PyGame实现简易五子棋对战
PyGame实现简易五子棋对战
——基于博弈树极大极小值搜索实现AI对弈
一.PyGame五子棋实现
游戏GUI设计
加载游戏背景与logo图片资源后绘制一个19×19的方格棋盘。
# 初始化
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((WIDTH, HEIGHT))
pygame.display.set_caption('五子棋')
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
all_sprites = pygame.sprite.Group() # 所有棋子精灵
# 获取加载各种资源的路径
base_folder = os.path.dirname(__file__)
img_folder = os.path.join(base_folder, 'images')
# 设置图标
ico = pygame.image.load(os.path.join(img_folder, 'ico.png'))
pygame.display.set_icon(ico)
# 获取背景图片的Surface与Rect对象
background_img = pygame.image.load(os.path.join(img_folder, 'back.png')).convert()
background = pygame.transform.scale(background_img, (WIDTH, HEIGHT))
back_rect = background.get_rect()
# 绘制背景版
def draw_background(surf):
# 加载背景图片
screen.blit(background, back_rect)
# 画网格线,棋盘为19*19
rect_lines = [
((GRID_WIDTH, GRID_WIDTH), (GRID_WIDTH, HEIGHT - GRID_WIDTH)),
((GRID_WIDTH, GRID_WIDTH), (WIDTH - GRID_WIDTH, GRID_WIDTH)),
((GRID_WIDTH, HEIGHT - GRID_WIDTH),
(WIDTH - GRID_WIDTH, HEIGHT - GRID_WIDTH)),
((WIDTH - GRID_WIDTH, GRID_WIDTH),
(WIDTH - GRID_WIDTH, HEIGHT - GRID_WIDTH)),
]
for line in rect_lines: # 迭代rect_lines[][0:4]
pygame.draw.line(surf, BLACK, line[0], line[1], 2)
for i in range(17):
pygame.draw.line(surf, BLACK,
(GRID_WIDTH * (2 + i), GRID_WIDTH),
(GRID_WIDTH * (2 + i), HEIGHT - GRID_WIDTH))
pygame.draw.line(surf, BLACK,
(GRID_WIDTH, GRID_WIDTH * (2 + i)),
(HEIGHT - GRID_WIDTH, GRID_WIDTH * (2 + i)))
circle_center = [
(GRID_WIDTH * 4, GRID_WIDTH * 4),
(WIDTH - GRID_WIDTH * 4, GRID_WIDTH * 4),
(WIDTH - GRID_WIDTH * 4, HEIGHT - GRID_WIDTH * 4),
(GRID_WIDTH * 4, HEIGHT - GRID_WIDTH * 4),
(GRID_WIDTH * 10, GRID_WIDTH * 10)
]
for cc in circle_center:
pygame.draw.circle(surf, BLACK, cc, 5)
游戏逻辑设计一:玩家落子
游戏主循环监听用户鼠标操作,当在合适位置点击时视为落子。
# 部分关键代码
for event in pygame.event.get():
# 检查是否关闭窗口
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
running = False
sys.exit()
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
move(screen, event.pos) # 落子
落子时调用move()函数,传入当前窗口对象与位置信息。并用pygame.draw.circle()函数绘制棋子。
def move(surf, pos):
"""
玩家落子函数
Args:
surf: 我们的屏幕
pos: 用户落子的位置
Returns a tuple or None:
None: if move is invalid else return a
tuple (bool, player):
bool: True is game is not over else False
player: winner (USER or AI)
"""
grid = (int(round(pos[0] / (GRID_WIDTH + .0))),
int(round(pos[1] / (GRID_WIDTH + .0))))
if grid[0] <= 0 or grid[0] > 19:
return
if grid[1] <= 0 or grid[1] > 19:
return
pos = (grid[0] * GRID_WIDTH, grid[1] * GRID_WIDTH)
if color_metrix[grid[0]][grid[1]] is not None:
return None
curr_move = (pos, BLACK)
add_coin(surf, BLACK, grid, USER)
if game_is_over(grid, BLACK):
return False, USER
# 绘制棋子
def draw_movements(surf):
for move in movements[:-1]:
pygame.draw.circle(surf, move[1], move[0], 16)
if movements:
pygame.draw.circle(surf, GREEN, movements[-1][0], 16)
游戏逻辑设计二:判断获胜
传入落子的位置信息与颜色,随即循环检测判断横竖撇捺四个方向的棋子:若为相同的颜色且未触碰边界值时使记录值++,连成五子游戏也就结束了。
# 检测游戏是否结束
def game_is_over(pos, color):
hori = 1
verti = 1
slash = 1
backslash = 1
left = pos[0] - 1
while left > 0 and color_metrix[left][pos[1]] == color:
left -= 1
hori += 1
right = pos[0] + 1
while right < 20 and color_metrix[right][pos[1]] == color:
right += 1
hori += 1
up = pos[1] - 1
while up > 0 and color_metrix[pos[0]][up] == color:
up -= 1
verti += 1
down = pos[1] + 1
while down < 20 and color_metrix[pos[0]][down] == color:
down += 1
verti += 1
left = pos[0] - 1
up = pos[1] - 1
while left > 0 and up > 0 and color_metrix[left][up] == color:
left -= 1
up -= 1
backslash += 1
right = pos[0] + 1
down = pos[1] + 1
while right < 20 and down < 20 and color_metrix[right][down] == color:
right += 1
down += 1
backslash += 1
right = pos[0] + 1
up = pos[1] - 1
while right < 20 and up > 0 and color_metrix[right][up] == color:
right += 1
up -= 1
slash += 1
left = pos[0] - 1
down = pos[1] + 1
while left > 0 and down < 20 and color_metrix[left][down] == color:
left -= 1
down += 1
slash += 1
# 若统计数>=5游戏结束
if max([hori, verti, backslash, slash]) >= 5:
return True
游戏开始与结束都需要绘制文字来提醒玩家,而在主循环检测到游戏结束时绘制文本显示胜利者(玩家或AI)与"you win!"(or"you lose!")。
# 绘制文字
def draw_text(surf, text, size, x, y, color=WHITE):
font = pygame.font.Font(font_name, size)
text_surface = font.render(text, True, color)
text_rect = text_surface.get_rect()
text_rect.midtop = (x, y)
surf.blit(text_surface, text_rect)
# 文字展示至界面
def show_go_screen(surf, winner=None):
note_height = 10
if winner is not None:
draw_text(surf, '你 {0}!'.format('赢 了' if winner == USER else '输 了'),
64, WIDTH // 2, note_height, RED)
else:
screen.blit(background, back_rect)
draw_text(surf, '简 易 五 子 棋', 64, WIDTH // 2, note_height + HEIGHT // 4, BLACK)
draw_text(surf, '按压任意键开始游戏...', 22, WIDTH // 2, note_height + HEIGHT // 1.5, BLUE)
pygame.display.flip()
waiting = True
while waiting:
clock.tick(FPS)
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
elif event.type == pygame.KEYUP:
waiting = False
二.AI落子实现
AI算法介绍
极大极小值搜索算法
五子棋看起来有各种各样的走法,而实际上把每一步的走法展开,就是一颗巨大的博弈树。在这个树中,从根节点为0开始,奇数层表示电脑可能的走法,偶数层表示玩家可能的走法。假设电脑先手,那么第一层就是电脑的所有可能的走法,第二层就是玩家的所有可能走法,以此类推。我们假设平均每一步有50种可能的走法,那么从根节点开始,往下面每一层的节点数量是上一层的 50 倍,假设我们进行4层思考,也就是电脑和玩家各走两步,那么这颗博弈树的最后一层的节点数为 50^4 = 625W 个。先不考虑这么多个节点需要多久能算出来。有了对博弈树的基本认识,我们就可以用递归来遍历这一棵树。
那么我们如何才能知道哪一个分支的走法是最优的,我们就需要一个评估函数能对当前整个局势作出评估,返回一个分数。我们规定对电脑越有利,分数越大,对玩家越有利,分数越小,分数的起点是0。我们遍历这颗博弈树的时候就很明显知道该如何选择分支了:
- 电脑走棋的层我们称为MAX层,这一层电脑要保证自己的利益最大化,那么就需要选分最高的节点。
- 玩家走棋的层我们称为MIN层,这一层玩家要保证自己的利益最大化,那么就会选分最低的节点。
这也就是极大极小值搜索算法的名称由来。这是维基百科上的一张图:
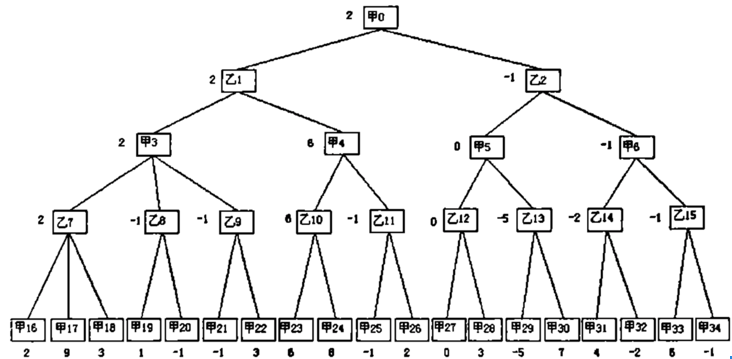
此图中甲是电脑,乙是玩家,那么在甲层的时候,总是选其中值最大的节点,乙层的时候,总是选其中最小的节点。
而每一个节点的分数,都是由子节点决定的,因此我们对博弈树只能进行深度优先搜索而无法进行广度优先搜索。深度优先搜索用递归非常容易实现,然后主要工作其实是完成一个评估函数,这个函数需要对当前局势给出一个比较准确的评分。
五子棋是一个 19×19 的棋盘,棋盘基本不会变动,这样看来用一个 19×19 的二维数组来实现是一个可行的选择。
α-β剪枝算法(AI仅单层搜索,未实现)
Alpha Beta 剪枝算法是一种安全的剪枝策略,也就是不会对棋力产生任何负面影响。它的基本依据是:棋手不会做出对自己不利的选择。依据这个前提,如果一个节点明显是不利于自己的节点,那么就可以直接剪掉这个节点。
前面讲到过,AI会在MAX层选择最大节点,而玩家会在MIN层选择最小节点。那么如下两种情况就是分别对双方不利的选择:
- 在MAX层,假设当前层已经搜索到一个最大值 X, 如果发现下一个节点的下一层(也就是MIN层)会产生一个比X还小的值,那么就直接剪掉此节点。
解释一下,也就是在MAX层的时候会把当前层已经搜索到的最大值X存起来,如果下一个节点的下一层会产生一个比X还小的值Y,那么之前说过玩家总是会选择最小值的。也就是说这个节点玩家的分数不会超过Y,那么这个节点显然没有必要进行计算了。通俗点来讲就是,AI发现这一步是对玩家更有利的,那么当然不会走这一步。
- 在MIN层,假设当前层已经搜索到一个最小值 Y, 如果发现下一个节点的下一层(也就是MAX层)会产生一个比Y还大的值,那么就直接剪掉此节点。
这个是一样的道理,如果玩家走了一步棋发现其实对AI更有利,玩家必定不会走这一步。
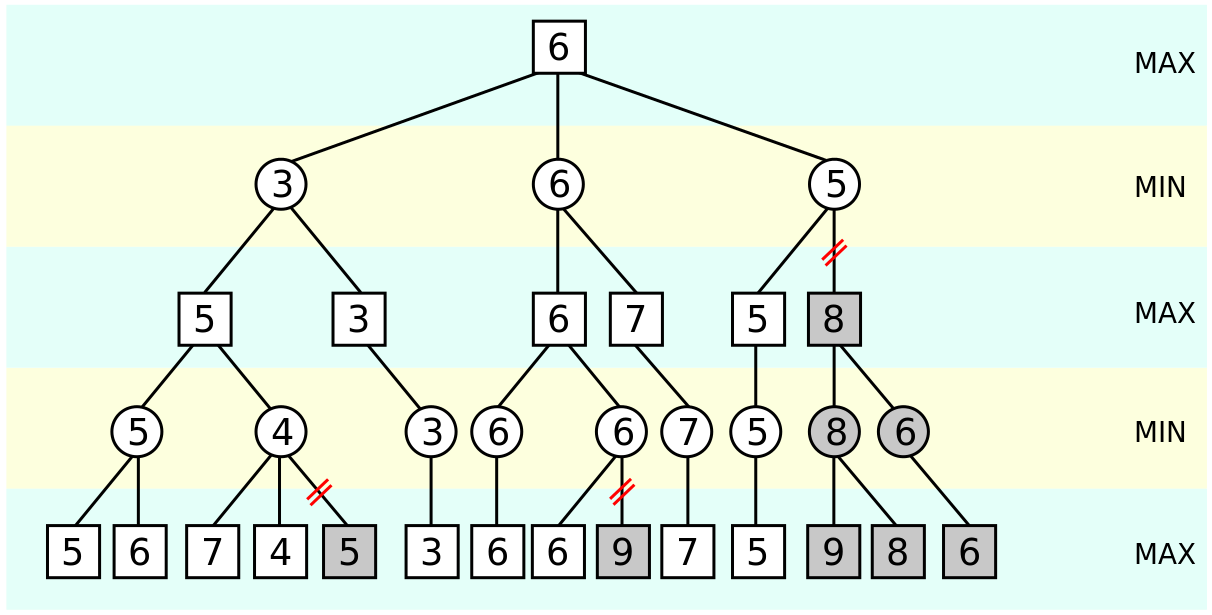
如上图所示,在第二层,也就是MIN层,当计算到第二层第三个节点的时候,已知前面有一个3和一个6,最大值至少是6。 在计算第三个节点的时候,发现它的第一个孩子的结果是5,因为当前是MIN节点,会选择孩子中的最小值,所以此节点值不会大于5。而第二层已经有一个6了,第二层第三个节点肯定不会被选择。因此此节点的后序孩子就没有必要计算了。
其实这个图里面第三层分数为7的节点也是不需要计算的。
这是 MAX 节点的剪枝,MIN节点的剪枝也是同样的道理。Alpha Beta 剪枝的 Alpha 和 Beta 分别指的是 MAX 和 MIN 节点。
AI算法实现
下面实现了一个主流的评估函数,以统计并记录垂直、水平、斜线、反斜线四个方向的决策值(连子个数)。对各种连子情况的基本评分规则,从 活一、死二、活二、死三、活三、死四、活四、连五,评分依次递增。
而每次落子都会调用update_score()分别计算并更新玩家分数矩阵或AI分数矩阵。
# 更新棋盘当前决策分数
def update_score(pos, color, ident):
hori = 1
verti = 1
slash = 1
backslash = 1
left = pos[0] - 1
while left > 0 and color_metrix[left][pos[1]] == color:
left -= 1
if hori == 4:
hori += 1
break
if left > 0 and (color_metrix[left][pos[1]] == color or color_metrix[left][pos[1]] is None):
hori += 1
right = pos[0] + 1
while right < 20 and color_metrix[right][pos[1]] == color:
right += 1
if hori == 4:
hori += 1
break
if right < 20 and (color_metrix[right][pos[1]] == color or color_metrix[right][pos[1]] is None):
hori += 1
hori = score_level[hori]
up = pos[1] - 1
while up > 0 and color_metrix[pos[0]][up] == color:
up -= 1
if verti == 4:
verti += 1
break
if up > 0 and (color_metrix[pos[0]][up] == color or color_metrix[pos[0]][up] is None):
verti += 1
down = pos[1] + 1
while down < 20 and color_metrix[pos[0]][down] == color:
down += 1
if verti == 4:
verti += 1
break
if down < 20 and (color_metrix[pos[0]][down] == color or color_metrix[pos[0]][down] is None):
verti += 1
verti = score_level[verti]
left = pos[0] - 1
up = pos[1] - 1
while left > 0 and up > 0 and color_metrix[left][up] == color:
left -= 1
up -= 1
if backslash == 4:
backslash += 1
break
if left > 0 and up > 0 and (color_metrix[left][up] == color or color_metrix[left][up] is None):
backslash += 1
right = pos[0] + 1
down = pos[1] + 1
while right < 20 and down < 20 and color_metrix[right][down] == color:
right += 1
down += 1
if backslash == 4:
backslash += 1
break
if right < 20 and down < 20 and (color_metrix[right][down] == color or color_metrix[right][down] is None):
backslash += 1
backslash = score_level[backslash]
right = pos[0] + 1
up = pos[1] - 1
while right < 20 and up > 0 and color_metrix[right][up] == color:
right += 1
up -= 1
if slash == 4:
slash += 1
break
if right < 20 and up > 0 and (color_metrix[right][up] == color or color_metrix[right][up] is None):
slash += 1
left = pos[0] - 1
down = pos[1] + 1
while left > 0 and down < 20 and color_metrix[left][down] == color:
left -= 1
down += 1
if slash == 4:
slash += 1
break
if left > 0 and down < 20 and (color_metrix[left][down] == color or color_metrix[left][down] is None):
slash += 1
slash = score_level[slash]
# print(pos, color, ident, (hori, verti, slash, backslash))
if ident == USER:
player_score_metrix[pos[0]][pos[1]] = int((hori + verti + slash + backslash) * 0.9)
else:
ai_score_metrix[pos[0]][pos[1]] = hori + verti + slash + backslash
以下代码实现了当玩家落子后,通过评估函数与博弈树极大极小值搜索函数计算AI的下一步落子对应的网格坐标。get_next_move()函数返回一个next_move元组,通过pygame.draw.circle()绘制棋子,随后更新分数矩阵。
另外around_grid()函数将返回落子四个方向步长为step的grid元组,从而遍历边长为 step + 1 的矩形框内的所有坐标化为一维数据并将其存入player_optimal_set集合中。迭代遍历player_optimal_set集合,在player_score_metrix与ai_score_metrix中获取最佳的落子坐标并返回。
def add_coin(surf, color, pos, ident=USER, radius=16):
"""
绘制棋子并计算最佳矩阵
:param surf: 棋盘Surface对象
:param color: 棋子白子or黑子
:param pos: 棋子位置的
:param ident: 身份1为USER,AI相反
:param radius: 半径
:return: None
"""
num_pos = gridpos_2_num(pos)
movements.append(((pos[0] * GRID_WIDTH, pos[1] * GRID_WIDTH), color))
remain.remove(num_pos)
if num_pos in player_optimal_set:
player_optimal_set.remove(num_pos)
player_score_metrix[pos[0]][pos[1]] = -1 - ident
ai_score_metrix[pos[0]][pos[1]] = -1 - ident
color_metrix[pos[0]][pos[1]] = color
pygame.draw.circle(surf, color, movements[-1][0], radius)
clock.tick(FPS)
around = around_grid(pos, 4)
# print(around)
for rx in range(around[0], around[1] + 1):
for ry in range(around[2], around[3] + 1):
num_pos = gridpos_2_num((rx, ry))
if num_pos in remain:
update_score((rx, ry), color, ident)
if color == BLACK:
tpcolor = WHITE
else:
tpcolor = BLACK
update_score((rx, ry), tpcolor, 1 - ident)
def get_next_move(movements, curr_move):
"""
博弈树最大最小搜索算法获取AI下一步
:param movements:
:param curr_move:
:return: next_move
"""
around = around_grid((curr_move[0][0] // GRID_WIDTH, curr_move[0][1] // GRID_WIDTH))
for rx in range(around[0], around[1] + 1):
for ry in range(around[2], around[3] + 1):
num_pos = gridpos_2_num((rx, ry))
if num_pos in remain:
player_optimal_set.add(gridpos_2_num((rx, ry)))
max_score = -1000000
next_move = 0
for i in player_optimal_set:
grid = num_2_gridpos(i)
if ai_score_metrix[grid[0]][grid[1]] >= score_level[5]:
next_move = i
break
if player_score_metrix[grid[0]][grid[1]] >= score_level[4]:
next_move = i
break
score = ai_score_metrix[grid[0]][grid[1]] + player_score_metrix[grid[0]][grid[1]]
if max_score < score:
max_score = score
next_move = i
elif max_score == score:
if (random.randint(0, 100) % 2) == 0:
next_move = i
around = around_grid(num_2_gridpos(next_move))
for rx in range(around[0], around[1] + 1):
for ry in range(around[2], around[1] + 1):
num_pos = gridpos_2_num((rx, ry))
if num_pos in remain:
player_optimal_set.add(gridpos_2_num((rx, ry)))
return next_move
def respond(surf, movements, curr_move):
"""
AI响应
:param surf: 棋盘对象
:param movements:
:param curr_move: 玩家的落子
:return:
"""
next_move = get_next_move(movements, curr_move)
grid_pos = num_2_gridpos(next_move)
# AI落子
add_coin(surf, WHITE, grid_pos, AI)
if game_is_over(grid_pos, WHITE):
return False, AI
三.基本演示
由于博弈树仅为单层搜索,AI对眼前局势的判别可能因为短视无法做出最佳策略。但AI决策模式已初见雏形,可以赢过部分初学者比如我。

文章参考:
[1]【纯C++】项目实战:AI五子棋、人机对战版本丨完整详细开发教程
[2]colingogogo/gobang_AI:基于博弈树α-β剪枝搜索的五子棋AI
[3]lihongxun945/gobang:JS五子棋AI,源码+教程,基于Alpha-Beta剪枝算法(不是神经网络)
[4]十分钟暴力讲解博弈树五子棋AI极大极小搜索Alpha-Beta剪枝
本文来自博客园,作者:TfiyuenLau,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tfiyuenlau/articles/16926102.html

 Python期末作业——使用PyGame库编写简单的五子棋小游戏,并使用博弈树极大极小值搜索实现五子棋对战AI对弈。
Python期末作业——使用PyGame库编写简单的五子棋小游戏,并使用博弈树极大极小值搜索实现五子棋对战AI对弈。
