Elasticsearch Go 客户端
本文代码来自于官方示例。
一、配置
此例演示的是配置客户端的传输Transport。
类例中的配置主要用于说明其作用,不适用于生产环境。
默认的传输就够用了。
package main
import (
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8"
)
func main() {
cfg := elasticsearch.Config{
Addresses: []string{"http://localhost:9200"},
Transport: &http.Transport{
MaxIdleConnsPerHost: 10,
ResponseHeaderTimeout: time.Millisecond,
DialContext: (&net.Dialer{Timeout: time.Nanosecond}).DialContext,
TLSClientConfig: &tls.Config{
MinVersion: tls.VersionTLS11,
},
},
}
es, err := elasticsearch.NewClient(cfg)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
resp, err := es.Info()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(resp)
// => panic: dial tcp: i/o timeout
}
二、自定义传输
自定义传输用于读取或操作请求和响应,自定义日志记录,将自定义 header 传递给请求等。
CountingTransport将自定义 header 添加到请求,记录有关请求和响应的信息,并统计请求次数。
由于它实现了http.RoundTripper接口,因此可以将其作为自定义 HTTP 传输实现传递给客户端。
type CountingTransport struct {
count uint64
}
// RoundTrip 发送一个请求,返回一个响应
func (t *CountingTransport) RoundTrip(req *http.Request) (*http.Response, error) {
var buf bytes.Buffer
atomic.AddUint64(&t.count, 1)
req.Header.Set("Accept", "application/yaml")
req.Header.Set("X-Request-ID", "foo-123")
res, err := http.DefaultTransport.RoundTrip(req)
buf.WriteString(strings.Repeat("-", 80) + "\n")
fmt.Fprintf(&buf, "%s %s", req.Method, req.URL.String())
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(&buf, "ERROR: %s\n", err)
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(&buf, "[%s] %s\n", res.Status, res.Header.Get("Content-Type"))
}
buf.WriteTo(os.Stdout)
return res, err
}
func main() {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
// 创建一个自定义传输
tp := new(CountingTransport)
// 将自定义传输放到客户端配置中
es, _ := elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{Transport: tp})
for i := 0; i < 25; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
es.Info()
}()
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println(strings.Repeat("=", 80))
fmt.Printf("%80s\n", fmt.Sprintf("Total Requests: %d", atomic.LoadUint64(&tp.count)))
}
三、日志
1 使用默认日志
默认日志有以下四种:
- estransport.TextLogger
- estransport.ColorLogger
- estransport.CurlLogger
- estransport.JSONLogger
func main() {
log.SetFlags(0)
var es *elasticsearch.Client
es, _ = elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{
Logger: &estransport.TextLogger{Output: os.Stdout},
})
run(es, "Text")
es, _ = elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{
Logger: &estransport.ColorLogger{Output: os.Stdout},
})
run(es, "Color")
es, _ = elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{
Logger: &estransport.ColorLogger{
Output: os.Stdout,
EnableRequestBody: true,
EnableResponseBody: true,
},
})
run(es, "Request/Response body")
es, _ = elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{
Logger: &estransport.CurlLogger{
Output: os.Stdout,
EnableRequestBody: true,
EnableResponseBody: true,
},
})
run(es, "Curl")
es, _ = elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{
Logger: &estransport.JSONLogger{
Output: os.Stdout,
},
})
run(es, "JSON")
}
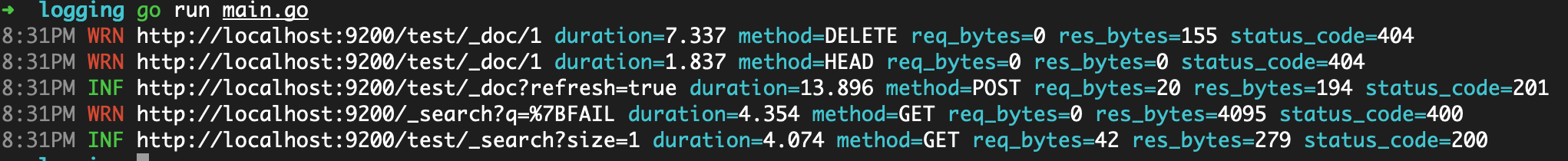
func run(es *elasticsearch.Client, name string) {
log.Println("███", fmt.Sprintf("\x1b[1m%s\x1b[0m", name), strings.Repeat("█", 75-len(name)))
es.Delete("test", "1")
es.Exists("test", "1")
es.Index(
"test",
strings.NewReader(`{"title": "logging"}`),
es.Index.WithRefresh("true"),
es.Index.WithPretty(),
es.Index.WithFilterPath("result", "_id"),
)
es.Search(es.Search.WithQuery("{FAIL"))
res, err := es.Search(
es.Search.WithIndex("test"),
es.Search.WithBody(strings.NewReader(`{"query": {"match": {"title": "logging"}}}`)),
es.Search.WithSize(1),
es.Search.WithPretty(),
es.Search.WithFilterPath("took", "hits.hits"),
)
s := res.String()
if len(s) <= len("[200 OK] ") {
log.Fatal("Response body is empty")
}
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error: %s", err)
}
log.Println()
}
四种日志的用途:
TextLogger:将请求和响应的基本信息以明文的形式输出ColorLogger:在开发时能在终端将一些信息以不同颜色输出CurlLogger:将信息格式化为可运行的curl命令,当启用EnableResponseBody时会美化输出JSONLogger:将信息以 json 格式输出,适用于生产环境的日志
如果要记录请求和响应的 body 内容,需要开启对应的选项:
EnableRequestBody:记录请求体EnableResponseBody:记录响应体
2 自定义日志
根据estransport.Logger接口,实现自定义日志。
日志包使用rs/zerolog。
package main
import (
"github.com/rs/zerolog"
)
// CustomLogger 实现 estransport.Logger 接口
type CustomLogger struct {
zerolog.Logger
}
// LogRoundTrip 打印请求和响应的一些信息
func (l *CustomLogger) LogRoundTrip(
req *http.Request,
res *http.Response,
err error,
start time.Time,
dur time.Duration,
) error {
var (
e *zerolog.Event
nReq int64
nRes int64
)
// 设置日志等级
switch {
case err != nil:
e = l.Error()
case res != nil && res.StatusCode > 0 && res.StatusCode < 300:
e = l.Info()
case res != nil && res.StatusCode > 299 && res.StatusCode < 500:
e = l.Warn()
case res != nil && res.StatusCode > 499:
e = l.Error()
default:
e = l.Error()
}
// 计算请求体和响应体的字节数
if req != nil && req.Body != nil && req.Body != http.NoBody {
nReq, _ = io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, req.Body)
}
if res != nil && res.Body != nil && res.Body != http.NoBody {
nRes, _ = io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, res.Body)
}
// 日志事件
e.Str("method", req.Method).
Int("status_code", res.StatusCode).
Dur("duration", dur).
Int64("req_bytes", nReq).
Int64("res_bytes", nRes).
Msg(req.URL.String())
return nil
}
// RequestBodyEnabled 输出请求体
func (l *CustomLogger) RequestBodyEnabled() bool { return true }
// ResponseBodyEnabled 输出响应体
func (l *CustomLogger) ResponseBodyEnabled() bool { return true }
func main() {
// 设置日志
log := zerolog.New(zerolog.ConsoleWriter{Out: os.Stderr}).
Level(zerolog.InfoLevel).
With().
Timestamp().
Logger()
// 客户端使用自定义的日志
es, _ := elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{
Logger: &CustomLogger{log},
})
{
es.Delete("test", "1")
es.Exists("test", "1")
es.Index("test", strings.NewReader(`{"title": "logging"}`), es.Index.WithRefresh("true"))
es.Search(
es.Search.WithQuery("{FAIL"),
)
es.Search(
es.Search.WithIndex("test"),
es.Search.WithBody(strings.NewReader(`{"query": {"match": {"title": "logging"}}}`)),
es.Search.WithSize(1),
)
}
}
结果如图:
四、批量索引
1 默认
此示例有意不使用任何抽象或辅助功能来展示使用 bulk api 的低级机制:准备元数据有效载荷,批量发送有效载荷,检查错误结果并打印报告。
请看代码注释:
package main
import (
"github.com/dustin/go-humanize"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8/esapi"
)
type Article struct {
ID int `json:"id"`
Title string `json:"title"`
Body string `json:"body"`
Published time.Time `json:"published"`
Author Author `json:"author"`
}
type Author struct {
FirstName string `json:"first_name"`
LastName string `json:"last_name"`
}
var (
_ = fmt.Print
count int
batch int
)
func init() {
flag.IntVar(&count, "count", 1000, "生成的文档数量")
flag.IntVar(&batch, "batch", 255, "每次发送的文档数量")
flag.Parse()
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
}
func main() {
log.SetFlags(0)
type bulkResponse struct {
Errors bool `json:"errors"`
Items []struct {
Index struct {
ID string `json:"_id"`
Result string `json:"result"`
Status int `json:"status"`
Error struct {
Type string `json:"type"`
Reason string `json:"reason"`
Cause struct {
Type string `json:"type"`
Reason string `json:"reason"`
} `json:"caused_by"`
} `json:"error"`
} `json:"index"`
} `json:"items"`
}
var (
buf bytes.Buffer
res *esapi.Response
err error
raw map[string]interface{}
blk *bulkResponse
articles []*Article
indexName = "articles"
numItems int
numErrors int
numIndexed int
numBatches int
currBatch int
)
log.Printf(
"\x1b[1mBulk\x1b[0m: documents [%s] batch size [%s]",
humanize.Comma(int64(count)), humanize.Comma(int64(batch)))
log.Println(strings.Repeat("_", 65))
// 创建客户端
es, err := elasticsearch.NewDefaultClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 生成文章
names := []string{"Alice", "John", "Mary"}
for i := 1; i < count+1; i++ {
articles = append(articles, &Article{
ID: i,
Title: strings.Join([]string{"Title", strconv.Itoa(i)}, " "),
Body: "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet...",
Published: time.Now().Round(time.Second).Local().AddDate(0, 0, i),
Author: Author{
FirstName: names[rand.Intn(len(names))],
LastName: "Smith",
},
})
}
log.Printf("→ Generated %s articles", humanize.Comma(int64(len(articles))))
fmt.Println("→ Sending batch ")
// 重新创建索引
if res, err = es.Indices.Delete([]string{indexName}); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Cannot delete index: %s", err)
}
res, err = es.Indices.Create(indexName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Cannot create index: %s", err)
}
if res.IsError() {
log.Fatalf("Cannot create index: %s", res)
}
if count%batch == 0 {
numBatches = count / batch
} else {
numBatches = count/batch + 1
}
start := time.Now().Local()
// 循环收集
for i, a := range articles {
numItems++
currBatch = i / batch
if i == count-1 {
currBatch++
}
// 准备元数据有效载荷
meta := []byte(fmt.Sprintf(`{ "index" : { "_id" : "%d" } }%s`, a.ID, "\n"))
// 准备 data 有效载荷:序列化后的 article
data, err := json.Marshal(a)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Cannot encode article %d: %s", a.ID, err)
}
// 在 data 载荷中添加一个换行符
data = append(data, "\n"...)
// 将载荷添加到 buf 中
buf.Grow(len(meta) + len(data))
buf.Write(meta)
buf.Write(data)
// 达到阈值时,使用 buf 中的数据(请求体)执行 Bulk() 请求
if i > 0 && i%batch == 0 || i == count-1 {
fmt.Printf("[%d/%d] ", currBatch, numBatches)
// 每 batch(本例中是255)个为一组发送
res, err = es.Bulk(bytes.NewReader(buf.Bytes()), es.Bulk.WithIndex(indexName))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failur indexing batch %d: %s", currBatch, err)
}
// 如果整个请求失败,打印错误并标记所有文档都失败
if res.IsError() {
numErrors += numItems
if err := json.NewDecoder(res.Body).Decode(&raw); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failure to parse response body: %s", err)
} else {
log.Printf(" Error: [%d] %s: %s",
res.StatusCode,
raw["error"].(map[string]interface{})["type"],
raw["error"].(map[string]interface{})["reason"],
)
}
} else { // 一个成功的响应也可能因为一些特殊文档包含一些错误
if err := json.NewDecoder(res.Body).Decode(&blk); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failure to parse response body: %s", err)
} else {
for _, d := range blk.Items {
// 对任何状态码大于 201 的请求进行处理
if d.Index.Status > 201 {
numErrors++
log.Printf(" Error: [%d]: %s: %s: %s: %s",
d.Index.Status,
d.Index.Error.Type,
d.Index.Error.Reason,
d.Index.Error.Cause.Type,
d.Index.Error.Cause.Reason,
)
} else {
// 如果状态码小于等于 201,对成功的计数器 numIndexed 加 1
numIndexed++
}
}
}
}
// 关闭响应体,防止达到 Goroutines 或文件句柄限制
res.Body.Close()
// 重置 buf 和 items 计数器
buf.Reset()
numItems = 0
}
}
// 报告结果:索引成功的文档的数量,错误的数量,耗时,索引速度
fmt.Println()
log.Println(strings.Repeat("▔", 65))
dur := time.Since(start)
if numErrors > 0 {
log.Fatalf(
"Indexed [%s] documents with [%s] errors in %s (%s docs/sec)",
humanize.Comma(int64(numIndexed)),
humanize.Comma(int64(numErrors)),
dur.Truncate(time.Millisecond),
humanize.Comma(int64(1000.0/float64(dur/time.Millisecond)*float64(numIndexed))),
)
} else {
log.Printf(
"Successfuly indexed [%s] documents in %s (%s docs/sec)",
humanize.Comma(int64(numIndexed)),
dur.Truncate(time.Millisecond),
humanize.Comma(int64(1000.0/float64(dur/time.Millisecond)*float64(numIndexed))),
)
}
}
count和batch为可选参数,在执行时可以自定义:
➜ go run main.go -count=100000 -batch=25000
Bulk: documents [100,000] batch size [25,000]
▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁
→ Generated 100,000 articles
→ Sending batch
[1/4] [2/4] [3/4] [4/4]
▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔
Successfuly indexed [100,000] documents in 2.79s (35,842 docs/sec)
2 索引器
此例演示使用esutil.BulkIndexer帮助程序来索引文档。
package main
import (
"github.com/dustin/go-humanize"
"github.com/cenkalti/backoff/v4"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8/esapi"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8/esutil"
)
type Article struct {
ID int `json:"id"`
Title string `json:"title"`
Body string `json:"body"`
Published time.Time `json:"published"`
Author Author `json:"author"`
}
type Author struct {
FirstName string `json:"first_name"`
LastName string `json:"last_name"`
}
var (
indexName string
numWorkers int
flushBytes int
numItems int
)
func init() {
flag.StringVar(&indexName, "index", "test-bulk-example", "索引名称")
flag.IntVar(&numWorkers, "workers", runtime.NumCPU(), "工作进程数量")
flag.IntVar(&flushBytes, "flush", 5e+6, "以字节为单位的清除阈值")
flag.IntVar(&numItems, "count", 10000, "生成的文档数量")
flag.Parse()
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
}
func main() {
log.SetFlags(0)
var (
articles []*Article
countSuccessful uint64
res *esapi.Response
err error
)
log.Printf(
"\x1b[1mBulkIndexer\x1b[0m: documents [%s] workers [%d] flush [%s]",
humanize.Comma(int64(numItems)), numWorkers, humanize.Bytes(uint64(flushBytes)))
log.Println(strings.Repeat("▁", 65))
// 使用第三方包来实现回退功能
retryBackoff := backoff.NewExponentialBackOff()
// 创建客户端。如果想使用最佳性能,请考虑使用第三方 http 包,benchmarks 示例中有写
es, err := elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{
// 429 太多请求
RetryOnStatus: []int{502, 503, 504, 429},
// 配置回退函数
RetryBackoff: func(attempt int) time.Duration {
if attempt == 1 {
retryBackoff.Reset()
}
return retryBackoff.NextBackOff()
},
// 最多重试 5 次
MaxRetries: 5,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error creating the client: %s", err)
}
// 创建批量索引器。要使用最佳性能,考虑使用第三方 json 包,benchmarks 示例中有写
bi, err := esutil.NewBulkIndexer(esutil.BulkIndexerConfig{
Index: indexName, // 默认索引名
Client: es, // es 客户端
NumWorkers: numWorkers, // 工作进程数量
FlushBytes: int(flushBytes), // 清除上限
FlushInterval: 30 * time.Second, // 定期清除间隔
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error creating the indexer: %s", err)
}
// 生成文章
names := []string{"Alice", "John", "Mary"}
for i := 1; i <= numItems; i++ {
articles = append(articles, &Article{
ID: i,
Title: strings.Join([]string{"Title", strconv.Itoa(i)}, " "),
Body: "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet...",
Published: time.Now().Round(time.Second).UTC().AddDate(0, 0, i),
Author: Author{
FirstName: names[rand.Intn(len(names))],
LastName: "Smith",
},
})
}
log.Printf("→ Generated %s articles", humanize.Comma(int64(len(articles))))
// 重新创建索引
if res, err = es.Indices.Delete([]string{indexName}, es.Indices.Delete.WithIgnoreUnavailable(true)); err != nil || res.IsError() {
log.Fatalf("Cannot delete index: %s", err)
}
res.Body.Close()
res, err = es.Indices.Create(indexName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Cannot create index: %s", err)
}
if res.IsError() {
log.Fatalf("Cannot create index: %s", res)
}
res.Body.Close()
start := time.Now().UTC()
// 循环收集
for _, a := range articles {
// 准备 data:序列化的 article
data, err := json.Marshal(a)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Cannot encode article %d: %s", a.ID, err)
}
// 添加 item 到 BulkIndexer
err = bi.Add(
context.Background(),
esutil.BulkIndexerItem{
// Action 字段配置要执行的操作(索引、创建、删除、更新)
Action: "index",
// DocumentID 是文档 ID(可选)
DocumentID: strconv.Itoa(a.ID),
// Body 是 有效载荷的 io.Reader
Body: bytes.NewReader(data),
// OnSuccess 在每一个成功的操作后调用
OnSuccess: func(c context.Context, bii esutil.BulkIndexerItem, biri esutil.BulkIndexerResponseItem) {
atomic.AddUint64(&countSuccessful, 1)
},
// OnFailure 在每一个失败的操作后调用
OnFailure: func(c context.Context, bii esutil.BulkIndexerItem, biri esutil.BulkIndexerResponseItem, e error) {
if err != nil {
log.Printf("ERROR: %s", err)
} else {
log.Printf("ERROR: %s: %s", biri.Error.Type, biri.Error.Reason)
}
},
},
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %s", err)
}
}
// 关闭索引器
if err := bi.Close(context.Background()); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %s", err)
}
biStats := bi.Stats()
// 报告结果:索引成功的文档的数量,错误的数量,耗时,索引速度
log.Println(strings.Repeat("▔", 65))
dur := time.Since(start)
if biStats.NumFailed > 0 {
log.Fatalf(
"Indexed [%s] documents with [%s] errors in %s (%s docs/sec)",
humanize.Comma(int64(biStats.NumFlushed)),
humanize.Comma(int64(biStats.NumFailed)),
dur.Truncate(time.Millisecond),
humanize.Comma(int64(1000.0/float64(dur/time.Millisecond)*float64(biStats.NumFlushed))),
)
} else {
log.Printf(
"Sucessfuly indexed [%s] documents in %s (%s docs/sec)",
humanize.Comma(int64(biStats.NumFlushed)),
dur.Truncate(time.Millisecond),
humanize.Comma(int64(1000.0/float64(dur/time.Millisecond)*float64(biStats.NumFlushed))),
)
}
}
四个可选参数,见init()函数:
➜ bulk go run indexer.go --workers=8 --count=100000 --flush=1000000
BulkIndexer: documents [100,000] workers [8] flush [1.0 MB]
▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁
→ Generated 100,000 articles
▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔▔
Sucessfuly indexed [100,000] documents in 1.584s (63,131 docs/sec)
五、编码
本示例中演示了如何使用 helper 方法和第三方 json 库。
1 第三方 json 库
1.1 tidwall/gjson
github.com/tidwall/gjson库允许在不将有效载荷转换为数据结构的前提下轻松访问属性。
package main
import (
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8"
"github.com/fatih/color"
"github.com/tidwall/gjson"
)
var (
faint = color.New(color.Faint)
bold = color.New(color.Bold)
)
func init() {
log.SetFlags(0)
}
func main() {
es, err := elasticsearch.NewDefaultClient()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error creating client: %s", err)
}
res, err := es.Cluster.Stats(es.Cluster.Stats.WithHuman())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error getting response: %s", err)
}
defer res.Body.Close()
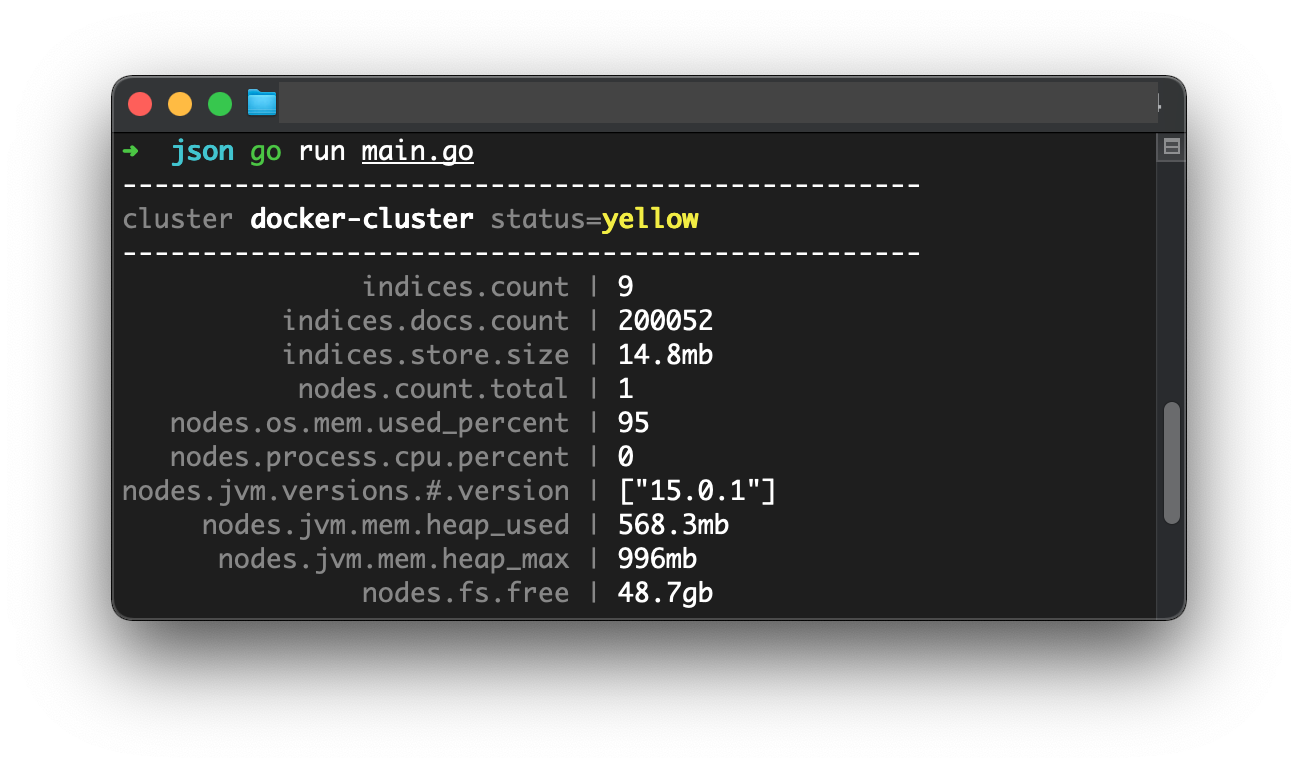
json := read(res.Body)
fmt.Println(strings.Repeat("-", 50))
faint.Print("cluster ")
// 获取集群名
bold.Print(gjson.Get(json, "cluster_name"))
faint.Print(" status=")
// 获取集群健康状态
status := gjson.Get(json, "status")
switch status.Str {
case "green":
bold.Add(color.FgHiGreen).Print(status)
case "yellow":
bold.Add(color.FgHiYellow).Print(status)
case "red":
bold.Add(color.FgHiRed).Print(status)
default:
bold.Add(color.FgHiRed, color.Underline).Print(status)
}
fmt.Println("\n" + strings.Repeat("-", 50))
stats := []string{
"indices.count",
"indices.docs.count",
"indices.store.size",
"nodes.count.total",
"nodes.os.mem.used_percent",
"nodes.process.cpu.percent",
"nodes.jvm.versions.#.version",
"nodes.jvm.mem.heap_used",
"nodes.jvm.mem.heap_max",
"nodes.fs.free",
}
var maxWidth int
for _, item := range stats {
if len(item) > maxWidth {
maxWidth = len(item)
}
}
for _, item := range stats {
pad := maxWidth - len(item)
fmt.Print(strings.Repeat(" ", pad))
faint.Printf("%s |", item)
// 从 json 动态获取状态
fmt.Printf(" %s\n", gjson.Get(json, item))
}
fmt.Println()
}
func read(r io.Reader) string {
var b bytes.Buffer
b.ReadFrom(r)
return b.String()
}
go run main.go
1.2 mailru/easyjson
mailru/easyjson可以用提供的结构体生成编码和解码的代码。
示例项目结构不适合在此处展示,故另写一篇文章,请参阅:Elasticsearch 的 easyjson 示例
1.3 ES 中的 JSONReader
esutil.JSONReader()方法将 struct、map 或任何其他可序列化对象转换为封装在 reader 中的 JSON,然后将其传递给WithBody()方法:
type Document struct{ Title string }
doc := Document{Title: "Test"}
es.Search(es.Search.WithBody(esutil.NewJSONReader(&doc)))
完整示例:
package main
import (
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8/esapi"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8/esutil"
)
func init() {
log.SetFlags(0)
}
func main() {
var (
res *esapi.Response
err error
)
es, err := elasticsearch.NewDefaultClient()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error creating the client: %s", err)
}
doc := struct {
Title string `json:"title"`
}{Title: "Test"}
res, err = es.Index("test", esutil.NewJSONReader(&doc), es.Index.WithRefresh("true"))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error getting response: %s", err)
}
log.Println(res)
query := map[string]interface{}{
"query": map[string]interface{}{
"match": map[string]interface{}{
"title": "test",
},
},
}
res, err = es.Search(
es.Search.WithIndex("test"),
es.Search.WithBody(esutil.NewJSONReader(&query)),
es.Search.WithPretty(),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error getting response: %s", err)
}
log.Println(res)
}
运行结果:
[201 Created] {"_index":"test","_type":"_doc","_id":"4l7aG3kBuWpKCVVn78cc","_version":1,"result":"created","forced_refresh":true,"_shards":{"total":2,"successful":1,"failed":0},"_seq_no":28,"_primary_term":4}
[200 OK] {
"took" : 18,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 2.3671236,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4l7aG3kBuWpKCVVn78cc",
"_score" : 2.3671236,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Test"
}
}
]
}
}
1.4 几个 json 库的基准测试结果
BenchmarkEncode/Article_-_json-8 671839 1677 ns/op 768 B/op 5 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncode/Article_-_JSONReader-8 712545 1685 ns/op 824 B/op 7 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncode/Article_-_easyjson-8 1503753 802.0 ns/op 760 B/op 6 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncode/map_-_json-8 934605 1279 ns/op 672 B/op 18 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncode/map_-_JSONReader-8 824247 1421 ns/op 728 B/op 20 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecode/Search_-_json-8 46322 25893 ns/op 9258 B/op 75 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecode/Search_-_easyjson-8 103856 11344 ns/op 12635 B/op 70 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecode/Cluster_-_json_-_map-8 23635 50752 ns/op 31603 B/op 385 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecode/Cluster_-_json_-_stc-8 38974 30788 ns/op 15160 B/op 20 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecode/Cluster_-_gjson-8 909138 1354 ns/op 256 B/op 3 allocs/op
mailru/easyjson 和 tidwall/gjson 在不同场景下都比标准库有更好的性能。
六、第三方 http 库
本例演示如何使用fasthttp替换默认的net/http,并测试二者的性能。
1 示例代码
package http
import (
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"strings"
"github.com/valyala/fasthttp"
)
// Transport 用 fasthttp 实现 es 接口
type Transport struct{}
// RoundTrip 发送请求,返回响应或错误
func (t *Transport) RoundTrip(req *http.Request) (*http.Response, error) {
freq := fasthttp.AcquireRequest()
defer fasthttp.ReleaseRequest(freq)
fres := fasthttp.AcquireResponse()
defer fasthttp.ReleaseResponse(fres)
t.copyRequest(freq, req)
err := fasthttp.Do(freq, fres)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
res := &http.Response{Header: make(http.Header)}
t.copyResponse(res, fres)
return res, nil
}
// copyRequest 将 http 请求转换为 fasthttp 请求
func (t *Transport) copyRequest(dst *fasthttp.Request, src *http.Request) *fasthttp.Request {
if src.Method == http.MethodGet && src.Body != nil {
src.Method = http.MethodPost
}
dst.SetHost(src.Host)
dst.SetRequestURI(src.URL.String())
dst.Header.SetRequestURI(src.URL.String())
dst.Header.SetMethod(src.Method)
for k, vs := range src.Header {
for _, v := range vs {
dst.Header.Set(k, v)
}
}
if src.Body != nil {
dst.SetBodyStream(src.Body, -1)
}
return dst
}
// copyResponse 将 fasthttp 响应转换为 http 响应
func (t *Transport) copyResponse(dst *http.Response, src *fasthttp.Response) *http.Response {
dst.StatusCode = src.StatusCode()
src.Header.VisitAll(func(key, value []byte) {
dst.Header.Set(string(key), string(value))
})
// 在响应被释放回响应池(fasthttp.ReleaseResponse)后,将 src.Body() 转换为字符串 Reader
dst.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(strings.NewReader(string(src.Body())))
return dst
}
2 基准测试
测试代码:
package http_test
import (
"elasticsearch/fasthttp/http"
"testing"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8"
)
func BenchmarkHTTPClient(b *testing.B) {
b.ReportAllocs()
client, err := elasticsearch.NewDefaultClient()
if err != nil {
b.Fatalf("ERROR: %s", err)
}
b.Run("Info()", func(b *testing.B) {
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
if res, err := client.Info(); err != nil {
b.Errorf("Unexpected error when getting a response: %s", err)
} else {
res.Body.Close()
}
}
})
}
func BenchmarkFastHTTPClient(b *testing.B) {
b.ReportAllocs()
client, err := elasticsearch.NewClient(
elasticsearch.Config{Transport: &http.Transport{}},
)
if err != nil {
b.Fatalf("ERROR: %s", err)
}
b.Run("Info()", func(b *testing.B) {
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
if res, err := client.Info(); err != nil {
b.Errorf("Unexpected error when getting a response: %s", err)
} else {
res.Body.Close()
}
}
})
}
结果:
...
BenchmarkHTTPClient/Info()-8 6067 2438072 ns/op 15908 B/op 120 allocs/op
...
BenchmarkFastHTTPClient/Info()-8 14690 811282 ns/op 2325 B/op 27 allocs/op
http 标准库的性能在慢慢提高,但是仍然与 fasthttp 有着不小的差距。
七、检测仪
此示例演示了如何检测 es 客户端。
1 OpenCensus
使用 ochttp.Transport自动检测客户端调用,并将有关信息打印到终端。
package main
import (
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8"
"github.com/fatih/color"
"go.opencensus.io/plugin/ochttp"
"go.opencensus.io/stats/view"
"go.opencensus.io/tag"
"go.opencensus.io/trace"
"golang.org/x/crypto/ssh/terminal"
)
const count = 100
var (
tWidth, _, _ = terminal.GetSize(int(os.Stdout.Fd()))
faint = color.New(color.Faint)
bold = color.New(color.Bold)
boldRed = color.New(color.FgRed).Add(color.Bold)
tagMethod, _ = tag.NewKey("method")
)
func init() {
if tWidth < 0 {
tWidth = 0
}
}
// ConsoleExporter 将状态和追踪轨迹打印到终端
type ConsoleExporter struct{}
// ExportView 打印状态
func (e *ConsoleExporter) ExportView(vd *view.Data) {
fmt.Println(strings.Repeat("─", tWidth))
for _, row := range vd.Rows {
faint.Print("█ ")
fmt.Printf("%-17s ", strings.TrimPrefix(vd.View.Name, "opencensus.io/http/client/"))
switch v := row.Data.(type) {
case *view.DistributionData:
bold.Printf("min=%-6.1f max=%-6.1f mean=%-6.1f", v.Min, v.Max, v.Mean)
case *view.CountData:
bold.Printf("count=%-3v", v.Value)
case *view.SumData:
bold.Printf("sum=%-3v", v.Value)
case *view.LastValueData:
bold.Printf("last=%-3v", v.Value)
}
faint.Print(" │ ")
for _, tag := range row.Tags {
faint.Printf("%-25s ", fmt.Sprintf("%v=%v", tag.Key.Name(), tag.Value))
}
fmt.Println()
}
}
// ExportSpan 打印追踪轨迹
func (e *ConsoleExporter) ExportSpan(sd *trace.SpanData) {
var c *color.Color
if sd.Status.Code > 0 {
c = color.New(color.FgRed)
} else {
c = color.New(color.FgGreen)
}
fmt.Println(strings.Repeat("─", tWidth))
fmt.Printf(
"░ %s %s %s\n",
c.Sprint(sd.Status.Message),
bold.Sprint(sd.Name),
sd.EndTime.Sub(sd.StartTime).Round(time.Millisecond))
faint.Printf("░ %x > %x\n", sd.SpanContext.TraceID[:], sd.SpanContext.SpanID[:])
if len(sd.Attributes) > 0 {
faint.Print("░ ")
var keys []string
for k := range sd.Attributes {
keys = append(keys, k)
}
sort.Strings(keys)
for i, k := range keys {
faint.Printf("%s=%v", k, sd.Attributes[k])
if i < len(keys)-1 {
faint.Printf(" │ ")
}
}
}
fmt.Println()
}
func main() {
log.SetFlags(0)
start := time.Now()
// Create new elasticsearch client ...
//
es, err := elasticsearch.NewClient(
elasticsearch.Config{
// >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
// ... 使用"ochttp" 封装检测仪
Transport: &ochttp.Transport{},
// <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("ERROR: %s", err)
}
// 创建 done 管道
//
done := make(chan os.Signal)
signal.Notify(done, os.Interrupt)
// 创建刻点
//
tickers := struct {
Info *time.Ticker
Index *time.Ticker
Health *time.Ticker
Search *time.Ticker
}{
Info: time.NewTicker(time.Second),
Index: time.NewTicker(500 * time.Millisecond),
Health: time.NewTicker(5 * time.Second),
Search: time.NewTicker(10 * time.Second),
}
defer tickers.Info.Stop()
defer tickers.Index.Stop()
defer tickers.Health.Stop()
defer tickers.Search.Stop()
// 使用 ochttp 插件注册视图
//
if err := view.Register(
ochttp.ClientRoundtripLatencyDistribution,
ochttp.ClientCompletedCount,
); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("ERROR: %s", err)
}
// 一段时间向 STDOUT 报告一次视图
//
view.SetReportingPeriod(5 * time.Second)
view.RegisterExporter(&ConsoleExporter{})
// 向 STDOUT 报告一部分轨迹
//
trace.ApplyConfig(trace.Config{DefaultSampler: trace.ProbabilitySampler(0.5)})
trace.RegisterExporter(&ConsoleExporter{})
// 初始化上下文
//
ctx, _ := tag.New(context.Background(), tag.Upsert(tagMethod, "main"))
// 调用 api
//
for {
select {
case <-done:
fmt.Print("\n")
fmt.Println(strings.Repeat("━", tWidth))
faint.Printf("Finished in %s\n\n", time.Now().Sub(start).Truncate(time.Second))
return
// -> Info
//
case <-tickers.Info.C:
res, err := es.Info(es.Info.WithContext(ctx))
if err != nil {
boldRed.Printf("Error getting response: %s\n", err)
} else {
res.Body.Close()
}
// -> Index
//
case t := <-tickers.Index.C:
// Artificially fail some requests...
var body io.Reader
if t.Second()%4 == 0 {
body = strings.NewReader(``)
} else {
body = strings.NewReader(`{"timestamp":"` + t.Format(time.RFC3339) + `"}`)
}
res, err := es.Index("test", body, es.Index.WithContext(ctx))
if err != nil {
boldRed.Printf("Error getting response: %s\n", err)
} else {
res.Body.Close()
}
// -> Health
//
case <-tickers.Health.C:
res, err := es.Cluster.Health(
es.Cluster.Health.WithLevel("indices"),
es.Cluster.Health.WithContext(ctx),
)
if err != nil {
boldRed.Printf("Error getting response: %s\n", err)
} else {
res.Body.Close()
}
// -> Search
//
case <-tickers.Search.C:
res, err := es.Search(
es.Search.WithIndex("test"),
es.Search.WithSort("timestamp:desc"),
es.Search.WithSize(1),
es.Search.WithContext(ctx),
)
if err != nil {
boldRed.Printf("Error getting response: %s\n", err)
} else {
res.Body.Close()
}
}
}
}
2 Elastic APM
使用Go agent for Elastic APM检测客户端:
- 配置多种类型的事务
- 在每个事务中创建自定义跨度
- 报告错误
使用 docker 示例。
2.1 docker-compose 配置文件
文件名:elasticstack.yml。
version: "3.2"
services:
# --- Application -----------------------------------------------------------
application:
container_name: application
build: .
networks: ["elasticstack"]
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
- kibana
- apm-server
# --- Elasticsearch ---------------------------------------------------------
elasticsearch:
image: elasticsearch:7.12.1
container_name: elasticsearch
volumes:
- es_data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data:delegated
networks: ["elasticstack"]
environment:
- "cluster.name=go-elasticsearch-instrumentation"
- "cluster.routing.allocation.disk.threshold_enabled=false"
- "discovery.type=single-node"
- "bootstrap.memory_lock=true"
- "xpack.security.enabled=false"
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms1g -Xmx1g"
expose:
- "9200"
ulimits:
memlock: -1
nproc: 65535
nofile: 65535
healthcheck:
test: curl --max-time 60 --retry 60 --retry-delay 1 --retry-connrefused --show-error --silent http://localhost:9200
# --- Kibana ----------------------------------------------------------------
kibana:
image: kibana:7.12.1
container_name: kibana
networks: ["elasticstack"]
environment:
- "ELASTICSEARCH_URL=http://elasticsearch:9200"
ports:
- "5601:5601"
depends_on: ["elasticsearch"]
healthcheck:
test: curl --max-time 60 --retry 60 --retry-delay 1 --retry-connrefused --show-error --silent http://localhost:5601
# --- APM Server ------------------------------------------------------------
apm-server:
image: elastic/apm-server:7.12.1
container_name: apm_server
networks: ["elasticstack"]
command: >
./apm-server run -e \
-E output.elasticsearch.hosts=http://elasticsearch:9200 \
-E setup.kibana.host=http://kibana:5601
expose:
- "8200"
depends_on: ["elasticsearch", "kibana"]
healthcheck:
test: curl --max-time 60 --retry 60 --retry-delay 1 --retry-connrefused --show-error --silent http://localhost:8200/healthcheck
networks:
elasticstack:
volumes:
es_data:
2.2 Dockerfile
FROM golang:1.16.3
RUN echo 'deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster main non-free contrib\n\
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian-security buster/updates main\n\
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-updates main non-free contrib\n\
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/debian/ buster-backports main non-free contrib\n'\
> /etc/apt/sources.list
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y gcc g++ ca-certificates make curl git jq
WORKDIR /go-elasticsearch-demo-instrumentation
RUN go env -w GO111MODULE=on && go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct
COPY go.mod .
RUN go mod download
ENV TERM xterm-256color
ENV ELASTICSEARCH_URL=${ELASTICSEARCH_URL:-http://elasticsearch:9200}
ENV ELASTIC_APM_SERVER_URL=${ELASTIC_APM_SERVER_URL:-http://apm_server:8200}
ENV ELASTIC_APM_SERVICE_NAME=go-elasticsearch-demo-instrumentation
ENV ELASTIC_APM_METRICS_INTERVAL=5s
ENV ELASTIC_APM_LOG_FILE=stderr
ENV ELASTIC_APM_LOG_LEVEL=debug
COPY apmelasticsearch.go opencensus.go ./
CMD go run apmelasticsearch.go
2.3 运行
elasticstack.yml 和 Dockfile 放在同一目录。
运行:
docker-compose --file elasticstack.yml up --build
删除示例 docker 文件:
docker-compose --file elasticstack.yml down --remove-orphans --volumes
八、扩展
此例演示如何扩展客户端,以便调用自定义 API。
main.go示例中定义了嵌入到常规客户端的自定义类型,添加一个实现了Example()方法的Custom命名空间。
package main
import (
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8/esapi"
"github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/v8/estransport"
)
const port = "9209"
// ExtendedClient 包括常规 api 和自定义 api
type ExtendedClient struct {
*elasticsearch.Client
Custom *ExtendedAPI
}
// ExtendedAPI 自定义 api
type ExtendedAPI struct {
*elasticsearch.Client
}
// Example 调用自定义 restful api,"GET /_cat/example"
func (e *ExtendedAPI) Example() (*esapi.Response, error) {
req, _ := http.NewRequest("GET", "/_cat/example", nil)
res, err := e.Perform(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &esapi.Response{StatusCode: res.StatusCode, Body: res.Body, Header: res.Header}, nil
}
func main() {
log.SetFlags(0)
started := make(chan bool)
// 启动代理服务
go startServer(started)
ec, err := elasticsearch.NewClient(elasticsearch.Config{
Addresses: []string{"http://localhost:" + port},
Logger: &estransport.ColorLogger{Output: os.Stdout, EnableRequestBody: true, EnableResponseBody: true},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error creating the client: %s", err)
}
es := ExtendedClient{
Client: ec,
Custom: &ExtendedAPI{ec},
}
<-started
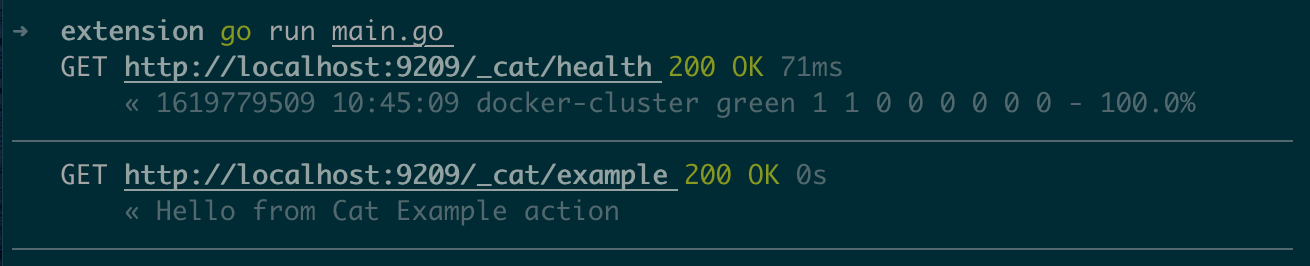
// 调用常规 api
es.Cat.Health()
// 调用自定义 api
es.Custom.Example()
}
func startServer(started chan<- bool) {
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(&url.URL{Scheme: "http", Host: "localhost:9200"})
// 在"GET /_cat/example"上以自定义内容响应,将其他请求代理到 es
//
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if r.Method == "GET" && r.URL.Path == "/_cat/example" {
io.WriteString(w, "Hello from Cat Example action")
return
}
proxy.ServeHTTP(w, r)
})
ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:"+port)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unable to start server: %s", err)
}
go http.Serve(ln, nil)
started <- true
}
结果:
九、安全
本例演示如何通过用自定义证书使用 TLS (传输层安全) 来加密和验证与 ES 集群的通信。
1 为集群创建证书
创建证书的命令如下:
OUTPUT="/certificates/bundle.zip"
if [[ -f $$OUTPUT ]]; then
echo "Certificates already present in [.$$OUTPUT]"; exit 1;
else
yum install -y -q -e 0 unzip tree;
bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert \
--pem \
--days 365 \
--keep-ca-key \
--in config/certificates/certificates-config.yml \
--out $$OUTPUT;
unzip -q $$OUTPUT -d /certificates;
chown -R 1000:0 /certificates; echo;
tree /certificates;
fi;
命令中用到的certificates-config.yml内容如下:
instances:
- name: elasticsearch
ip: [0.0.0.0, 127.0.0.1]
dns: ["localhost", "example_elasticsearch_1", "example_elasticsearch_2", "example_elasticsearch_3"]
既然是示例,创建一个即用即毁的环境是很有必要的,所以使用一个 docker 容器运行上面的命令是最好的选择。
docker-compose 文件:
version: "3.7"
services:
create_certificates:
image: elasticsearch:7.12.1
container_name: certificates_generator
user: root
working_dir: /usr/share/elasticsearch
command: >
bash -c '
OUTPUT="/certificates/bundle.zip"
if [[ -f $$OUTPUT ]]; then
echo "Certificates already present in [.$$OUTPUT]"; exit 1;
else
yum install -y -q -e 0 unzip tree;
bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert \
--pem \
--days 365 \
--keep-ca-key \
--in config/certificates/certificates-config.yml \
--out $$OUTPUT;
unzip -q $$OUTPUT -d /certificates;
chown -R 1000:0 /certificates; echo;
tree /certificates;
fi;
'
volumes:
- ./certificates:/certificates
- ./certificates-config.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/certificates-config.yml
运行 docker 容器:
docker-compose --file certificates-create.yml run --rm create_certificates
运行完成后,当前目录中就会生成一个包含证书的certificates文件夹。
现在有了证书,下面就可以创建一个开启安全认证的集群。
docker-compose 文件:
version: "3.7"
services:
elasticsearch:
image: elasticsearch:${ELASTIC_VERSION}
volumes:
- es-data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
- ./certificates:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/
networks:
- elasticstack
ports:
- 9200:9200
environment:
- node.name=example_elasticsearch_1
- cluster.name=golang-example-security
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=example_elasticsearch_1
- discovery.seed_hosts=example_elasticsearch_1
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- network.host=example_elasticsearch_1,_local_
- network.publish_host=example_elasticsearch_1
- ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms1G -Xmx1G -Des.transport.cname_in_publish_address=true
# Security & TLS
- ELASTIC_PASSWORD=${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}
- xpack.security.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.http.ssl.key=/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.key
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate=/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.crt
- xpack.security.http.ssl.certificate_authorities=/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/ca/ca.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled=true
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode=certificate
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.key=/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.key
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate=/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.crt
- xpack.security.transport.ssl.certificate_authorities=/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/ca/ca.crt
ulimits: { nofile: { soft: 262144, hard: 262144 }, memlock: -1 }
healthcheck:
test: curl --cacert /usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certificates/ca/ca.crt --max-time 120 --retry 120 --retry-delay 1 --show-error --silent https://elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}@localhost:9200
networks:
elasticstack: { labels: { elasticstack.description: "Network for the Elastic Stack" }}
volumes:
es-data: { labels: { elasticstack.description: "Elasticsearch data" }}
运行集群:
docker-compose --file elasticsearch-cluster.yml up --remove-orphans --detach
用证书访问配合账号密码访问:
curl --cacert certificates/ca/ca.crt https://elastic:elastic@localhost:9200
会得到正确响应。
2 使用 Go 客户端安全访问
2.1 使用客户端配置中的证书字段
先从文件中读取证书内容,然后将证书放到客户端配置中:
// --> 从文件中读取证书
cert, _ := ioutil.ReadFile(*cacert)
es, _ := elasticsearch.NewClient(
elasticsearch.Config{
// ...
// --> 将证书放到配置中
CACert: cert,
})
2.2 根据证书创建自定义传输
cert, _ := ioutil.ReadFile(*cacert)
// 复制默认传输
tp := http.DefaultTransport.(*http.Transport).Clone()
// 初始化一个根证书颁发机构
tp.TLSClientConfig.RootCAs, _ = x509.SystemCertPool()
// 添加自定义证书颁发机构
tp.TLSClientConfig.RootCAs.AppendCertsFromPEM(cert)
es, _ := elasticsearch.NewClient(
elasticsearch.Config{
Addresses: []string{"https://localhost:9200"},
Username: "elastic",
Password: *password,
// --> 将自定义传输添加到客户端配置中
//
Transport: tp,
},
)
十、示例应用
爬取掘金热门推荐的页面的信息保存到 es 中,并进行查询。
示例项目地址:thep0y/juejin-hot-es-example
查询时使用命令行进行,示例项目的命令如下:
juejin allows you to index and search hot-recommended article's titles
Usage:
juejin [command]
Available Commands:
help Help about any command
index Index juejin hot-recommended articles into Elasticsearch
search Search juejin hot recommended articles
Flags:
-h, --help help for juejin
-i, --index string Index name (default "juejin")
Use "juejin [command] --help" for more information about a command.
可选参数为index和search。
其中index也有可选命令:
--pages int The count of pages you want to crawl (default 5)
--setup Create Elasticsearch index
本项目使用的是本地 es ,推荐用 docker 创建,es 中需要安装 ik 中文分词插件。
1 创建索引
go run main.go index --setup
默认会根据项目中指定的 mapping 创建索引,并爬取存储 5 页、共 100 条信息。
结果如下所示:
8:10PM INF Creating index with mapping
8:10PM INF Starting the crawl with 0 workers at 0 offset
8:10PM INF Stored doc Article ID=6957974706943164447 title="算法篇01、排序算法"
8:10PM INF Stored doc Article ID=6953868764362309639 title="如何处理浏览器的断网情况?"
...
8:10PM INF Skipping existing doc ID=6957726578692341791
8:10PM INF Skipping existing doc ID=6957925118429364255
8:10PM INF Skipping existing doc ID=6953868764362309639
8:10PM INF Skipping existing doc ID=6957981912669519903
8:10PM INF Skipping existing doc ID=6953059119561441287
8:10PM INF Skipping existing doc ID=6955336007839383588
...
8:10PM INF Stored doc Article ID=6957930535574306847 title="Node系列-阻塞和非阻塞的理解"
8:10PM INF Stored doc Article ID=6956602138201948196 title="《前端领域的转译打包工具链》上篇"
8:10PM INF Stored doc Article ID=6957982556885090312 title="JS篇:事件流"
终端结果截图:
因为每页有 20 条,共爬 5 页,所以理论上应存储 100 条信息,但其中可能会存在几条重复信息,所以最后保存时可能会小于 100 条。
2 爬取 10 页
go run main.go index --pages 10
运行这条命令时,不会再创建索引,而是直接开始爬虫,因为只是示例项目,所以没有增加起始页和最终页的选择,只提供最终页码作为可选参数。
运行结果与上小节基本相同:
3 查询
查询时,使用的是词组查询,中文更适合使用词组查询,不然每个查询词被拆分成单字查询,结果一般不是我们想要的。
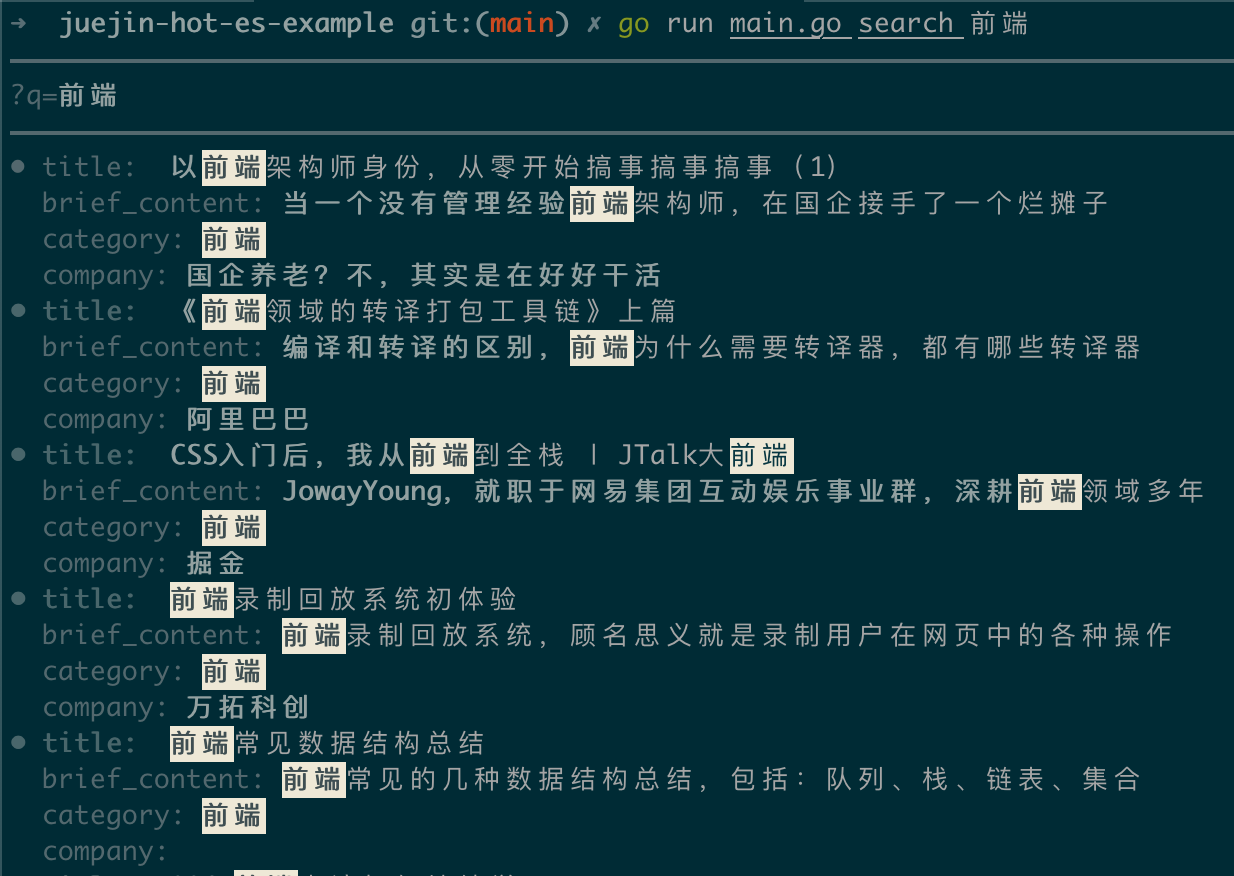
go run main.go search 前端
查询到的结果中会将查询词高亮显示: