1. 聚合函数
MySQL聚合函数:max\min\sum\count\avg
from django.db.models import Max, Min, Sum, Avg, Count
res = models.Book.objects.aggregate(Max('price'))
print(res) # {'price__max': Decimal('56777.98')}
'''没有分组也可以使用聚合函数 默认整体就是一组'''
print(models.Book.objects.aggregate(Max('price')))
print(models.Book.objects.aggregate(Min('price')))
print(models.Book.objects.aggregate(Sum('price')))
print(models.Book.objects.aggregate(Avg('price')))
print(models.Book.objects.aggregate(Count('price')))

2. 分组查询
MySQL分组操作:group by
ORM执行分组操作 如果报错 可能需要去修改sql_mode 移除only_full_group_by
# 统计每本书的作者个数
res = models.Book.objects.annotate(author_num=Count('authors__pk')).values('title', 'author_num')
print(res)
print(res.query)
# 统计每个出版社卖的最便宜的书的价格
res = models.Publish.objects.annotate(min_price=Min('book__price')).values('name', 'min_price')
print(res)
print(res.query)
# 统计不止一个作者的图书
res = models.Book.objects.annotate(author_num=Count('authors__pk')).filter(author_num__gt=1).values('title','author_num')
print(res)
print(res.query)
# 统计每个作者出的书的总价格
from django.db.models import Sum
res = models.Author.objects.annotate(book_sum_price=Sum('book__price')).values('name','book_sum_price')
print(res)
print(res.query)
"""上述操作都是以表为单位做分组 如果想要以表中的某个字段分组如何操作"""
models.Author.objects.values('age').annotate()
# 统计每个出版社主键值对应的书籍个数
res = models.Book.objects.values('publish_id').annotate(book_num=Count('pk')).values('publish_id','book_num')
print(res)

3. F与Q查询
F查询:
"""
当表中已经有数据的情况下 添加额外的字段 需要指定默认值或者可以为null
方式1
IntegerField(verbose_name='销量',default=1000)
方式2
IntegerField(verbose_name='销量',null=True)
方式3
在迁移命令提示中直接给默认值
"""
# 查询库存大于销量的书籍
# res = models.Book.objects.filter(kucun > maichu) 不行
# res = models.Book.objects.filter(kucun__getmaichu) 不行# 当查询条件的左右两表的数据都需要表中的数据 可以使用F查询
from django.db.models import F
res = models.Book.objects.filter(kucun__gt=F('maichu'))
print(res)
print(res.query)
# 将所有书的价格提升1000块
res = models.Book.objects.update(price=F('price') + 1000)
print(res)
res = models.Book.objects.values('title', 'price')
print(res)
print(res.query)
# 将所有书的名称后面加上_爆款后缀
res = models.Book.objects.update(title=F('title') + '_爆款') # 不可以
'''如果要修改char字段咋办(千万不能用上面对数值类型的操作!!!) 需要使用下列两个方法'''
from django.db.models.functions import Concat
from django.db.models import Value
models.Book.objects.update(title=Concat(F('title'), Value('爆款')))
res = models.Book.objects.values('title')
print(res)
print(res.query)
# 查询价格大于20000或者卖出大于1000的书籍
# res = models.Book.objects.filter(price__gt=20000,maichu__gt=1000)
# print(res)
# print(res.query)
'''filter括号内多个条件默认是and关系 无法直接修改'''
from django.db.models import Q
'''使用Q对象 就可以支持逻辑运算符'''
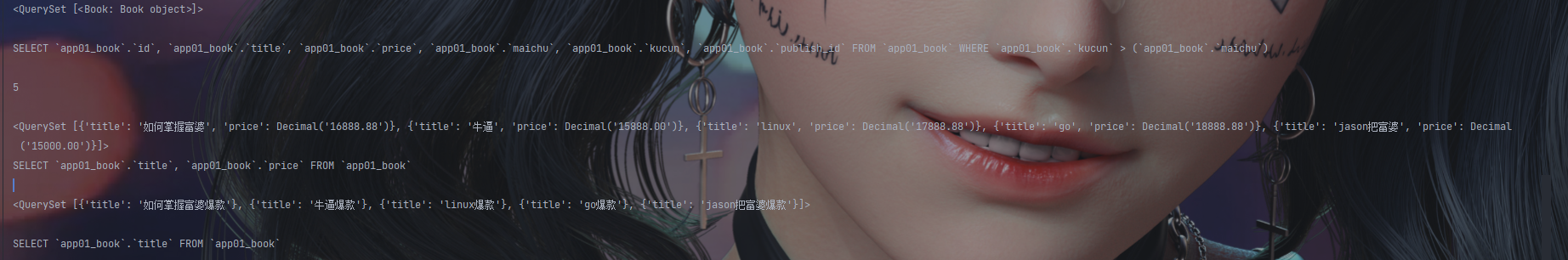
res = models.Book.objects.filter(Q(price__gt=20000), Q(maichu__gt=1000)) # 逗号是and关系
print(res)
print(res.query)
res = models.Book.objects.filter(Q(price__gt=20000) | Q(maichu__gt=1000)) # 管道符是or关系
print(res)
print(res.query)
res = models.Book.objects.filter(~Q(price__gt=20000)) # ~是not操作
print(res)
print(res.query)
'''
Q对象进阶用法
filter(price=100)
filter('price'=100)
当我们需要编写一个搜索功能 并且条件是由用户指定 这个时候左边的数据就是一个字符串
'''
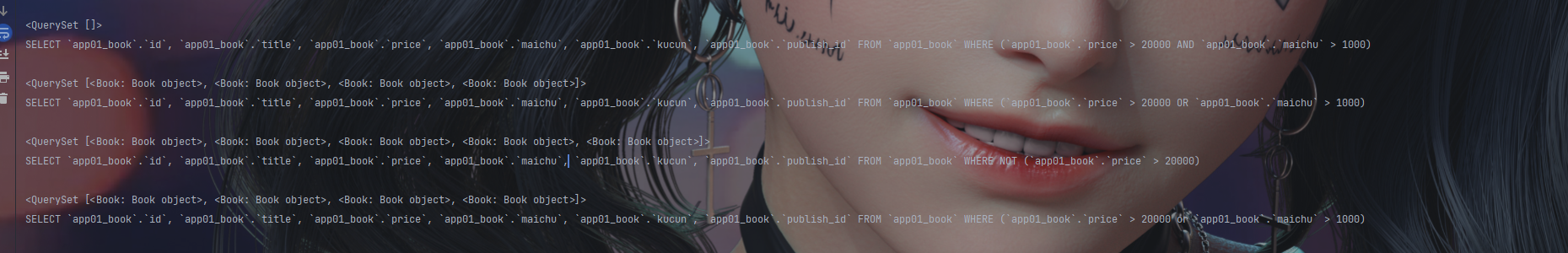
q_obj = Q()
q_obj.connector = 'or' # 默认是and 可以改为or
q_obj.children.append(('price__gt',20000))
q_obj.children.append(('maichu__gt',1000))
res = models.Book.objects.filter(q_obj)
print(res)
print(res.query)
4. ORM查询优化
# 1.orm查询默认都是惰性查询(能不消耗数据库资源就不消耗)
光编写orm语句并不会直接指向SQL语句 只有后续的代码用到了才会执行
# 2.orm查询默认自带分页功能(尽量减轻单次查询数据的压力)
'''需求:单个结果还是以对象的形式展示 可以直接通过句点符操作'''
for i in res:
print(i.get('title'))
print()
res = models.Book.objects.only('title', 'price')
for obj in res:
print(obj.title, obj.price)
print()
"""
only会产生对象结果集 对象点括号内出现的字段不会再走数据库查询
但是如果点击了括号内没有的字段也可以获取到数据 但是每次都会走数据库查询
"""
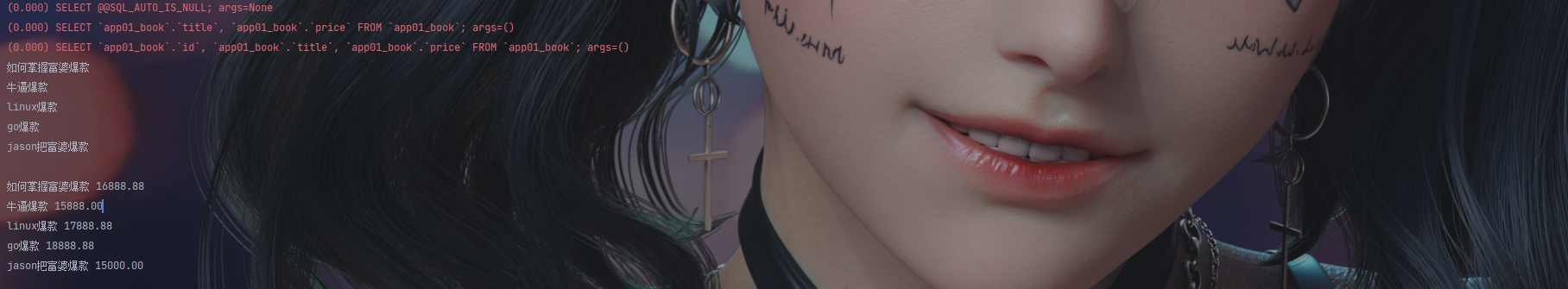
res = models.Book.objects.defer('title','price')
for obj in res:
print(obj.title)
print(obj.price)
print(obj.publish_time)
"""
defer与only刚好相反 对象点括号内出现的字段会走数据库查询
如果点击了括号内没有的字段也可以获取到数据 每次都不会走数据库查询
"""

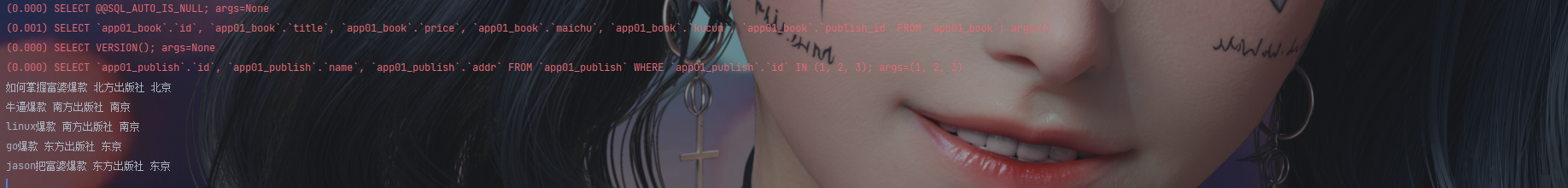
res = models.Book.objects.select_related('publish')
for obj in res:
print(obj.title, obj.publish.name, obj.publish.addr)
print()
"""
select_related括号内只能传一对一和一对多字段 不能传多对多字段
效果是内部直接连接表(inner join) 然后将连接之后的大表中所有的数据全部封装到数据对象中
后续对象通过正反向查询跨表 内部不会再走数据库查询
"""

res = models.Book.objects.prefetch_related('publish')
for obj in res:
print(obj.title, obj.publish.name, obj.publish.addr)
"""
prefetch_related 将多次查询之后的结果封装到数据对象中 后续对象通过正反向查询跨表 内部不会再走数据库查询
"""
5. ORM常见字段
AutoField()
int auto_increment
CharField()
必须提供max_length参数 对应的数据库中是varchar类型
IntergerField()
int
DecimalField()
decimal
DateField()
date auto_now auto_now_add
DateTimeField()
datetime auto_now auto_now_add
BigIntergerField()
bigint
BooleanField()
传布尔值 存0和1
TextField()
存储大段文本
FileField()
传文件自动保存到指定位置并存文件路径
EmailField()
本质还是varchar类型
URLField()
本质还是varchar类型,Django Admin以及ModelForm中提供验证 URL
# 自定义字段类型
class MyCharField(models.Field):
def __init__(self, max_length, *args, **kwargs):
self.max_length = max_length
super().__init__(max_length=max_length, *args, **kwargs)
def db_type(self, connection):
return 'char(%s)' % self.max_length
6. 重要参数
primary_key
主键
max_length
最大长度
verbose_name
备注
null
是否为空
default
默认值
max_digits
小数总长度
decimal_places
小数位长度
unique
是否为唯一值
db_index
是否为索引
auto_now
创建数据记录的时候会把当前时间添加到数据库,不人为修改,不会改变
auto_now_add
每次更新数据记录的时候会更新该字段
choices
用于可以被列举完全的数据
eg:性别 学历 工作经验 工作状态
class User(models.Model):
username = models.CharField(max_length=32)
password = models.IntegerField()
gender_choice = (
(1,'男性'),
(2,'女性'),
(3,'变性')
)
gender = models.IntegerField(choices=gender_choice)
user_obj.get_gender_display()
# 有对应关系就拿 没有还是本身
to
要关联的表
to_field
要关联的表的字段
db_constraint
是否为外键约束
ps:外键字段中可能还会遇到related_name参数
"""
外键字段中使用related_name参数可以修改正向查询的字段名
"""
7. 事务操作
MySQL事务:四大特性(ACID)
原子性
一致性
独立性
持久性
start transcation;
rollback;
commit;
# 开启事务处理
try:
with transaction.atomic():
# 创建一条订单数据
models.Order.objects.create(num="110110111", product_id=1, count=1)
# 能执行成功
models.Product.objects.filter(id=1).update(kucun=F("kucun")-1, maichu=F("maichu")+1)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
8. ORM执行原生SQL
# 方式1
from django.db import connection, connections
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor = connections['default'].cursor()
# 在QuerySet的基础上继续执行子语句
cursor.execute("""SELECT * from auth_user where id = %s""", [1])
cursor.fetchone()
# 方式2
# select和select_params是一组,where和params是一组,tables用来设置from哪个表
models.UserInfo.objects.extra(
select={'newid':'select count(1) from app01_usertype where id>%s'},
select_params=[1,],
where = ['age>%s'],
params=[18,],
order_by=['-age'],
tables=['app01_usertype']
)
9. 多对多三种创建方式
# 全自动(常见)
orm自动创建第三张表 但是无法扩展第三张表的字段
authors = models.ManyToManyField(to='Author')
# 全手动(使用频率最低)
优势在于第三张表完全自定义扩展性高 劣势在于无法使用外键方法和正反向
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
class Book2Author(models.Model):
book_id = models.ForeignKey(to='Book')
author_id = models.ForeignKey(to='Author')
# 半自动(常见)
正反向还可以使用 并且第三张表可以扩展 唯一的缺陷是不能用
add\set\remove\clear四个方法
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
authors = models.ManyToManyField(
to='Author',
through='Book2Author', # 指定表
through_fields=('book','author') # 指定字段
)
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
'''多对多建在任意一方都可以 如果建在作者表 字段顺序互换即可'''
books = models.ManyToManyField(
to='Book',
through='Book2Author', # 指定表
through_fields=('author','book') # 指定字段
)
class Book2Author(models.Model):
book = models.ForeignKey(to='Book')
author = models.ForeignKey(to='Author')




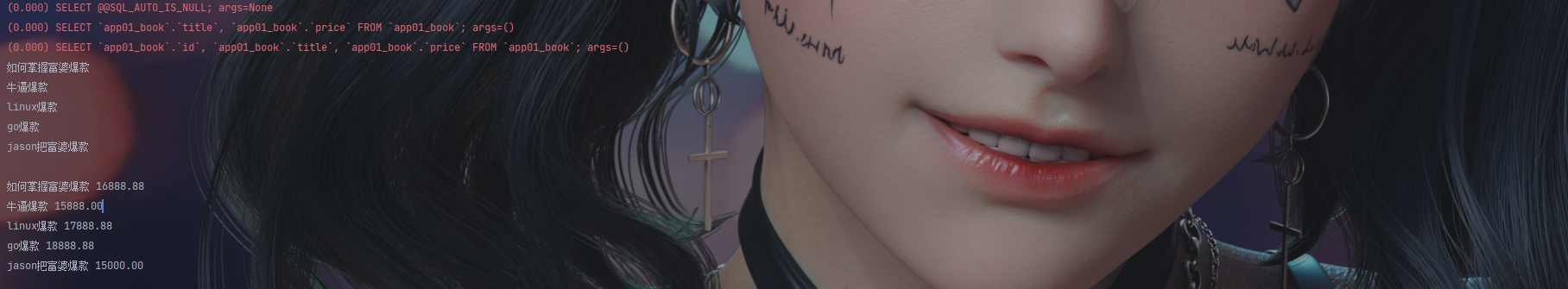









【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下