IEnumerable和IEnumerator 详解
http://blog.csdn.net/byondocean/article/details/6871881
初学C#的时候,老是被IEnumerable、IEnumerator、ICollection等这样的接口弄的糊里糊涂,我觉得有必要切底的弄清楚IEnumerable和IEnumerator的本质。
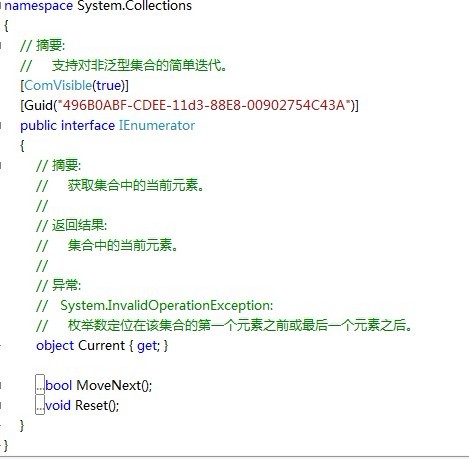
下面我们先看IEnumerable和IEnumerator两个接口的语法定义。其实IEnumerable接口是非常的简单,只包含一个抽象的 方法GetEnumerator(),它返回一个可用于循环访问集合的IEnumerator对象。IEnumerator对象有什么呢?它是一个真正的 集合访问器,没有它,就不能使用foreach语句遍历集合或数组,因为只有IEnumerator对象才能访问集合中的项,假如连集合中的项都访问不 了,那么进行集合的循环遍历是不可能的事情了。那么让我们看看IEnumerator接口有定义了什么东西。看下图我们知道IEnumerator接口定 义了一个Current属性,MoveNext和Reset两个方法,这是多么的简约。既然IEnumerator对象时一个访问器,那至少应该有一个 Current属性,来获取当前集合中的项吧。
MoveNext方法只是将游标的内部位置向前移动(就是移到一下个元素而已),要想进行循环遍历,不向前移动一下怎么行呢?

详细讲解:
说到IEnumerable总是会和IEnumerator、foreach联系在一起。
C# 支持关键字foreach,允许我们遍历任何数组类型的内容:
//遍历数组的项
int[] myArrayOfInts = {10,20,30,40};
foreach(int i in my myArrayOfInts)
{
Console.WirteLine(i);
}
虽然看上去只有数组才可以使用这个结构,其实任何支持GetEnumerator()方法的类型都可以通过foreach结构进行运算。
- public class Garage
- {
- Car[] carArray = new Car[4]; //在Garage中定义一个Car类型的数组carArray,其实carArray在这里的本质是一个数组字段
- //启动时填充一些Car对象
- public Garage()
- {
- //为数组字段赋值
- carArray[0] = new Car("Rusty", 30);
- carArray[1] = new Car("Clunker", 50);
- carArray[2] = new Car("Zippy", 30);
- carArray[3] = new Car("Fred", 45);
- }
- }
理想情况下,与数据值数组一样,使用foreach构造迭代Garage对象中的每一个子项比较方便:
- //这看起来好像是可行的
- lass Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Console.WriteLine("*********Fun with IEnumberable/IEnumerator************\n");
- Garage carLot = new Garage();
- //交出集合中的每一Car对象吗
- foreach (Car c in carLot)
- {
- Console.WriteLine("{0} is going {1} MPH", c.CarName, c.CurrentSpeed);
- }
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
让人沮丧的是,编译器通知我们Garage类没有实现名为GetEnumerator()的方法(显然用foreach遍历Garage对象是 不可能的事情,因为Garage类没有实现GetEnumerator()方法,Garage对象就不可能返回一个IEnumerator对象,没有 IEnumerator对象,就不可能调用方法MoveNext(),调用不了MoveNext,就不可能循环的了)。这个方法是有隐藏在 System.collections命名空间中的IEnumerable接口定义的。(特别注意,其实我们循环遍历的都是对象而不是类,只是这个对象是一个集合对象)
支持这种行为的类或结构实际上是宣告它们向调用者公开所包含的子项:
//这个接口告知调方对象的子项可以枚举
public interface IEnumerable
{
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}
可以看到,GetEnumerator方法返回对另一个接口System.Collections.IEnumerator的引用。这个接口提供了基础设施,调用方可以用来移动IEnumerable兼容容器包含的内部对象。
//这个接口允许调用方获取一个容器的子项
public interface IEnumerator
{
bool MoveNext(); //将游标的内部位置向前移动
object Current{get;} //获取当前的项(只读属性)
void Reset(); //将游标重置到第一个成员前面
}
所以,要想Garage类也可以使用foreach遍历其中的项,那我们就要修改 Garage类型使之支持这些接口,可以手工实现每一个方法,不过这得花费不少功夫。虽然自己开发GetEnumerator()、 MoveNext()、Current和Reset()也没有问题,但有一个更简单的办法。因为System.Array类型和其他许多类型(如 List)已经实现了IEnumerable和IEnumerator接口,你可以简单委托请求到System.Array,如下所示:
- namespace MyCarIEnumerator
- {
- public class Garage:IEnumerable
- {
- Car[] carArray = new Car[4];
- //启动时填充一些Car对象
- public Garage()
- {
- carArray[0] = new Car("Rusty", 30);
- carArray[1] = new Car("Clunker", 50);
- carArray[2] = new Car("Zippy", 30);
- carArray[3] = new Car("Fred", 45);
- }
- public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
- {
- return this.carArray.GetEnumerator();
- }
- }
- }
- //修改Garage类型之后,就可以在C#foreach结构中安全使用该类型了。
- //除此之外,GetEnumerator()被定义为公开的,对象用户可以与IEnumerator类型交互:
- namespace MyCarIEnumerator
- {
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Console.WriteLine("*********Fun with IEnumberable/IEnumerator************\n");
- Garage carLot = new Garage();
- //交出集合中的每一Car对象吗
- foreach (Car c in carLot) //之所以遍历carLot,是因为carLot.GetEnumerator()返回的项时Car类型,这个十分重要
- {
- Console.WriteLine("{0} is going {1} MPH", c.CarName, c.CurrentSpeed);
- }
- Console.WriteLine("GetEnumerator被定义为公开的,对象用户可以与IEnumerator类型交互,下面的结果与上面是一致的");
- //手动与IEnumerator协作
- IEnumerator i = carLot.GetEnumerator();
- while (i.MoveNext())
- {
- Car myCar = (Car)i.Current;
- Console.WriteLine("{0} is going {1} MPH", myCar.CarName, myCar.CurrentSpeed);
- }
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
下面我们来看看手工实现IEnumberable接口和IEnumerator接口中的方法:
- namespace ForeachTestCase
- {
- //继承IEnumerable接口,其实也可以不继承这个接口,只要类里面含有返回IEnumberator引用的GetEnumerator()方法即可
- class ForeachTest:IEnumerable {
- private string[] elements; //装载字符串的数组
- private int ctr = 0; //数组的下标计数器
- /// <summary>
- /// 初始化的字符串
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="initialStrings"></param>
- ForeachTest(params string[] initialStrings)
- {
- //为字符串分配内存空间
- elements = new String[8];
- //复制传递给构造方法的字符串
- foreach (string s in initialStrings)
- {
- elements[ctr++] = s;
- }
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 构造函数
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="source">初始化的字符串</param>
- /// <param name="delimiters">分隔符,可以是一个或多个字符分隔</param>
- ForeachTest(string initialStrings, char[] delimiters)
- {
- elements = initialStrings.Split(delimiters);
- }
- //实现接口中得方法
- public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
- {
- return new ForeachTestEnumerator(this);
- }
- private class ForeachTestEnumerator : IEnumerator
- {
- private int position = -1;
- private ForeachTest t;
- public ForeachTestEnumerator(ForeachTest t)
- {
- this.t = t;
- }
- #region 实现接口
- public object Current
- {
- get
- {
- return t.elements[position];
- }
- }
- public bool MoveNext()
- {
- if (position < t.elements.Length - 1)
- {
- position++;
- return true;
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- public void Reset()
- {
- position = -1;
- }
- #endregion
- }
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- // ForeachTest f = new ForeachTest("This is a sample sentence.", new char[] { ' ', '-' });
- ForeachTest f = new ForeachTest("This", "is", "a", "sample", "sentence.");
- foreach (string item in f)
- {
- System.Console.WriteLine(item);
- }
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- }
- }
IEnumerable<T>接口
实现了IEnmerable<T>接口的集合,是强类型的。它为子对象的迭代提供类型更加安全的方式。
- public class ListBoxTest:IEnumerable<String>
- {
- private string[] strings;
- private int ctr = 0;
- #region IEnumerable<string> 成员
- //可枚举的类可以返回枚举
- public IEnumerator<string> GetEnumerator()
- {
- foreach (string s in strings)
- {
- yield return s;
- }
- }
- #endregion
- #region IEnumerable 成员
- //显式实现接口
- System.Collections.IEnumerator System.Collections.IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
- {
- return GetEnumerator();
- }
- #endregion
- //用字符串初始化列表框
- public ListBoxTest(params string[] initialStrings)
- {
- //为字符串分配内存空间
- strings = new String[8];
- //复制传递给构造方法的字符串
- foreach (string s in initialStrings)
- {
- strings[ctr++] = s;
- }
- }
- //在列表框最后添加一个字符串
- public void Add(string theString)
- {
- strings[ctr] = theString;
- ctr++;
- }
- //允许数组式的访问
- public string this[int index]
- {
- get {
- if (index < 0 || index >= strings.Length)
- {
- //处理不良索引
- }
- return strings[index];
- }
- set {
- strings[index] = value;
- }
- }
- //发布拥有的字符串数
- public int GetNumEntries()
- {
- return ctr;
- }
- }
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- //创建一个新的列表框并初始化
- ListBoxTest lbt = new ListBoxTest("Hello", "World");
- //添加新的字符串
- lbt.Add("Who");
- lbt.Add("Is");
- lbt.Add("Douglas");
- lbt.Add("Adams");
- //测试访问
- string subst = "Universe";
- lbt[1] = subst;
- //访问所有的字符串
- foreach (string s in lbt)
- {
- Console.WriteLine("Value:{0}", s);
- }
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- }
综上所述,一个类型是否支持foreach遍历,必须满足下面条件:
方案1:让这个类实现IEnumerable接口
方案2:这个类有一个public的GetEnumerator的实例方法,并且返回类型中有public 的bool MoveNext()实例方法和public的Current实例属性。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通