Asp.Net Core异常处理整理
目前版本是Asp.Net Core v1.1,这个版本的感觉对Http请求中的错误处理方便不是很完善。
没有HttpException异常类,不能在任何的地方自由的抛出对应的异常状态。
一、默认的异常处理配置
1.默认配置在StartUp文件的Configure中注册错误处理
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); loggerFactory.AddDebug(); if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } else { app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); } }
特别说明:
1.env.IsDevelopment() 用于判断当前运行环境是否是测试环境
2.app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); 如果是测试环境则启用开发者异常页面
开发者异常页面
当在Web处理管道放生了一个位置异常时,开发者异常页面会显示有用的调试信息。页面包含几个选项卡显示Stack、Query、Cookie、Header异常信息。
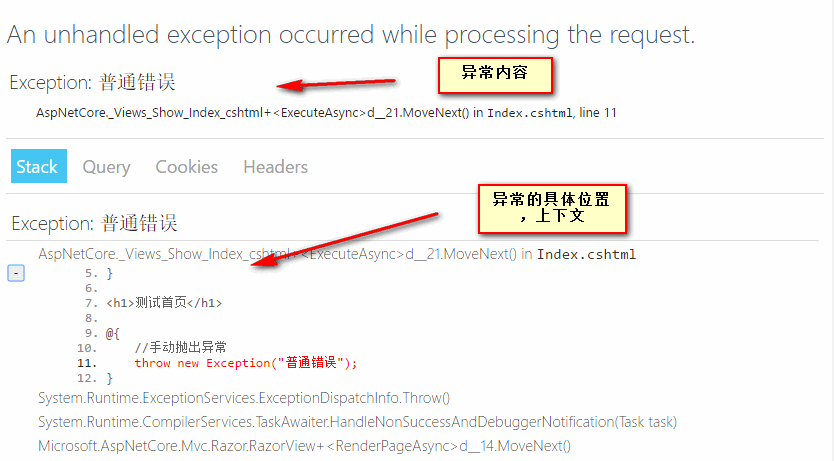
3.app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); 在正式运行环境中输出异常的内容信息。
4.默认的异常处理对于404没有处理,如果是404的地址则返回空内容。
5.业务逻辑404的抛出
使用状态视图
public IActionResult Test2() { //手动抛出404 页面 return StatusCode(404, "你要访问的页面不存在"); }
或者修改相应上下文的状态码
@{ //自定义抛出404异常 this.Context.Response.StatusCode = 404; } <h1>404状态的页面</h1>
二、错误处理扩展,使用委托
1.
//此处的404页面,只能用于处理路由中不匹配的404页面 //如果是程序逻辑中的404不予以处理 //并且对于程序中Exception 也不做处理,直接相应500,内容为空 RequestDelegate handler = async context => { var resp = context.Response; if (resp.StatusCode == 404) { await resp.WriteAsync($"当前是404页面,暂时没有获取到异常内容"); } }; app.UseStatusCodePages(builder => { builder.Run(handler); });
2.
//使用StatusCodePagesMiddleware 指定状态对应的显示页面 Func<StatusCodeContext, Task> handler = async context => { var resp = context.HttpContext.Response; if (resp.StatusCode == 404) { //需要 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; await resp.WriteAsync($"当前是404页面,暂时没有获取到异常内容", Encoding.UTF8); } else if (resp.StatusCode == 500) { await resp.WriteAsync($"当前是500页面,暂时没有获取到异常内容", Encoding.UTF8); } }; app.UseStatusCodePages(handler);
三、错误处理扩展,使用自定义扩展类
Asp.Net Core三种呈现错误也的方式都可以扩展
1.DeveloperExceptionPageMiddleware中间件的扩展可以自定义开发者异常页面,当前略过
2.ExceptionHandlerMiddleware中间件,可以自定义扩展异常处理
示例,处理异常并制定异常的响应页面
public class ErrorHandlingMiddleware { private RequestDelegate _next; private ExceptionHandlerOptions _options; public ErrorHandlingMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IOptions<ExceptionHandlerOptions> options) { _next = next; _options = options.Value; } public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) { try { await _next(context); } catch { //虽然此处指定500,但是出现异常,再次执行异常页面则响应的是200 context.Response.StatusCode = 500; context.Response.Clear(); if (_options.ExceptionHandlingPath.HasValue) { context.Request.Path = _options.ExceptionHandlingPath; } RequestDelegate handler = _options.ExceptionHandler ?? _next; await handler(context); } } }
使用扩展方法为IApplicationBuilder扩展内容
public static class ErrorHandlingExtensions { public static IApplicationBuilder UseErrorHandling(this IApplicationBuilder builder, ExceptionHandlerOptions options) { return builder.UseMiddleware<ErrorHandlingMiddleware>(Options.Create(options)); } }
在 Configure中注册当前错误处理
//使用自定义异常处理 app.UseErrorHandling(new ExceptionHandlerOptions() { //注意此处的路径不能使用~符号 ExceptionHandlingPath = "/Home/Error" });
3.StatusCodePagesMiddleware中间件可以根据正常的相应内容(没有抛出异常的情况下) 扩展状态相应页面
public interface IStatusCodePagesFeature { bool Enabled { get; set; } } public class StatusCodePagesFeature : IStatusCodePagesFeature { public bool Enabled { get; set; } = true; } public class StatusCodePagesMiddleware { private RequestDelegate _next; private StatusCodePagesOptions _options; public StatusCodePagesMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IOptions<StatusCodePagesOptions> options) { _next = next; _options = options.Value; } public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) { //可以用于阻止异常处理 StatusCodePagesFeature feature = new StatusCodePagesFeature(); context.Features.Set<IStatusCodePagesFeature>(feature); await _next(context); HttpResponse response = context.Response; //对于响应的状态编码,返回内容 //if ((response.StatusCode >= 400 && response.StatusCode <= 599) && !response.ContentLength.HasValue && string.IsNullOrEmpty(response.ContentType)) if (response.StatusCode >= 400 && response.StatusCode <= 599 && feature.Enabled) { //触发 默认处理 //await _options.HandleAsync(new StatusCodeContext(context, _options, _next)); //对于非异常的页面,执行Clear抛出异常 //response.Clear(); //response.Body.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); await response.WriteAsync($"当前HttpCode={response.StatusCode}"); } } }
使用扩展方法注册中间件
public static class ErrorHandlingExtensions {//注册3中处理方式 public static IApplicationBuilder UseStatusCodeHandling(this IApplicationBuilder builder) { return builder.UseMiddleware<StatusCodePagesMiddleware>(); } public static IApplicationBuilder UseStatusCodeHandling(this IApplicationBuilder app, StatusCodePagesOptions options) { return app.UseMiddleware<StatusCodePagesMiddleware>(Options.Create(options)); } public static IApplicationBuilder UseStatusCodeHandling(this IApplicationBuilder app, Func<StatusCodeContext, Task> handler) { return app.UseStatusCodePages(new StatusCodePagesOptions { HandleAsync = handler }); } }
在Configure中注册使用
Func<StatusCodeContext, Task> handler = async context => { var resp = context.HttpContext.Response; //在以下的相应数据时,会清空原页面的相应内容 if (resp.StatusCode == 404) { //需要 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; await resp.WriteAsync($"当前是404页面,暂时没有获取到异常内容", Encoding.UTF8); } else if (resp.StatusCode == 500) { await resp.WriteAsync($"当前是500页面,暂时没有获取到异常内容", Encoding.UTF8); } }; app.UseStatusCodeHandling(handler);
4.可以在扩展中综合使用处理,如下示例

public class ErrorHandlingMiddleware { private readonly RequestDelegate next; private ExceptionHandlerOptions _options; public ErrorHandlingMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IOptions<ExceptionHandlerOptions> options) { this.next = next; this._options = options.Value; } public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) { try { await next(context); } catch (Exception ex) { var statusCode = context.Response.StatusCode; if (ex is ArgumentException) { statusCode = 200; } await HandleExceptionAsync(context, statusCode, ex.Message); } finally { var statusCode = context.Response.StatusCode; var msg = ""; if (statusCode == 401) { msg = "未授权"; } else if (statusCode == 404) { //msg = "未找到服务"; //如果是404 返回404页面 if (_options.ExceptionHandlingPath.HasValue) { context.Request.Path = _options.ExceptionHandlingPath; } RequestDelegate handler = _options.ExceptionHandler ?? next; await handler(context); } else if (statusCode == 502) { msg = "请求错误"; } else if (statusCode != 200) { msg = "未知错误"; } if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(msg)) { await HandleExceptionAsync(context, statusCode, msg); } } } private static Task HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, int statusCode, string msg) { var data = new { code = statusCode.ToString(), is_success = false, msg = msg }; var result = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new { data = data }); try { //特别说明ContentType属性在 HttpResponse初始化完成之后就不能修改了 //如果试图修改则抛出异常 //异常内容:Headers are read-only, response has already started. //context.Response.ContentType = "application/json;charset=utf-8"; //特别说明对于准备输出的Response,执行Clear()清空抛出异常 //The response cannot be cleared, it has already started sending. context.Response.Clear(); //判断输出流是否已经开始 //context.Response.HasStarted } catch (Exception ex) { //throw ex; } //清楚已经完成的相应内容 return context.Response.WriteAsync(result); } }
原文参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/artech/p/error-handling-in-asp-net-core-1.html
更多:



