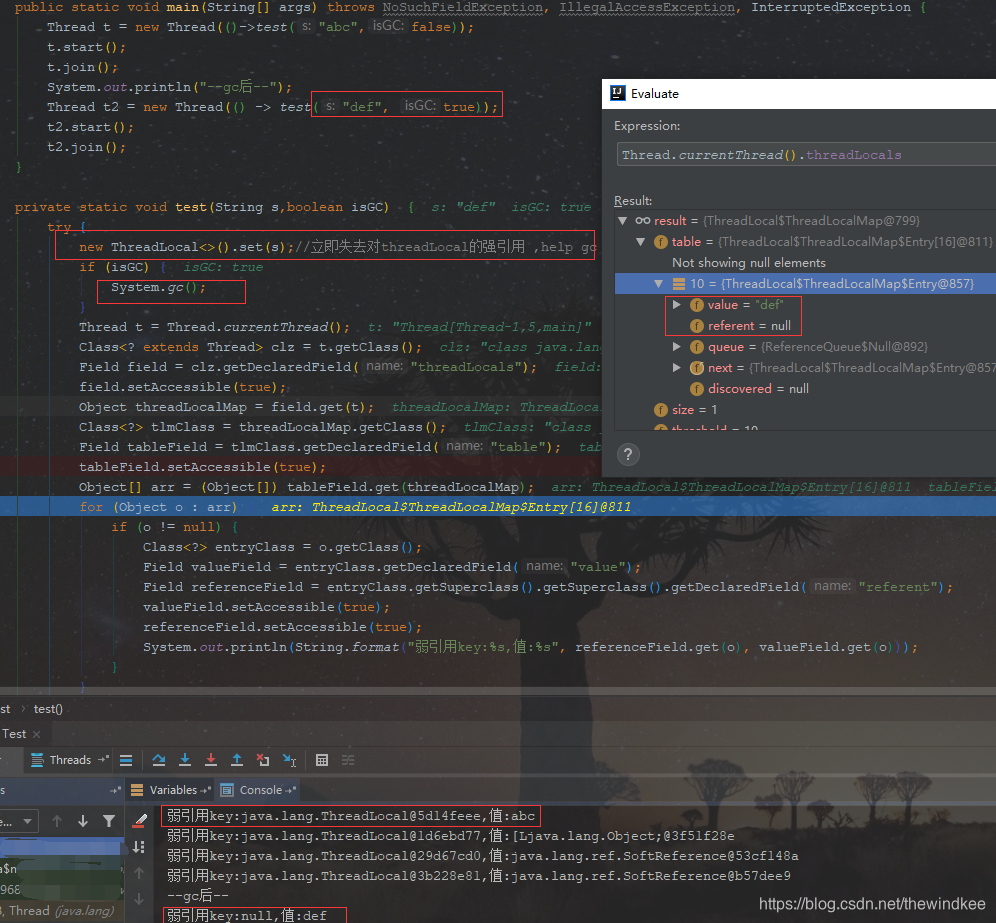
【内存泄漏】测试ThreadLocal 在gc后引发的threadLocalMap的key为null,但value不为null的情况
效果
gc后key为null,但是值不为null。
需要注意的是,这里立即释放了对threadLocal实例的强引用,帮助gc回收。查看弱引用的使用方法
原因
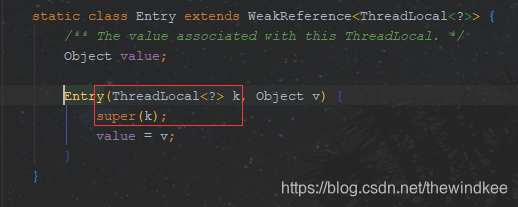
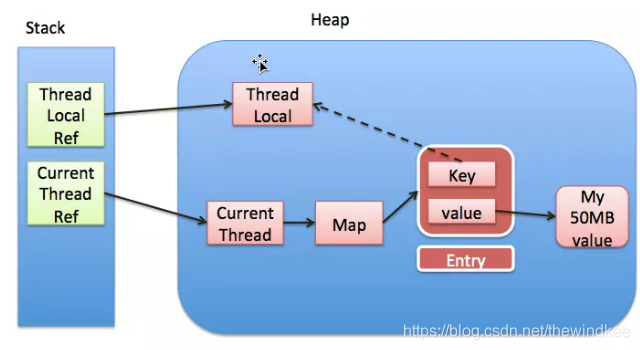
ThreadLocal#set后会将threadLocal实例本身作为key 放入 Thread.currentThread().threadLocalMap中,与set的value构成一对Entry。而Entry使用了threadLocal的实例作为 弱引用。因此当发生gc的时候,弱引用的key会被回收掉,而作为强引用的value还存在。
作为key的弱引用的ThreadLocal
此次借用网图帮助理解
注意
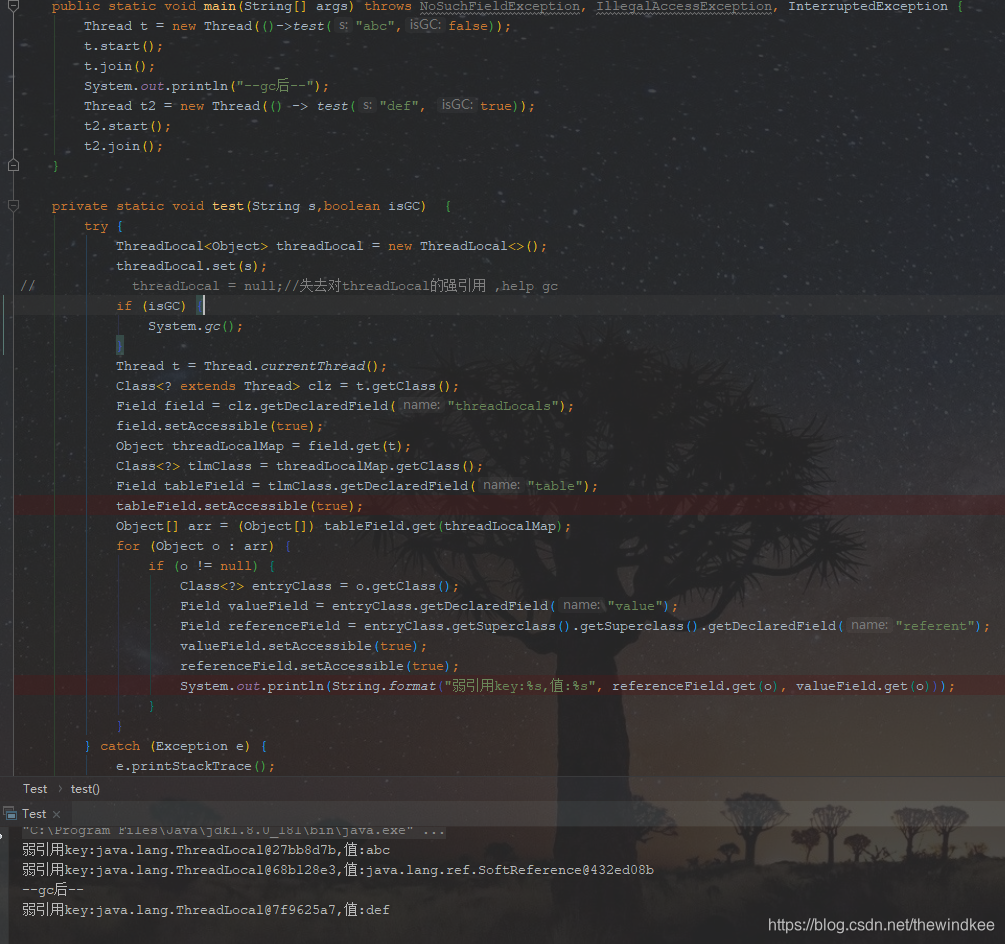
正如我在注释中写的那样,如果没有失去对ThreadLocal本身的强引用,那么不会回收threadLocal。
而我们平时代码中写的那样,使用static final修饰threadLocal保留一个全局的threadLocal方便传递其他value(threadLocal一直被强引用)。这样就不会让gc回收 作为key的threadLocal。即不会导致key为null。
使用ThreadLocal关键之处还是在于,使用完毕要记得remove。特别是在线程池中使用的时候。(否则会等到下一次set的时候才替换掉value–>作为key的threadLocal为同一个所以是替换)
threadLocal被强引用 引用,无法被回收
代码
/**
* 测试ThreadLocal 在gc后引发的threadLocalMap的key为null,但value不为null的情况
* @Author thewindkee
* @Date 2019/12/27 9:28
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->test("abc",false));
t.start();
t.join();
System.out.println("--gc后--");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> test("def", true));
t2.start();
t2.join();
}
private static void test(String s,boolean isGC) {
try {
ThreadLocal<Object> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(s);
threadLocal = null;//失去对threadLocal的强引用 ,help gc
if (isGC) {
System.gc();
}
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
Class<? extends Thread> clz = t.getClass();
Field field = clz.getDeclaredField("threadLocals");
field.setAccessible(true);
Object threadLocalMap = field.get(t);
Class<?> tlmClass = threadLocalMap.getClass();
Field tableField = tlmClass.getDeclaredField("table");
tableField.setAccessible(true);
Object[] arr = (Object[]) tableField.get(threadLocalMap);
for (Object o : arr) {
if (o != null) {
Class<?> entryClass = o.getClass();
Field valueField = entryClass.getDeclaredField("value");
Field referenceField = entryClass.getSuperclass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField("referent");
valueField.setAccessible(true);
referenceField.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(String.format("弱引用key:%s,值:%s", referenceField.get(o), valueField.get(o)));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号