Python【第十四篇续】前端之CSS
css概念
上一篇介绍HTML时,已经说了,如果把HTML比作一个裸男的话,那么CSS就是为这个裸男穿上衣服,搭配一些换看的发型。
官方的术语是,css是英文Cascading Style Sheets的缩写,称为层叠样式表,用于对页面进行美化,CSS的可以使页面更加的美观。基本上所有的html页面都或多或少的使用css。
css选择器
存在的方式有三种:
- 元素内联(直接在标签中使用) 语法为:style='xxx:xxxxx'
- 页面嵌入 语法如:< style type="text/css"> </style > #在头部指定CSS样式
- 外部引用 语法如:<link rel="stylesheet" href="common.css" />
存在方式有三种,那么肯定存在一个优先级关系:
元素内联>页面嵌入>外部引用, 这个仅限于同样的样式冲突时才有用
可能上述看着有点蒙下面看代码比较直观一点。
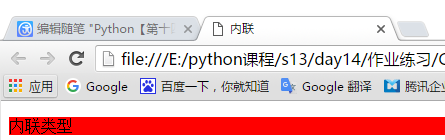
元素内联:
直接在标签上使用,代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>内联</title> </head> <body> <p style="background-color: red"> 内联类型 </p> </body> </html>
显示效果:
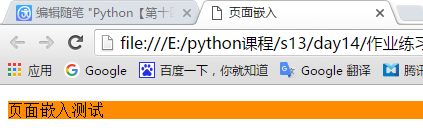
页面嵌入:
在head处写好css样式,在应用这样的好处就是可以重复利用,如下代码:
注:(class是css选择器的一种后面会详细介绍)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>页面嵌入</title> <!--在头部设定好css样式(名字随意),在标签里使用class="样式名字"(class是css选择器的一种后面会详细介绍)--> <style> .css{ background-color: darkorange; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <!--调用头部的css样式--> <p class="css"> 页面嵌入测试 </p> </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
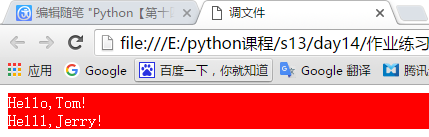
外部引用 :
把样式写到一个css文件中,然后去调用:
css文件中的样式文件名为common.css代码如下:
div{
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
html代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>调文件</title> <!--导入文件--> <link rel="stylesheet" href="common.css"> </head> <body> <div> <!--调取头部导入的文件里,定义的样式为div的,这里也是css选择器的一种--> Hello,Tom! </div> <div> Helll,Jerry! </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
1、标签选择器
为标签类型设置的样式如:<div>、<a>、<span>、<p>等标签,如以下代码:
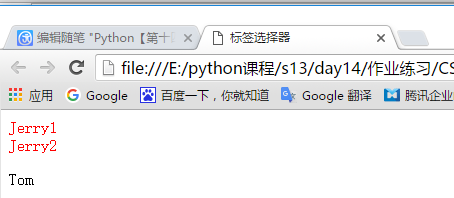
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>标签选择器</title> <style> /*标签为div(也可以设置为a、p等标签)的默认使用以下样式*/ div{ color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <!--div标签默认使用头部定义的样式--> <div>Jerry1</div> <div>Jerry2</div> <!--p标签没有定义样式不调用--> <p>Tom</p> </body> </html>
显示效果:
2、ID选择器
指定ID设置的样式
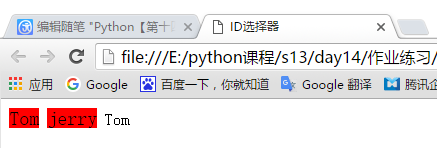
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>ID选择器</title> <style> /*ID选择器*/ #i1{ font-size: 20px; background-color: red; color: black; } </style> </head> <body> <!--这里的id不能是相同的--> <a id="i1">Tom</a> <a id="i3">jerry</a> <a id="i2">Tom</a> </body> </html>
显示效果:
3、类选择器
一般情况下用的都是类选择器,类名可以是相同的。如下代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>类选择器</title> <style> .cls{ background-color: red; font-size: 25px; } </style> </head> <body> <!--这里的任何标签都可以调用类选择器--> <div class="cls">TOM1</div> <a class="cls">TOM2</a> <p class="cls">TOM3</p> <span class="cls">TOM4</span> </body> </html>
显示效果:

4、关联选择器
关联选择器:应用场景为某标签下面的标签设置指定的样式:
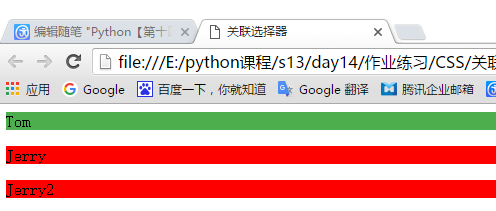
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>关联选择器</title> <style> /*为一个标签使用,cls类选择器下的div下的p标签使用*/ .cls div p{ background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <!--这个div应用了cls类选择器,那么他下面的div下的所有p标签将应用上面设置的样式--> <div class="cls"> <div style="background-color: #4cae4c">Tom</div> <div> <p>Jerry</p> <p>Jerry2</p> </div> </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
也可以关联类选择器的方式:如下代码
<style> /*关联选择器:为应用了container下面的子元素下应用了l类选择器下面的应用了p类选择器设置样式*/ .container .l .p { background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="l"> test <div> <ul> <!--这里需要注意,他们只要是有包换关系就行,不一定非得挨着--> <li class="p"> hello shuaige </li> </ul> </div> </div> </div>
显示效果:

5、组合选择器
如果两个或多个关联类选择器都需要相同的样式怎么整?其实不需要重写一个
看以下样式:
.cls .a .b1 {
background-color: pink;
}
.cls .a .b2 {
background-color: pink;
}
解决办法:组合选择器(“逗号”就是或的关系)一般不常用
.cls .a .b1,.cls .a .b2 {
background-color: pink;
}
#如果前面两个类都相同的话也可以再次做简化
.cls .a .b1,b2 {
background-color: pink;
}
实例代码:
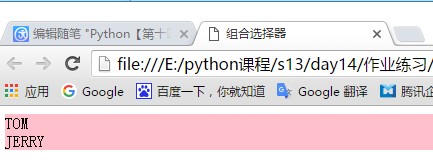
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>组合选择器</title> <style> .cls .b1,.cls1 .b2 { background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cls"> <div class="b1">TOM</div> </div> <div class="cls1"> <div class="b2">JERRY</div> </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
6、属性选择器
表单验证的时候会经常用到,看以下例子:
需要给input下找到类型为text的标签,并且给这个标签设置上样式,上面讲的可以组合标签、关系等选择器,最小单位是标签,不能定义type属性!
<div> <input type="text" /> <input type="password" /> <input type="file" /> <input type="checkbox"/> <input type="button"/> <input type="reset"/> </div>
其实在组合选择器后面加上[type=“text”]就ok了如下:注意(input[type=“text”]中间不能有空格)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>属相选择器</title> <style> .cls input[type="text"]{ border: 2px solid red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cls"> 姓名<input type="text"/> 密码<input type="password"/> 爱好<input type="checkbox"/> <input type="file"/> </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
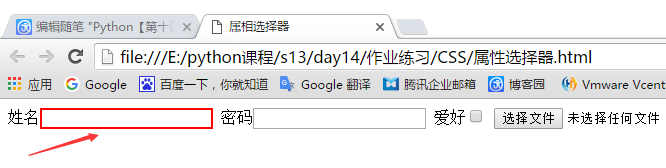
那么问题又来了,想到到input标签属性为type=text并且name等于Tom的input标签咋整,如下?
<div class="cls"> 输入<input type="text" name="Tom"/> 姓名<input type="text" /> 密码<input type="password"/> 爱好<input type="checkbox"/> <input type="file"/> </div>
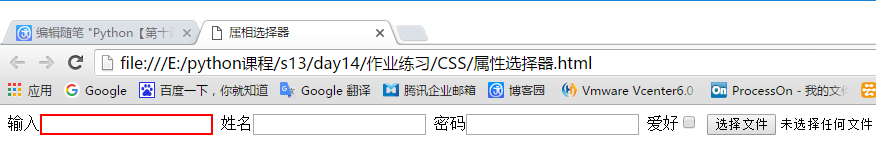
办法总是有的,再添加一个属性就解决了如下代码:
<style> .cls input[type="text"][name="Tom"]{ border: 2px solid red; } </style>
显示效果:
属性标签经常用
也可以使用自定义属性来定义,并且所有的标签都可以使用自定义属性
css常用属性
1、background 【背景】
- 1、background-color
背景颜色 前面多少也有运用到,这个就不多做介绍了
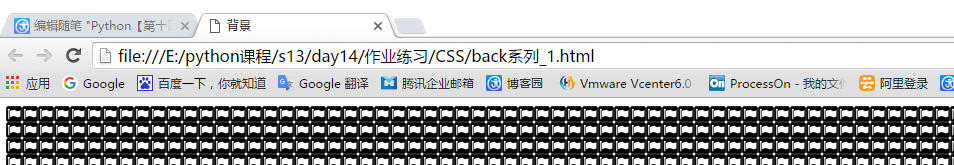
- 2、background-image 背景图片
运用代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>背景</title> </head> <body> <div style="background-image: url(favicon.ico);height: 60px;"> <!--url为图片的路径,height高度占多少像素--> </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
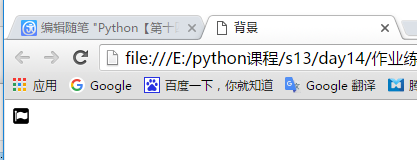
背景图片不重复:
因为div是块级标签会占一整行,要想只显示一个单独的图片如以下代码
<div style="background-image: url(favicon.ico);height: 60px;background-repeat: no-repeat"> <!--background-repeat: no-repeat 就是为了让图片不重复--> </div>
显示效果:
- 3、background-position 图片移位
应用场景,在实际的生产环境中咱们在网页上看到的小图片不是一个一个的零散的小图片的,咱们只是看到了大图片的一部分。比如一个大图片,我只让他显示一部分并不全部显示怎么做?
如下图片我只想在页面上显示指定图形:
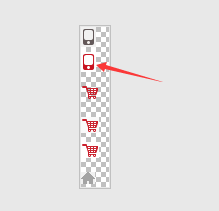
代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>图片移位</title> <style> .position{ /*导入图片*/ background-image:url("jd.png"); /*指定窗口大小*/ height: 30px; width: 30px; /*图片不重复*/ background-repeat: no-repeat; /*定义图片的位置,这里是可以改变到你想要的位置(页面上只显示自己定义图片的位置)*/ background-position: 1px -21px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="position"></div> </body> </html>
显示结果:

2、border【边框】
设置边框,分为实线、虚线、点的线形式如下代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>边框</title> </head> <body> <!--第一种:设置一个线粗2像素、实线、红色、框高20像素(不写框高线就重叠了)、框里面的内容为hello--> <div style="border: 2px solid red;height: 20px">hello</div> <!--第二种:设置线粗2像素、点形式的线、黑色、框高20像素,框里面的内容为hello2--> <br /><div style="border: 2px dotted black;height: 20px">hello2</div> <!--第三种:设置线粗2像素、虚线、蓝色、框高20像素,框里面的内容为hello3--> <br/><div style="border: 2px dashed blue;height: 20px">hello3</div> </body> </html>
显示效果:

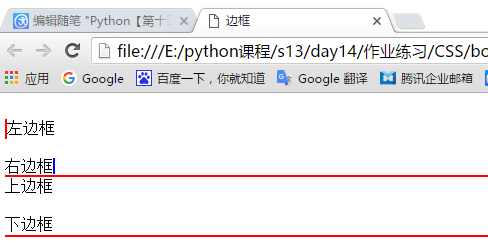
边框也可以单独的设置一个边如只显示单个的上、下、左或右
<!--设置上下左右的单边--> <br/><div style="border-left: 2px solid red;height: 20px">左边框</div> <br/><span style="border-right: 2px solid blue;height: 20px">右边框</span> <br/><div style="border-top: 2px solid red;height: 20px">上边框</div> <br/><div style="border-bottom: 2px solid red;height: 20px">下边框</div>
显示效果如下:
3、cursor 鼠标停放所显示的效果
把鼠标放上去显示小手或不同的形状,如以下代码,效果自己试吧!
