android逆向奇技淫巧二十一:ida反反调试&加密算法跟踪(未完待续)(六)
上周用ida调试x音的时候遇到了大量的弹窗,要是一不小心选择了“pass to app”,结果大概率直接崩掉......... 弹窗这个问题困扰我好久了,如果不解决,后面的trace就没法做了,该怎么解决了?这就要从弹窗的原理说起了!近期用ida调试时遇到的弹窗提示整理如下:
3B745B60: got SIGSEGV signal (Segmentation violation) (exc.code b, tid 17222) 3B745B60: got SIGSEGV signal (Segmentation violation) (exc.code b, tid 17222 C2087AB6: got SIGILL signal (Illegal instruction) (exc.code 4, tid 23457) C197C3BA: got SIGSEGV signal (Segmentation violation) (exc.code b, tid 8991) C1984B64: got SIGCHLD signal (Child status has changed) (exc.code 11, tid 8973) C1710B64: got SIGCHLD signal (Child status has changed) (exc.code 11, tid 23546) C17083BA: got SIGSEGV signal (Segmentation violation) (exc.code b, tid 23565) D736D93C: got SIGSTOP signal (Stop unblockable) (exc.code 13, tid 23384) C1FEF3BA: got SIGSEGV signal (Segmentation violation) (exc.code b, tid 3838) F739B2B8: got SIGABRT signal (Abort) (exc.code 6, tid 3980)
主要有segmentation violation、illegal instrction、child status has changed、abort、stop unblocked等,可谓是五花八门,什么样的都有!大家有没有想过为什么会弹窗了(这不废话么,当然是客户端为了保护自己故意反调试的啦)? 弹窗本质上也是一段代码,既然展示了出来,说明这段代码肯定被执行了!可是我们明明正在调试主线程,这些弹窗的代码都是怎么执行的了? 那就只能时另一种可能了:其他线程执行的!这些弹窗都是通过信号量提示的,说明不同的线程在利用信号量通信!在导入表里面搜索,确实能找到sigaction和pthrad_cond_signal函数,并且还在好几个地方被其他函数调用过!如果直接简单粗暴地NOP这些代码,我担心破坏原有正常的业务逻辑,所以就只能挂起其他线程了!这里直接使用看雪大佬YANG的脚本来挂起其他线程,然后再调试,整个ida再也没有弹窗,清爽多了!
上次分析到:sub_6221C函数内部使用了base64码表,通过ida调试也在内存发现了疑似X-Argus、X-Ladon、X-Tyhon的字符串,这里为了进一步确认,从函数头开始逐行调试,整个逻辑清晰多了:
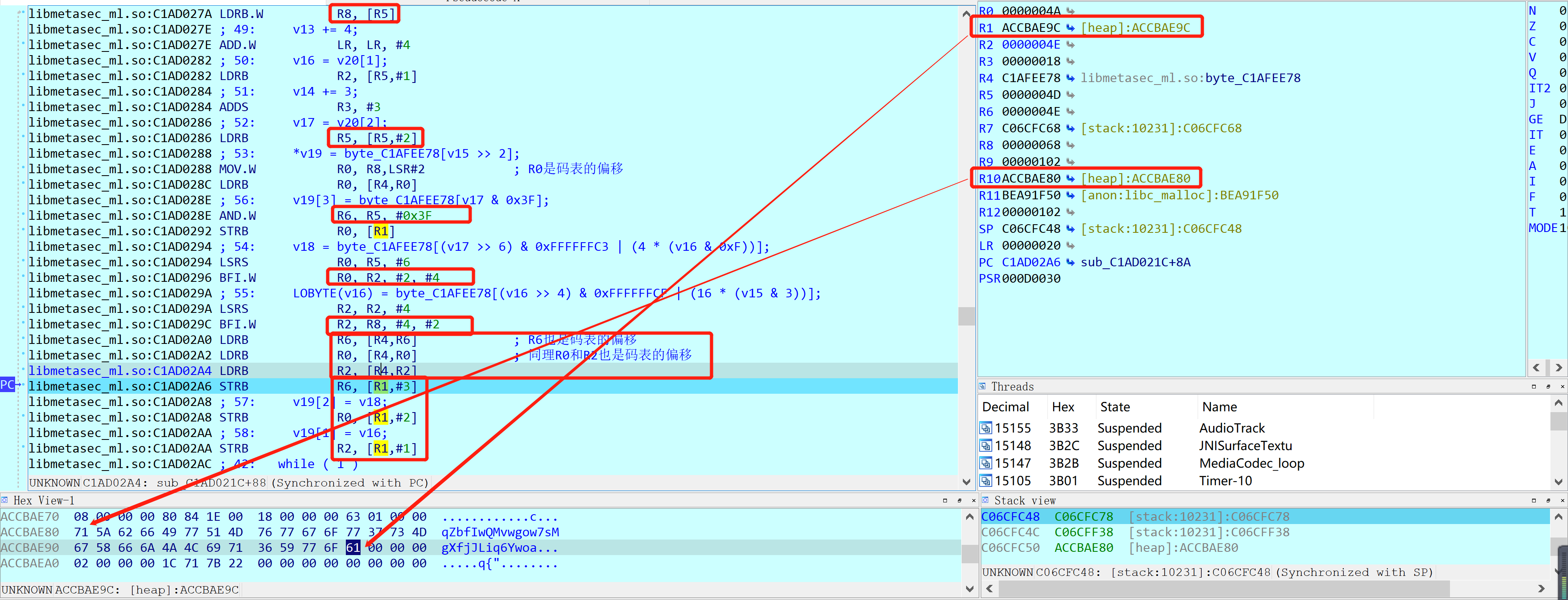
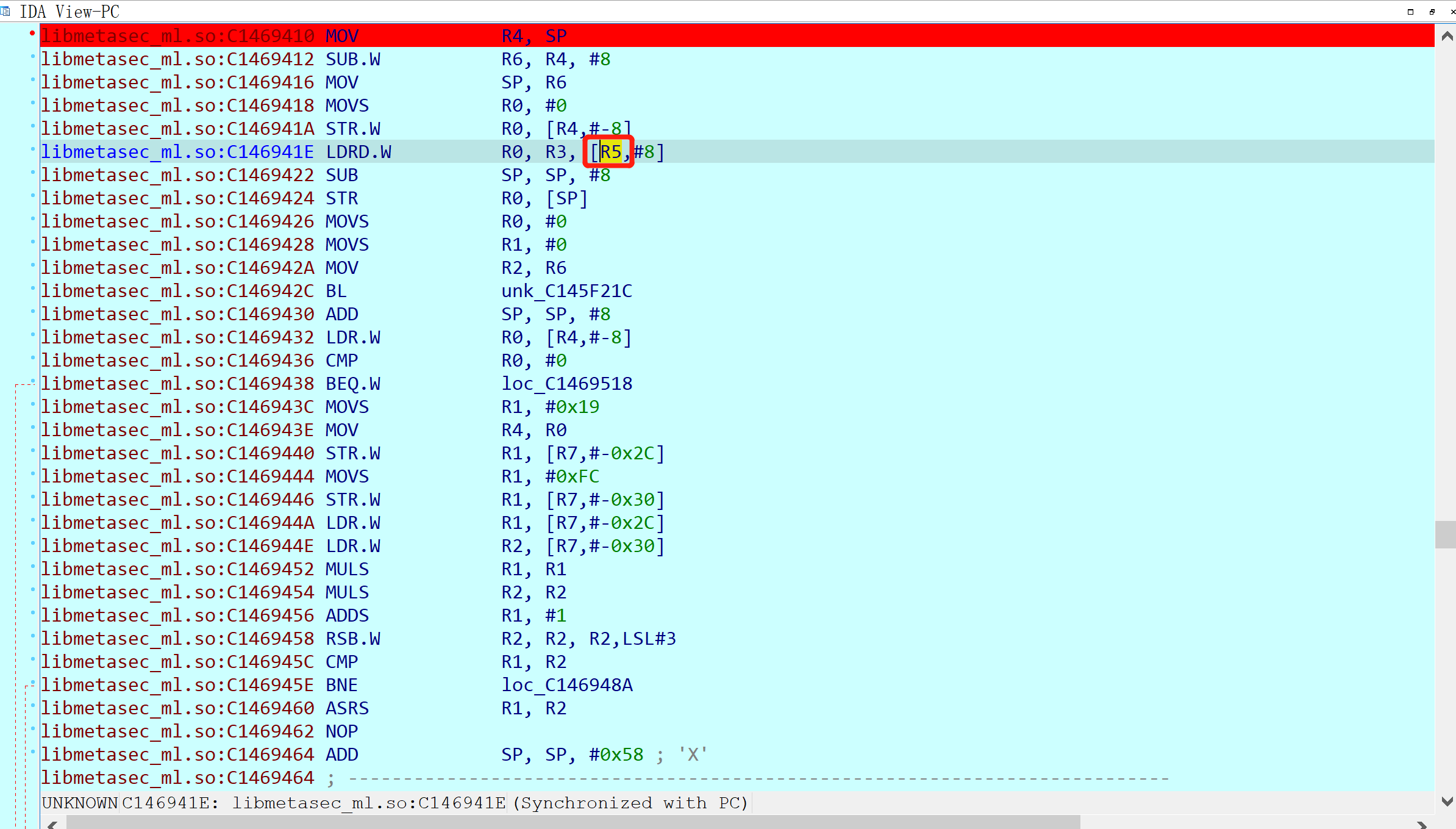
R1指向加密字符串的末尾,每次移动4字节;加密字节分别存放在R0、R1和R6中,分别通过不同的偏移从R4指向的码表中取值!所以现在的关键就是确认这些码表内偏移是怎么得到的了!继续往上追溯:这几个偏移都是从R5计算而来的,而R5又是通过下面的方式得到:从这里可以看出,R5或R11指向的内存区域并不是字符串,这里有点失望!
一般情况下:服务端为了确认接收到的数据没被篡改,会让客户端将加密的校验字段和原文一起发送;服务端接收后用同样的加密算法计算原文,如果和客户端发送的校验字段一致,说明原文没被篡改(数字证书就用到了这个原理);我原本的猜想:客户端会选择一下https包的原文字符串通过加密算法计算出校验字段,然后把校验字段和原文一起发送,所以在逐行调试时应该能找到原文字符串,结果大失所望,这里并不是!
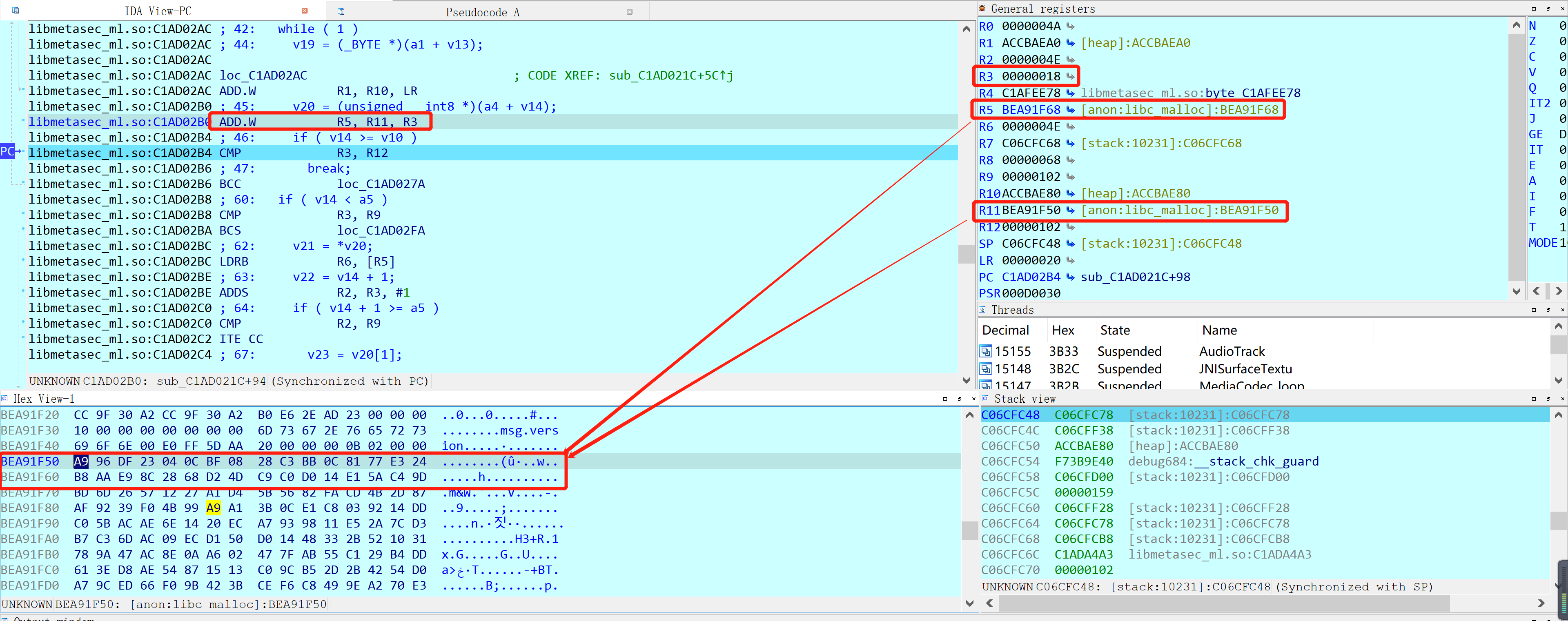
估计是网上追溯的层次不够,那就继续追呗!在sub_6221C开始的地方发现R11是R3得到的,这个R3应该是上层函数调用的参数:
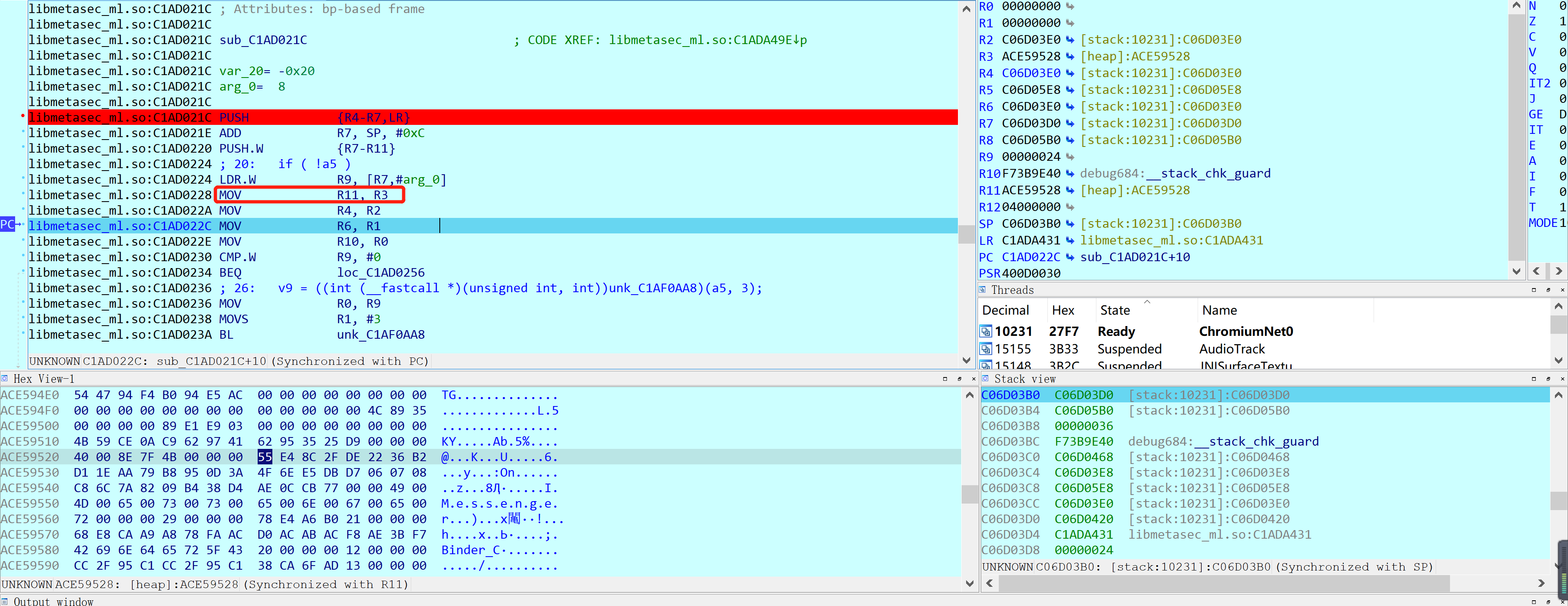
继续往上一层函数追溯,发现这里直接跳转过来了,所以R3又是由R5决定的!
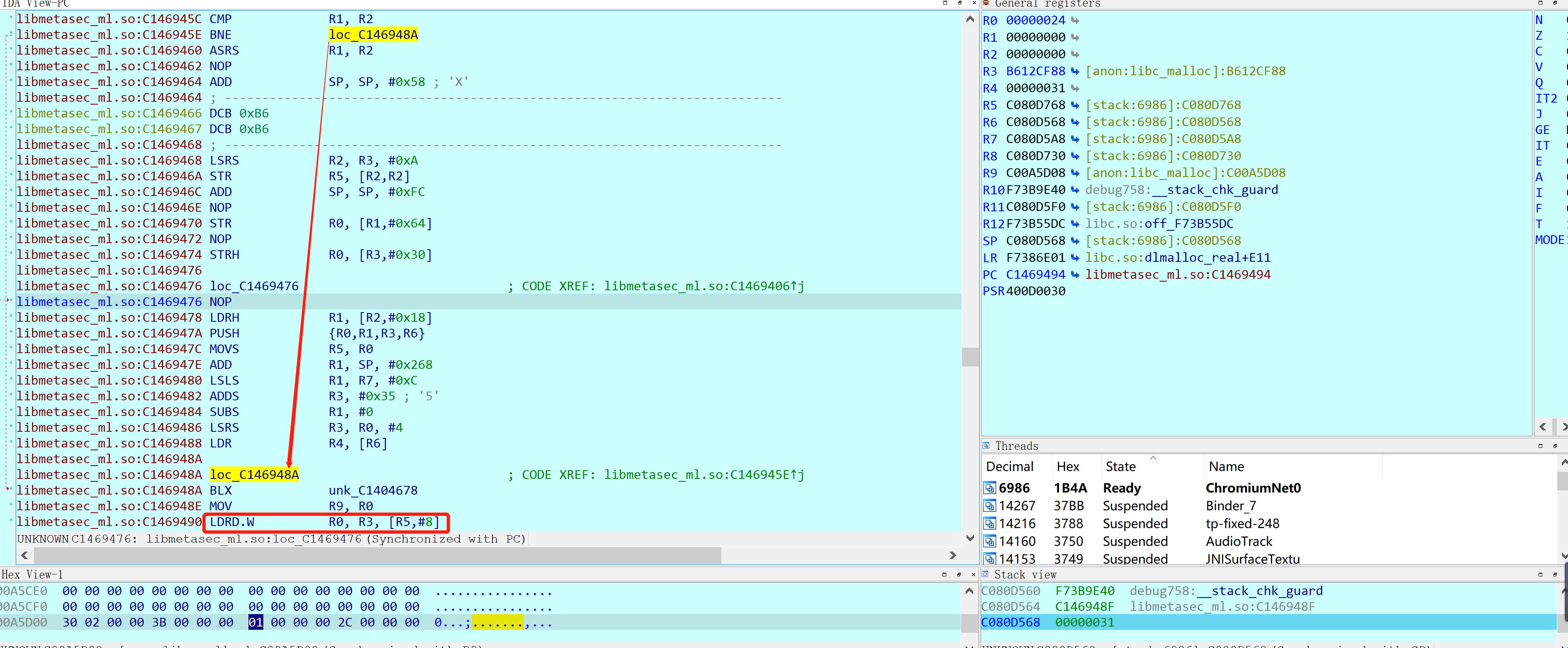
已经追溯到偏移为0x6C41E的地方,暂时还没找到https包的用来加密的原文,下一步打算根据栈回溯来挨个查找!
小结:
(1)这里确认找到了加密字段的生成代码,但是还没找到生成加密字段的原文是啥,需要继续追踪!
(2)信号量:主线程和子线程之间的通信方式,可能的反调试手段有:
-
- 子线程不停地读取主线程status,一旦发现tracerpid不为0说明被调试了,可以发个kill或其他的信号,然后被调试器捕获,就弹窗给使用人员看了
- 子线程和主线程通过信号量通信,一旦发现对方长时间不回复,说明“出事”了,所以要挂起其他线程,只留主线程
脚本:可挂起线程、指令级别地trace;
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import idaapi import idc import re import ida_dbg import ida_idd from idaapi import * from collections import OrderedDict import logging import time import datetime import os debughook = None def xx_hex(ea): return hex(ea).rstrip("L").lstrip("0x") def set_breakpoint(ea): #idc.SetReg(ea, "T", 1) #idc.MakeCode(ea)#ida7.5报错:AttributeError: module 'idc' has no attribute 'MakeCode',新版本ida不兼容旧版本的api,链接有替代的接口 idc.create_insn(ea)#https://hex-rays.com/products/ida/support/ida74_idapython_no_bc695_porting_guide.shtml idc.add_bpt(ea) def my_get_reg_value(register): rv = ida_idd.regval_t() ida_dbg.get_reg_val(register, rv) current_addr = rv.ival return current_addr def suspend_other_thread(): current_thread = idc.get_current_thread() thread_count = idc.get_thread_qty() for i in range(0, thread_count): other_thread = idc.getn_thread(i) if other_thread != current_thread: idc.suspend_thread(other_thread) def resume_process(): current_thread = idc.get_current_thread() thread_count = idc.get_thread_qty() for i in range(0, thread_count): other_thread = idc.getn_thread(i) if other_thread != current_thread: idc.resume_thread(other_thread) idc.resume_thread(current_thread) idc.resume_process() class MyDbgHook(DBG_Hooks): """ Own debug hook class that implementd the callback functions """ def __init__(self, modules_info, skip_functions, end_ea): super(MyDbgHook, self).__init__() self.modules_info = modules_info self.skip_functions = skip_functions self.trace_step_into_count = 0 self.trace_step_into_size = 1 self.trace_total_size = 300000 self.trace_size = 0 self.trace_lr = 0 self.end_ea = end_ea self.bpt_trace = 0 self.Logger = None self.line_trace = 0 print("__init__") def start_line_trace(self): self.bpt_trace = 0 self.line_trace = 1 self.start_hook() def start_hook(self): self.hook() print("start_hook") def dbg_process_start(self, pid, tid, ea, name, base, size): print("Process started, pid=%d tid=%d name=%s" % (pid, tid, name)) def dbg_process_exit(self, pid, tid, ea, code): self.unhook() if self.Logger: self.Logger.log_close() print("Process exited pid=%d tid=%d ea=0x%x code=%d" % (pid, tid, ea, code)) def dbg_process_detach(self, pid, tid, ea): self.unhook() self.Logger.log_close() return 0 def dbg_bpt(self, tid, ea): print("Break point at 0x%x tid=%d" % (ea, tid)) if ea in self.end_ea: ida_dbg.enable_insn_trace(False) ida_dbg.enable_step_trace(False) ida_dbg.suspend_process() return 0 return 0 def dbg_trace(self, tid, ea): #print("Trace tid=%d ea=0x%x" % (tid, ea)) # return values: # 1 - do not log this trace event; # 0 - log it if self.line_trace: in_mine_so = False for module_info in self.modules_info: # print (module_info) so_base = module_info["base"] so_size = module_info["size"] if so_base <= ea <= (so_base + so_size): in_mine_so = True break self.trace_size += 1 if (not in_mine_so) or (ea in self.skip_functions): if (self.trace_lr != 0) and (self.trace_step_into_count < self.trace_step_into_size): self.trace_step_into_count += 1 return 0 if (self.trace_lr != 0) and (self.trace_step_into_count == self.trace_step_into_size): ida_dbg.enable_insn_trace(False) ida_dbg.enable_step_trace(False) ida_dbg.suspend_process() if self.trace_size > self.trace_total_size: self.trace_size = 0 ida_dbg.request_clear_trace() ida_dbg.run_requests() ida_dbg.request_run_to(self.trace_lr) ida_dbg.run_requests() self.trace_lr = 0 self.trace_step_into_count = 0 return 0 if self.trace_lr == 0: self.trace_lr = my_get_reg_value("LR") #arm thumb LR, arm64 X30:注意这里的返回寄存器根据不同的指令选不同的寄存器 return 0 def dbg_run_to(self, pid, tid=0, ea=0): # print("dbg_run_to 0x%x pid=%d" % (ea, pid)) if self.line_trace: ida_dbg.enable_insn_trace(True) ida_dbg.enable_step_trace(True) ida_dbg.request_continue_process() ida_dbg.run_requests() def unhook(): global debughook # Remove an existing debug hook try: if debughook: print("Removing previous hook ...") debughook.unhook() debughook.Logger.log_close() except: pass def starthook(): global debughook if debughook: debughook.start_line_trace() def main(): global debughook unhook() skip_functions = [] modules_info = [] start_ea = 0 end_ea = [] so_modules = ["libmetasec_ml.so"] for module in idc._get_modules(): module_name = os.path.basename(module.name) for so_module in so_modules: if re.search(so_module, module_name, re.IGNORECASE): print("modules_info append %08X %s %08X" % (module.base, module.name, module.size)) if module_name == "libmetasec_ml.so": modules_info.append({"base": module.base, "size": module.size, "name": module.name}) #start_ea = (module.base + 0x69d9c+1) #X-Gorgon相关函数的开头 #end_ea = [((module.base + 0x6a44a+1))] #函数结尾 start_ea = (module.base + 0x6221C+1) #另外3个相关函数的开头 end_ea = [((module.base + 0x62312+1))] #函数结尾 break if start_ea: set_breakpoint(start_ea) if end_ea: for ea in end_ea: set_breakpoint(ea) if skip_functions: print("skip_functions") for skip_function in skip_functions: print ("%08X" % skip_function) debughook = MyDbgHook(modules_info, skip_functions, end_ea) pass if __name__ == "__main__": main() pass
补充:
1、我这里的逆向方式有点“不走寻常路”:是先找加密代码,再回溯输入;因为arm有LR寄存器,所以函数调用时返回地址会先放入LR寄存器;如果存在函数嵌套调用,就会把LR的值push入栈,函数执行完后再pop到PC达到返回的目的(对比了一下,感觉还是x86更容易做栈回溯,因为有ebp栈帧;ebp+4就是返回地址,ebp+8就是参数),所以用ida回溯有两种方式:
- LR回溯
- 根据栈回溯
2、“寻常路”的做法:参考第4条有个脚本,可以hook到native方法的注册;运行后发现libmetasec_ml.so被某个java层的函数唯一注册,对应的偏移是0x1094d;至于java层的哪个函数,感兴趣的小伙伴建议自行尝试一下,很容易找到的!可以用ida从0x1094d开始调式,看看java层的输入是怎么一步一步到加密函数的,也就能够确定java层的哪些输入字符串被so层的函数加密了!
===========================================2022.1.28跟新============================
linux系统有个工具叫strace,可以打印所有的系统调用。我用这个工具监控了x音的运行,发现x音在短时间内调用了51次的mprotect,统计数据如下:
% time seconds usecs/call calls errors syscall ------ ----------- ----------- --------- --------- ---------------- 54.99 2.782190 43 64358 epoll_pwait 18.10 0.915582 6 150710 5549 futex 14.07 0.711901 2 458975 clock_gettime 2.62 0.132363 2 66234 write 2.09 0.105982 2 61567 44490 recvfrom 1.90 0.096350 5 18275 read 1.64 0.082757 2 44132 getpid 1.39 0.070302 3 27640 gettimeofday 1.31 0.066187 2 44085 getuid32 1.01 0.051138 3 19039 2707 ioctl 0.35 0.017961 3 6673 madvise 0.17 0.008358 3 3076 2707 openat 0.10 0.004959 6 879 fcntl64 0.07 0.003334 6 595 mmap2 0.06 0.003086 7 415 close 0.05 0.002520 6 400 pread64 0.04 0.002007 3 761 sendto 0.03 0.001582 2 893 lseek 0.01 0.000491 1 425 fstat64 0.01 0.000257 0 647 564 faccessat 0.00 0.000177 1 200 munmap 0.00 0.000092 4 23 dup 0.00 0.000030 6 5 sched_yield 0.00 0.000000 0 26 clone 0.00 0.000000 0 51 mprotect 0.00 0.000000 0 9 writev 0.00 0.000000 0 26 prctl 0.00 0.000000 0 1 rt_sigreturn 0.00 0.000000 0 68 rt_sigprocmask 0.00 0.000000 0 104 24 fstatat64 ------ ----------- ----------- --------- --------- ---------------- 100.00 5.059606 970292 56041 total
进一步查看日志明细,发现大部分mportect的调用如下:发现第三个参数是PROT_NONE,这可够狠的!直接让这块4096byte的内存没有了任何的访问权限。当用ida调试这块内存时,会立即触发SIGSEGV 信号!
21:04:26.421202 mprotect(0x891a1000, 4096, PROT_NONE) = 0 <0.000007>
参考:
1、https://www.cnblogs.com/wblyuyang/archive/2012/11/13/2768923.html sigaction函数
2、https://www.cnblogs.com/coffee520/p/10770918.html APP加固反调试汇总
3、https://gtoad.github.io/2017/06/25/Android-Anti-Debug/ Android反调试技术整理与实践
4、https://github.com/lasting-yang/frida_hook_libart/blob/master/hook_RegisterNatives.js registerNative的hook函数,可以查找所有的native函数注册地址(注意:第15行也就是for循环结束那行一定要加个break,否则会找到错误的registerNativeMethod地址,导致hook不到native方法)
5、https://linuxtools-rst.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/tool/strace.html strace工具介绍
6、https://blog.csdn.net/ustc_dylan/article/details/6941768 mprotect内存保护


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号