matlab练习程序(离散点平滑算法)
路径平滑方法有很多。
如果有预测量可以使用卡尔曼滤波。
如果只是单纯的离散点也可以用多项式拟合、样条插值、回旋曲线或者均值滤波来平滑。
这里这个算法是Apollo里面的算法,单独拿出来看一下吧。
首先算法是利用最优化的方法来求解的,待优化参数就是所有的离散点(xk,yk),如下图:
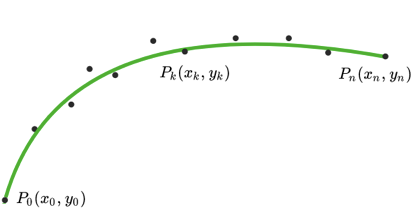 设定损失函数为 cost = cost_smooth + cost_length + cost_deviation。
设定损失函数为 cost = cost_smooth + cost_length + cost_deviation。
其中cost_smooth为平滑度代价,函数定义为:
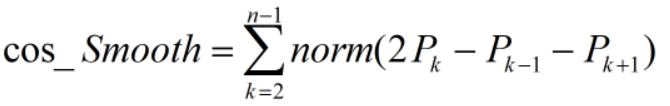
其中cost_length为长度代价,函数定义为:
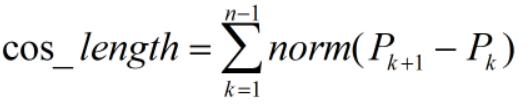
其中cost_deviation为偏离原始点代价,函数定义为:
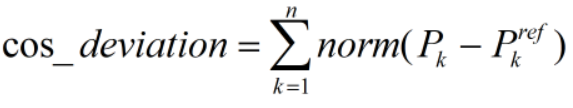
最后迭代优化参数(xk,yk),最终使其cost最小即可。
下面没有再自己写优化方法了,用的matlab中lsqnonlin方法,其实还是LM优化方法。
matlab代码如下:
clear all;close all;clc; x = 0.1:0.1:2*pi; y = sin(x)+log(x).*cos(x) + rand(length(x),1)'*0.5; x = x + rand(length(x),1)'*0.2; plot(x,y,'r-o'); axis equal; Ref = [x' y']; par = [x' y']; %待优化参数 options.Algorithm = 'levenberg-marquardt'; f = @(par) func(par,Ref); lb = []; ub = []; [par,res]= lsqnonlin(f,par,lb,ub,options); hold on; plot(par(:,1),par(:,2),'g-o'); function re = func(par,Ref) %构建优化模型,re为损失误差 cost_s = 0; cost_l = 0; cost_d = 0; for i = 2:length(par)-1 cost_s = cost_s + norm(2 * par(i,:) - par(i-1,:) - par(i+1,:)); cost_l = cost_l + norm(par(i+1,:) - par(i,:)); cost_d = cost_d + norm(par(i,:) - Ref(i,:)); end re = cost_s+cost_l+cost_d; end
结果如下:
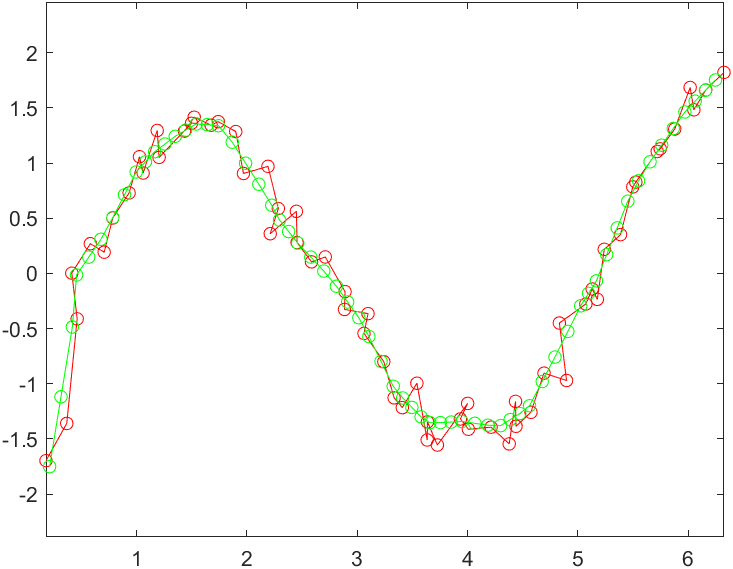
参考:离散点曲线平滑原理



