oop题目集04-06总结性blog
oop题目集04
* 菜单计价程序-3
* 有重复的数据
* 去掉重复的数据
*单词统计与排序
*面向对象编程(封装性)
*GPS测绘中度分秒转换
*判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数
oop题目集05
* 正则表达式训练-QQ号校验
import java.util.Scanner; class DateUtil{ Day day;//定义一个day类型的对象 public DateUtil() { } public DateUtil(int d,int m,int y) { this.day = new Day(d,m,y); } //getter public Day getDay(){ return day; } //setter public void setDay(Day d){ this.day=d; } //检验数据是否合法 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate()&&this.getDay().getMonth().validate()&&day.validate()) return true; else return false; } //判断两个日期的先后顺序 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return true; else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return true; else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&&this.getDay().getValue() < date.getDay().getValue()) return true; else return false; } //判定两个日期是否相等 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ if(this.getDay().getValue() == date.getDay().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&& this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return true; else return false; } //日期值格式化 public String showDate(){ return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue(); } //求下N天 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { int[]mon_maxnum = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29; while(n > mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]){ n = n - mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]; if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 12){ this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else mon_maxnum[2] = 28; this.getDay().getMonth().resetMin(); } else this.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement(); } for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){ if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 12&&this.getDay().getValue() == 31){ //跨年 this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); this.getDay().getMonth().resetMin(); this.getDay().resetMin(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; else mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()!=12&&this.getDay().getValue()==mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]){//跨月 this.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement(); this.getDay().resetMin(); } else if(this.getDay().getValue() != mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]){//跨日 this.getDay().dayIncrement(); } } int y = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); int m = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); int d = this.getDay().getValue(); return new DateUtil(y, m, d); } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ int[]oop = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) oop[2] = 29; while(n > oop[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1]){ if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 1){ n = n - 31; this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) oop[2] = 29; else oop[2] = 28; this.getDay().getMonth().resetMax(); } else{ n = n-oop[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1]; this.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction(); } } for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){ if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 1&&this.getDay().getValue() == 1){ this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); this.getDay().getMonth().resetMax(); this.getDay().resetMax();; if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) oop[2] = 29; else oop[2] = 28; } else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() != 1 && this.getDay().getValue() == 1){ this.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction(); this.getDay().resetMax(); } else if(this.getDay().getValue() != 1){ this.getDay().dayReduction(); } } int y = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); int m = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); int d = this.getDay().getValue(); return new DateUtil(y, m, d); } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ int []mon_maxnum = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int sum1 = 0; for (int another = 1; another < this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); another++) { if (another % 4 == 0&&another % 100 !=0|| another%400 == 0) { sum1 = sum1+366; } else sum1 = sum1 + 365; } for (int another = 1; another < this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); another++) { if (another == 2 && this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { sum1 = sum1 + 29; } else sum1 = sum1 + mon_maxnum[another]; } sum1 += this.getDay().getValue(); int sum2 = 0; for (int another = 1; another < date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); another++) { if (another % 4==0&&another % 100 !=0|| another%400 == 0) { sum2 = sum2 + 366; } else sum2 = sum2 + 365; } for (int i = 1; i < date.