java parallelStream 线程堵塞问题笔记
定义:
Stream(流)是JDK8中引入的一种类似与迭代器(Iterator)的单向迭代访问数据的工具。ParallelStream则是并行的流,它通过Fork/Join 框架(JSR166y)来拆分任务,加速流的处理过程。最开始接触parallelStream很容易把其当做一个普通的线程池使用,因此也出现了上面提到的开始的时候打标,结束的时候去掉标的动作。
ForkJoinPool又是什么
ForkJoinPool是在Java 7中引入了一种新的线程池,其简单类图如下:

可以看到ForkJoinPool是ExecutorService的实现类,是一种线程池。创建了ForkJoinPool实例之后,可以通过调用submit(ForkJoinTask task) 或invoke(ForkJoinTask task)方法来执行指定任务。 ForkJoinTask表示线程池中执行的任务,其有两个主要的抽象子类:RecusiveAction和RecusiveTask。其中RecusiveTask代表有返回值的任务,而RecusiveAction代表没有返回值的任务。它们的类图如下:
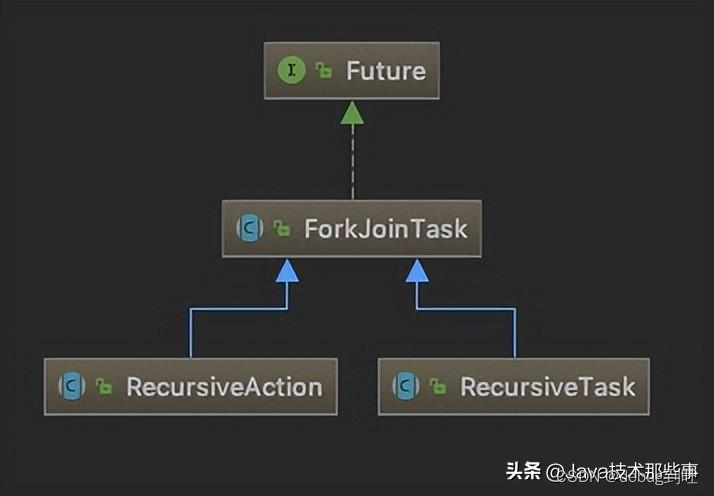
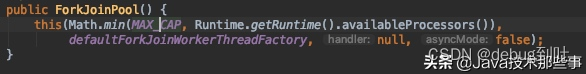
ForkJoinPool来支持使用分治法(Divide-and-Conquer Algorithm)来解决问题,即将一个任务拆分成多个“小任务”并行计算,再把多个“小任务”的结果合并成总的计算结果。相比于ThreadPoolExecutor,ForkJoinPool能够在任务队列中不断的添加新任务,在线程执行完任务后可以再从任务列表中选择其他任务来执行;并且可以选择子任务的执行优先级,因此能够方便的执行具有父子关系的任务。ForkJoinPool内部维护了一个无限队列来保存需要执行的任务,而线程的数量则是通过构造函数传入,如果没有向构造函数中传入希望的线程数量,那么当前计算机可用的CPU数量会被设置为线程数量作为默认值(最大为MAX_CAP = 0x7fff)。
ParallelStream可能引起阻塞
对CPU密集型的任务来说,并行流使用ForkJoinPool,为每个CPU分配一个任务,这是非常有效率的,但是如果任务不是CPU密集的,而是I/O密集的,并且任务数相对线程数比较大,那么直接用ParallelStream并不是很好的选择。
-
package com.chenkang.test.util;
-
-
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
-
-
import java.util.Date;
-
import java.util.List;
-
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
-
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
-
/**
-
* @author chenkang
-
* @date 2022/9/27 13:03
-
*/
-
public class ParallelStream {
-
-
/* public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
-
List<Integer> lists = Lists.newArrayList();
-
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20);
-
//获取jvm 核数
-
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
-
for (int i = 0; i < Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); i++) {
-
lists.add(i);
-
}
-
Date start = new Date();
-
System.out.println(lists.size());
-
CountDownLatch countDownLatch= new CountDownLatch(3);
-
new Thread(()->{
-
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
-
forkJoinPool.submit(() -> {
-
lists.parallelStream().forEach(e -> {
-
try {
-
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
-
e1.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
});
-
System.out.println("执行1down");
-
countDownLatch.countDown();
-
});
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(()->{
-
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
-
forkJoinPool.submit(() -> {
-
lists.parallelStream().forEach(e -> {
-
try {
-
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
-
e1.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
});
-
System.out.println("执行2down");
-
countDownLatch.countDown();
-
});
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(()->{
-
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
-
forkJoinPool.submit(() -> {
-
lists.parallelStream().forEach(e -> {
-
try {
-
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
-
e1.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
});
-
System.out.println("执行3down");
-
countDownLatch.countDown();
-
});
-
}).start();
-
-
countDownLatch.await();
-
Date end = new Date();
-
-
System.out.println((end.getTime() - start.getTime()) / 1000);
-
}*/
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
-
List<Integer> lists = Lists.newArrayList();
-
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20);
-
//获取jvm 核数
-
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
-
for (int i = 0; i < Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); i++) {
-
lists.add(i);
-
}
-
Date start = new Date();
-
System.out.println(lists.size());
-
CountDownLatch countDownLatch= new CountDownLatch(3);
-
new Thread(()->{
-
lists.parallelStream().forEach(e -> {
-
try {
-
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
-
e1.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
});
-
System.out.println("执行1down");
-
countDownLatch.countDown();
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(()->{
-
lists.parallelStream().forEach(e -> {
-
try {
-
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
-
e1.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
-
});
-
System.out.println("执行2down");
-
countDownLatch.countDown();
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(()->{
-
lists.parallelStream().forEach(e -> {
-
try {
-
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
-
e1.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
});
-
System.out.println("执行3down");
-
countDownLatch.countDown();
-
}).start();
-
-
countDownLatch.await();
-
Date end = new Date();
-
-
System.out.println((end.getTime() - start.getTime()) / 1000);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
}
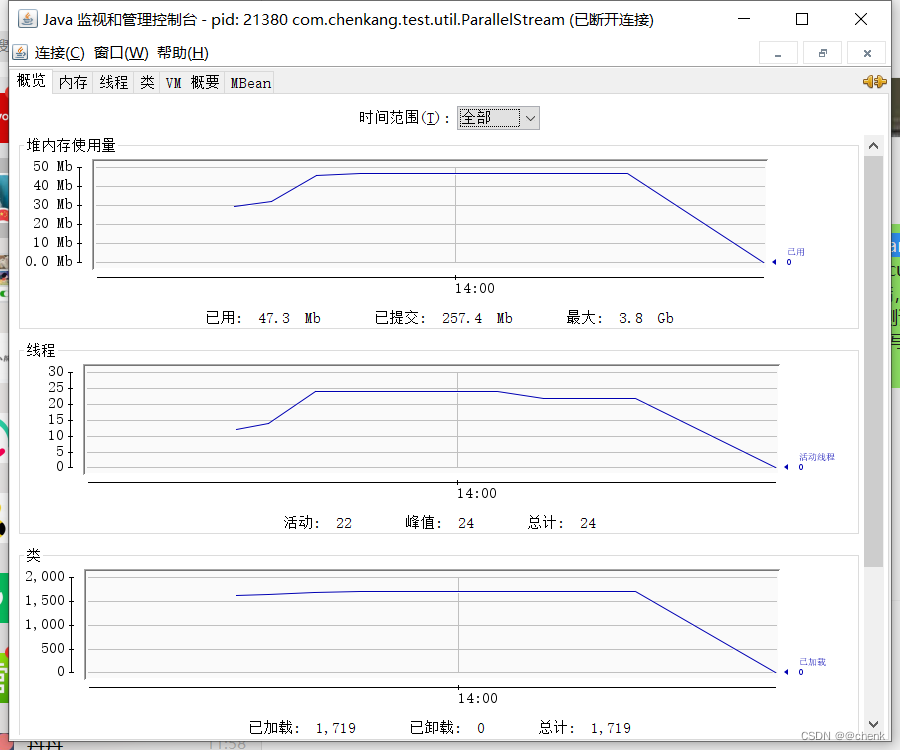
1.分别执行查看执行时间 链接jconsole 查看线程数量 这个是第二种
第一种
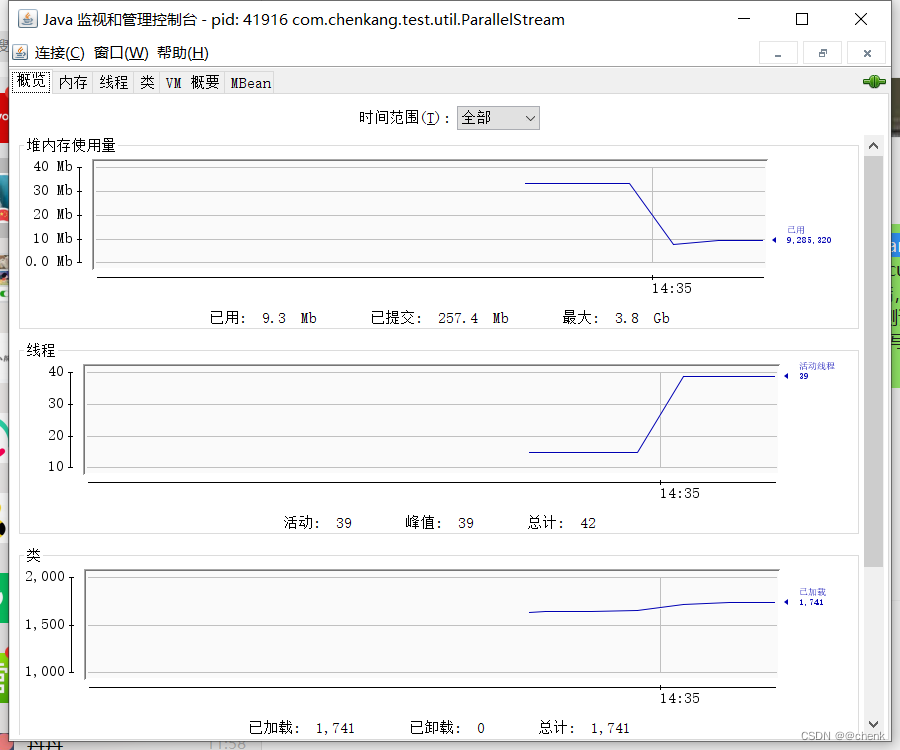
可以看到线程数量提升 执行效率提高 第二种是因为commonpool 线程限制的原因
原文:https://www.csdn.net/tags/MtjaEg1sODI5MzctYmxvZwO0O0OO0O0O.html
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38845058/article/details/127070935





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!
2022-07-19 git查看分支创建于哪个分支
2018-07-19 说说Java中的资源文件的读取
2015-07-19 ASP.NET异步处理
2015-07-19 C# TPL学习