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>鼠标小手</title> </head> <body> <p style="cursor:pointer">停放在这里显示小手(pointer)</p> <p style="cursor:help">停放在这里显示问号(help)</p> <p style="cursor:wait">停放在这里显示一个圈正在加载形状(wait)</p> <p style="cursor:move">停放在这里显示移动(move)</p> <p style="cursor:crosshair">停放在这里显示定位(crosshair)</p> </body> </html>
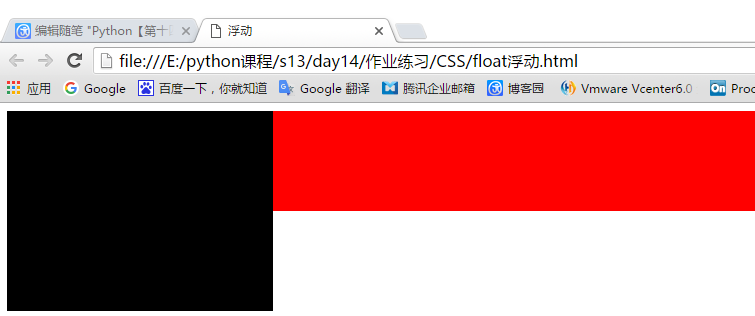
4、float 浮动 、漂 (用来布局使用,常用)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>浮动</title> <style> .float-l{ width:20%; background-color: black; height: 200px; float: left; /*float:left意思都是往左飘*/ /*这里的宽度和高度都可以用百分比来制定*/ } .float-r{ width:80%; background-color: red; height: 100px; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <!--引用头部定义的样式--> <div class="float-l"></div> <div class="float-r"></div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
5、margin外边距
margin用于设置对象标签之间距离间隔,比如2个上下排列的DIV盒子,我们就可以使用margin样式实现上下2个盒子间距。Margin呈现是位于对象边框外侧,紧贴于边框,marign与padding位置却相反css padding却是紧贴边框位于边框内侧。
margin是设置对象四边的外延边距,没有背景颜色也无颜色。
1、margin语法
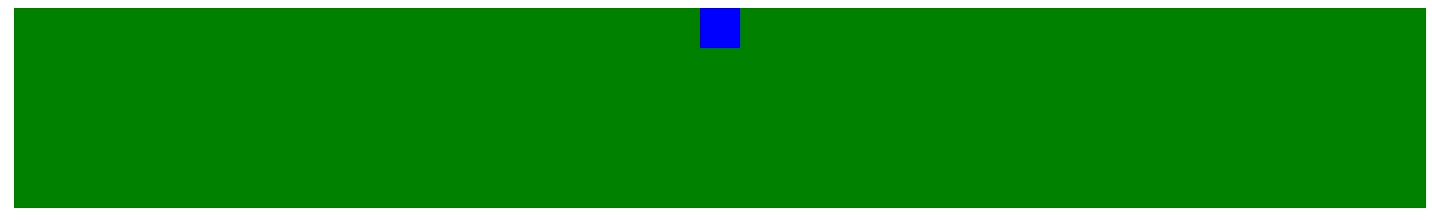
Margin:10px
Margin的值是数字+html单位,同时也可以为auto(自动、自适应)
如下代码:
<div style="background-color: green;height: 200px;"> <div style="margin-left: auto; margin-right:auto; background-color: blue; height: 20px; width:20px; "> </div> </div>
效果如下:
margin是设置对象外边距外延边距离。
margin的值有三种情况,可以为正整数和负整数并加单位如PX像素(margin-left:20px);可以为auto自动属性(margin-left:auto 自动);可以为百分比(%)值(margin-left:3%)。
2、Margin说明
Margin延伸(单独设置四边间距属性单词)
margin-left 对象左边外延边距 (margin-left:5px; 左边外延距离5px)
margin-right 对象右边外延边距 (margin-right:5px; 右边外延距离5px)
margin-top 对象上边外延边距 (margin-top:5px; 上边外延距离5px)
margin-bottom 对象下边外延边距 (margin-bottom:5px; 下边外延距离5px)
如以下代码:
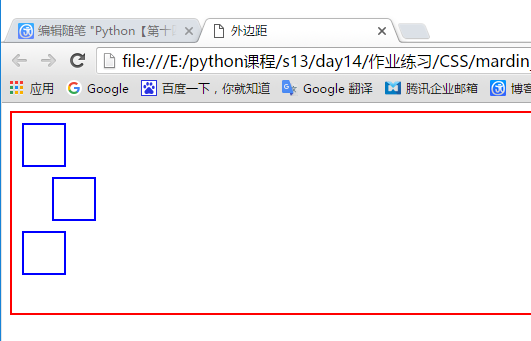
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>外边距</title> </head> <body> <div style="border: 2px solid red;height: 200px"> <div style="border: 2px solid blue;height: 40px;width: 40px; /*距离左边框10像素*/ margin-left: 10px; /*距离上边框10像素*/ margin-top: 10px; "></div> <div style="border: 2px solid blue;height: 40px;width: 40px; /*距离左边框百分之3的距离*/ margin-left:3%; /*距离上一个框百分之3的高度*/ margin-top: 3%; "></div> <div style="border: 2px solid blue;height: 40px;width: 40px; margin-left: 10px; margin-top: 10px; "></div> </div> </body> </html>