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); i++) { if (i == 2 && date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { sum2 = sum2 + 29; } else sum2 = sum2 + mon_maxnum[i]; } sum2 = sum2 + date.getDay().getValue(); int betweendays = Math.abs(sum2 -sum1); return betweendays; } } class Day{ int value; Month month; int []mon_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; //无参构造方法 public Day() { } //有参构造方法 public Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue) { this.month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue); this.value=dayValue; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(Month value) { this.month = value; } //日期复位 public void resetMin() { this.value = 1; } public void resetMax() { this.value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]; } //天数判断是否正确 public boolean validate() { if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { mon_maxnum[1] = 29; }//调用闰年判断函数 if(this.value >= 1 && this.value <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]) return true; else return false; } //日期增一 public void dayIncrement() { this.value = this.value + 1; } //日期减一 public void dayReduction() { this.value = this.value -1; } } class Month{ int value; Year year; //无参构造方法 public Month() { } //有参构造方法 public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue) { this.year = new Year(yearValue); this.value = monthValue; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } //get public Year getYear() { return year; } //set public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } //月份复位 public void resetMin() { this.value = 1; } //月份设置为12 public void resetMax() { this.value = 12; } //检验数据是否合法; public boolean validate() { if(this.value >= 1 && this.value<=12) return true; else return false; } //月份加一 public void monthIncrement() { this.value = this.value+1; } public void monthReduction() { this.value = this.value-1; } } class Year{ int value; public Year() { } public Year(int value) { this.value = value; }//上一个类需要new一个,那么在对应的类中需要对应的构造方法。 public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public boolean isLeapYear() { if(this.value % 4 == 0 && this.value % 100 !=0 || this.value % 400 == 0) return true; else return false; } //检验数据是否合法 public boolean validate() { if(this.value>=1900&&this.value<=2050) return true; else return false; } //年份加一 public void yearIncrement() { this.value = this.value + 1; } public void yearReduction() { this.value = this.value - 1; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); Year y = new Year(); y.value = year; Month n = new Month(); n.value = month; Day d = new Day(); d.value = day; DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int w = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); Year y = new Year(); y.value = year; Month a= new Month(); a.value = month; Day d = new Day(); d.value = day; DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } w = input.nextInt(); if (w < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(date.getPreviousNDays(w).showDate()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } }
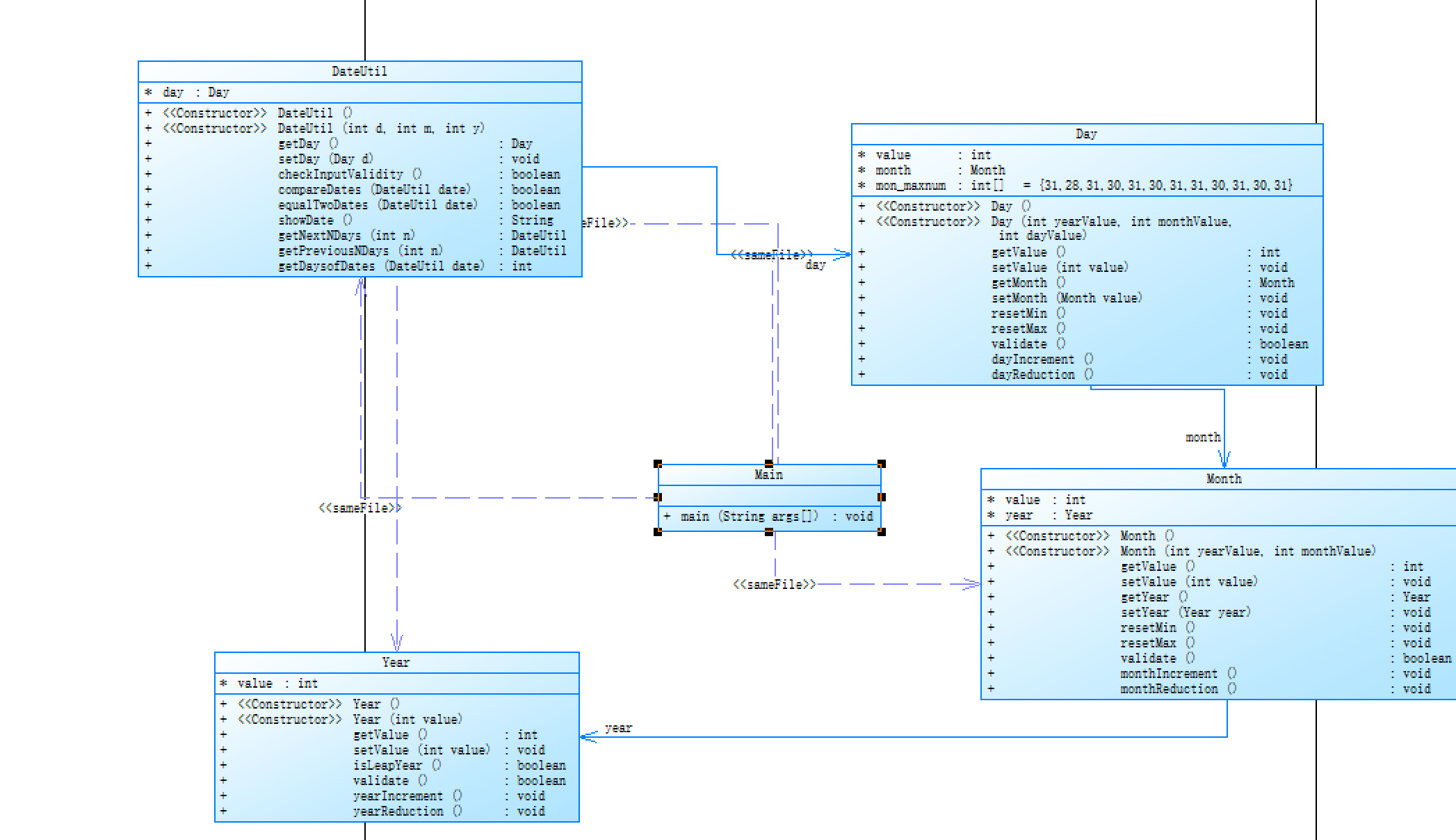
本题小结:无需多言,这道题目是之前日期题目的又一次迭代,一开始拿到这道题目确实有点无从下手,但是在仔细分析了题目所给的类图后,会发现这道题目其实是一层层调用的过程。将不同的类作为上一个类的属性,一层层套用不同类中的属性,将原来的代码稍作修改即可。由于在上一道的日期类题目,我没有得到满分(由于在计算两个日期之间相隔天数时算法有错误),没想到这里还需要迭代,在询问了同学之后,找到了一个简单的方法:可以先分别计算两个日期和01年01月之间的天数,然后相减,即可得到相差的天数。
下面是我用powerdesigner生成的类图
import java.util.Scanner; class DateUtil{ Day day;//定义一个day类型的对象 Month month; Year year; int[]mon_maxnum=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public DateUtil() { } public DateUtil(int d,int m,int y) { this.day = new Day(d); this.month = new Month(m); this.year = new Year(y); } //getter public Day getDay(){ return day; } //setter public void setDay(Day d){ this.day=d; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(Month month) { this.month = month; } public Year getYear() { return year; } //set public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } public void setDayMin() { this.day.value = 1;; } public void setDayMax() { if(this.year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29; this.day.value = mon_maxnum[this.month.value]; } //检验数据是否合法 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ if(year.validate() && month.validate() && day.getValue() >= 1 && day.getValue() <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) return true; else return false; } //判断两个日期的先后顺序 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.getYear().getValue() < date.getYear().getValue()) return true; else if(this.getYear().getValue() == date.getYear().getValue()&&this.getMonth().getValue() < getMonth().getValue()) return true; else if(this.getYear().getValue() == date.getYear().getValue()&&this.getMonth().getValue() == date.getMonth().getValue()&&this.getDay().getValue() < date.getDay().getValue()) return true; else return false; } //判定两个日期是否相等 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ if(this.getDay().getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()&&this.getMonth().getValue()==date.getMonth().getValue()&& this.getYear().getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()) return true; else return false; } //日期值格式化 public String showDate(){ return this.getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue(); } //求下N天 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { int[]mon_maxnum=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; while(n>mon_maxnum[this.getMonth().getValue()]){ n=n-mon_maxnum[this.getMonth().getValue()]; if(this.getMonth().getValue()==12){ this.getYear().yearIncrement(); if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; else mon_maxnum[2]=28; this.getMonth().resetMin(); } else this.getMonth().monthIncrement(); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(this.getMonth().getValue() == 12&&this.getDay().getValue() == 31){ //跨年 this.getYear().yearIncrement(); this.getMonth().resetMin(); this.setDayMin(); if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; else mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else if(this.getMonth().getValue()!=12&&this.getDay().getValue()==mon_maxnum[this.getMonth().getValue()]){//跨月 this.getMonth().monthIncrement(); this.setDayMin(); } else if(this.getDay().getValue() != mon_maxnum[this.getMonth().getValue()]){//跨日 this.getDay().dayIncrement(); } } int y = this.getYear().getValue(); int m = this.getMonth().getValue(); int d = this.getDay().getValue(); return new DateUtil(d, m, y); } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ int[]oop=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) oop[2]=29; while(n>oop[this.getMonth().getValue()-1]){ if(this.getMonth().getValue()==1){ n=n-31; this.getYear().yearReduction(); if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) oop[2]=29; else oop[2]=28; this.getMonth().resetMax(); } else{ n=n-oop[this.getMonth().getValue()-1]; this.getMonth().monthReduction(); } } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(this.getMonth().getValue()==1&&this.getDay().getValue()==1){ this.getYear().yearReduction(); this.getMonth().resetMax(); this.setDayMax();; if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) oop[2]=29; else oop[2]=28; } else if(this.getMonth().getValue()!=1&&this.getDay().getValue()==1){ this.getMonth().monthReduction(); this.setDayMax(); } else if(this.getDay().getValue()!=1){ this.getDay().dayReduction(); } } int y = this.getYear().getValue(); int m = this.getMonth().getValue(); int d = this.getDay().getValue(); return new DateUtil(d, m, y); } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ int []mon_maxnum = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int sum1 = 0; for (int another = 1; another < this.getYear().getValue(); another++) { if (another % 4==0&&another % 100 !=0|| another%400 == 0) { sum1 = sum1+366; } else sum1 = sum1 + 365; } for (int another = 1; another < this.getMonth().getValue(); another++) { if (another == 2 && this.getYear().isLeapYear()) { sum1 = sum1 + 29; } else sum1 = sum1 + mon_maxnum[another]; } sum1 += this.getDay().getValue(); int sum2 = 0; for (int another = 1; another < date.getYear().getValue(); another++) { if (another % 4==0&&another % 100 !=0|| another%400 == 0) { sum2 = sum2 + 366; } else sum2 = sum2 + 365; } for (int i = 1; i < date.getMonth().getValue(); i++) { if (i == 2 && date.getYear().isLeapYear()) { sum2 = sum2 + 29; } else sum2 = sum2 + mon_maxnum[i]; } sum2 = sum2 + date.getDay().getValue(); int betweendays = Math.abs(sum2 -sum1); return betweendays; } } class Day{ int value; //无参构造方法 public Day() { } //有参构造方法 public Day(int value) { this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } //日期增一 public void dayIncrement() { this.value = this.value + 1; } //日期减一 public void dayReduction() { this.value = this.value -1; } } class Month{ int value; //无参构造方法 public Month() { } //有参构造方法 public Month(int Value) { this.value = Value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } //月份复位 public void resetMin() { this.value = 1; } //月份设置为12 public void resetMax() { this.value = 12; } //检验数据是否合法; public boolean validate() { if(this.value >= 1 && this.value<=12) return true; else return false; } //月份加一 public void monthIncrement() { this.value = this.value+1; } public void monthReduction() { this.value = this.value-1; } } class Year{ int value; public Year() { } public Year(int value) { this.value = value; }//上一个类需要new一个,那么在对应的类中需要对应的构造方法。 public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public boolean isLeapYear() { if(this.value % 4 == 0 && this.value % 100 !=0 || this.value % 400 == 0) return true; else return false; } //检验数据是否合法 public boolean validate() { if(this.value >= 1820&&this.value <= 2020) return true; else return false; } //年份加一 public void yearIncrement() { this.value = this.value + 1; } public void yearReduction() { this.value = this.value - 1; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); Year y = new Year(); y.value = year; Month n = new Month(); n.value = month; Day d = new Day(); d.value = day; DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " next " + m + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int w = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); Year y = new Year(); y.value = year; Month a= new Month(); a.value = month; Day d = new Day(); d.value = day; DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } w = input.nextInt(); if (w < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print( year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " previous " + w + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(w).showDate()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(day, month, year); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherDay, anotherMonth, anotherYear); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } }
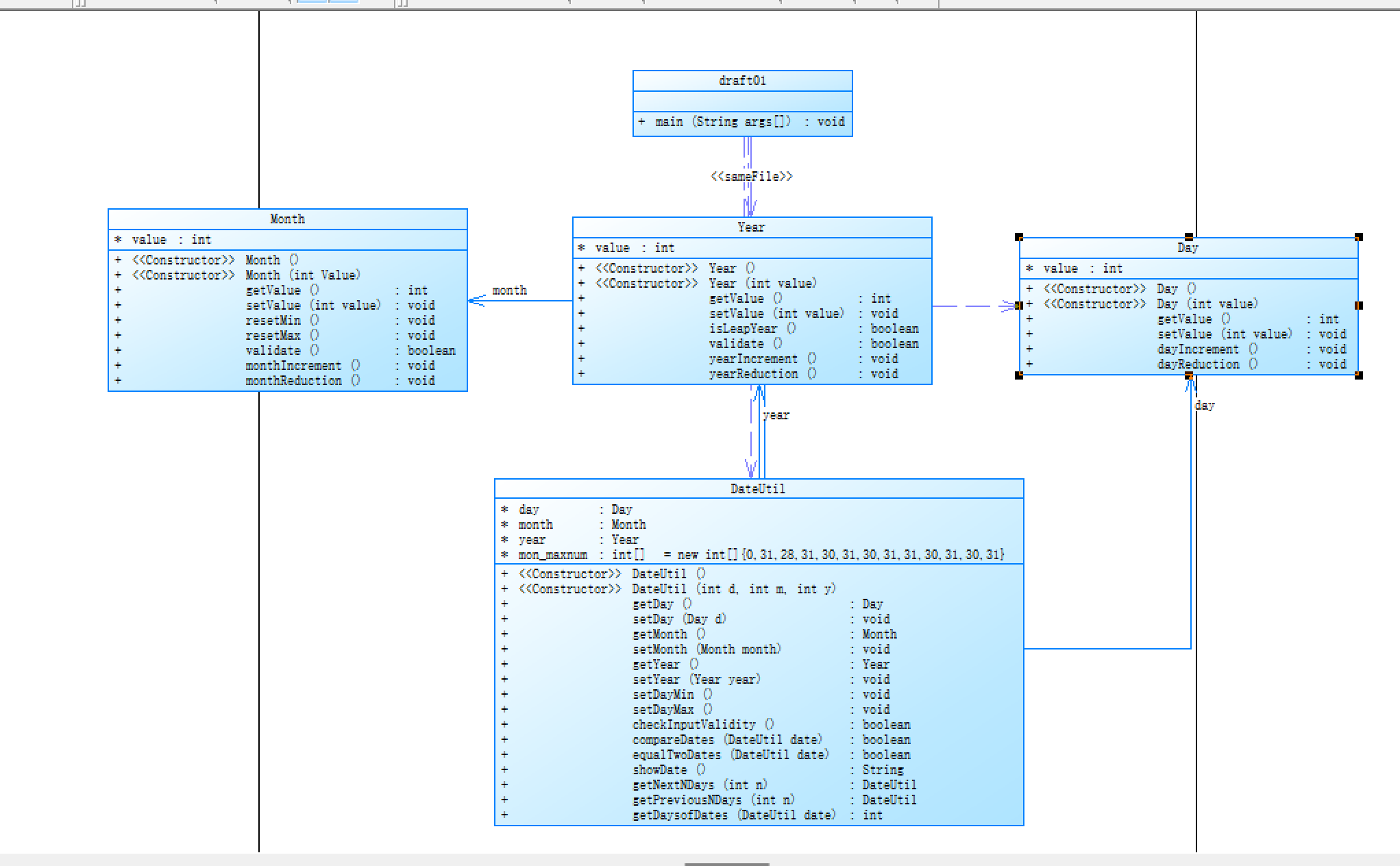
具体类图如下
本题小结:
在我看来,这道题相比于前面一题又是一个解耦的过程,前面一题是Month,Day,Year等类之间层层调用的过程,然而这一题在DateUtil类中添加了不同类的调用方法,大大的降低了耦合性。
关于菜单oop题目集4-01以及6-01
首先在这我要很诚恳地说,我对这两道题目并没有上心,当时有一种从众以及畏难心理,听大家说这道题非常难,想着大家都做不出来那我也肯定做不出来,甚至没有尝试,在这里我对我的学习态度以及畏难心理表示深深的忏悔,当时4-01没有做出来后,开始做6-01的时候就毫无头绪,不知道从何下手,所以即使想写时间上也来不及。
踩坑心得
这次题目集的让我印象深刻的题目是
单词统计和排序
一开始我的代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String text = input.nextLine(); String middle; String[]word = text.split("\\.|,| "); for(int i=0;i<word.length-1;i++) { for(int j=0;j<word.length-1-i;j++) { if(word[j].length()<word[j+1].length()) { middle=word[j+1]; word[j+1]=word[j]; word[j]=middle; } } } char a; char b; for(int i=0;i<word.length;i++) { for(int j=0;j<i;j++) { if(word[j].length()==word[i].length()) {//长度相等 for(int m=0;m<word[j].length();m++) {// if(word[j].charAt(m)>=97) a=(char) (word[j].charAt(m)-32); else a=word[j].charAt(m); if(word[i].charAt(m)>=97) b=(char) (word[i].charAt(m)-32); else b=word[i].charAt(m); if(a>b) { middle=word[j]; word[j]=word[i]; word[i]=middle; } } } } } for(int i=0;i<word.length-1;i++) { if(!word[i].equals(word[i+1])) System.out.println(word[i]); } System.out.print(word[word.length-1]); } }
可以看出我一开始用了很多个循环嵌套不断比较两个字母,给两个单词进行排序,经过我的反复思考我觉得我的算法是没有问题的,然而无法过测试点

然后去问了同学,这是我们的聊天记录
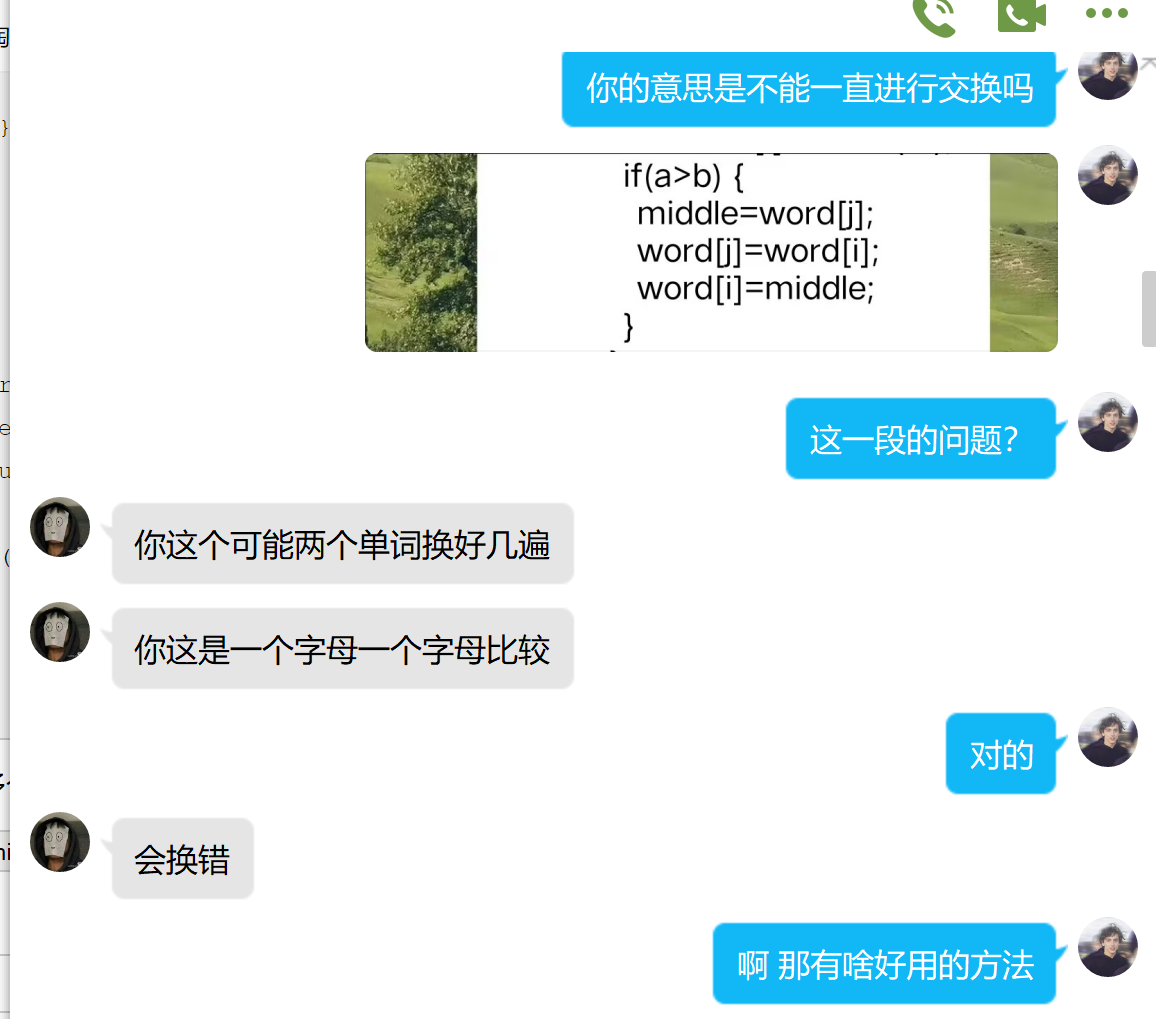
他指出是我循环交换用的次数太多了,会导致交换错误。
后来直接用word[i].compareToIgnoreCase(word[j])方法进行比较(),修改后的代码如下
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String text = input.nextLine(); String middle; String[]word = text.split("\\.|,| "); for(int i=0;i<word.length-1;i++) { for(int j=0;j<word.length-1-i;j++) { if(word[j].length()<word[j+1].length()) { middle=word[j+1]; word[j+1]=word[j]; word[j]=middle; } } } for(int i=0;i<word.length;i++) { for(int j=0;j<i;j++) { if(word[j].length()==word[i].length()) {//长度相等 if(word[i].compareToIgnoreCase(word[j])<0) { middle=word[i]; word[i]=word[j]; word[j]=middle; } } } } for(int i=0;i<word.length-1;i++) { if(!word[i].equals(word[i+1])) System.out.println(word[i]); } System.out.print(word[word.length-1]); } }
运行正确

这给我的教训是:不要随便套用循环进行数据之间的交换,在题目条件允许的情况下,可以采取一些Java自带的类和方法,可以大大提高代码效率。
改进建议
通过这次题目集我深刻地意识到了类图的重要性,特别是日期的题目,类图好像一张地图,指导我们写代码。
所以在自己写复杂程序之前可以尝试画类图,提高效率。
同时,可以在题目集结束的时候,把具体的题目的具体的测试点展示出来。
总结
通过这次题目集,我对封装性有了更深刻的理解(日期类的设置),同时我了解到了HashSet,LinkedHashSet,ArrayList等其他方便的类和方法
我深刻意识到了“迭代”的可怕,真是一环扣一环,前面的题目做不出来会严重后面题目以及得分,所以我要深刻检讨自己的畏难以及从众心理,合理规划时间,端正自己的学习态度,花更多时间和精力完成题目(不然迭代会更痛苦)。
在做复杂的题目前要先理解类与类之间的关系,有事半功倍的效果。



