Self-paced Clustering Ensemble自步聚类集成论文笔记
Self-paced Clustering Ensemble自步聚类集成论文笔记
0.摘要
- 现有的聚类集成方法大多利用所有的数据来学习一致的聚类结果,没有充分考虑一些困难实例所带来的不利影响。
- 为了解决这个问题,提出Self-Paced Clustering Ensemble(SPCE)方法。逐步将例子从简单到困难的纳入到集成学习中。
- 将实例的难易度评价和集成学习集成在一个框架中
- 联合学习算法获得最终的一致的聚类结果
1.introduction
-
传统聚类的问题
- 在给定的数据集中,不同的目标函数会有非常不同的结构。
- 没有ground truth
- 比如k-means,高度依赖初始化
-
clustering ensemble定义
- Clustering ensemble provides an elegant framework for combining multiple weak base clusterings of a data set to generate a consensus clustering.
-
之前的clustering ensemble方法
- information theoretic based clustering ensemble methods 基于信息论的集成聚类方法
[3] A. Strehl and J. Ghosh, “Cluster ensembles — a knowledge reuse framework for combining multiple partitions,” Journal of Machine Learning Research, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 583–617, 2003.
[4] A. Topchy, A. K. Jain, and W. F. Punch, “Combining multiple weak clusterings,” in ICDM, 2003, pp. 331–338.
-
an alignment method to combine multiple k-means clustering results 一种组合多个k均值聚类结果的对齐方法
[5] Z. Zhou and W. Tang, “Clusterer ensemble,” Knowledge Based Systems, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 77–83, 2006.
-
extended graph cut method into clustering ensemble 扩展图切割的方法到集成聚类
[8]X. Z. Fern and C. E. Brodley, “Solving cluster ensemble problems by bipartite graph partitioning,” in ICML, 2004, p. 36
-
spectral clustering based ensemble method 基于谱聚类的集成方法
[9] H. Liu, T. Liu, J. Wu, D. Tao, and Y. Fu, “Spectral ensemble clustering,” in SIGKDD, 2015, pp. 715–724.
[10] Z. Tao, H. Liu, and Y. Fu, “Simultaneous clustering and ensemble.” in AAAI, 2017, pp. 1546–1552.
-
utilized non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) to learn a consensus clustering result 利用非负矩阵分解来学习一致的聚类结果
[11] T. Li, C. H. Q. Ding, and M. I. Jordan, “Solving consensus and semisupervised clustering problems using nonnegative matrix factorization,” in ICDM, 2007, pp. 577–582.
[12] T. Li and C. H. Q. Ding, “Weighted consensus clustering.” in SDM, 2008, pp. 798–809.
-
introduced probabilistic graphical model into clustering ensemble 将概率图模型引入集成聚类
[13] H. Wang, H. Shan, and A. Banerjee, “Bayesian cluster ensembles,” in SDM, 2009, pp. 211–222.
[14] D. Huang, J. Lai, and C. Wang, “Ensemble clustering using factor graph,” Pattern Recognition, vol. 50, pp. 131–142, 2016.
- Besides these work which ensemble all base clustering results, some work tried to select some informative and non-redundant base clustering results for ensemble. 除了这些集合所有基本聚类结果的工作之外,还有的工作致力于为集成学习选择一些信息性和非冗余的基本聚类结果。
-
adaptive clustering ensemble selection method to select the base results 自适应聚类集成选择方法选择基础结果
[15] J. Azimi and X. Fern, “Adaptive cluster ensemble selection,” in Twenty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2009.
-
transferred the clustering selection to feature selection and designed a hybrid strategy to select base results 将聚类选择转移到特征选择并设计混合策略以选择基础结果
[16] Z. Yu, L. Li, Y. Gao, J. You, J. Liu, H. Wong, and G. Han, “Hybrid clustering solution selection strategy,” Pattern Recognition, vol. 47,no. 10, pp. 3362–3375, 2014.
-
Zhao et al. proposed internal validity indices for clustering ensemble selection 提出内部有效性指标来进行集成聚类选择
[17] X. Zhao, J. Liang, and C. Dang, “Clustering ensemble selection for categorical data based on internal validity indices,” Pattern Recognition, vol. 69, pp. 150–168, 2017.
-
存在问题
- 使用所有的数据进行聚类集成,可能有些样本很难聚类,甚至有些是异常值,可能会导致聚类性能差。
-
改进
- 将基础的聚类集成到课程学习(Curriculum Learning)框架中。
- 课程学习关键思想是,在早期,模型相对较弱,需要一些简单的实例进行训练;随着时间的推移,模型的能力越来越强,可以处理越来越多的困难实例;最后,它足够强大,可以处理几乎所有的实例。
- 将权重矩阵学习和一致连接矩阵学习集成在一个目标函数中。
- 将基础的聚类集成到课程学习(Curriculum Learning)框架中。
2.Related Work
2.1聚类集成相关定义
- 给定数据集,对数据集做m次聚类可以得到m个聚类结果 [Math Processing Error]C^i = \{C^1, C^2, …,C^m\}Ci={C1,C2,…,Cm},每一个聚类结果[Math Processing Error]C^iCi包含簇的集合[Math Processing Error]\{\pi_1^i,\pi_2^i,…,\pi_k^i\}{π1i,π2i,…,πki},[Math Processing Error]kk是[Math Processing Error]C^iCi中的簇的数目。
- 根据聚类结果可以得到实例之间的关系,根据[Math Processing Error]C^iCi可以构建连接矩阵[Math Processing Error]S^{(i)} \in R^{n*n}S(i)∈Rn∗n
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- 聚类集成的目标就是从[Math Processing Error]S^{(1)},S^{(2)},…,S^{(m)}S(1),S(2),…,S(m)中学习一个一致矩阵[Math Processing Error]SS,最后的聚类结果就可以直接从[Math Processing Error]SS中获得。
2.2Self-paced Learning自步学习
[Math Processing Error]f(\omega_i, \lambda)f(ωi,λ)是自步正则化项,最优的[Math Processing Error]\omega_i^*ωi∗随着[Math Processing Error]\lambdaλ的增加而增加,随着[Math Processing Error]l_ili的增加而减小。也就是说损失越小,越简单,权重越大,越先学习。[Math Processing Error]\lambdaλ随着学习的过程的进行而增加,越来越多的实例被采用。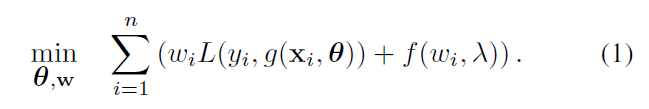
3.自步聚类集成
目标函数
- (1)S是一致矩阵,我们希望使得它与所有连接矩阵之间的差异性越小越好,既 [Math Processing Error]\sum_{i=1}^m\Vert S-S^{(i)}\Vert_F^2∑i=1m∥S−S(i)∥F2
- (2)但是不能每种结果都是相同的权重,加个权重:[Math Processing Error]\sum_{i=1}^m\alpha_i\Vert S-S^{(i)}\Vert_F^2∑i=1mαi∥S−S(i)∥F2
- (3)[Math Processing Error]\alphaα的取值采用auto-weighted的方法,定义[Math Processing Error]\alpha_i=\frac{1}{\Vert S-S^(i)\Vert_F}αi=∥S−S(i)∥F1,也就是说越相似,权重越大。objective function:
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- (4)添加自步学习框架:添加自步函数 [Math Processing Error]f(W, \lambda)=-\lambda\Vert W\Vert_1f(W,λ)=−λ∥W∥1
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- (5)Theorem 1 说明如果S的拉普拉斯矩阵的秩为 n-c,就可以直接得到一致矩阵有c个连通分量,也就是c个簇。所以添加约束[Math Processing Error]rank(L)=n-crank(L)=n−c。
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- (6)又希望一致矩阵S尽可能的稀疏,这样得到的聚类结果会更加清晰,会占喜出更加清晰的图结构、聚类结构。所以对S添加一个一范约束。[Math Processing Error]\gammaγ是调节S稀疏程度的超参数。
![在这里插入图片描述]()


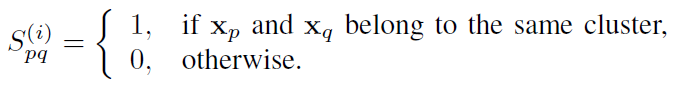
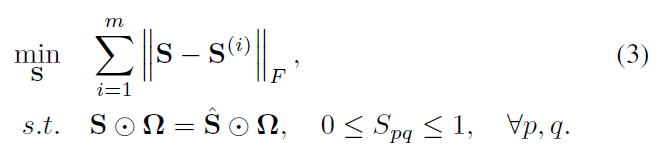
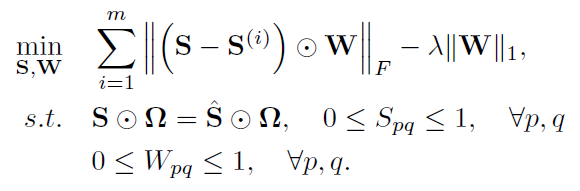



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号