Office OpenXML-WordprocessingML 解析(二):字符和字符格式
1. 字符
在 OpenXML 文档中,文本字符通过以下形式表示:
<w:p> // Paragraph
<w:r> // Run
<w:t>中文English</w:t> // Text
</w:r>
</w:p>
其中 p(Paragraph) 元素表示段落,r(Run) 元素表示一个文本范围,其中包含多个字符,即便这些字符属于不同语言。
2. 字符格式
字符格式位于 rPr(RunProperties) 元素中,如下所示:
<w:r> // Run
<w:rPr> // RunProperties
<w:rFonts w:ascii="Times New Roman" w:hAnsi="Times New Roman" w:eastAsia="微软雅黑" w:cs="Times New Roman" w:hint="eastAsia" /> // RunFonts
<w:sz w:val="20" /> // FontSize
<w:bold /> // Bold
</w:rPr>
<w:t>中文English</w:t>
</w:r>
其中包含字体(rFonts)、字号(sz)和加粗(bold)格式,下面主要对这3种格式进行介绍。
2.1 字体
字体在 rFonts(RunFonts) 元素中进行声明:
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:ascii="Times New Roman" w:hAnsi="Times New Roman" w:eastAsia="微软雅黑" w:cs="Times New Roman" w:hint="eastAsia" />
</w:rPr>
我们可以看到,rFonts 元素分别定义了 ascii、hAnsi、eastAsia 和 cs 4种属性以及对于的字体名称。这4种属性的含义如下表所示:
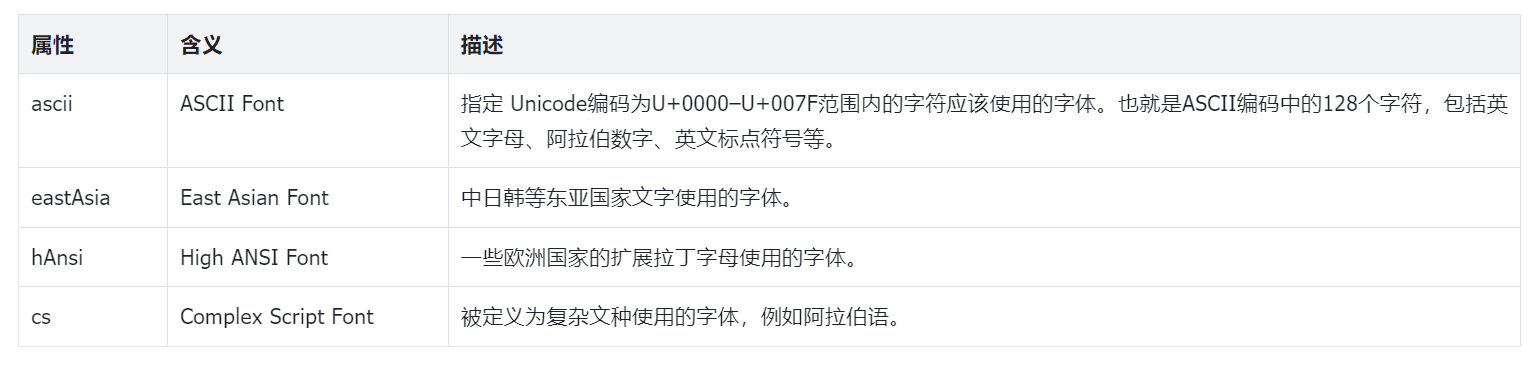
另外,还定义了一个 hint 属性,这个属性的值有以下三种:
- Default (High ANSI Font);
- EastAsia (East Asian Font);
- ComplexScript (Complex Script Font).
