KDTree C++实现
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qing101hua/article/details/53228668
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#define KDtreeSize 1000
#define UL unsigned long
using namespace std;
struct coordinate
{
double x = 0;
double y = 0;
UL index = 0;
};
struct TreeNode
{
struct coordinate dom_elt;
UL split = 0;
struct TreeNode* left = nullptr;
struct TreeNode* right = nullptr;
};
bool cmp1(const coordinate& a, const coordinate& b){
return a.x < b.x;
}
bool cmp2(const coordinate& a, const coordinate& b){
return a.y < b.y;
}
bool equal(const coordinate& a, const coordinate& b){
return (a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y);
}
void ChooseSplit(coordinate exm_set[], UL size, UL &split, coordinate &SplitChoice){
/*compute the variance on every dimension. Set split as the dismension that have the biggest
variance. Then choose the instance which is the median on this split dimension.*/
/*compute variance on the x,y dimension. DX=EX^2-(EX)^2*/
double tmp1, tmp2;
tmp1 = tmp2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
tmp1 += 1.0 / (double)size * exm_set[i].x * exm_set[i].x;
tmp2 += 1.0 / (double)size * exm_set[i].x;
}
double v1 = tmp1 - tmp2 * tmp2; //compute variance on the x dimension
tmp1 = tmp2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
tmp1 += 1.0 / (double)size * exm_set[i].y * exm_set[i].y;
tmp2 += 1.0 / (double)size * exm_set[i].y;
}
double v2 = tmp1 - tmp2 * tmp2; //compute variance on the y dimension
split = v1 > v2 ? 0:1; //set the split dimension
if (split == 0)
{
sort(exm_set,exm_set + size, cmp1);
}
else{
sort(exm_set,exm_set + size, cmp2);
}
//set the split point value
SplitChoice.x = exm_set[size / 2].x;
SplitChoice.y = exm_set[size / 2].y;
}
TreeNode* build_kdtree(coordinate exm_set[], UL size, TreeNode* T){
//call function ChooseSplit to choose the split dimension and split point
if (size == 0){
return nullptr;
}
else{
UL split;
coordinate dom_elt;
ChooseSplit(exm_set, size, split, dom_elt);
coordinate exm_set_right [KDtreeSize];
coordinate exm_set_left [KDtreeSize];
UL size_left ,size_right;
size_left = size_right = 0;
if (split == 0)
{
for (UL i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
if (!equal(exm_set[i],dom_elt) && exm_set[i].x <= dom_elt.x)
{
exm_set_left[size_left].x = exm_set[i].x;
exm_set_left[size_left].y = exm_set[i].y;
size_left++;
}
else if (!equal(exm_set[i],dom_elt) && exm_set[i].x > dom_elt.x)
{
exm_set_right[size_right].x = exm_set[i].x;
exm_set_right[size_right].y = exm_set[i].y;
size_right++;
}
}
}
else{
for (UL i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
if (!equal(exm_set[i],dom_elt) && exm_set[i].y <= dom_elt.y)
{
exm_set_left[size_left].x = exm_set[i].x;
exm_set_left[size_left].y = exm_set[i].y;
size_left++;
}
else if (!equal(exm_set[i],dom_elt) && exm_set[i].y > dom_elt.y)
{
exm_set_right[size_right].x = exm_set[i].x;
exm_set_right[size_right].y = exm_set[i].y;
size_right++;
}
}
}
T = new TreeNode;
T->dom_elt.x = dom_elt.x;
T->dom_elt.y = dom_elt.y;
T->split = split;
T->left = build_kdtree(exm_set_left, size_left, T->left);
T->right = build_kdtree(exm_set_right, size_right, T->right);
return T;
}
}
double Distance(coordinate a, coordinate b){
double tmp = (a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y);
return sqrt(tmp);
}
void searchNearest(TreeNode * Kd, coordinate target, coordinate &nearestpoint, double & distance){
//1. 如果Kd是空的,则设dist为无穷大返回
//2. 向下搜索直到叶子结点
stack<TreeNode*> search_path;
TreeNode* pSearch = Kd;
coordinate nearest;
double dist;
while(pSearch != nullptr)
{
//pSearch加入到search_path中;
search_path.push(pSearch);
if (pSearch->split == 0)
{
if(target.x <= pSearch->dom_elt.x) /* 如果小于就进入左子树 */
{
pSearch = pSearch->left;
}
else
{
pSearch = pSearch->right;
}
}
else{
if(target.y <= pSearch->dom_elt.y) /* 如果小于就进入左子树 */
{
pSearch = pSearch->left;
}
else
{
pSearch = pSearch->right;
}
}
}
//取出search_path最后一个赋给nearest
nearest.x = search_path.top()->dom_elt.x;
nearest.y = search_path.top()->dom_elt.y;
search_path.pop();
dist = Distance(nearest, target);
//3. 回溯搜索路径
TreeNode* pBack;
while(search_path.empty())
{
//取出search_path最后一个结点赋给pBack
pBack = search_path.top();
search_path.pop();
if(pBack->left == nullptr && pBack->right == nullptr) /* 如果pBack为叶子结点 */
{
if( Distance(nearest, target) > Distance(pBack->dom_elt, target) )
{
nearest = pBack->dom_elt;
dist = Distance(pBack->dom_elt, target);
}
}
else
{
UL s = pBack->split;
if (s == 0)
{
if( fabs(pBack->dom_elt.x - target.x) < dist) /* 如果以target为中心的圆(球或超球),半径为dist的圆与分割超平面相交, 那么就要跳到另一边的子空间去搜索 */
{
if( Distance(nearest, target) > Distance(pBack->dom_elt, target) )
{
nearest = pBack->dom_elt;
dist = Distance(pBack->dom_elt, target);
}
if(target.x <= pBack->dom_elt.x) /* 如果target位于pBack的左子空间,那么就要跳到右子空间去搜索 */
pSearch = pBack->right;
else
pSearch = pBack->left; /* 如果target位于pBack的右子空间,那么就要跳到左子空间去搜索 */
if(pSearch != nullptr)
//pSearch加入到search_path中
search_path.push(pSearch);
}
}
else {
if( fabs(pBack->dom_elt.y - target.y) < dist) /* 如果以target为中心的圆(球或超球),半径为dist的圆与分割超平面相交, 那么就要跳到另一边的子空间去搜索 */
{
if( Distance(nearest, target) > Distance(pBack->dom_elt, target) )
{
nearest = pBack->dom_elt;
dist = Distance(pBack->dom_elt, target);
}
if(target.y <= pBack->dom_elt.y) /* 如果target位于pBack的左子空间,那么就要跳到右子空间去搜索 */
pSearch = pBack->right;
else
pSearch = pBack->left; /* 如果target位于pBack的右子空间,那么就要跳到左子空间去搜索 */
if(pSearch != nullptr)
// pSearch加入到search_path中
search_path.push(pSearch);
}
}
}
}
nearestpoint.x = nearest.x;
nearestpoint.y = nearest.y;
distance = dist;
}
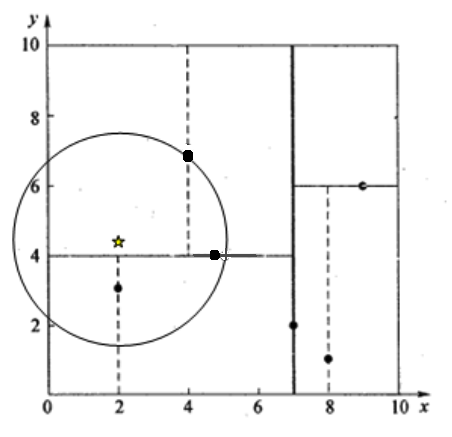
void test_kdtree(){
coordinate exm_set[6];
exm_set[0].x = 2; exm_set[0].y = 3;
exm_set[1].x = 5; exm_set[1].y = 4;
exm_set[2].x = 9; exm_set[2].y = 6;
exm_set[3].x = 4; exm_set[3].y = 7;
exm_set[4].x = 8; exm_set[4].y = 1;
exm_set[5].x = 7; exm_set[5].y = 2;
struct TreeNode * root = nullptr;
root = build_kdtree(exm_set, 6, root);
coordinate nearestpoint;
double distance;
coordinate target;
target.x = 2.1;
target.y = 3.2;
searchNearest(root, target, nearestpoint, distance);
cout<<"The nearest distance is "<<distance<<",and the nearest point is "<<nearestpoint.x<<","<<nearestpoint.y<<endl;
}
int main(){
test_kdtree();
return 0;
}




