matlab练习程序(dubins曲线)
dubins曲线是在满足曲率约束和规定的始端和末端的切线方向的条件下,连接两点的最短路径。
计算方法:
1. 给定起始终点位置和方向,并且设定最小转弯半径r。
2. 坐标转换,以起始点作为原点,起始点到结束点向量作为x轴,其垂直方向作为y轴构建新坐标系,在新坐标系下求解路径。
3. 根据论文《Classification of the Dubins set》中六个公式计算六种情况下起点到终点的距离,论文参考参考网址1。
4. 选择最短的距离所代表的转弯方向并计算路径中间所有的点。
5. 连接所有点得到从起点到终点的完整路径。
六种情况分为'LSL','LSR','RSL','RSR','RLR','LRL'。
LSL:
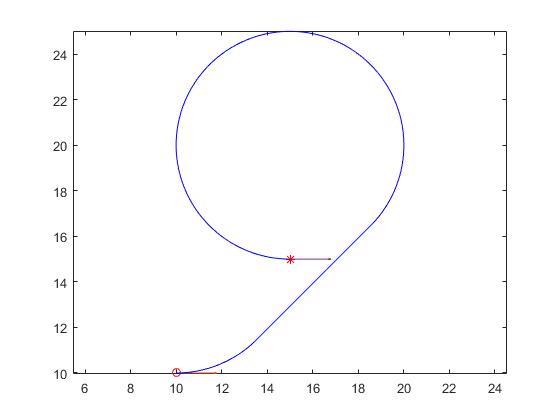
LSR:
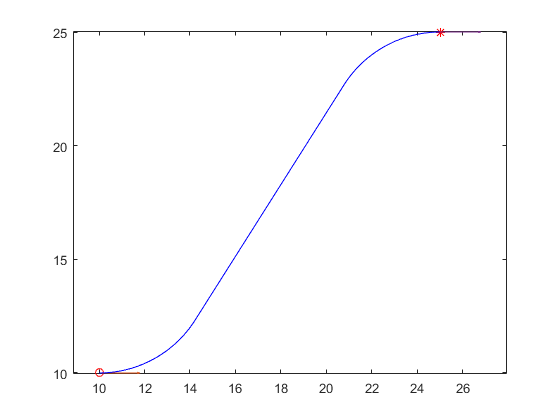
RSL:
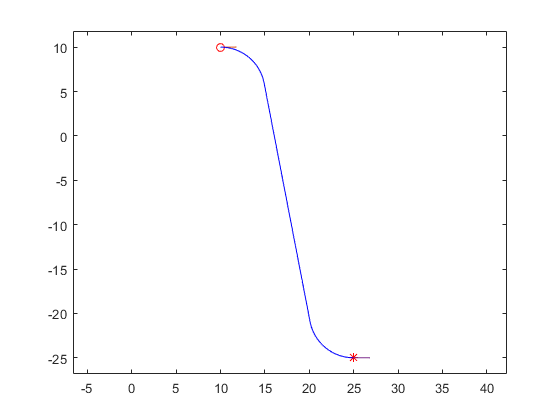
RSR:
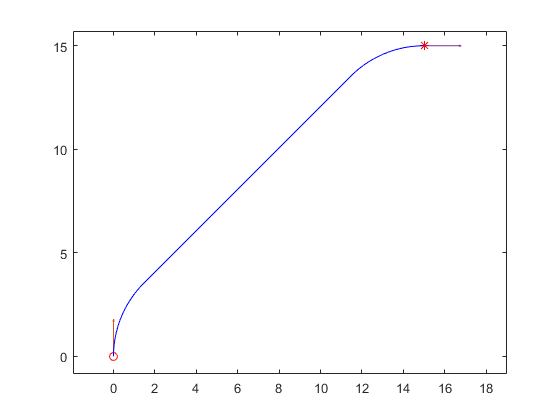
RLR:
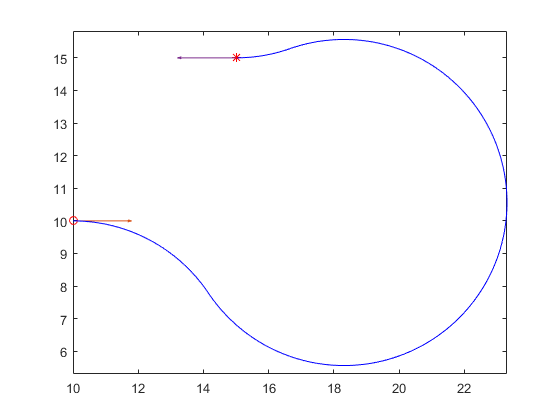
LRL:
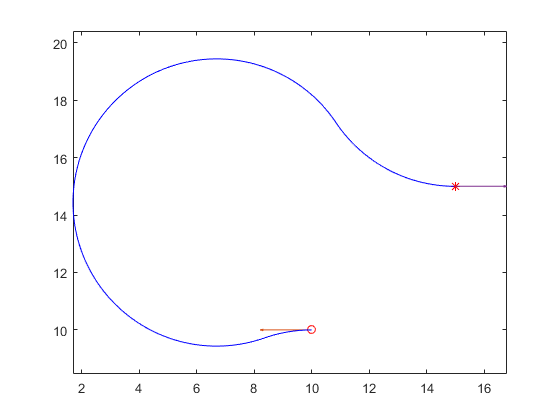
matlab代码如下:
main.m:
clear all; close all; clc; r=5; %LSL p1 = [10 10 0*pi/180]; p2 = [15 15 0*pi/180]; %LSR % p1 = [10 10 0*pi/180]; % p2 = [25 25 0*pi/180]; % % %RSL % p1 = [10 10 0*pi/180]; % p2 = [25 -25 0*pi/180]; % % %RSR % p1 = [0 0 90*pi/180]; % p2 = [15 15 0*pi/180]; % % %RLR % p1 = [10 10 0*pi/180]; % p2 = [15 15 180*pi/180]; % % %LRL % p1 = [10 10 180*pi/180]; % p2 = [15 15 0*pi/180]; dx = p2(1) - p1(1); dy = p2(2) - p1(2); d = sqrt( dx^2 + dy^2 ) / r; theta = mod(atan2( dy, dx ), 2*pi); alpha = mod((p1(3) - theta), 2*pi); beta = mod((p2(3) - theta), 2*pi); L = zeros(6,4); L(1,:) = LSL(alpha,beta,d); L(2,:) = LSR(alpha,beta,d); L(3,:) = RSL(alpha,beta,d); L(4,:) = RSR(alpha,beta,d); L(5,:) = RLR(alpha,beta,d); L(6,:) = LRL(alpha,beta,d); [~,ind] = min(L(:,1)); types=['LSL';'LSR';'RSL';'RSR';'RLR';'LRL']; p_start = [0 0 p1(3)]; mid1 = dubins_segment(L(ind,2),p_start,types(ind,1)); mid2 = dubins_segment(L(ind,3), mid1,types(ind,2)); path=[]; for step=0:0.05:L(ind,1)*r t = step / r; if( t < L(ind,2) ) end_pt = dubins_segment( t, p_start,types(ind,1)); elseif( t < L(ind,2)+L(ind,3) ) end_pt = dubins_segment( t-L(ind,2),mid1,types(ind,2)); else end_pt = dubins_segment( t-L(ind,2)-L(ind,3),mid2,types(ind,3)); end end_pt(1) = end_pt(1) * r + p1(1); end_pt(2) = end_pt(2) * r + p1(2); end_pt(3) = mod(end_pt(3), 2*pi); path=[path;end_pt]; end plot(p1(1),p1(2),'ro'); hold on; quiver(p1(1),p1(2),2*cos(p1(3)),2*sin(p1(3))); plot(p2(1),p2(2),'r*'); quiver(p2(1),p2(2),2*cos(p2(3)),2*sin(p2(3))); plot(path(:,1),path(:,2),'b'); axis equal;
dubins_segment.m:
function seg_end = dubins_segment(seg_param, seg_init, seg_type) if( seg_type == 'L' ) seg_end(1) = seg_init(1) + sin(seg_init(3)+seg_param) - sin(seg_init(3)); seg_end(2) = seg_init(2) - cos(seg_init(3)+seg_param) + cos(seg_init(3)); seg_end(3) = seg_init(3) + seg_param; elseif( seg_type == 'R' ) seg_end(1) = seg_init(1) - sin(seg_init(3)-seg_param) + sin(seg_init(3)); seg_end(2) = seg_init(2) + cos(seg_init(3)-seg_param) - cos(seg_init(3)); seg_end(3) = seg_init(3) - seg_param; elseif( seg_type == 'S' ) seg_end(1) = seg_init(1) + cos(seg_init(3)) * seg_param; seg_end(2) = seg_init(2) + sin(seg_init(3)) * seg_param; seg_end(3) = seg_init(3); end end
LSL.m:
function L = LSL(alpha,beta,d) tmp0 = d + sin(alpha) - sin(beta); p_squared = 2 + (d*d) -(2*cos(alpha - beta)) + (2*d*(sin(alpha) - sin(beta))); if( p_squared < 0 ) L = [inf inf inf inf]; else tmp1 = atan2( (cos(beta)-cos(alpha)), tmp0 ); t = mod((-alpha + tmp1 ), 2*pi); p = sqrt( p_squared ); q = mod((beta - tmp1 ), 2*pi); L=[t+p+q t p q]; end end
LSR.m:
function L = LSR(alpha,beta,d) p_squared = -2 + (d*d) + (2*cos(alpha - beta)) + (2*d*(sin(alpha)+sin(beta))); if( p_squared < 0 ) L = [inf inf inf inf]; else p = sqrt( p_squared ); tmp2 = atan2( (-cos(alpha)-cos(beta)), (d+sin(alpha)+sin(beta)) ) - atan2(-2.0, p); t = mod((-alpha + tmp2), 2*pi); q = mod(( -mod((beta), 2*pi) + tmp2 ), 2*pi); L=[t+p+q t p q]; end end
RSL.m:
function L = RSL(alpha,beta,d) p_squared = (d*d) -2 + (2*cos(alpha - beta)) - (2*d*(sin(alpha)+sin(beta))); if( p_squared< 0 ) L = [inf inf inf inf]; else p = sqrt( p_squared ); tmp2 = atan2( (cos(alpha)+cos(beta)), (d-sin(alpha)-sin(beta)) ) - atan2(2.0, p); t = mod((alpha - tmp2), 2*pi); q = mod((beta - tmp2), 2*pi); L=[t+p+q t p q]; end end
RSR.m:
function L = RSR(alpha,beta,d) tmp0 = d-sin(alpha)+sin(beta); p_squared = 2 + (d*d) -(2*cos(alpha - beta)) + (2*d*(sin(beta)-sin(alpha))); if( p_squared < 0 ) L = [inf inf inf inf]; else tmp1 = atan2( (cos(alpha)-cos(beta)), tmp0 ); t = mod(( alpha - tmp1 ), 2*pi); p = sqrt( p_squared ); q = mod(( -beta + tmp1 ), 2*pi); L=[t+p+q t p q]; end end
RLR.m:
function L = RLR(alpha,beta,d) tmp_rlr = (6. - d*d + 2*cos(alpha - beta) + 2*d*(sin(alpha)-sin(beta))) / 8.; if( abs(tmp_rlr) > 1) L = [inf inf inf inf]; else p = mod(( 2*pi - acos( tmp_rlr ) ), 2*pi); t = mod((alpha - atan2( cos(alpha)-cos(beta), d-sin(alpha)+sin(beta) ) + mod(p/2, 2*pi)), 2*pi); q = mod((alpha - beta - t + mod(p, 2*pi)), 2*pi); L=[t+p+q t p q]; end end
LRL.m:
function L = LRL(alpha,beta,d) tmp_lrl = (6. - d*d + 2*cos(alpha - beta) + 2*d*(- sin(alpha) + sin(beta))) / 8.; if( abs(tmp_lrl) > 1) L = [inf inf inf inf]; else p = mod(( 2*pi - acos( tmp_lrl ) ), 2*pi); t = mod((-alpha - atan2( cos(alpha)-cos(beta), d+sin(alpha)-sin(beta) ) + p/2), 2*pi); q = mod((mod(beta, 2*pi) - alpha -t + mod(p, 2*pi)), 2*pi); L=[t+p+q t p q]; end end
参考:
https://www.ixueshu.com/document/69acbaea39bf8204318947a18e7f9386.html