该属性的作用是当字符处于 eastAsia 、 hAnsi或cs 字体的交叉区域中时,决定应该使用哪种字体。
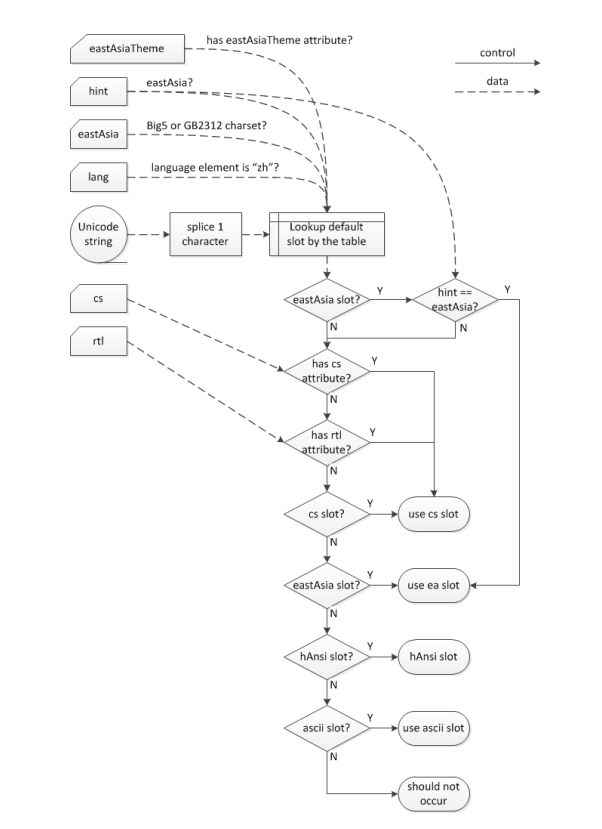
综上,我们通过下列步骤来确定字符应该使用的字体:
- 查阅表格(见本文末尾的字体编码表)初步确定字符应该使用的字体;
- 如果字符为
eastAsia字体并且hint的值为 eastAsia,那么该字符就应该使用eastAsia指定的字体;否则,如果rPr元素中定义了cs或者rtl元素,那么字符就应该使用cs字体,不管它的 Unicode 编码在哪个区域 (不过在使用 MS Word 2019 验证时,微软似乎并未遵守此规则,实际情况是:只要rPr元素中定义了cs或者rtl元素,不管hint的值是不是 eastAsia,所有字符使用的都是cs指定的字体);否则,使用第1步中的字体。
步骤图如下:
示例:
例1:下面这个 r 元素中同时存在中文字符和英文字符,
<w:r>
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:ascii="Arial" w:eastAsia="微软雅黑" />
</w:rPr>
<w:t>中文English</w:t>
</w:r>
在 rFonts 元素中,指定了 ASCII 和 EastAsia 2种字体,根据前面的规则,我们可以得知,“中文” 字符应用微软雅黑字体,“English” 字符应用Arial字体。
例2:
<w:r>
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:hint="eastAsia" w:ascii="Arial" w:eastAsia="微软雅黑" w:cs="宋体" />
<w:cs />
</w:rPr>
<w:t>中文English</w:t>
</w:r>
在这个例子中, 由于声明了 cs 元素且 hint 的值为 eastAsia,按照上面的规则,“中文” 字符应该应用微软雅黑字体,“English” 字符应该应用宋体字体;然而,在使用 Word 2019 验证时,“中文”和“English” 字符应用的都是宋体字体。
2.1.1 主题字体
另外,rFonts 元素还有 asciiTheme、eastAsiaTheme、hAnsiTheme 和 cstheme 4种主题字体,分别表示用来替换ascii、eastAsia、hAnsi 和 cs 属性的字体。也就是说,如果 rFonts 元素中声明了主题字体属性,那么对应的属性会被忽略。主题字体的属性值有以下8种:
- majorEastAsia: Major East Asian Theme Font;
- majorBidi: Major Complex Script Theme Font;
- majorAscii: Major ASCII Theme Font;
- majorHAnsi: Major High ANSI Theme Font;
- minorEastAsia: Minor East Asian Theme Font;
- minorBidi: Minor Complex Script Theme Font;
- minorAscii: Minor ASCII Theme Font;
- minorHAnsi: Minor High ANSI Theme Font.
主题字体的值引用的是 OpenXML 文档中ThemePart中的字体,如下所示:
点击查看
<a:theme>
<a:themeElements>
<a:fontScheme name="Calibri">
<a:majorFont>
<a:latin typeface="Calibri" panose="020F0502020204030204" />
<a:ea typeface="" />
<a:cs typeface="" />
<a:font script="Jpan" typeface="メイリオ" />
<a:font script="Hang" typeface="맑은 고딕" />
<a:font script="Hans" typeface="宋体" />
<a:font script="Hant" typeface="新細明體" />
<a:font script="Arab" typeface="Arial" />
<a:font script="Hebr" typeface="Arial" />
<a:font script="Thai" typeface="Cordia New" />
<a:font script="Ethi" typeface="Nyala" />
<a:font script="Beng" typeface="Vrinda" />
<a:font script="Gujr" typeface="Shruti" />
<a:font script="Khmr" typeface="DaunPenh" />
<a:font script="Knda" typeface="Tunga" />
<a:font script="Guru" typeface="Raavi" />
<a:font script="Cans" typeface="Euphemia" />
<a:font script="Cher" typeface="Plantagenet Cherokee" />
<a:font script="Yiii" typeface="Microsoft Yi Baiti" />
<a:font script="Tibt" typeface="Microsoft Himalaya" />
<a:font script="Thaa" typeface="MV Boli" />
<a:font script="Deva" typeface="Mangal" />
<a:font script="Telu" typeface="Gautami" />
<a:font script="Taml" typeface="Latha" />
<a:font script="Syrc" typeface="Estrangelo Edessa" />
<a:font script="Orya" typeface="Kalinga" />
<a:font script="Mlym" typeface="Kartika" />
<a:font script="Laoo" typeface="DokChampa" />
<a:font script="Sinh" typeface="Iskoola Pota" />
<a:font script="Mong" typeface="Mongolian Baiti" />
<a:font script="Viet" typeface="Tahoma" />
<a:font script="Uigh" typeface="Microsoft Uighur" />
<a:font script="Geor" typeface="Sylfaen" />
</a:majorFont>
<a:minorFont>
<a:latin typeface="Calibri" panose="020F0502020204030204" />
<a:ea typeface="" />
<a:cs typeface="" />
<a:font script="Jpan" typeface="メイリオ" />
<a:font script="Hang" typeface="맑은 고딕" />
<a:font script="Hans" typeface="宋体" />
<a:font script="Hant" typeface="新細明體" />
<a:font script="Arab" typeface="Arial" />
<a:font script="Hebr" typeface="Arial" />
<a:font script="Thai" typeface="Cordia New" />
<a:font script="Ethi" typeface="Nyala" />
<a:font script="Beng" typeface="Vrinda" />
<a:font script="Gujr" typeface="Shruti" />
<a:font script="Khmr" typeface="DaunPenh" />
<a:font script="Knda" typeface="Tunga" />
<a:font script="Guru" typeface="Raavi" />
<a:font script="Cans" typeface="Euphemia" />
<a:font script="Cher" typeface="Plantagenet Cherokee" />
<a:font script="Yiii" typeface="Microsoft Yi Baiti" />
<a:font script="Tibt" typeface="Microsoft Himalaya" />
<a:font script="Thaa" typeface="MV Boli" />
<a:font script="Deva" typeface="Mangal" />
<a:font script="Telu" typeface="Gautami" />
<a:font script="Taml" typeface="Latha" />
<a:font script="Syrc" typeface="Estrangelo Edessa" />
<a:font script="Orya" typeface="Kalinga" />
<a:font script="Mlym" typeface="Kartika" />
<a:font script="Laoo" typeface="DokChampa" />
<a:font script="Sinh" typeface="Iskoola Pota" />
<a:font script="Mong" typeface="Mongolian Baiti" />
<a:font script="Viet" typeface="Tahoma" />
<a:font script="Uigh" typeface="Microsoft Uighur" />
<a:font script="Geor" typeface="Sylfaen" />
</a:minorFont>
</a:fontScheme>
</a:themeElements>
</a:theme>
其中,字体由两个部分组成:majorFont 和 minorFont。每个部分包含 latin、ea、cs 以及表示不同国家语言的 font 元素。
那么,主题字体的8种属性与上面字体是如何对应的呢?这还与 DocumentSettingsPart 中的 themeFontLang 元素有关。此元素声明如下:
<w:settings>
<w:themeFontLang w:val="en-US" w:eastAsia="zh-CN" w:bidi="ar-SA" />
</w:settings>
其中 val 属性指定的 en-US 代表英语-美国,eastAsia 属性指定的 zh-CN 代表中文-中华人民共和国,bidi 属性指定的 ar-SA 代表阿拉伯语-沙特阿拉伯(见参考中的国家语言代码表)。
通过该元素,我们可以得到下列映射关系:
- majorAscii/majorHAnsi 对应的字体为
val属性值指定的语言所使用的字体, 对应的是majorFont中latin元素的typeface,也就是Calibri; - majorEastAsia 对应的字体为
eastAsia属性指定的语言所使用的字体,对应的是majorFont中script为 Hans 的font元素的typeface,也就是宋体; - majorBidi 对应的字体为
bidi属性指定的语言所使用的字体,对应的是majorFont中script为 Arab 的font元素的typeface,也就是Arial; - minorAscii/majorHAnsi 对应的字体为
val属性值指定的语言所使用的字体, 对应的是minorFont中latin元素的typeface,也就是Calibri; - minorEastAsia 对应的字体为
eastAsia属性指定的语言所使用的字体,对应的是minorFont中script为 Hans 的font元素的typeface,也就是宋体; - minorBidi 对应的字体为
bidi属性指定的语言所使用的字体,对应的是minorFont中script为 Arab 的font元素的typeface,也就是Arial。
不过,如果 DocumentSettingsPart 中未指定 themeFontLang 元素,那么映射关系将如下所示:
- majorAscii/majorHAnsi 对应的字体为
majorFont中latin元素的typeface,也就是Calibri; - majorEastAsia 对应的字体为
majorFont中ea元素的typeface,也就是空; - majorBidi 对应的字体为
majorFont中cs元素的typeface,也就是空; - minorAscii/majorHAnsi 对应的字体为
minorFont中latin元素的typeface,也就是Calibri; - minorEastAsia 对应的字体为
minorFont中ea元素的typeface,也就是空; - minorBidi 对应的字体为
minorFont中cs元素的typeface,也就是空。
2.2 字号
字号在 sz(FontSize) 和 szCs(FontSizeComplexScript) 元素中声明,如下所示:
<w:rPr>
<w:sz w:val="24" />
<w:szCs w:val="32" />
</w:rPr>
其中,字号的大小为 val 属性值的1/2磅。当元素中字符应用的是 Complex Script 字体时,生效的是 szCs 的字号(16磅),否则,sz 元素的字号生效,也就是12磅。
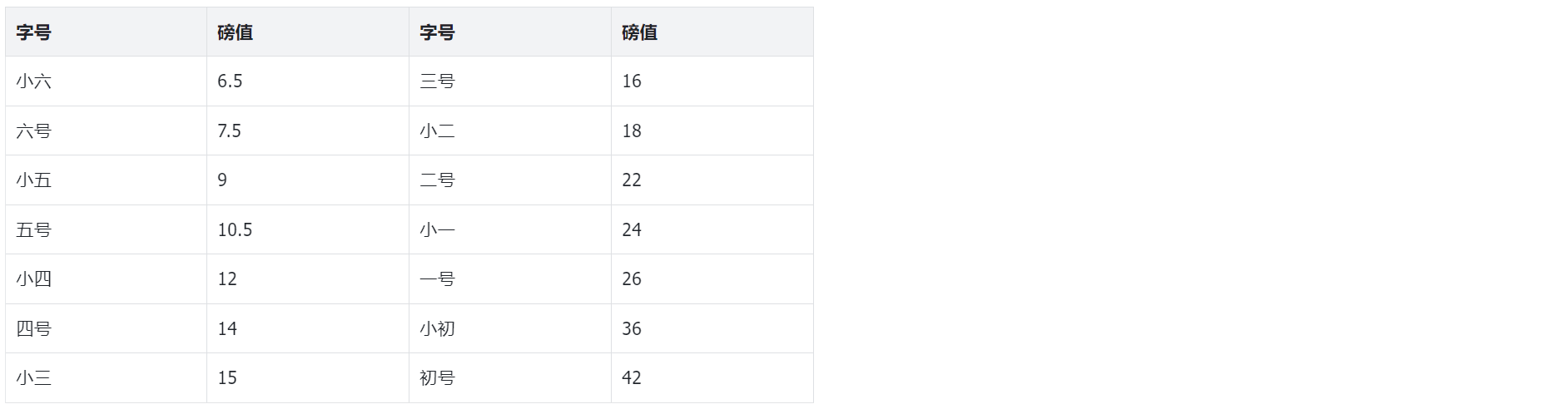
下表为中文字号对应的磅值:
示例:
<w:r>
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:hint="eastAsia" />
<w:sz w:val="24" />
<w:szCs w:val="32" />
<w:cs />
</w:rPr>
<w:t>中文English</w:t>
</w:r>
在这个例子中, 由于声明了 cs 元素且 hint 的值为 eastAsia,按照上面的规则,“中文” 字符的字号应该是24/2=12磅,“English” 字符应该是32/2=16磅;然而,在使用 Word 2019 验证时,“中文”和“English” 字符的字号都是16磅。
2.3 加粗
加粗字形通过 b(Bold) 和 bCs(BoldComplexScript) 元素表示,如下所示:
<w:rPr>
<w:b w:val="false" />
<w:bCs w:val="true" />
</w:rPr>
其中,val 属性的值可以为 false/true 或者 0/1。如果未指定元素,则表示不加粗;如果指定了元素但未指定元素的 val 属性,则值为true,也就是加粗。当元素中字符应用的是 Complex Script 字体时,生效的是 bCs 元素的值,否则,b 元素的值生效。
示例:
<w:r>
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:hint="eastAsia" />
<w:bCs />
<w:cs />
</w:rPr>
<w:t>中文English</w:t>
</w:r>
在这个例子中, 由于声明了 cs 元素且 hint 的值为 eastAsia,按照上面的规则,“中文” 字符的字形不应该加粗,而 “English” 字符应该加粗;然而,在使用 Word 2019 验证时,“中文”和“English” 字符的字形都是加粗的。
3. 样式层级
在 OpenXML 文档中,影响段落中字符的格式的除了当前 r 元素中的 rPr 元素,还有字符样式、段落样式以及文档默认样式中的 rPr 元素。例如下面的字符:
<w:p>
<w:pPr>
<w:pStyle w:val="1" />
</w:pPr>
<w:r>
<w:rPr>
<w:rStyle w:val="10" />
<w:rFonts w:hint="eastAsia" w:eastAsia="宋体" />
</w:rPr>
<w:t>中文</w:t>
</w:r>
</w:p>
其中,字符的 East Asia 字体为宋体,并且应用了如下的字符样式如下:
<w:style w:type="character" w:styleId="10" w:customStyle="1">
<w:name w:val="标题 1 字符" />
<w:basedOn w:val="a0" />
<w:link w:val="1" />
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:eastAsia="微软雅黑" />
</w:rPr>
</w:style>
字符样式的 East Asia 字体为微软雅黑。
同时,字符所在段落应用了如下的段落样式:
<w:style w:type="paragraph" w:styleId="1">
<w:name w:val="heading 1" />
<w:basedOn w:val="a" />
<w:next w:val="a" />
<w:link w:val="10" />
<w:qFormat />
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:eastAsia="楷体" />
</w:rPr>
</w:style>
// 默认段落样式
<w:style w:type="paragraph" w:styleId="a" w:default="1" xmlns:w="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/wordprocessingml/2006/main">
<w:name w:val="Normal" />
<w:qFormat />
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:eastAsia="宋体" />
</w:rPr>
</w:style>
段落样式的 East Asia 字体为楷体,默认段落样式的 East Asia 字体为宋体。
文档的默认格式如下:
<w:docDefaults>
<w:rPrDefault>
<w:rPr>
<w:rFonts w:asciiTheme="minorHAnsi" w:hAnsiTheme="minorHAnsi" w:eastAsiaTheme="minorEastAsia" w:cstheme="minorBidi" />
</w:rPr>
</w:rPrDefault>
</w:docDefaults>
文档默认格式的 East Asia 字体为主题字体 minorEastAsia。
从上面的例子中可以看到,“中文” 字符应用了多层样式,那么在确定该字符的格式时将按照如下步骤查找(以East Asia字体为例):
- 如果当前字符所在的
r元素中定义了EastAsia(或EastAsiaTheme)字体,则应用该字体,否则下一步; - 如果当前字符所在的
r元素中定义了字符样式(rStyle元素)且字符样式中定义了EastAsia(或EastAsiaTheme)字体,则应用该字体,否则下一步: - 如果当前字符所在的
p元素中定义了段落样式(pStyle元素)且段落样式或它的基样式中定义了EastAsia(或EastAsiaTheme)字体,则应用该字体,否则下一步; - 如果默认段落样式中定义了EastAsia(或EastAsiaTheme)字体,则应用该字体,否则下一步;
- 如果文档的默认格式中定义了EastAsia(或EastAsiaTheme)字体,则应用该字体。
4. 字体编码表
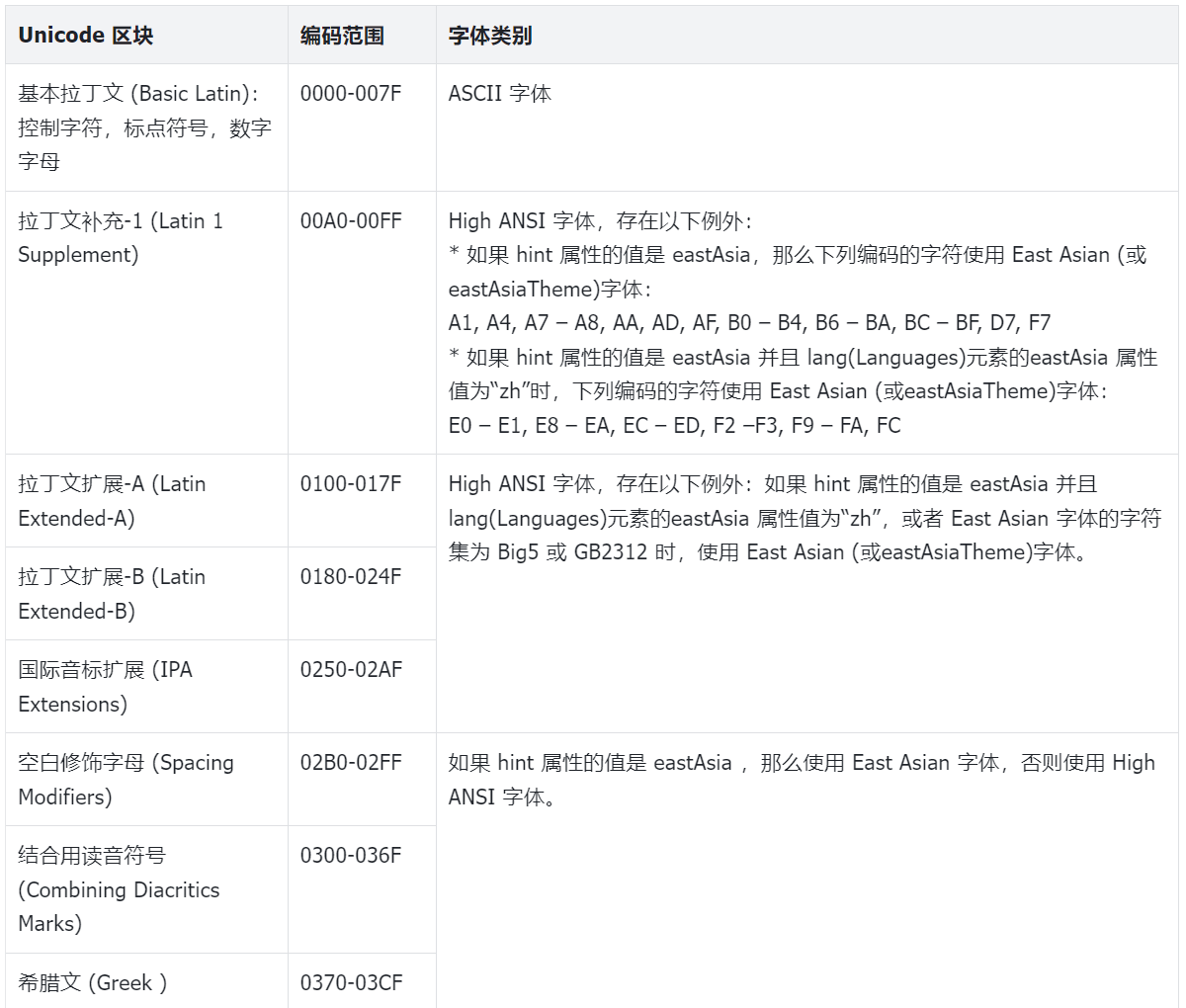
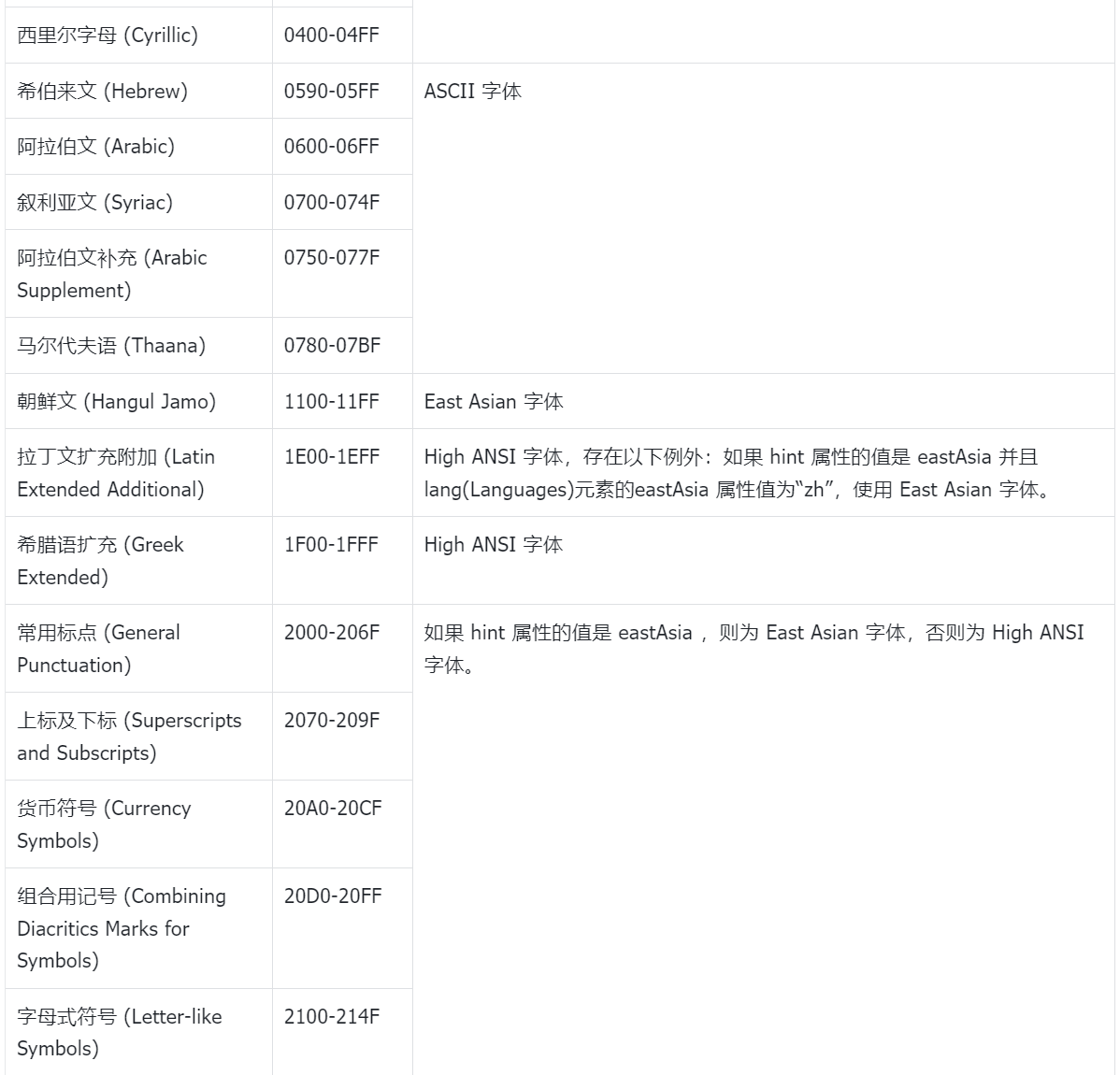
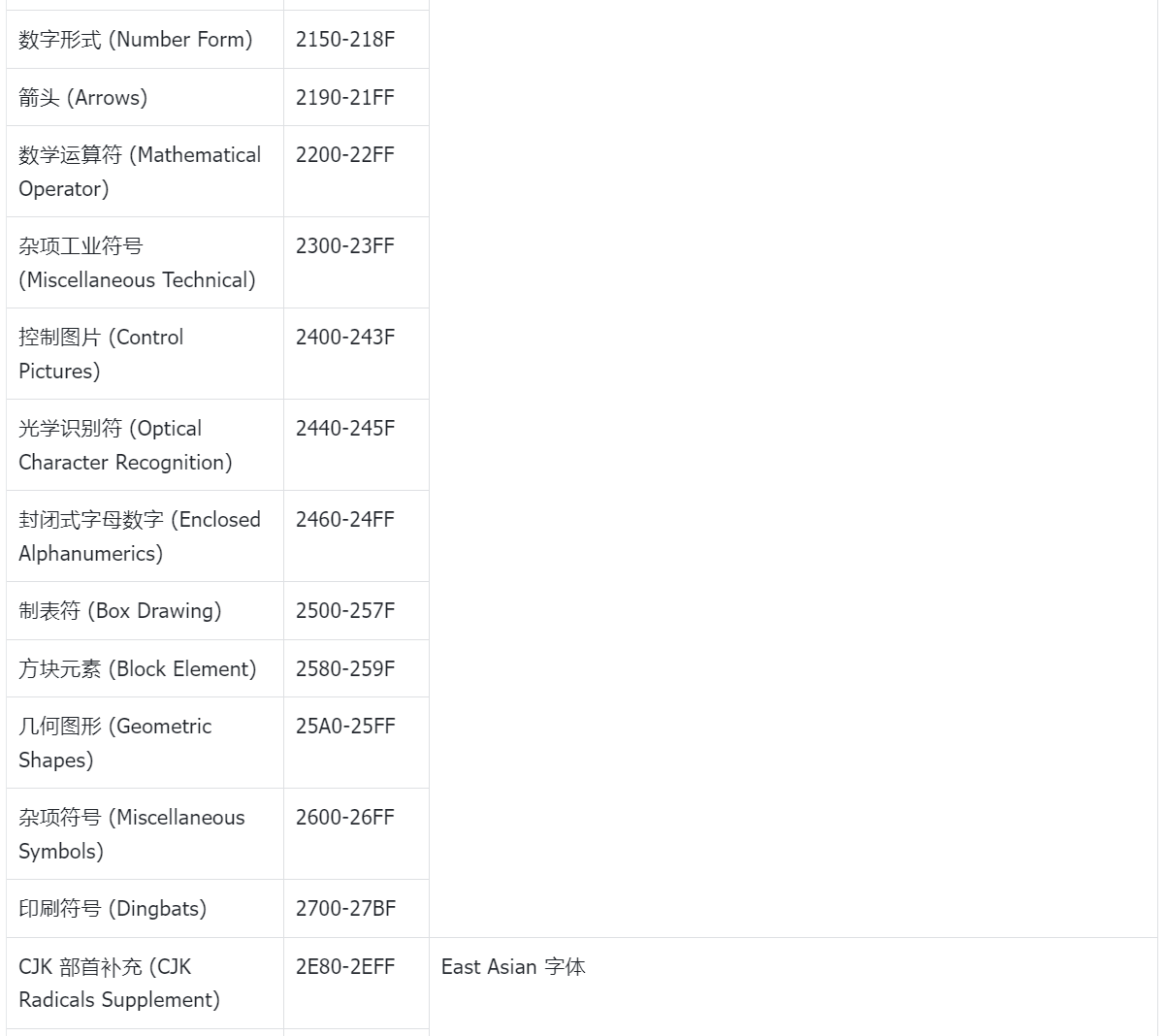

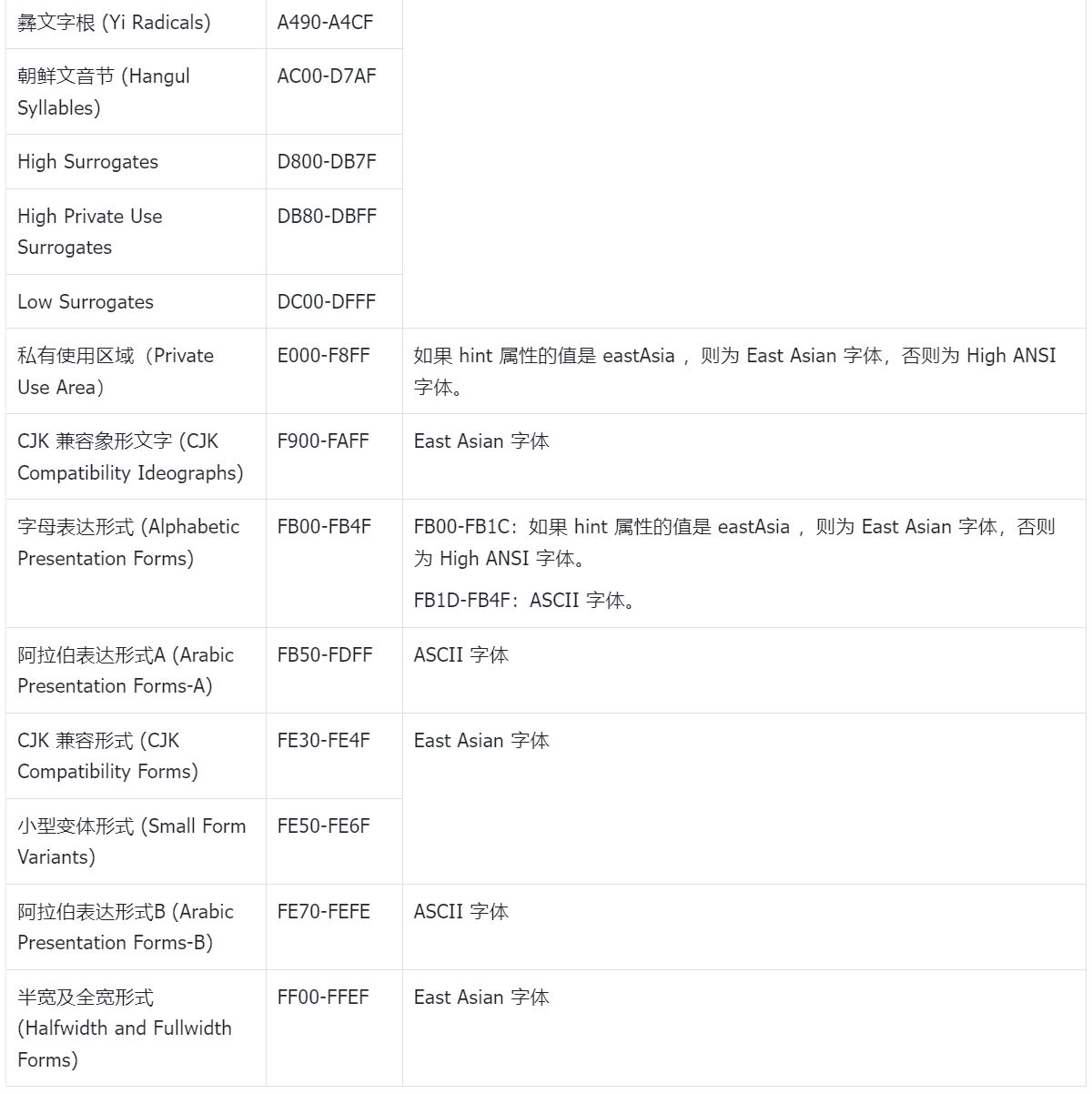
5. 参考
[1] ECMA-376-1:2016,Office Open XML File Formats — Fundamentals and Markup Language Reference,§17.3.2.26 Run Fonts
[2] 国家语言代码表
作者:扬帆,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/theyangfan/p/17071861.html
--- 💖 来自博客园 ---






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通