效果如下:
6、 padding内边距
语法上与外边距一样,唯一区别是,外边距是本身不增加,内边距是本身增加:
具体查看以下实例:
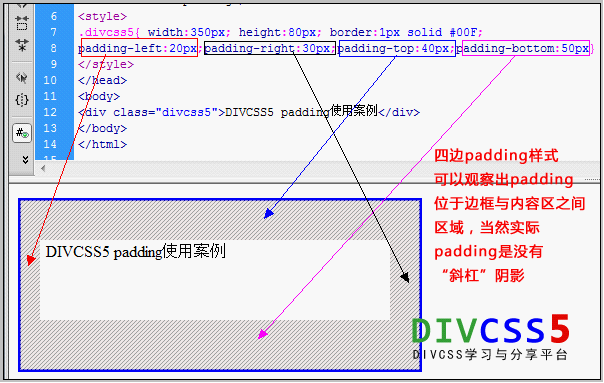
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>内边距</title> <style> .cls{ width:500px;height: 100px;border: 2px solid red; padding-left:20px ; padding-right: 30px; padding-top:40px ; padding-bottom: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cls">padding实例</div> </body> </html>
效果:
7、position定位
常常使用position用于层的绝对定位,比如我们让一个层位于一个层内具体什么位置,为即可使用position:absolute和position:relative实现。
position参数:
- fixed:特殊的absolute,即fixed总是以body为定位对象的,按照浏览器的窗口进行定位,滚动鼠标位置不移动
- absolute : 将对象从文档流中拖出,使用left,right,top,bottom等属性进行绝对定位。按照浏览器的窗口进行定位,滚动鼠标,位置会跟着移动
- relative : 单独写没有什么什么效果,给absolute 结合才能出现化学反应,可以固定在指定的哪个框里面的位。
fixed示例:
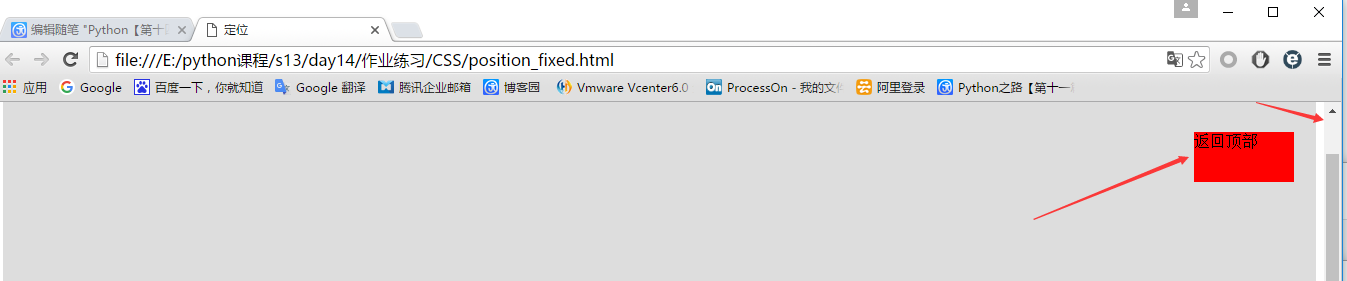
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>定位</title> </head> <body> <div style="background-color: #dddddd;height: 1000px"></div> <!--在浏览器窗口右上角固定位置,鼠标怎么滚动位置都不会变--> <div style="position: fixed;right:30px;top:30px;background-color: red;height: 50px;width: 100px"> 返回顶部 </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
absolute:
单独使用absolute用法给fixed语法一样区别在于,固定的浏览器窗口位置会随着鼠标的滚动而移动。
absolute + relative:
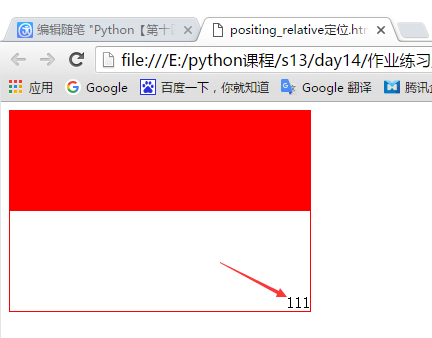
定义一个边框,在边框里面固定位置,如下代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <div style="height: 200px;width: 300px;border: 1px solid red;position: relative"> <div style="height: 100px;background-color: red;"> <!--配合 relative使用,固定在指定了 relative的父类中位置,没有指定relative的父类不生效--> <div style="position: absolute;bottom: 0;right: 0;">111</div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
8、overflow隐藏与滚动条
Overflow可以实现隐藏超出对象内容,同时也有显示与隐藏滚动条的作用。
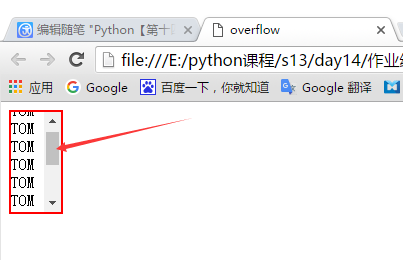
应用场景,有这么一种情况,在一个div内有很多的的内容,如果div的框体不是很大超出去了怎么办?
如下图我不想把"Tom"超出我定义的边框样式:

解决办法:增加overflow滚动条样式,如下代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>overflow</title> </head> <body> <!--添加overflow样式,出现滚动条的效果--> <div style="overflow:auto;border: 2px solid red;height: 100px;width: 50px"> TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM <br />TOM </div> </body> </html>
显示效果:
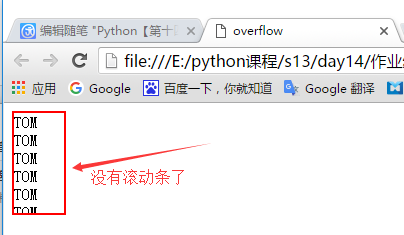
还有一种方法是超出div区域将会自动隐藏,代码如下:
<!--添加overflow样式,自动隐藏的效果--> <div style="overflow:hidden;border: 2px solid red;height: 100px;width: 50px">
效果如下:
9、opacity透明度
透明度,如果父类的div定义了一个样式,子类div覆盖整个页面,但是还想显示父类的div内容,但不能操作,这个时候就可以用opacity了
如下实例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>透明度</title> <style> .cls{ background-color: red; height: 200px; width: 400px; margin-top: 70px; margin-left: 30px; z-index: 9; } .cls2{ background-color: black; position: fixed; top:0; left: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; /*透明度0.5 范围是0.1-1之间*/ opacity: 0.5; /*z-index 标签优先级,越大层级越在外面 ;*/ z-index: 10; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cls" style="color: #4cae4c;"> hellohellohellhellohellohellhellohelloh<br/> hellohellohellhellohellohellhellohelloh<br/> hellohellohellhellohellohellhellohelloh<br/> hellohellohellhellohellohellhellohelloh<br/> hellohellohellhellohellohellhellohelloh<br/> hellohellohellhellohellohellhellohelloh<br/> </div> <div class="cls2"></div>
显示结果:

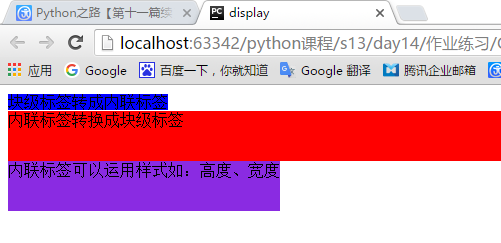
10、display显示与隐藏
我们常常会用到display对应值有block、none、inline这三个值
- 1、使用display:none;来隐藏所有信息(无空白位占据)
- 2、display:block;用来把内联标签变成块级标签
- 3、display:inline;用来把块级标签变成内联标签
- 4、display:inline-block;把内联标签可以运用样式如:高度,或宽度
如以下代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>display</title> </head> <body> <!--把内联标签变成块级标签--> <p style="display:inline;background-color: blue;height: 50px;"> 块级标签转成内联标签 </p> <div style="display: none"> display: none此标签隐藏</div> <span style="display:block;background-color: red;height: 50px;">内联标签转换成块级标签</span> <span style="display: inline-block;height: 50px; background-color:blueviolet;">内联标签可以运用样式如:高度、宽度</span> </body> </html>
效果如下: