SpringBoot2.x入门:依赖管理
前提
这篇文章是《SpringBoot2.x入门》专辑的第1篇文章,使用的SpringBoot版本为2.3.1.RELEASE,JDK版本为1.8。
主要梳理一下SpringBoot2.x的依赖关系和依赖的版本管理,依赖版本管理是开发和管理一个SpringBoot项目的前提。
SpringBoot其实是通过starter的形式,对spring-framework进行装箱,消除了(但是兼容和保留)原来的XML配置,目的是更加便捷地集成其他框架,打造一个完整高效的开发生态。
SpringBoot依赖关系
因为个人不太喜欢Gradle,所以下文都以Maven举例。
和SpringCloud的版本(SpringCloud的正式版是用伦敦地铁站或者说伦敦某地名的英文名称作为版本号,例如比较常用的F版本Finchley就是位于伦敦北部芬奇利)管理不同,SpringBoot的依赖组件发布版本格式是:X.Y.Z.RELEASE。因为SpringBoot组件一般会装箱为starter,所以组件的依赖GAV一般为:org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-${组件名}:X.Y.Z.RELEASE,其中X是主版本,不同的主版本意味着可以放弃兼容性,也就是SpringBoot1.x和SpringBoot2.x并不保证兼容性,而组件名一般是代表一类中间件或者一类功能,如data-redis(spring-boot-starter-data-redis,提供Redis访问功能)、jdbc(spring-boot-starter-jdbc,提供基于JDBC驱动访问数据库功能)等等。以SpringBoot当前最新的发布版本2.3.1.RELEASE的org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:jar:2.3.1.RELEASE为例,用mvn dependency:tree分析它的依赖关系如下:

这个依赖树也印证了starter是基于Spring项目装箱和扩展的。
SpringBoot依赖管理
如果使用Spring Initializr创建一个SpringBoot项目的话,那么会发现项目的POM文件中会加入了一个parent元素:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
其实spring-boot-starter-parent相当于作为了当前项目的父模块,在父模块里面管理了当前指定的SpringBoot版本2.3.1.RELEASE所有依赖的第三方库的统一版本管理,通过spring-boot-starter-parent上溯到最顶层的项目,会找到一个properties元素,里面统一管理Spring框架和所有依赖到的第三方组件的统一版本号,这样就能确保对于一个确定的SpringBoot版本,它引入的其他starter不再需要指定版本,同时所有的第三方依赖的版本也是固定的。如项目的POM文件如下:
<!-- 暂时省略其他的配置属性 -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
这样只需要修改parent元素中的版本号,就能全局更变所有starter的版本号。这种做法其实本质上是把当前项目作为spring-boot-starter-parent的子项目,其实在一定程度上并不灵活。这里推荐使用另一种方式:通过dependencyManagement元素全局管理SpringBoot版本,适用于单模块或者多模块的Maven项目。项目的(父)POM文件如下:
<!-- spring-boot-guide 父POM -->
<properties>
<spring.boot.version>2.3.1.RELEASE</spring.boot.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.version}</version>
<scope>import</scope>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
然后需要用到其他starter的时候,只需要在dependencies直接引入即可,不再需要指定版本号,版本号由dependencyManagement中定义的版本号统一管理。
<!-- spring-boot-guide/ch0-dependency 子POM -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
SpringBoot依赖覆盖
有些特殊的情况,可能项目中大部分的starter使用的是相对低的版本,但是由于部分新的功能需要使用到更高版本的个别starter,则需要强制引入该高版本的starter。这里举一个例子,项目用到的SpringBoot组件的版本是2.1.5.RELEASE,使用的中间件服务Elasticsearch的版本是7.x,而spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch支持的版本如下:
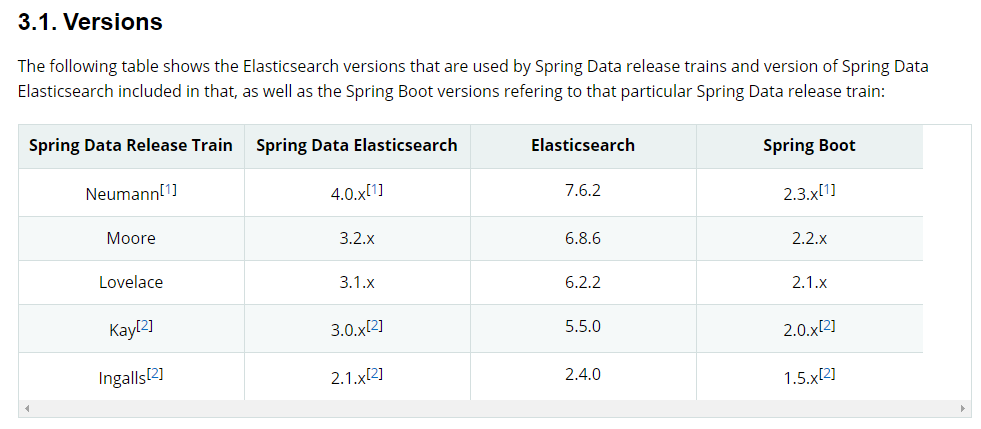
理论上可以一下子升级SpringBoot到2.3.1.RELEASE,其实也可以直接指定spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch的版本覆盖掉全局的SpringBoot组件版本,这里应用了Maven的依赖调解原则:
<!-- 父POM或者全局POM -->
<properties>
<spring.boot.version>2.1.5.RELEASE</spring.boot.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.version}</version>
<scope>import</scope>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
这样就能单独提升spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch的版本为2.3.1.RELEASE,其他组件的版本依然保持为2.1.5.RELEASE。
小结
目前有两种常用的方式管理SpringBoot组件的版本(两种方式二选一):
- 配置
parent元素,通过项目继承的方式指定SpringBoot组件的版本号,这是Spring Initializr生成的项目中默认的配置方式。 - 配置
dependencyManagement元素(推荐此方式),通过(父)POM文件统一指定SpringBoot组件的版本号。
另外,SpringBoot的1.x和2.x之间有兼容性问题(最明显的一点是2.x中删除了1.x中大量的内建类,如果用到了这些SpringBoot中的内建类,容易出现ClassNotFoundException),降级或者升级都有比较大的风险。一般情况下,建议使用同一个大版本进行项目开发,如果确定需要进行大版本切换,请务必做完备的功能测试。
(本文完 c-1-d e-a-20200628)
技术公众号(《Throwable文摘》,id:throwable-doge),不定期推送笔者原创技术文章(绝不抄袭或者转载):



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号