]]) res.push_back(left[i]); else res.push_back(right[i]); } } return res; } }; int main() { int a[4]={3,1,4,2}; MaxTree A; vector<int> arr(a,a+4),res; res=A.buildMaxTree(arr,4); for(vector<int>::iterator iter=res.begin();iter!=res.end();iter++) cout<<*iter<<" "; return 0; }

思路:
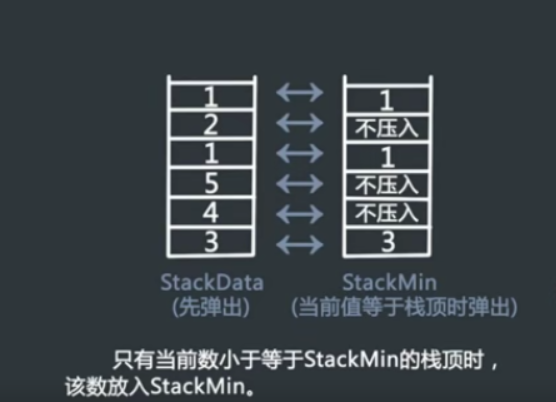

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<stack>//pop,top,push using namespace std; class Solution { public: stack<int> soruce_data,min_data; void push(int value) { soruce_data.push(value); if(min_data.empty()||min_data.top()>=value) min_data.push(value); else min_data.push(min_data.top()); } void pop() { soruce_data.pop(); min_data.pop(); } int top() { return soruce_data.top(); } int min() { return min_data.top(); } }; int main() { Solution A; A.push(3); A.push(4); A.push(5); int c=A.min(); cout<<c; return 0; }

思路:



#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<deque>//pop,top,push #include<vector> using namespace std; class SlideWindow { public: vector<int> slide(vector<int> arr, int n, int w) { if(w==1) return arr; deque<int> deq; vector<int> res; int i; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { if(deq.empty()||arr[deq.back()]>arr[i]) deq.push_back(i); else { while(!deq.empty()&&arr[deq.back()]<=arr[i]) deq.pop_back(); deq.push_back(i); } while((i-deq.front())>=w) deq.pop_front(); if(i<w-1) continue; res.push_back(arr[deq.front()]); } return res; } }; int main() { int a[8]={4,3,5,4,3,3,6,7}; SlideWindow A; vector<int> arr(a,a+8),res; res=A.slide(arr,8,3); for(vector<int>::iterator iter=res.begin();iter!=res.end();iter++) cout<<*iter<<" "; return 0; }





